1. Background
Infertility affects nearly one-fifth of couples (1), with males primarily responsible for 20 - 30% of infertility cases (2). Infertility is characterized by the inability to conceive following at least 12 months of regular unprotected intercourse (3). Several medical conditions have been linked to male factor infertility, including endocrine disorders, malignancy, urogenital tract abnormalities, immunological factors, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) (4).
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is among the most prevalent STIs in both males and females of reproductive age, with an infection rate of up to 40% worldwide (5). It consists of double-stranded, non-enveloped DNA viruses. So far, about 228 different HPV genotypes have been found (6) and categorized as low-risk or high-risk based on their oncogenic potential (7). Genital warts may be caused by low-risk HPV genotypes, while high-risk types can cause malignant transformation of cells in the cervix, vagina, vulva, penis, anus, and mouth (8).
In males, HPV DNA is detected in the shaft of the penis, glans penis, vas deferens, epididymis, testes, and urethra (9). This virus is quite common in semen, with semen samples from 16% of infertile men and 10% of the general population infected (10), raising concerns about its possible role in male infertility (11).
With these in mind, one of the potential mechanisms of the association between sperm HPV infection and infertility is the reduced semen parameters (12). For instance, multiple studies have indicated a strong association between HPV infection in semen and altered sperm parameters, such as sperm count, vitality, motility, and morphology (13-18). These findings may be due to alterations in semen composition, such as pH, semen viscosity, leukocyte count, anti-sperm antibodies, or increased DNA fragmentation (19, 20). However, several studies have identified no association between altered sperm parameters and HPV infection in infertile men (21, 22). In this regard, few studies have been conducted in Iran, showing inconsistent results (22, 23). Since the prevalence of HPV infection and its different genotypes depends on the geographical area (24), it appears necessary to investigate the possible relationship between this infection and semen quality in populations from different geographical areas, such as Iran. For this purpose, we evaluated semen samples from infertile men regarding anti-sperm antibody levels, fructose and zinc levels, sperm DNA integrity, and nuclear maturation.
2. Objectives
The present study sought to determine the potential association between seminal HPV infection and reduced semen quality in Iranian men undergoing assisted reproductive technology treatment.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Population
One hundred forty infertile Iranian men were selected from the male partners of couples seeking fertility assessment at Taleghani Hospital's Infertility Center between March and October 2021. All subjects ranged in age from 20 to 55. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1400.482), and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Exclusion criteria included a previous history of vasectomy, testicular cancer, cryptorchidism, varicocele, abnormal karyotype, urogenital infection, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B or C positive serological tests, skin lesion compatible with HPV infection, orchitis, and current infection with Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma, Mycoplasma, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, or other seminal infections.
3.2. Semen Collection and Analysis
Semen samples were obtained through masturbation after 3 - 5 days of abstinence in sterile polypropylene containers and placed in a 37°C incubator. After liquefaction, a standard semen analysis (semen volume, viscosity, pH, sperm concentration, progressive motility, and morphology) was conducted according to the guidelines set by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2021 (3).
3.3. Semen Leukocyte Assessment
After peroxidase staining using a Leuko Detection kit (IVF Company, Iran), the number of leukocytes (polymorphnuclear granulocytes (PMNs)) in semen samples was counted using a hemocytometer slide.
3.4. Sperm DNA Integrity Assessment
The sperm chromatin dispersion (SCD) test was conducted to analyze the sperm DNA fragmentation index (DFI) using the sperm DNA fragmentation assay (SDFA) kit (IVF Company, Iran) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After staining, sperms without DNA fragmentation showed large or medium halos, whereas sperms with fragmented DNA showed little or no halos. The DFI was considered pathological if it was ≥ 30% (25).
3.5. Sperm Chromatin Maturation Assessment
The evaluation of sperm chromatin maturity was assessed according to the instructions of the sperm chromatin maturation assessment (SCMA) kit (IVF Company, Iran). Briefly, sperms with pink and blue heads were considered to have mature and immature chromatin, respectively. The result was reported as the percentage of sperm with immature chromatin.
