1. Background
Playing wind instruments has been considered a demanding psychophysiological task (1, 2), as well as an attentional and cognitive task, sometimes leading to mood discomfort or even emotional problems like music performance anxiety (2, 3). This can lead to sympathetic hyperactivation and autonomic worsening (4). In fact, anxiety-related disorders and emotional distress are well-known, causing factors for cardiovascular disease (5, 6). In addition, the elevated heart rate (HR) responses evoked during demanding musical performances have been related to the possibility of increased cardiovascular problems and health risks, at least for those professional musicians in poor physical condition (1, 7).
On the other hand, besides being an artistic and pleasant activity, music playing has the potential to induce cardiovascular benefits similar to exercise, especially cardio-protection (8). Regular music practice has been suggested to lead to the same increase in the somatosensory nerve traffic in the brainstem, with the consequence of enhanced modulation in the autonomic cardiac control (8). Playing wind instruments may also imply an added enhancement in the cardiac autonomic regulation due to the continuous changes in the breathing patterns while playing (1, 9, 10). In parallel, big expiratory efforts in the high notes have been related to a strenuous expiratory strain similar to the Valsalva maneuver (9), where the acute baroreflex stress evokes a parasympathetic reactivation oriented to quickly coupling cardiac and respiratory functioning (9, 11). This strain leads to an improvement in so-called respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA), with a reduction in the sympathetic arousal and the increasing of the vagal tone (1, 9, 10), all of which are important contributors to cardiovascular health.
Hence, modulation of cardiac autonomic control is associated with both music playing and psychophysiological health and changes in the cardiac function, leading to fatigue, overreaching, or performance anxiety, among others. In this context of controversy with regard to the neurological and cardiovascular health of musicians (i.e., enhanced/impaired sympathetic and vagal responses), heart rate variability (HRV) appears as a cheap and non-invasive marker of the autonomic cardiac function/dysfunction, thereby helping to analyze acute or chronic autonomic responses following music interpretation (4), as well as the health status of the musicians (9). Based on the analysis of the fluctuation of the heartbeat periods over time, HRV is considered an important marker of psychological well-being and general cardiovascular health, as well as a major predictor of mortality (12). Affective, cognitive, and physiological states act as parallel outputs of the central autonomic network with HRV, reflecting its homeostatic organization and response (13). This can be very useful in the assessment of musicians’ psychophysiological responses.
To the best of our knowledge, it is still unknown whether the autonomic response to playing highly-demanding music performances, as compared to easier ones, may enhance or impair the autonomic modulation of the wind musicians, what can be of interest for their cardiovascular health.
2. Objectives
Therefore, the present study aimed to analyze the HRV in a group of professional musicians while playing wind instruments in intense and highly demanding wind performances, as compared to mild ones. This is the first study investigating differences in the autonomic control of the heart with regard to the task demands (TD), avoiding emotional influences (rehearsal performance). Whether a strenuous autonomic strain due to higher requirements is one path by which playing music exerts its therapeutic effect on cardiovascular health, is an association that has yet to be fully explored (5). This should help further understanding the acute impact of hard performance requirements (i.e., larger TD) on the cardiovascular health of musicians.
3. Methods
3.1. Participants and Protocol
Eight healthy male wind instrument musicians (29.13 ± 7.33 years; 69.36 ± 10.31 kg), participated in this quantitative study with a no-experimental, cross-sectional, and descriptive design. The inclusion criteria were: (1) age between 20 and 50 years; (2) male gender; (3) playing a wind instrument; and (4) professionals or students of the local conservatory in their last year. The exclusion criteria were: (1) playing organ, accordion or harmonium (wind instrument but do not sound by blowing air), and (2) missing one day of the assessment. The participants ranked a list of well-known performances in terms of the perception of TD. This perception has been suggested to act as one of these cognitive and emotional psychophysiological stressors, with changes in cardiac responses and skin conductance in response to increased TD (14). Owing to the multifactorial nature of music performance requirements, we looked for a single item, which would be a good indicator of the overall load. The TD scores were calculated on the basis of four items, including perceived difficulty, physical exertion, psychological effort, and length of the different musical pieces. Individual Likert scales (1 - 5) for each item were elaborated in order to rank the overall score and select the hardest (H) and mildest (M) piece in each instrument. The results of this rating were communicated to the musicians two weeks before their performance (Table 1).
