1. Hepatitis Monthly, a Short History
Hepatitis monthly (HM), the thirteen-year-old publication of the Baqiyatallah research center for gastroenterology and liver diseases, is a journal in the field of hepatology. The purpose of establishing this journal was to enhance the knowledge of gastroenterologists, hepatologists, internists, and infectious disease specialists regarding liver-related diseases, with a particular focus on hepatitis diseases (1).
Initially published four times per year, HM was changed by the editorial board to a monthly publication beginning in 2011, based on the number of manuscripts submitted to the journal. HM was indexed in web of science (WOS) and Scopus in 2007 and 2008, respectively. In 2009, it was listed in journal citation reports (JCR) and received its first impact factor (IF) (0.716). It now ranks first among all Iranian Medical Journals, as well as middle eastern journals, in the category of gastroenterology and hepatology (2, 3).
2. An Expected Road Map for an Effective Journal
A journal can have different roles in its publishing country and also in related regions. If the journal can attract sufficient quality and value, it can graduate from being a regional publication to play an international role globally as a universal journal. This might represent the expected road map as a journal becomes an effective universal publication.
We believe that every scientific journal should always conduct self-evaluation to determine its placement among other related journals, both regionally and globally. Therefore, self-evaluation should be an important consideration of the editorial board of a journal, who should calculate the gap between the actual situation of the journal and the final goals for that journal. Only with this approach, a journal can be promoted in its field. Raising the level of a journal in a region clearly can help in promoting the level of knowledge of readers of that journal, who are physicians, healthcare personnel, and health policy makers in the case of HM. Consequently, this growth in knowledge level can lead to an increase in the regional health status.
Consider the role of a regional medical journal in controlling the health status of that region. For example, a journal that publishes papers related to a specific disease can determine the prevalence and related important risk factors for that disease in that area. These projects can be performed over time and can investigate the effects of different health programs, like preventive strategies such as vaccination and educational programs, on the control of a specific disease. These projects would be specific to a given region, so other international journals might have not enough incentive to publish them, and this is one of the well recognized roles of a journal. Obviously, as the journal promotes its situation, it can play a key role for other countries of that region. Furthermore, a journal has an important duty to publish papers and deliver new data to all related readers across the globe. This important duty cannot be done without the journal being indexed in valuable international databases like WOS, PubMed, and Scopus, which provide more visibility for the journal.
Generally, the numbers of papers that are published by a journal, together with the number of citations that a journal receives, are indicative of the quality of that journal. These are also the main factors used in the calculation of scientometric indices, like the impact factor and the h-index (4, 5). Here, and with use of some databases, including WOS, Scopus, and journal citation reports, we evaluated the situation for HM both regionally and globally.
3. An Overview of Hepatitis Monthly
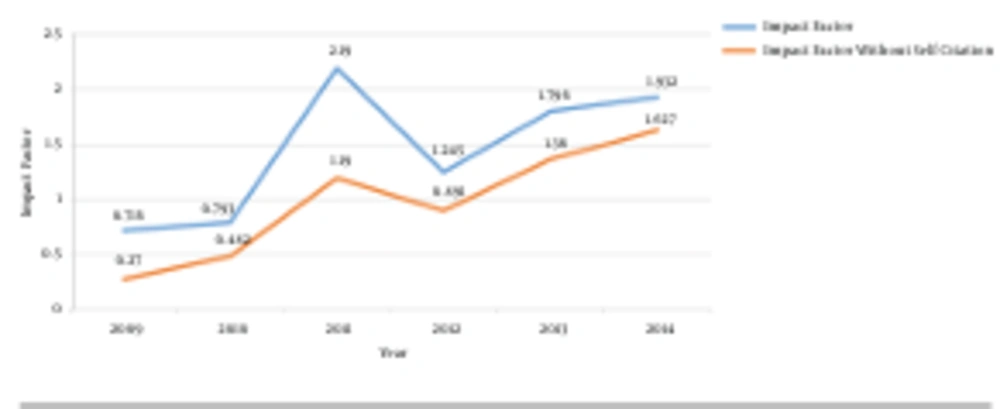
The web of science (WOS) indicates that HM has published 902 papers to date. We obtained data from WOS on 5th February, 2016. The published papers included 590 articles (original research, brief reports, and case reports) and 96 reviews. HM has also published 118 papers as letters to the editor, which indicates the special emphasis the editorial board of this journal places on the importance of post publication review. At present, HM has received 2930 citations. On average, the journal receives 293 citations per year and 3.25 citations per paper. Only 23.52% of the total citations received by HM were citations of its own papers. Figure 1 shows the impact factor of HM based on the year, with and without self-citation, and it shows a growing trend. The h-index for HM is currently 18.
