1. Context
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 began with many people reporting pneumonia in the Wuhan district of China sometime in December 2019. The outbreak was thereon found to be triggered by a new human coronavirus, which was subsequently named severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (1). The WHO declared SARS-CoV-2 as a public health emergency of international concern on 30 January 2020, and the world is still struggling to combat its menace (2). As of 11 July 2021, there were 187,419,263 reported cases and 4,045,647 deaths worldwide (www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/) due to SARS-CoV-2 of which, 3,08,37,222 cases and 4,08,040 deaths were reported from India (www.mygov.in/covid-19). The journey of coronaviruses and human diseases has many prior incidents of which SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been known to cause severe diseases. Others, including OC43, HKU1, NL63, and 229E were reported to be responsible for minor indicators (3, 4). In the present review, we discuss the origin of SARS-CoV-2 by comparing the genome, host range, its target receptor, viral spike protein, and strength of interaction of receptor binding domain (RBD) with its host receptor with those of earlier reported coronaviruses.
2. Evidence Acquisition
The data for the present review were accessed through different publications and preprint repositories.
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Variation of SARS-CoV-2
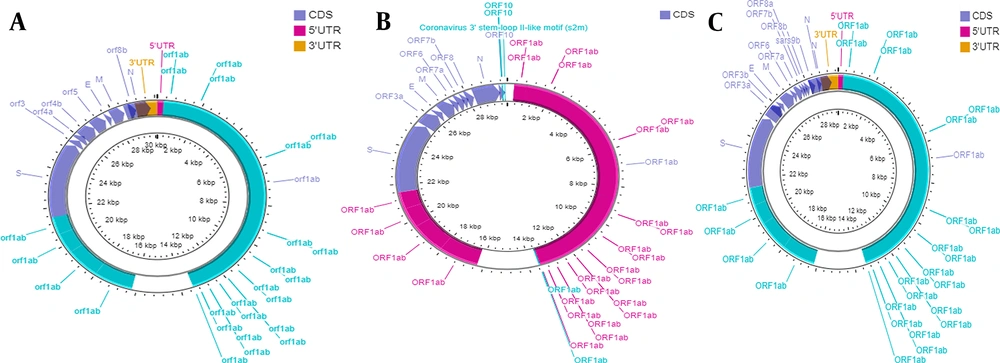
As known, SARS-CoV-2 belongs to beta-coronaviruses. Morphologically, it may be round or oval of about 60 - 140 nm. Its characteristic crown-shaped appearance under an electron microscope led to the basis of the name ‘Coronavirus’ (5). Besides beta (β), the Coronaviridae family also has other genera, namely α, γ, and δ. Among them, members of α and β genera are known to have mammals and humans as the host. The coronaviruses harbor a single-stranded RNA genome of about 26 kb to 32 kb (6). Among those infecting humans, the MERS-CoV genome has been reported to be of ~ 30.1 kb RNA (+) (7), while the SARS-CoV-2 reference genome is 29.9 kb (8). The SARS-CoV-2 genome has been reported to harbor around 26 proteins whose details and comparative mutation profiles across deceased and asymptomatic patients have been reported by our group recently (9). The 3’ end of the genome encodes four structural proteins: (1) spike (S), (2) envelope (E), (3) membrane (M), and (4) nucleocapsid (N), of which the S protein is known to interact and attach to the host cell aiding in viral entry.
The genomes of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV have more than 80% identity to human coronavirus (SARS-like bat CoV) (10). The common entity includes ORF1ab with 16 non-structural proteins (NSPs) and four structural proteins. However, SARS-CoV-2 ORF3b and ORF10 have little similarity to those of SARS-CoV. Further, ORF8 is undivided in the former and split as ORF8a and 8b in the latter (7). A comparative illustration of the genomes of SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and MERS-CoV is shown in Figure 1. There are similarities and dissimilarities at the protein level. For instance, there are 154 amino acid 3b proteins in SARS-CoV as compared to just 22 amino acids in SARS-CoV-2 (10). Contrastingly, NSP7, NSP13, envelope, matrix, and accessory proteins have no amino acid substitutions, whereas there are variations in NSP2, NSP3, and S protein (11). Of these, NSP2 and NSP3 mutations are known to affect infectivity (12). The new emerging variants are discussed later.
