1. Background
Eradicating Helicobacter pylori often alleviates symptoms, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Diagnostic methods include the urea breath test (UBT), fecal antigen tests for detecting active infections, histology for examining biopsy samples, stool PCR tests for assessing antibiotic resistance, and serological tests to detect anti-H. pylori antibodies (1-3).
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapies, such as clarithromycin-based triple therapy, face challenges due to antibiotic resistance and side effects, which can impact patient adherence (4). Alternative treatments include bismuth quadruple therapy, which is particularly beneficial in cases of clarithromycin resistance (5). Levofloxacin- and metronidazole-based triple therapy, which combines levofloxacin, metronidazole, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), has shown high success rates with fewer severe side effects, making it a preferred option following clarithromycin-based treatment failure (6). However, increasing antibiotic resistance to drugs like metronidazole and clarithromycin remains a significant challenge, driven by factors such as over-prescription and patient noncompliance. This emphasizes the need for judicious antibiotic use and consistent monitoring (7).
2. Objectives
This study aims to assess the efficacy of levofloxacin-metronidazole therapy in H. pylori eradication in Zakho, Iraq. It also seeks to evaluate diagnostic tools such as the fecal antigen test, UBT, and endoscopy for H. pylori detection, document patient histories of H. pylori tests and treatments, and confirm post-treatment eradication while identifying any correlations with patient histories or characteristics.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
This prospective study, conducted from July 2022 to October 2023 in Zakho, Iraq, enrolled 100 patients with chronic, recurrent epigastric pain.
3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Eligible patients had chronic epigastric pain, a positive H. pylori test (via fecal antigen test, UBT, or biopsy), and a history of incomplete H. pylori eradication. Exclusions included individuals under 18 years old, those resistant to levofloxacin/metronidazole therapy, or those who had previously received bismuth quadruple therapy. The study adhered to the STROBE checklist (8).
3.3. Patient Assessment
Patients' H. pylori test history, prior treatments, confirmatory tests, and PPI usage were reviewed. Diagnostic methods were determined based on recent PPI use: Fecal antigen testing for recent PPI users and UBT for those who had been off PPIs for two weeks. Endoscopy was used for patients with negative fecal antigen test results.
3.4. Sample Size and Data Collection
Data were collected using the census method and gathered through structured questionnaires, which were recorded electronically to cover medical history, demographics, and clinical outcomes, ensuring a comprehensive analysis.
3.5. Sample Collection
Endoscopic tissue samples were stored at 2 - 8°C, while stool samples were either preserved or frozen at -20°C to maintain sample integrity.
3.6. Diagnostic and Assessment Tools
The UBT (14C- UBT) required fasting for six hours, discontinuation of antibiotics for four weeks, and PPI discontinuation for two weeks, with elevated labeled carbon indicating H. pylori. The fecal antigen test detected H. pylori antigens using the EpiTuub® lateral flow immunoassay. Histological examination involved formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded biopsy specimens.
3.7. Treatment Regimens
Patients received a triple therapy regimen comprising esomeprazole or pantoprazole (40 mg/day), levofloxacin (750 mg/day), and metronidazole (500 mg three times daily) for 10 - 14 days, followed by 2 - 4 weeks of PPI monotherapy.
3.8. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics provided an overview of the data. Inferential methods, including chi-square and Kruskal-Wallis H tests, were used for in-depth analysis. Multivariate techniques such as logistic regression and multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) were employed to control for potential confounders and explore relationships between variables. Hypothesis testing was performed at a significance level of P < 0.05. Data processing was conducted using statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS) version 27.0.
3.9. Potential Confounders
Confounders, including prior medication use, dietary habits, and demographic factors, were adjusted for using multivariate regression analyses to ensure accurate outcomes.
4. Results
This study, conducted in Zakho, Iraq, from July 2022 to October 2023, evaluated the efficacy of levofloxacin- and metronidazole-based triple therapy for H. pylori eradication in patients with chronic epigastric pain.