3.6. Seminal Anti-sperm Antibodies Detection
This method is based on binding human IgG-sensitized latex particles to viable spermatozoa in the presence of an anti-serum against the Fc fragment of human IgG (26). To determine the IgG class anti-sperm antibody (ASA), a direct mixed anti-globulin reaction (MAR) test (FertiPro., Belgium) was used as instructed by the manufacturer, and the moving sperm attached to the latex particles were counted. Results of 10% or more were considered positive (26).
3.7. Semen Fructose and Zinc
Semen samples were centrifuged at 600 g for ten minutes. Following that, supernatants were used for fructose and zinc evaluation. Fructose levels were assessed by spectrophotometry using the method previously described by Karvonen and Malm (27). It should be noted that the normal range of fructose in semen samples is 120 - 450 mg/dL (3).
Seminal plasma was diluted at a ratio of 1:100 with deionized water to evaluate zinc levels, and serum samples were used to plot the standard curve. The concentration of zinc was then measured using flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry (Perkin-Elmer 306, Norwalk, CT, USA).
3.8. DNA Extraction and Human Papillomavirus DNA Detection with the Nested-Polymerase Chain Reaction
The Sperm Genomic DNA Isolation kit (Viragene Company, Iran) was used for DNA extraction according to the manufacturer's instructions. It is important to note that polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene was carried out to assess the quality of the extracted DNA (28) (Table 1). Next, the nested PCR was used to identify HPV DNA (by amplifying the HPV L1), as described in the previous study (28).
| Sequences of Primers | |
|---|---|
| MY-9 | 5′-CGTCC(A/C)A(A/G)(A/G)GGA(A/T)ACTGATC-3′ |
| MY-11 | 5′-GC(A/C)CAGGG(A/T)CTATAA(C/T)AATGG-3′ |
| GP-5 | 5′-TTTGTTACTGTGGTAGATACTAC-3′ |
| GP-6 | 5′-AAAAATAAACTGTAAATCATATTC-3′ |
| GAPDH F | 5′-ATGTTCGTCATGGGTGTGAA-3′ |
| GAPDH R | 5′-GGTGCTAAGCAGTTGGTGGT-3′ |
Nucleotide Sequences of Primers
3.9. Human Popillomavirus Genotyping
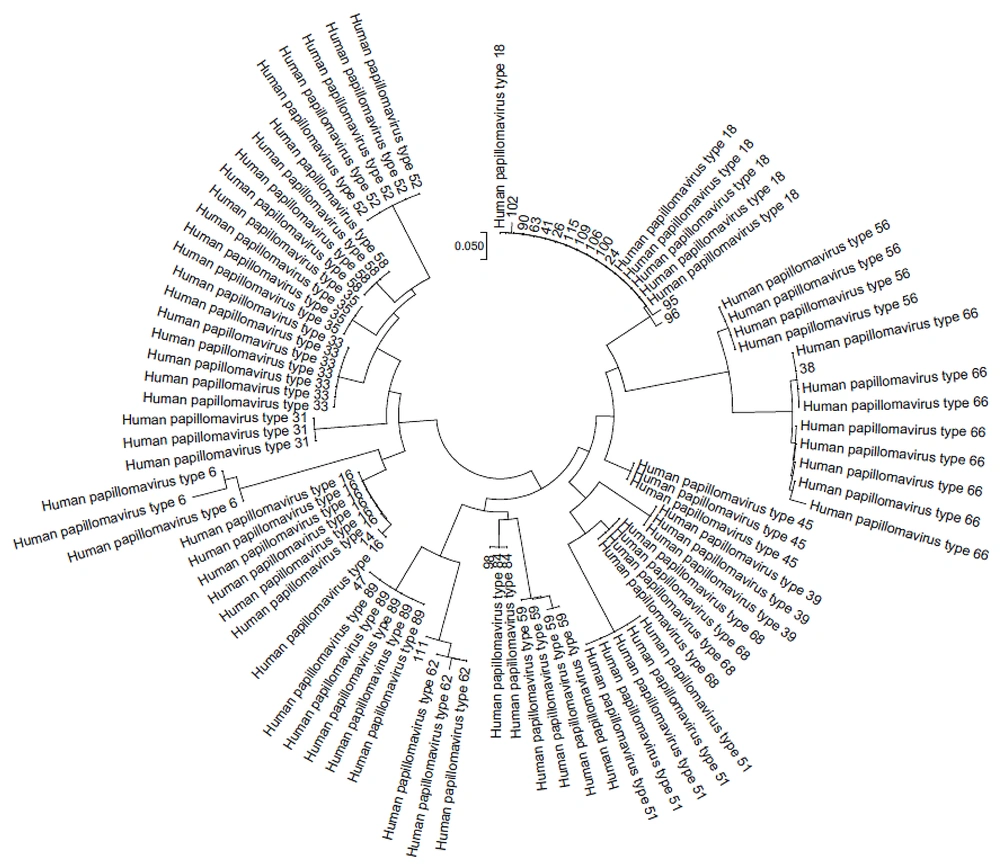