Genome organization of three different beta coronaviruses. A, SARS-CoV; B, SARS-CoV-2; and C, MERS-CoV. Figure were developed by using CGView DNA Plotter (13).
3.2. Definitive and Intermediate Host Range
The SARS-Cov-2 pandemic owes its origin to a seafood market, and efforts have been made to study the animals in the market acting as hosts. Snakes have been one of the probable candidates supported by similar codon usage (14). The high level of similarity between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-like bat coronavirus at the genome level supports the bats acting as reservoirs (15). This was also supported by phylogenetic studies that not only placed the bat-derived coronaviruses across all the five subgenera of beta-coronavirus but also found SARS-CoV-2 was evolutionarily closest to bat-SL-CoVZC45 and bat-SL-CoVZXC21 (16). Further evidence is provided by over 96% genome similarity between bat CoV RaTG13 and SARS-CoV-2 (2). Moreover, similar receptor sequences across species indicate that turtles, pangolin, and snakes can also act as intermediate hosts (17). It is noteworthy to mention that SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV also have bats as natural reservoirs and masked palm civets or dromedary camels as intermediate hosts. Needless to say that humans are the terminal hosts (18). The transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from bat to human may have happened through animals being sold at the Wuhan market.
Metagenomic analysis of samples from pangolins reported the presence of β-CoV28 in most. One of the studied samples showed almost 99% similarity to SARS-CoV-2. This supports the candidature of pangolin as an intermediate host (19). It was also supported by several pangolin Coronaviruses from pangolin with identical sequences at important positions of RNA binding domain (RBD) of the S protein, implying the ability to bind to human ACE2 receptor, facilitating their movement to humans (20).
3.3. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) as Target Receptor
The S protein is a glycosylated protein found on the surface of coronaviruses, appearing as a spike. It mediates viral entry by binding RBD to ACE2 receptors on the host cell (21). As known, ACE2 encodes for an exopeptidase enzyme, which is responsible for angiotensin conversion to different forms (22). Besides, SARS-CoV-2 is believed to employ a similar method to enter the host cell as uses SARS-CoV (23).
The implication of ACE2 receptor in viral entry makes the cells expressing this receptor susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Diverse cells acting as hosts would imply the severity of symptoms. The major cells known to express this receptor include the epithelial cells of lung alveoli, the smooth muscle cells of the artery, the epithelium of the kidney tubule, and the epithelium of the small intestine (23). Though SARS-CoV-2 has been known to be primarily associated with respiratory problems, the presence of ACE2 receptors across tissues makes the body more vulnerable. Corresponding physiological manifestations have been reported as well, with diarrhea being present in the sample followed by the presence of virus in feces (22).
Expectedly, there are variations in the expression levels of ACE2 across tissues adding to the dynamics. Its expression is normally low in the lungs but can be enhanced under some physiological manifestations (24). The possibility of co-receptors aiding ACE2 is also very much plausible. Aminopeptidase N (ANPEP) and dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4) are candidates for the same (25).
3.4. ACE2 Receptor Diversity in Nature
The ACE2 expression is reported across fish to mammals. Moreover, it shows structural conservation, as well. Human ACE2, when analyzed with that of the civet, bat, bird, snake, frog, and fish, showed amino acid sequence identities of 83, 81, 83, 61, 60, and 59%, respectively (24). Thus, ACE2 from these species can potentially interact with the RBD of SARS-CoV-2, making these animals not only prone to infection but also as reservoirs. This also highlights the host adaptability of the virus (24).
