1. Introduction
Myofibrillar myopathies (MFM, [MIM 601419]) are a group of clinically and genetically heterogeneous neuromuscular disorders defined by ectopic expression of proteins, such as desmin, and myofibrillar disorganization starting at the Z-disk and protein aggregates in muscle fibers (1). The clinical phenotypes of myofibrillar myopathies are widely heterogeneous. Patients usually present with progressive muscle weakness that can involve both proximal and distal muscles, with the age of onset ranging from infancy to late in adulthood, but in most cases the symptoms appear in the fourth and fifth decades. However, other features are extremely variable. The diagnosis of MFM is frequently difficult because of the substantial phenotypic and pathomorphological variability (2, 3). In recent years, an increasing number of genes have been recognized to be involved in MFM pathogenesis, causing subgroups of the disease. Until now, mutations in nine genes have been identified to cause MFM: titin (TTN), DNA J homolog subfamily B member 6 (DNAJB6), bcl-2 associated athanogene protein 3 (BAG3), four and a half LIM domain protein 1 (FHL1), Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ containing protein (ZASP, also LDB3), αB-crystallin (CRYAB), desmin (DES), filamin C (FLNC) and myotilin (MYOT, also TTID) (4-11). More than 50% of cases are caused by unresolved gene defects. In this report, we describe the first dominant acting heterozygous mutation in the LDB3 gene, which affects a family with severe myofibrillar myopathy. This mutation produces novel protein coding transcripts that might explain the MFM phenotype in the patient.
2. Case Presentation
The patient was a 21-year-old man, and the last child of consanguineous parents of southwest Iran. He was admitted to the neurologist for investigation of slowly progressive walking difficulties that began two years previously. He also had slowly progressive hand and foot weakness (distal muscles) and occasional stiffness and cramping of the leg muscles after exercise. He had severe weakness of toe extensor, anterior tibial and peroneal muscles, and mild weakness of iliopsoas, quadriceps, hamstring and finger extensor muscles. His parents were relative (his father died at age 70 and had suffered from Parkinson and his mother was 60 years old and was reported to be unaffected).
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral leukocytes of the patient and controls, using standard procedures (12), and PCR sequencing was performed to investigate the possible cause of muscular dystrophies, including analysis of the mutations in LDB3 (ZASP) in the patient with MFM phenotypes.
PCR was conducted under the following conditions: 200 μM deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), 100 ng genomic DNA, 2.5 units supertaq polymerase, 1.5 mm MgCl, and 25 pmol each primer (Table 1) (13). Amplification was carried out in 25 μL volumes and 35 cycles: 94°C for one minute, 65°C for 35 seconds and 72°C for one minute. The sequencing reactions were carried out and the sequences were compared to the reported gene sequence using the BLASTN program.
| Exon/Primer | Primer Sequence (5 - 3) T | PCR Product Size, bp |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 221 | |
| ZASP 1F | GTGCCCTCTCACTCAACCCT | |
| ZASP 1R | ACACATGCCCTCCTCCAAGC | |
| 2 | 335 | |
| ZASP 2F | TGGCCTTTCCTCAGGACCAC | |
| ZASP 2R | TCCTGCACAGTTTTGTAGCC | |
| 3 | 230 | |
| ZASP 3F | TGACTCTGGCTCTCTCTTGCT | |
| ZASP 3R | TCCAGGAACCAGGGCTGAGT | |
| 4 | 506 | |
| ZASP 4F | GGCTCGCGCTAACACATCTG | |
| ZASP 4R | GCCACCTGTGGAGAGCTGTA | |
| 5 | 266 | |
| ZASP 5F | CACTCCTTGCTCTCCTCACC | |
| ZASP 5R | CTCTATCCACGCCAGACACA | |
| 6 | 380 | |
| ZASP 6F | TGTAACCGCCACCTGTTGCC | |
| ZASP 6R | TCCAGGAGGTCCAACGTGAG | |
| 7 | 353 | |
| ZASP 7F | CCACCAATGGGCATGGAGCA | |
| ZASP 7R | AGCAGGACTCCCTGGCTTCT | |
| 8 | 178 | |
| ZASP 8F | TTGCTGTGTCTCCCGTGAGT | |
| ZASP 8R | GAGGTCCCTTCCATGAGTGA | |
| 9 | 317 | |
| ZASP 9F | GGTGAACACATTCCCTAACC | |
| ZASP 9R | CCCAGCAGAGTTATACATTG | |
| 10 | 331 | |
| ZASP 10F | GCTCCCTTGACCTGTTGTCT | |
| ZASP 10R | GCCCTAACTACCTTGGACAC | |
| 11 | 257 | |
| ZASP 11F | GGCTGTCCTTCTGGGTGTAA | |
| ZASP 11R | TCTTGGCTCTTGTGGCTCCT | |
| 12A | 348 | |
| ZASP 12AF | CATTTCTCTGGCTAGGAGTG | |
| ZASP 12AR | CTGGGAGAAGCTATCATCTG | |
| 12B | 352 | |
| ZASP 12BF | TGCACCCTCGGTGGCCTACA | |
| ZASP 12BR | CTCCCAACCAGGGCTCAGAC | |
| 13 | 267 | |
| ZASP 13F | GTTCTGGGAGCTGCCTTACT | |
| ZASP 13R | GGAAGAGACATGGGTCAGAG | |
| 14 | 200 | |
| ZASP 14F | AGTCAAGCCCGCTCCCTCTC | |
| ZASP 14R | CACATGCCATCGAAGTGTTC | |
| 15 | 290 | |
| ZASP 15F | TGATTTGGGGTTTGTCTTGG | |
| ZASP 15R | CTAGCGTGGCAAGGTATGTA | |
| 16 | 229 | |
| ZASP 16F | GTCTCACGCAGGTCTGTTCT | |
| ZASP 16R | GCTTCCTCTCTCTCCCCATT |
Primers Used for the Screening of the LDB3 Gene
The search for rare variants (MAF, 1%) that were specifically found in the affected man was carried out with different open access Web tools. The effect of the candidate variant in protein structure and phylogenetic conservation was predicted by using bioinformatics tools, such as PolyPhen-2 (Polymorphism Phenotyping v2), SIFT (Sort Intolerant from Tolerant) and Mutation Taster, to estimate the pathogenicity risk for the variant.