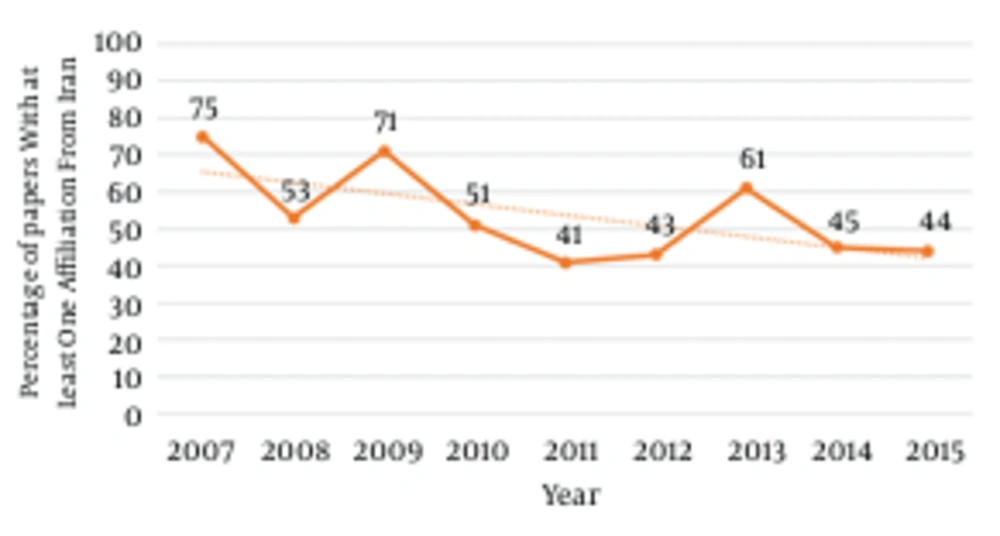
After Iran (n = 457), the following countries have published the most papers in HM: China (n = 105), Italy (n = 62), Turkey (n = 47), Egypt (n = 32), USA (n = 29), Pakistan (n = 23), Germany (n = 16), Romania (n = 16), Poland (n = 15), Canada (n = 15), and Japan (n = 15). Figure 2 shows the percentages of papers published annually by HM with at least one affiliation from Iran. In total, about 50% of the papers published by HM are from countries other than Iran, which shows the growing role of HM as an international journal.
4. Citing and Cited Countries
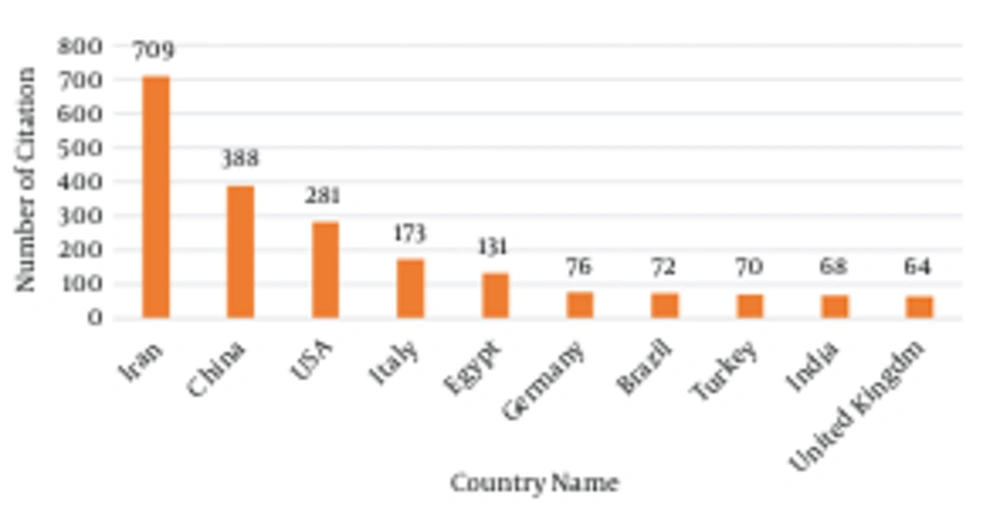
Journals that have an effective impact on science can be seen and read by researchers from different countries and therefore cited by them. We used Scopus to determine the countries that cite HM or were cited by this journal. Based on this database, China, the USA, and Italy are the top three countries (excluding Iran) that cited HM the most (Figure 3). The countries that have been cited the most by HM included the USA (n = 4197), Italy (n = 1369), Japan (n = 1381), the UK (1027), France (n = 971), Germany (n=935), Iran (n = 750), China (n = 738), Spain (n = 542), and Canada (n = 446).