3.5. Spike Glycoprotein
The role of spike (S) glycoprotein in mediating the entry of SARS-CoV-2 in human host cells is well documented. At the protein level, it is comprised of an ectodomain at the N terminal, followed by a transmembrane region and a C-terminal intracellular tail (21). This ectodomain region makes up subunits S1 (receptor-binding) and S2 (membrane-fusion). The RBD, which is critical for interacting with host receptors, is localized in the S1 region. Interestingly, the S2 region is greatly conserved with 99% identity to not only SARS-CoV but also several bat coronaviruses (24). Once it is fused to the target receptor, S1 is thereon acted on by S2, as well as host protein cleaving enzymes (26). The induced changes in conformation can lead to the activation of membrane fusion proteins (27).
In terms of variation, the RBD of the S protein is highly diverse, but there are six amino acids, which, if affected, will directly impact the interaction with the host receptor. They are summarized in Table 1. Structural comparison of RBD reveals that it is almost superimposing for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. The only exception is a loop. The structure is primarily of beta-sheets with no breakers and multiple disulfide bonds forming cysteinyl residues: C366/C418 and C467/C474 (24). The S protein is also conserved concerning 22 glycosylation sites, with the exception of N370 being present only in SARS-CoV-2 (28).
| S. No. | SARS-CoV | SARS-CoV-2 | Effect on RBD/ACE2 Interaction | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N442 | L455 | RBD of SARS-CoV-2 has better efficiency than that of SARS-CoV | (29) |
| 2 | L472 | F486 | Hot spot 31; Adds flexibility to the interaction | (24) |
| 3 | N479 | Q493 | Hot spot 31; Promotes the civet to human transmission | (30) |
| 4 | D480 | S494 | Enhances viral binding to human ACE2 | (18) |
| 5 | T487 | N501 (hot spot 353) | RBD/ACE2 interaction is more efficient in SARS-CoV-2 | (24) |
| 6 | Y491 | Y505 | This Y491/Y505 alteration has the enhanced RBD/ACE2 interaction at various temperature. | (31) |
| 7 | T499 | P499 | P499 forms better adaptation for host binding in SARS-CoV-2 | (32) |
| 8 | CTPPALNC; 68 - 471 | CNGVEGFNC; 482 - 485 | Flexibility to RBD/ACE2 interaction | (24) |
| 9 | RRAR (cleavage site) | PRRA | The addition of Proline makes the cleavage site more unique and affects transmission and pathogenesis in the animal model | (19) |
Amino Acid Changes in Spike Protein Between SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2
Also, SARS-CoV-2 has a polybasic cleavage site (RRAR) which on cleavage influences viral infectivity and host range. For instance, if it changes to PRRA, it creates a cleavage site exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. This mutation has helped the spike protein evolve to be able to bind to human ACE2 (19).
3.6. RBD and ACE2 Interaction
The binding energy for the interaction between RBD and ACE2 receptors has been shown to be positive and involves two b-sheets and three loop structures. The residues directly associated with this interaction, if altered, will have implications in viral entry and hence pathogenesis (24). There are a total of 14 residues in the ACE2/RBD interface. Of these, nine are conserved, and four are variable (33). At the 479-position, amino acid aspergine (N) was mutated to lycine (K) & arginine (R) in civet and bat respectively. This phenomenon determines the species barrier of host preference in SARS-CoV infections. The N479K mutation reduces binding affinity drastically (34). Contrastingly, the S487T mutation enhances RBD/ACE2 interaction (33). Thus, mutations favoring this interaction would support transmission to humans and vice versa. As an example, SARS-CoV with T487S mutation, which hugely decreases binding affinity, exhibited no human to human transmission, implying the importance of the hydroxyl group (34).
The presence of hydrophobic amino acid L472 is crucial for RBD/ACE binding, which is substituted by proline and phenylalanine in SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 (F486), respectively. It is localized in the loop region formed by C467/C474. This loop differs from CTPPALNC in SARS-CoV to CNGVEGFNC in SARS-CoV-2 (Table 1). The substitution of prolines by glycines alters the structure flexibility. Aromatic residues, when present in the region, further increases binding efficiency (24). Another substitution at P499 in SARS-CoV-2 has been reported to lead to better adaptability (32). Another important aspect of the S protein is the glycosylation sites. Of the reported 23 sites of this type, only two are present on RBD, but their importance in RBD/ACE2 interaction, if any, needs to be ascertained.