| Mild PTD | Hard PTD | |
|---|---|---|
| Oboe | Oboe concerto in A minor, RV 461 (Vivaldi, A) | Six metamorphoses after Ovid Op. 49 for oboe solo (Britten, B) |
| Trumpet | Concert piece Op. 12 (Brandt, V) | Trumpet concerto in E flat major (Haydn, J) |
| French horn | Villanelle for horn (Dukas, P) | Horn concerto no.1 (Strauss, R) |
| Saxophone | Rhapsody for orchestra and saxophone (Debussy, C) | Concerto for alto saxophone and orchestra (Binge, R) |
| Tuba | Monologue no. 9, for tuba (Von Koch, E) | Concerto no. 1, for tuba (Lebedjew, A) |
| Trombone | Sonata in A minor, for trombone (Benedetto, M) | Trombone concertino, Op.4 (David, F) |
Later on, in two normal rehearsals with no audience, each musician played one mild and one hard piece, on two non-consecutive days. After 10 minutes of warm-up, they played during two laps of 20 minutes, interspersed with 5 minutes of recovery. The HRV was recorded, always in a sitting position, 20 minutes at baseline -early in the morning, in fasting condition- in both laps, and 20 minutes after cessation [baseline; Per1; Per2 & post-performance]. All individuals were previously explained, and written informed consent was obtained to participate in this study, which was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Valencia (number: H143029150232).
3.2. Heart Rate Variability and Other Biological Variables
Heart rate data were continuously registered using a Polar RS800CX (Polar Electro, Kempele, Finland) in RR interval mode with the transmitter belt adjusted to the thorax after applying the conductive gel. Later on, HR data were transferred to the Polar Pro-Trainer software V. 5 (Polar Electro, Kempele, Finland), and exported for further HRV analysis by the Kubios Software V. 2.1 (Biomedical Signal and Medical Imaging Analysis Group, Department of Applied Physics, University of Kuopio, Finland). Importantly, the length of the registers (20 minutes) allowed us to keep the last 500 beats in each segment, once discarded their last 15 seconds.
Artifacts were corrected and detrended (Smooth priors, λ = 500) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, always by the same researcher to ensure consistency. Owing to the non-stationarity of the cardiac signal, only the interval between R waves in the signal (RRi), the root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD) and the two Poincare Plot indexes (SD1, SD2, ratio SD1/SD2) were considered with some of them log-transformed to normalize the distribution (lnRMSSD and lnSD1).
Moreover, biological data were collected during the process of participants’ selection in order to characterize the samples. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were collected with a monitor OMRON M3 (IM-HEM-7131-E); arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) was determined with a pulse oximeter attached to the fourth finger of the left hand (WristOx2-3150; Nonin, Plymouth, MN, USA); and some variables of body composition like height, and weight and body fat (BF) were evaluated on the first day of the assessments by bioimpedance (Tanita BC-601, Tokyo, Japan; Tallimeter SECA 222).
3.3. Statistical Analysis
Finally, the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) V. 17 was used to carry out the statistical analysis. A repeated measure ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni post hoc, was conducted to evaluate significant differences regarding TD (between-subject factor), and the interaction between TD and the Time-Course of the performance (within factor). A P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
Table 2 represents the description of the sample before the data collection, including some variables of body composition, health control variables, and resting data of HRV. Univariate contrast with regard to TD revealed significant higher outputs in H (lnRMSSD, lnSD1, and SD2), with no differences in RRi and SD1/SD2 (Table 2, upper section). The interaction Time-Course × TD (Table 3, lower section) showed differences in SD1/SD2 (P < 0.05) with the indices of lnRMSSD and lnSD1 clearly trending to it (P = 0.055).