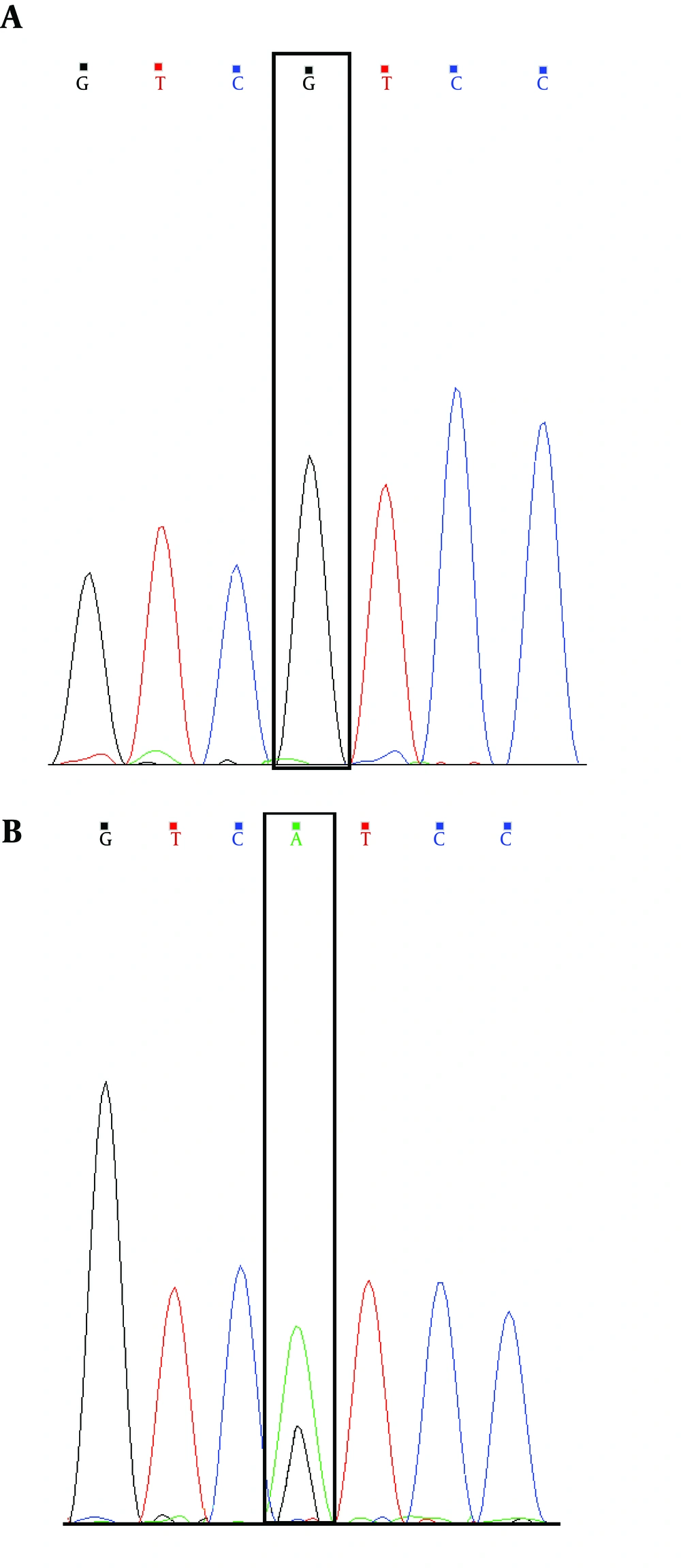
Analysis of DNA sequences in coding exons of the LDB3 gene represents a novel heterozygous missense. So far, the substitution (the c.1687A > G, p.Ile563Val mutation in exon 10 of LDB3 (Figure 1)) has neither been observed as a polymorphism in the latest 1000 Genomes Project databases, nor as a causative mutation in any accessible disease mutation database (for example, HGMD: Human Gene Mutation Database) (Table 2).