3.7. Various New Strains of SARS-CoV-2 Lineage
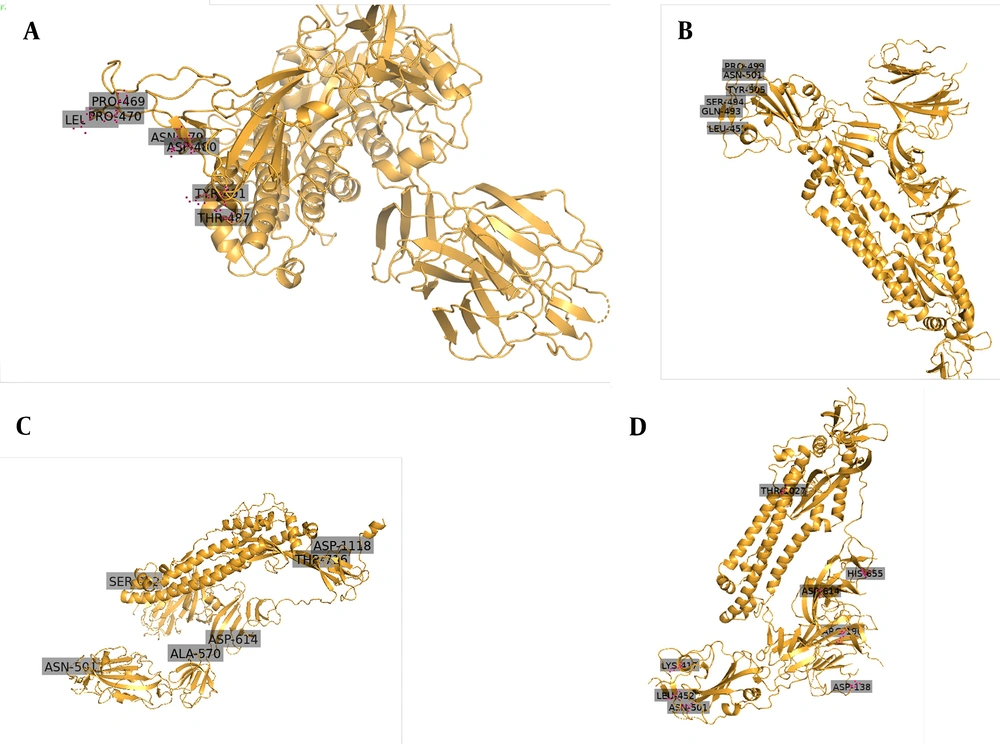
Since November 2020, a new strain of SARS-CoV-2 has manifested in Britain. It is believed that 60% of recent infections happened in London by this new strain. As of 20 December 2020, a large number of areas in London, as well as South-East and East England, showed confirmed cases of this new variant. Scientists have named the new strain as “VUI-202012/01” (originally termed as B.1.1.7 by Public Health England), which became dominant over existing versions of SARS-CoV-2 (35). The 3D images have been shown in Figure 2, indicating the locations of key mutations of SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, B.1.1.7 lineage, and B.1.617 lineage. High rates of mutation were shown in a short period in immunodeficient and immunosuppressed people infected by SARS-CoV-2 (36). This strain inhabited nonsynonymous mutations and deletion (36).
A study showed eminent changes in the Spike protein, importantly position 501 in RBD changes N (aspergine) to Y (tyrosine). That enhances the binding to human ACE2. This N501Y mutation can increase its ACE2 receptor binding affinity (37). The N501Y mutation also enhances virus adaption in the animal model (38). This mutation raises virus transmissibility by 70% (39). Another important mutation, P681H, occurs in the S1/S2 furin cleavage site (40). This furin cleavage site has been shown to enhance access to respiratory epithelial cells and also helps in virus transmission in the animal model (41). A deletion at 69-70HV in the N terminal of the spike protein has also been reported (42). Other important nonsynonymous mutations in the Spike protein include A570D, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H, and Y144 deletion (40).