4.1. Demographic Characteristics of Study Patients
Of the participants, 66% were female and 34% were male, with an average age of 37.85 years (SD = 1.18). In the 15 - 25 age group, females comprised 72.73%, and the largest age group was 31 - 40 years (44%). The 26 - 30 age range showed the highest gender disparity, with females constituting 90%. A chi-squared test revealed a significant gender disparity (P < 0.001) and a significant deviation in age distribution (P < 0.001), as shown in Table 1.
| Age Group | Female | Male | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 - 25 | 8 (72.73) | 3 (27.27) | 11 |
| 26 - 30 | 9 (90.00) | 1 (10.00) | 10 |
| 31 - 40 | 29 (65.91) | 15 (34.09) | 44 |
| 41 - 50 | 11 (55.00) | 9 (45.00) | 20 |
| 51 - 60 | 5 (62.50) | 3 (37.50) | 8 |
| > 60 | 4 (57.14) | 3 (42.86) | 7 |
| Total | 66 | 34 | 100 |
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
4.2. Laboratory Results for Helicobacter pylori Tests
Among the 60 patients tested using the fecal H. pylori antigen test, 96.5% showed positive results. For the 40 patients tested with the UBT, the positive rate was 97.5%. Negative results were minimal: 2.5% for the UBT and 3.5% for the fecal antigen test, as shown in Table 2.
| Test | Frequency Positive | Positive Rate (%) | Frequency Negative | Negative Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal Helicobacter pylori Ag | 58/60 | 96.5 | 2 | 3.5 |
| Urea breath test | 39/40 | 97.5 | 1 | 2.5 |
| EGD and biopsy for Helicobacter pylori | 3/3 | 100 | - | - |
Abbreviation: EGD, esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
4.3. Distribution of Test Results by Gender
The positive rates were 37.88% for females and 41.18% for males, with males exhibiting a slightly higher H. pylori prevalence based on both diagnostic tests. The Kruskal-Wallis H test found no significant gender differences in detection rates (P = 0.3679).
4.4. Treatment Regimens
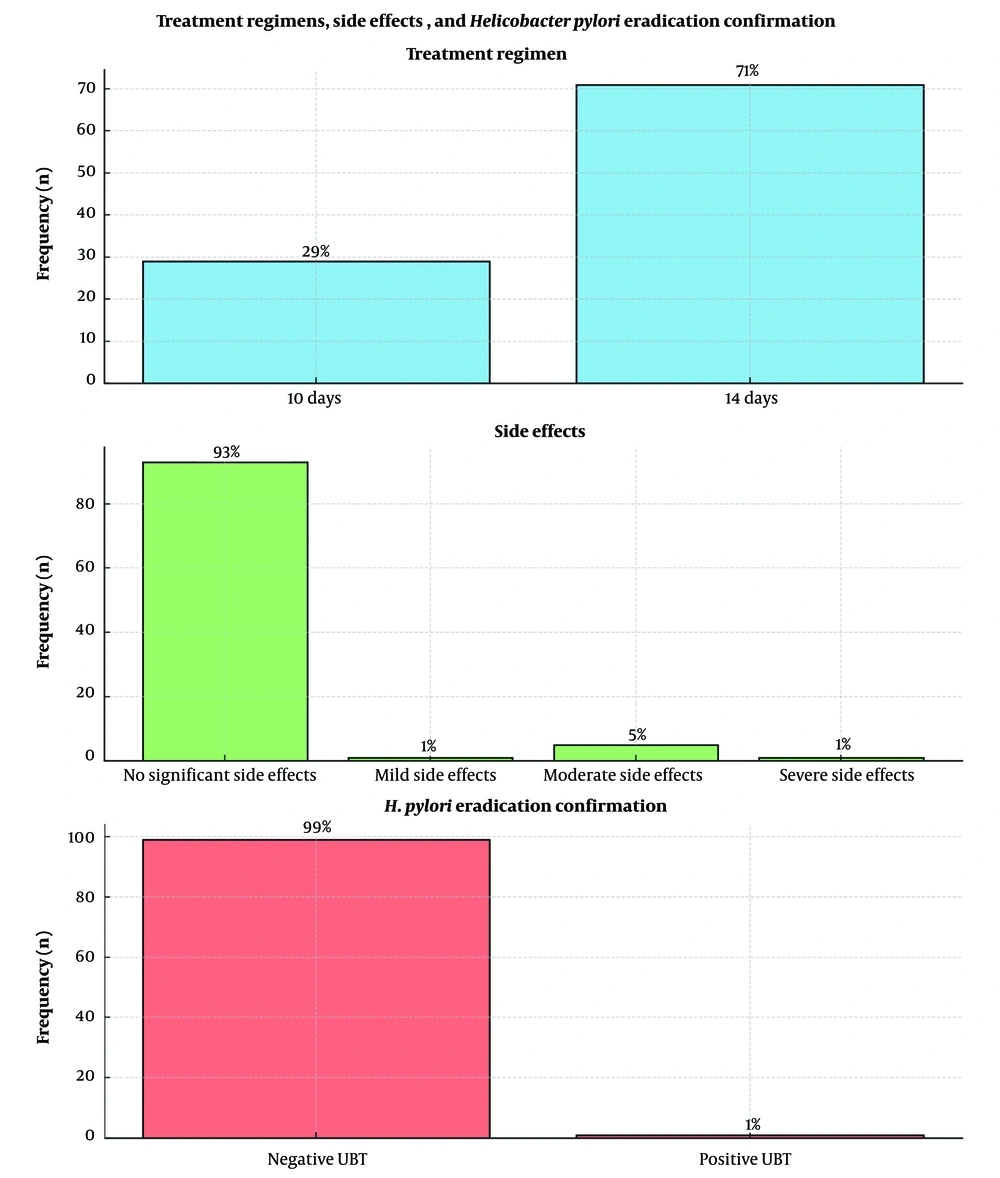
Patients received levofloxacin, metronidazole, and either esomeprazole or pantoprazole for 10 or 14 days, with 71% on the 14-day regimen. Side effects were minimal, with 93% of patients reporting none. Post-treatment, H. pylori was eradicated in 99% of cases, demonstrating high efficacy and tolerability (Figure 1).
5. Discussion
Globally, H. pylori infection rates average 50.8% in developing nations, compared to 34.7% in developed regions (9). This study reported a 33.33% prevalence in Zakho, with higher rates among males. Similar studies by Pshtewan and Khoshnaw (10, 11) showed prevalence rates of 53.3% in Erbil, 51.2% in Sulaymaniyah, and 28% in Dohuk, emphasizing the need for localized research to understand regional variations.
Only 3% of patients in this study were diagnosed using esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and biopsy, reflecting the invasive nature of this method. The study prioritized non-invasive diagnostics, aligning with global trends favoring patient-friendly approaches (12).