| No. | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 8 | 29.13 | 7.33 |
| Height (m) | 8 | 1.73 | 0.04 |
| Weight (kg) | 8 | 69.36 | 10.31 |
| Body fat (%) | 8 | 17.01 | 5.96 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 8 | 76.00 | 7.37 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 8 | 118.75 | 9.85 |
| SaO2 (%) | 8 | 97.31 | 0.70 |
| RRi (ms) | 8 | 915.93 | 147.25 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 8 | 67.10 | 9.35 |
| RMSSD (ms) | 8 | 31.26 | 14.41 |
| lnRMSSD | 8 | 3.37 | 0.38 |
| SD1 (ms) | 8 | 22.12 | 10.20 |
| lnSD1 | 8 | 3.02 | 0.38 |
| SD2 (ms) | 8 | 46.51 | 10.58 |
| Sum Squares | Df | F | P | η2 | 1 - β | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task demand (TD) | ||||||
| RRi | 4993.57 | 1 | 1.690 | 0.235 | 0.194 | 0.204 |
| lnRMSSD | 0.390 | 1 | 6.686 | 0.036a | 0.489 | 0.604 |
| lnSD1 | 0.390 | 1 | 6.686 | 0.036a | 0.489 | 0.604 |
| SD2 | 1320.958 | 1 | 5.890 | 0.046a | 0.457 | 0.552 |
| SD1/SD2 | 0.002 | 1 | 0.995 | 0.352 | 0.124 | 0.139 |
| Time-Course × TD | ||||||
| RRi | 7222.545 | 3 | 0.787 | 0.515 | 0.101 | 0.190 |
| lnRMSSD | 0.427 | 3 | 2.964 | 0.055b | 0.297 | 0.616 |
| lnSD1 | 0.427 | 3 | 2.964 | 0.055b | 0.297 | 0.616 |
| SD2 | 561.974 | 3 | 1.248 | 0.318 | 0.151 | 0.285 |
| SD1/SD2 | 0.044 | 3 | 7.311 | 0.002 | 0.511 | 0.960 |
aP < 0.050.
bP < 0.010.
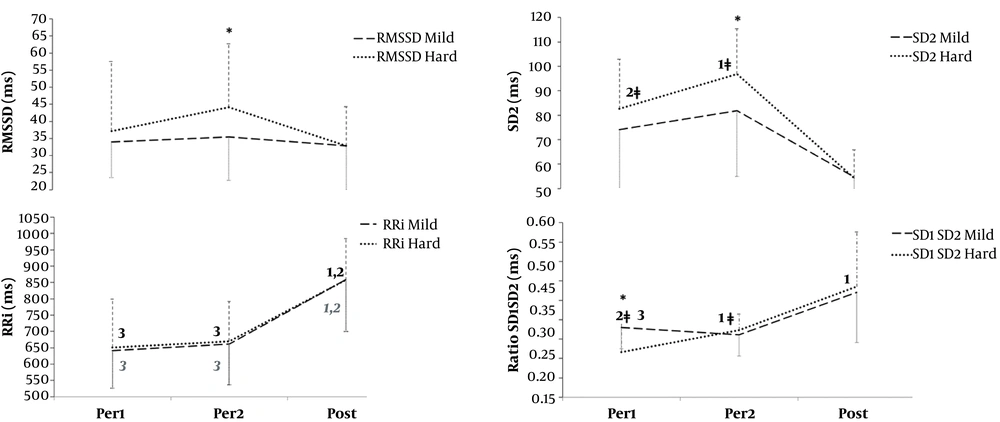
Bonferroni post hoc test (Figure 1) confirmed that lnRMSSD and lnSD1 were significantly higher in the second lap (Per2) of the most demanding performance (P = 0.026), and displayed exactly the same autonomic response (lnSD1 not represented). Notwithstanding, the interaction of TD × Time Course always affected RRi, the hardest piece also affected SD2 and SD1/SD2.
Bonferroni post hoc adjustments considering the interaction of Task Demand × Time-Course. Per1 (first lap of 20 minutes); Per2 (second lap of 20 minutes); Post (20 minutes of immediate recovery). Asterisks display significant differences with regard to TD at the same sampling condition. Numbers display significant differences considering Time-Course in Mild (grey) and Hard (black) separately. *, P < 0.5; ǂ, P < 0.1 [P= 0.1 in Per1 vs. Per2 for lnRMSSD in harder performances (H) (-upper left section of the chart, not represented-).