After purifying all PCR products, the forward direction was sequenced using the ABI PRISM 310 Gene Analyzer (Applied BioSystems Inc.) and the ABI PRISM BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction kit (Applied BioSystems Inc.). The HPV L1 sequence results were aligned using the CLUSTAL W tool in MEGA 6.0.6 with reference sequences from the GenBank database. Neighbor-joining was employed to analyze phylogenetic trees. All the results were submitted in GenBank database and the accession numbers of them were OR513853-OR513869.
3.10. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., CA). Categorical data were presented as frequencies, percentages, and charts, and quantitative data were presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to determine the normality. Independent samples t-tests were used to compare sperm parameters between the HPV-positive and HPV-negative groups. The frequency of the specified parameters was compared between two groups using Fisher’s exact test. Significance was indicated by P < 0.05.
4. Results
4.1. The Prevalence of Semen Human Papillomavirus Infection and the Different Genotypes Detected
As presented in Table 2, 18 (12.85%) out of 140 semen samples were found to be HPV-positive. The mean ages of HPV-positive and HPV-negative patients were 39.33 and 35.28 years, respectively. The presence of HPV in semen was not related to the age of the participants (P = 0.36).
| Genotypes | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| High-risk | |
| 18 | 12 (70.58) |
| 16 | 1 (5.88) |
| 66 a | 1 (5.88) |
| Low-risk | |
| 62 | 1 (5.88) |
| 84 | 1 (5.88) |
| 89 | 1 (5.88) |
Human Papillomavirus Genotypes in Human Papillomavirus-Positive Semen Samples (n = 17)
Of the 18 sperm samples with HPV infection, 13 (76.47%) were tested positive for high-risk genotypes, while only 3 (17.64%) were detected with low-risk genotypes. One sample was diagnosed with probable high-risk HPV66, and one was excluded due to poor sequencing quality. Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic tree of the detected HPV genotypes. Regarding genotype distribution, HPV18 was the most prevalent type (70.58%) (Table 2).
4.2. Comparison of Semen Parameters Between Human Papillomavirus-Positive and Human Papillomavirus-Negative Patients
Table 3 summarizes the characteristics and sperm parameters for the HPV-positive and HPV-negative patients.