The fecal antigen test demonstrated 96.5% accuracy, proving its reliability as a non-invasive, quick diagnostic option (13). With accuracy exceeding 90%, stool antigen testing (SAT) is both cost-effective and convenient for detecting H. pylori, as noted by Cardos et al. (14) and Elbehiry et al. (15). Its utility extends to post-treatment assessments, making it invaluable across patient demographics.
The UBT yielded a 97.5% positivity rate, with minimal false negatives, supporting its reliability in diagnosing H. pylori. These findings align with Gomollon et al. (16), who confirmed UBT's high sensitivity and specificity.
Using the Kruskal-Wallis H test, no significant age-based differences in H. pylori detection were found (P ≈ 0.4159). However, the 51 - 60 age group exhibited a higher susceptibility, potentially due to prolonged exposure or delayed diagnoses. This highlights the need for targeted interventions for older demographics to mitigate H. pylori-associated risks (17).
The study evaluated one of the primary H. pylori treatment regimens using levofloxacin and metronidazole combined with either esomeprazole or pantoprazole. Treatment duration (10 or 14 days) was based on infection severity, with 71% of patients receiving the 14-day regimen for enhanced efficacy.
Levofloxacin's superior efficacy over clarithromycin, especially in resistant regions, was evident, corroborated by Keikha et al. (6). Studies from northeastern Poland also demonstrated levofloxacin-based triple therapy (L-TT) as a potent treatment option (18).
Using UBT to assess treatment outcomes, this study achieved a 99% H. pylori eradication rate. The high success rate, combined with minimal adverse effects, underscores the effectiveness and safety of the modified regimen.
5.1. Practical Significance and Implications
This study highlights age-related variations in H. pylori prevalence, advocates for non-invasive diagnostic methods, and demonstrates the efficacy of levofloxacin-metronidazole therapy. It provides valuable insights for improving patient outcomes and contributes to clinical practice and policy-making.
5.2. Study Limitations
Despite the significant sample size, selection and recall biases may affect the generalizability of the findings. Unvalidated instruments and uncontrolled confounders present potential measurement errors and causality issues in this cross-sectional study, highlighting the need for further research.
5.3. Conclusions
This study offers valuable insights into H. pylori prevalence, diagnostic methods, and treatment efficacy. It underscores age and gender patterns, advocates for non-invasive diagnostics, and highlights the superior efficacy of levofloxacin-metronidazole therapy. Policymakers should allocate resources to support these findings to optimize H. pylori management.