5. Discussion
The present study sought to further understanding the acute impact of hard performance requirements (i.e., larger TD) on the autonomic and cardiovascular health of the wind musicians. As the main finding, our study points out that despite fatigue, musicians displayed larger parasympathetic responses in the hardest wind instrument performance after half an hour of playing. As expected, HR (RRi) was sensible to neuromuscular requirements while playing (i.e. Per1 and Per2) whatever the TD, coming back to lower values (i.e. higher RRi) in the recovery period with no intergroup differences. Unexpectedly, HRV vagal indices, including lnRMSSD, lnSD1, and SD2 (short- and long-term variability respectively), were larger, the higher the TD (i.e., in Per2). Moreover, SD2 and SD1/SD2 were affected only in the hardest piece, improving with Time-Course. According to these results, the higher the TD (i.e. higher perceived difficulty, physical exertion, and psychological effort), the better the autonomic modulation, confirming the acute beneficial effects of playing wind instruments.
In order to sound a wind instrument, musicians change their usual breathing, with each musical score demanding exactly where and how to breathe during the performance. Overall, we observed that vagal control diminished in the first lap, where musicians may be coping with rate dynamics to these continuous changes in breathing, but this initial discomfort may cause the autonomic reactivation that follows in Per2. The thrust of the diaphragmatic musculature in the expiration activates the vagus nerve endings (11, 15) what would explain this parasympathetic reactivation. In addition, the polyvagal theory (16) describes that during the expiration, there is an increase of the vagal excitation towards the Sino-atrial nodule. The longest duration of breathing can be associated with the greater amplitude of the Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia, thus with better values of HRV. This can be interpreted as the improvement in the coordination between breathing and cardiovascular function (reflected in the RSA). In this sense, the rehearsal perceived as the hardest one had more difficult technical passages and more lively tempos (more than acute notes) that might have required greater depth in breathing. Given that it is proved that slow and deep breaths increase HRV (17), playing more demanding musical pieces might be a more beneficial activity for the autonomic health, resulting in higher requirements for breathing and neural coupling.
Despite fatigue, enhanced acute autonomic cardiac responses when coping with more demanding performances in our study (i.e., increased vagal indexes with no differences in sympathetic arousal) support the idea of better pulmonary and cardiac synchronic coupling (4, 17) in response to highly demanding performances in healthy professionals. Similar to the exercise, regular practice and higher intensities might indeed augment the somatosensory nerve traffic in the brainstem (8), increasing its cardio-protector benefits. Although some studies (1) previously showed that playing wind instruments increased HR in professional musicians, others (5) already highlighted that HRV was able to detect changes in response to subtle manipulations neglected by HR dynamics. That is the vagal reactivation in the hardest TD in our study parallel to the increase in HR.
Since it has been suggested that continuing to play music during the aging process can be physically sustaining and cognitively beneficial, if the musician also pays adequate attention to technique, training schedules, and physical conditioning to avoid overload from other causes (18), playing wind instruments becomes largely recommendable in terms of quality of life through the lifespan. Based on the assumption of the cardiac autonomic modulation as reflecting psychophysiological health (5), HRV would be useful to monitor autonomic fatigue and help musicians to periodize the alternation of high demanding music training or performing, with short periods of rest or light training looking for autonomic recovery, similar to sports training periodization (19).
5.1. Conclusions
In conclusion, playing wind instruments is established to be healthy in terms of autonomic modulation and cardiovascular functioning, and HRV is also confirmed to be useful in this field. However, it is important to point out that we had a very small sample, and we analyzed only acute responses, which is a limitation of our study. Our conclusions might be also limited because we had different instruments and pieces of music and the fact that participants had different academic levels and may have influenced the perception of the TD, thereby becoming a potential source of bias. Future studies with larger heterogeneous samples and direct measures of the breathing and cardiac neural coupling will help better understanding of these cardio-protection relationships, so we recommend that other authors should do this work with larger and specifier sample sizes.