| Codon Change | Amino Acid Change | Codon Number | Phenotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAC/AAC | Asp/Asn | 117 | Cardiomyopathy, dilated | (13) |
| AAG/ATG | Lys/Met | 136 | Cardiomyopathy, dilated | (13) |
| GCC/ACC | Ala/Thr | 147 | Myofibrillar myopathy | (8) |
| GCC/GTC | Ala/Val | 165 | Myofibrillar myopathy | (8) |
| GCC/ACC | Ala/Thr | 174 | Myofibrillar myopathy | (14) |
| CGC/TGC | Arg/Cys | 268 | Myofibrillar myopathy | (8) |
| ATC/GTC | Ile/Val | 563 | Myofibrillar myopathy | Present study. 2015 |
Missense Mutations Available of the LDB3 Gene in the HGMD
LIM domain binding 3 (LDB3 [ENSG00000122367]) is at position chr10:88476524 A.G. In humans, LDB3 has nine annotated protein coding transcripts. The novel mutation produces an amino acid alter (Ile to Val) that modifies four of the nine coding isoforms predicted in the Ensembl database, and the function of this mutation is unknown.
Bioinformatics analyses indicate that the I563V mutation most probably causes LDB3 dysfunction, leading to the MFM clinical phenotype. Furthermore, analysis using various programs, e.g., SIFT (deleterious, score 0.00), Mutation Taster (disease causing, P value 1.0) and Polyphen-2 (probably damaging, score 1.00) indicated p.Ile563Val was predicted to be disease causing and probably damaging (Table 3). Unfixed muscle tissue of this patient was not accessible and no muscle biopsy could be obtained in order to conduct supplementary proteomic analyses for further clarification. Furthermore, family members were not accessible for segregation analysis to clarify the pathogenicity.
| LDB3/Software | SIFT Score | PolyPhen Score | Mutation Taster |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENST00000429277, I563V | 0.01 (DAMAGING) | 0.993 (PROBABLY DAMAGING) | Disease causing |
Various in Silico Bioinformatics Tools Have Been Developed That Predict the Novel Mutation
3. Discussion
In the present study, using direct sequencing, we looked for mutations in this patient in the LDB3 gene previously associated with MFM or muscular dystrophy. We identified the c.1687A > G (p.Ile563Val) mutation in exon 10 of this gene in members of a consanguineous family with an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance with severe MFM. So far, this mutation has not been reported in any of the information banks. All bioinformatics tools applied classified the identified substitution as pathogenic.
The LDB3 gene (OMIM: 605906) has 16 exons and spans approximately 70 kb (15). There are three isoforms of LDB3 in human skeletal muscle, which are produced by alternative splicing of exons 9 and 10. The prenatal long isoform (ZASP-L) contains exon 10 and the postnatal long isoform (ZASP-Ldelex10) lacks exon 10. Both long isoforms include a PDZ domain, ZASP-like motif encoded by exon 6 and 3 LIM domains. The short isoform (ZASP-S) lacks the LIM domains, because it has a stop codon in exon 9 (15). PDZ domain-containing proteins interact with a number of proteins involved in clustering and targeting of membrane proteins or with each other in cytoskeletal assembly. LIM domain-binding protein 3 encoded by this gene is a key Z-disk protein that interacts with α-actinin and protein kinase C. LDB3 protein also interacts with all members (MYOZ1, MYOZ2, MYOZ3) of the myozenin family (16, 17).
The three different missense mutations in the LDB3 gene (A147T, A165V, and R268C), recently published by Selcen and Engel, were found in patients in a heterozygous form, causing myofibrillar myopathy. The first two mutations occurred in exon 6, but R268C occurred in exon 9 (8). Since both mutations were detected on the same gene in LDB3, a similar phenotype might be expected in the patients of both families such as progressive proximal and/or distal weakness, cardiac involvement and peripheral neuropathy. Mutant LIM domain-binding protein 3 (ZASP) is predicted to weaken the linkage of Z-disk filaments to thin filaments. This novel mutation (c.1687A > G (p.Ile563Val) mutation in exon 10) may change the function of the ZASP-L and LIM domains.
In summary, in this study we identified by direct sequencing the first dominant and heterozygous mutation in the LDB3 gene causing MFM and the first in a non-European patient. Consequently, defects in this protein could destabilize the muscle cell membrane and, at the same time, weaken myofibrils. This may eventually result in clinical and molecular features resembling MFM. Our finding confirms previous reports that the muscle phenotype associated with LDB3 mutations is consistent.