5. Citing and Cited Journal
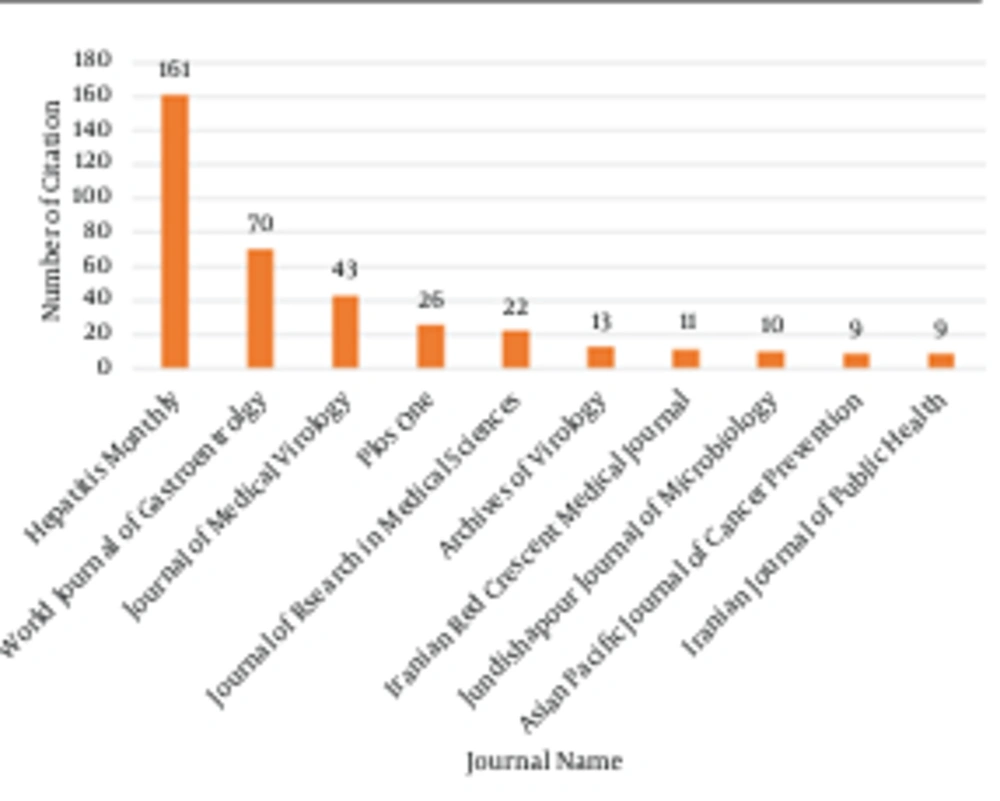
Interactions between journals are very important for evaluation of the prestige of a journal. One way to determine the scientific position of a journal is to evaluate the journals that cite it. Citation in prestigious journals demonstrates the importance of the data published by that journal. The WOS indicates that HM is primarily cited (excluding HM) in the World Journal of Gastroenterology, the Journal of Medical Virology, and PLOS ONE (Figure 4). The top ten journals cited the most by HM, on the other hand, are Hepatology (n = 219), HM (n = 161), the Journal of Hepatology (n = 115), Gastroenterology (n = 99), the World Journal of Gastroenterology (70), the Journal of Viral Hepatitis (n = 63), the Journal of Virology (n = 62), the American Journal of Gastroenterology (n = 50), the Journal of Medical Virology (n = 50), and PLOS ONE (n = 49).
6. Conclusion
Over the past 13 years, HM has contributed considerably to the body of knowledge, with a total of 902 papers, 2930 citations, and a high degree of international collaboration in research projects. We believe that offering this type of journal will certainly help to promote knowledge among relevant readers in related regions, which should attract particular attention from universities and health policy makers for support for these journals.