| HPV-Positive (n = 18; 12.85%) | HPV-Negative (n = 122; 87.14%) | P-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semen volume (mL/ejaculate) | 4.26 ± 0.45 | 3.91 ± 0.29 | 0.66 |
| Abnormal viscosity (%) b | 10.53 | 22.13 | 0.36 |
| pH of semen | 7.76 ± 0.21 | 7.69 ± 0.03 | 0.56 |
| Sperm concentration (× 106/mL) | 49.33 ± 7.81 | 58.96 ± 3.68 | 0.34 |
| Total motility (%) | 47.28 ± 5.49 | 50.72 ± 1.72 | 0.48 |
| Progressive sperm motility (%) | 37.94 ± 5.20 | 39.41 ± 2.06 | 0.79 |
| Normal morphology (%) | 1.55±0.46 | 2.00 ± 0.21 | 0.44 |
| WBC count (× 106/mL) | 1.31 ± 5.16 | 0.67 ± 0.76 | 0.02 c |
| DFI (%) | 33.94 ± 4.10 | 28.30 ± 0.81 | 0.03 c |
| Sperm with immature chromatin (%) | 33.58 ± 4.53 | 32.12 ± 1.78 | 0.74 |
| Semen fructose (mg/dL) | 296.7 ± 33.87 | 281.7 ± 27.38 | 0.74 |
| Semen zinc (mg/dL) | 8205 ± 581.8 | 8475 ± 392.6 | 0.69 |
Comparison of Semen Parameters Between Human Papillomavirus-Positive and Human Papillomavirus-Negative Patients a
The comparison of semen and sperm parameters between HPV-positive and HPV-negative patients shows significant differences between the mentioned groups in some parameters, such as semen WBC and sperm DFI.
The WBC count was considerably higher in the HPV-positive than in the HPV-negative group (P = 0.02); also, DFI was increased in the HPV-positive group (P = 0.03).
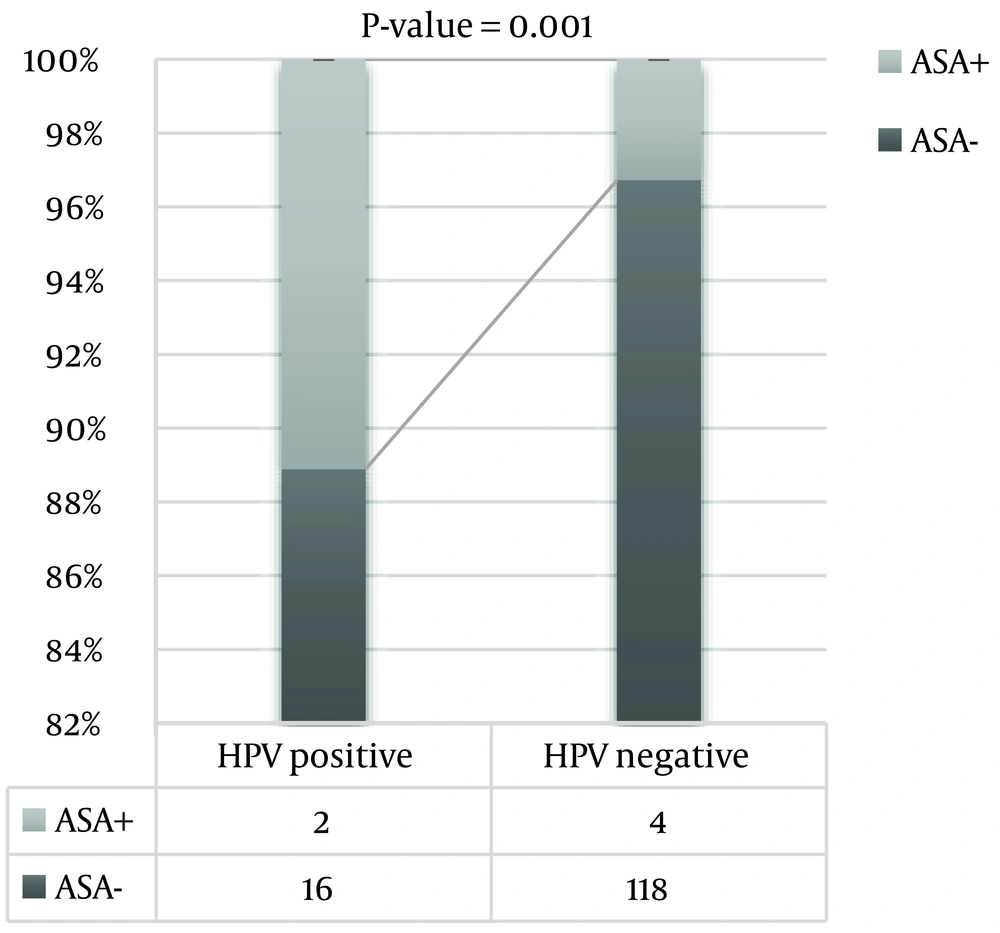
As shown in Figure 2, the presence of ASA was significantly higher in the HPV-positive group than in the HPV-negative group (P = 0.001).