A study suggested that SARS-CoV-2 lineage aggregate one to two mutations per month (43). Various SARS-CoV-2 lineages emerge throughout the world, and a few important mutations are listed in Table 2. Some mutations help viruses escape from the immune system and resist antibodies. Multiple mutations give rise to a new strain. Mutations in viruses are often a result of low polymerase fidelity and a survival mechanism to adjust a new host tropism (44). Recently an Indian variant named B.1.617 emerged with two mutations in the spike protein (L452 and E484Q mutations) separately (45). These two E484K and L452R mutations coexist and enhance the affinity for binding to ACE2 receptors (46). As per the World Health Organization, lineage B.1.617.2 was named as ‘delta variant’ with substitutions T478K, P681R, and L452R. Further, the B.1.617 variant also carries another unusual combinational mutation L452R & E484Q (designated as B.1.617.1 or kappa variant) and V383L mutation along with L452R & E484Q (known as B.1.63.3) [Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation reports (who.int)].
| S No. | Lineage B.1.1.7 or 501Y.V1/Alpha (UK) | Lineage B.1.351 or 501Y.V2 /Beta (South Africa) | Lineage B.1.1.24 or P.1/ Gamma Variant (Brazil) | B.1.617.2/Delta (India) | B.1.617.1/Kappa (India) | B.1.617.3 | Effect of Amino Acid Changes in the New Strain | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HV 69-70 del | L18F; D80A | L18F; T20N; P26S | T19R; 156-148 del | T19R; 156-148 del | T19R; 156-148 del | The H69/V70 single mutant showed two-fold more infectivity compared to the wild-type virus. | (47) |
| 2 | Y144 del | D215G; 242-245 del; R246I | D138Y; R190S | L452R mutation (without E484Q) | L452R. | V383L mutation along with L452R | Also present in California B.1.427/B.1.429. Affecting resistance to antibodies | (46) |
| 3 | E484K a; N501Y a | K417N; E484K a; N501Y a | K417T; E484K a; N501Y a | T478K | E484Q a | E484Q a | 1.N501Y mutation was associated with increased transmissibility of the virus; 2.The E484K was reported to be an escape mutation from a monoclonal antibody, which neutralizes SARSCoV-2; 3.E484 in RBM interacts with the K31 interaction hotspot, enhancing binding affinity; 4. K417N mutation has a functional significance in the receptor-binding domain; 5. E484K mutation in B.1.351, P.1, and P.3 imparts partial resistance to antibodies. | (31, 37, 45, 47, 48) |
| 4 | D614G a; A570D | D614G a; A701V | D614G a; H655Y | D614G a | D614G a | D614G a | Scientists showed that the 614 position of spike protein has a serine protease elastase 2 proteolytic site. This D614G mutation participates in proteolytic activity, which enhances viral entry into 293T-ACE2 cells. | (49) |
| 5 | P681H; T716L | - | - | P681R | P681R | P681R | P681H mutation is involved in creating a furin cleavage site at S1/S2, which promotes the entry of coronavirus to respiratory epithelial cells and animal model; 2.P681R arrived due to an increase in the amount of cleaved spike protein (S) on virions. | (40, 41, 46) |
| 6 | Q27Stop | Located in ORF8, it is a stop mutation that truncates the protein making it inactive. | (40) |
Important Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Lineages
4. Conclusions
The biggest scientific challenge in combating the present pandemic has been the interpretation of constantly accumulating data from all over the world. The spike glycoprotein has emerged as the frontrunner therapeutic candidate, but its mutations and their impacts make it highly unpredictable. The widespread presence of ACE2 receptors in the body has led to varying physiological manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection. With long-term effects of the infection still unknown, a comprehensive understanding of the disease remains elusive, but the strong correlation at both genome and proteome levels with other coronaviruses should help us manage the pandemic.