No statistically significant associations were found between the presence of HPV in semen and other examined seminal parameters (i.e., semen volume, abnormal viscosity and pH, sperm concentration, motility, normal morphology, and chromatin maturation).
Zinc and fructose semen levels also show no significant difference between HPV-positive and HPV-negative patients (Table 3).
5. Discussion
Human papillomavirus infection in men was thought to be transient with no clinical consequences. According to current studies, however, it may impair fertility and reduce the efficiency of assisted reproductive technology (11). Since the effect of HPV infection on semen and male fertility potential is still controversial, this cross-sectional study explored the prevalence of HPV infection in semen and its relationship with sperm parameters in infertile Iranian male partners of couples seeking infertility treatment.
We found the prevalence of HPV-positive semen samples to be 12.85%. Some studies in Iran have confirmed our results. Previous studies have shown that the prevalence of HPV infection in semen samples of infertile Iranian men was 11.43% to 28.88 % (17, 18, 23). In this regard, our results were closer to Moghimi et al.’s study (11.43%) (18). The prevalence differences may be due to different geographical areas, demographic and social characteristics, lifestyle and behavioral factors, sexual behaviors, and utilization of different diagnostic tests to detect HPV (29). Moreover, HPV genotype distribution also differs between countries and populations, and even in various parts of the same country (30). In the present study, among 140 infertile Iranian men, high-risk and low-risk HPV genotypes were identified in 14 (10%) and 3 (2.14%) patients, respectively. The most common genotype was HPV 18 (Table 3), which is consistent with the previous study conducted by our team (28). It has been shown that HPV 6, 11, and 16 were the most common genotypes among Iranian individuals with positive HPV DNA (30). Perhaps this difference in genotype results is because the distribution of HPV varies between different regions of the same country (30).
One of the most commonly proposed mechanisms to explain the relationship between HPV infection and male fertility is impaired semen and sperm parameters. Men with HPV-positive semen samples have considerably lower sperm concentrations, total sperm counts, and semen volumes (31). A recent systematic review summarized 14 studies examining the consequences of HPV infection on semen quality. Four studies found no relationship between HPV seminal infection and sperm parameters (32). In the present study, the WBC count was considerably higher in the HPV-positive group than in the HPV-negative group (Table 2). These results are in line with previously reported data (33, 34). Discrepantly, a study found no association between HPV infection and leukocytospermia (13). This discrepancy may be due to the small sample size in the mentioned article (8 samples were detected for HPV infection).
An increase in WBC may be due to different reasons, including male accessory gland infection (MAGI). Since HPV is an important viral cause of MAGI, causing higher WBC counts in semen, leukocytospermia is considered one of the characteristic symptoms of MAGI (35). Given that the majority of seminal HPV infections are asymptomatic, leukocytospermia may be considered an important diagnostic indicator (35). Leukocytospermia in MAGI is linked to elevated levels of reactive oxygen species and reduced sperm quality and function (36). Notably, HPV-antigen identification in semen and circulating leukocytes (37) can lead to both humoral (38) and cell-mediated immune responses (39). A higher number of WBCs can result in oxidative stress, with over-production of reactive oxygen species culminating in lipid peroxidation and increased DFI (40).
In the field of reproductive medicine, sperm DNA fragmentation has received practical relevance. It is also included in the recent literature on HPV infection in semen (41, 42). Sperm DNA integrity is a sensitive parameter for assessing fertility (43). There is currently convincing evidence that infertile males have a remarkably higher DFI than fertile men (44-46). Similar to the previous reports, we found that HPV-positive semen samples had considerably higher DFI values compared to HPV-negative samples. The etiology of the higher DFI is likely to be multifactorial. These elevated DFI values in this study may be due to the increased number of WBCs in the semen and, subsequently, the reactive oxygen species production. Oxidative stress in semen samples is closely connected to sperm DNA damage (47). Accordingly, HPV has been linked to male infertility by reducing sperm DNA integrity. Expression of E6 and E7 oncoproteins in HPV-positive cells plays a significant role in the generation of reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress, leading to DNA damage. Moreover, pro‐inflammatory cytokines like IL‐1, IL‐6, and TNF‐α are upregulated by HPV and also cause the sperm cells to undergo apoptosis and DNA fragmentation (48, 49).
Nevertheless, several studies on this subject have shown discrepant results (50, 51) that might be due to a smaller number of samples or/and the different methods for measuring DFI in those studies.
Another possible explanation for male infertility in patients with HPV-positive semen is ASAs, which may impair male fertility by compromising sperm motility and sperm-oocyte binding (14). According to our findings, HPV-infected patients showed a significantly higher frequency of ASAs-positive samples compared to uninfected individuals; this result is similar to previous reports (14, 17). It has already been confirmed that the presence of HPV DNA on the sperm surface is often associated with ASAs of IgA and IgG classes and impaired sperm motility in infertile patients (14). This data implies that the HPV DNA on the sperm surface may stimulate ASA formation. When ASA binds to the sperm surface, it causes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that interfere with sperm motility and fertility after viral clearance time (approximately 24 months) (14). It has also been reported that the presence of ASAs in HPV-positive semen samples is associated with reduced semen volume, sperm count, motility, and normal morphology (17). The results of this study show significantly lower sperm motility in the ASA-positive group (21.25% in the ASA-positive group versus 70.5% in the ASA-negative group).
It has been found that there is a considerable association between HPV-infected semen samples and hypospermia, abnormal seminal viscosity, higher pH, and a higher number of leukocytes (33). It was also hypothesized that males with HPV-infected semen samples may have an alteration in the proportion of fluid secreted by the male accessory glands, including the seminal vesicles and prostate (33). Fructose is the main carbohydrate source in seminal plasma (52). It is essential for sperm motility and metabolism (3). The WHO guideline recommends the measurement of seminal fructose as an indicator of seminal vesicle function (3). Measurement of its concentration in semen samples has been used to investigate obstructive azoospermia and male accessory gland inflammation (53). In this article, fructose was evaluated as a seminal vesicle marker, and zinc as a prostate secretion marker. The results showed that fructose levels were not significantly different between HPV-infected and non-infected semen samples, which is consistent with previous studies (13). It has been revealed that, overall, STI infections are associated with lower fructose concentrations, while HPV infection is not. It was also shown that leukocytospermia was associated with reduced fructose concentration in semen samples (13). Conversely, in the present study, higher WBC count was not associated with altered fructose concentration. This inconsistency may be due to the fact that the aforementioned study (13) measured the association between leukocytospermia and fructose concentration in semen samples infected with several STI pathogens (our study focused only on HPV-positive samples), and their results cannot be solely related to HPV-positive samples (13).
Zinc appears to be essential for semen quality. It is first excreted into the prostatic fluid. Measuring zinc levels in seminal plasma seems important in assessing male fertility status, as there have been reports of low zinc levels in sperm samples from infertile men (54). These findings might be attributable to impaired prostatic excretory function or an asymptomatic prostate infection (54). A high prevalence of HPV genotypes has been shown in asymptomatic patients with prostate infection, but there is a lack of information about the relationship between HPV infection and zinc levels in semen (55). Here, in the present research, we reported for the first time that seminal zinc levels are not different between HPV-positive and HPV-negative sperm samples. This result provides further insight into the relationship between HPV infection and less-noticed measures of semen quality.
5.1. Conclusions
This study confirms that HPV DNA is common in semen samples of Iranian male partners of couples seeking infertility treatment. It also shows that the presence of HPV seminal is associated with a higher presence of anti-sperm antibodies, WBC counts, and increased sperm DFI values. Overall, these findings highlight the importance of a thorough investigation of seminal HPV in men with infertility, along with other infertility tests. Additionally, more extensive studies should be conducted for a more in-depth assessment of the impact of HPV on male infertility.