1. Background
Malignant lymphoproliferative disorders (MLDs) are a heterogeneous group of disorders that result from the clonal proliferation of B, T, and NK cells (1). Common lymphoproliferative disorders include: chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), lymphomas and multiple myeloma (2). There are several inherited gene mutations that have been identified to cause MLDs. Researchers also claim that viral, genetic, environmental and immunological factors may be involved in the pathogenesis of MLDs (3-5).
Reactive oxygen species (ROSs) are formed as obligatory intermediates in a variety of enzyme reactions. Furthermore, white blood cells generate radicals and utilize them to kill invading pathogens (6). Cells exposed to abnormal environments such as hypoxia or hyperoxia generate abundant and often damaging reactive oxygen species (7). A number of drugs have oxidizing effects on cells and lead to production of oxygen radicals. Ionizing radiation is also known to generate oxygen radicals within biological systems (7, 8).
Reactive oxygen species, when generated in excess or inappropriately controlled, can be harmful to the cells (9). Direct toxic effects of oxygen radicals can damage macromolecules, including lipids, proteins and DNA. As a result of these toxic effects, cells may undergo changes leading to carcinogenesis (10).
Normally, ROS are neutralized by specific biochemical pathways within the host cells (11). These pathways can be affected by genetic background and mutations in genes encoding components of these pathways and have been implicated in the pathogenesis of some MLDs (12, 13). One such mechanism utilizes superoxide dismutases (SODs), which can catalyze the conversion of two superoxide anions into a molecule of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and oxygen (O2) and this constitutes the first line of defense against ROS. There are three SOD types in mammals; Cu/Zn SOD (SOD1) is found in the cytosol as well as in many of the organelles of eukaryotic cells. There is also an extracellular Cu/Zn SOD (SOD3) that binds to the glycosaminoglycan of the extracellular matrix. The Mn-SOD (SOD2) is found in the matrix of mitochondria and detoxifies superoxide anions produced during electron transfer (14).
The Mn-SOD protein is coded by the nuclear genome. Its gene is located on the long arm of chromosome six and has five exons and four introns (15). Approximately three hundred and seventy (370) polymorphisms have been reported for the Mn-SOD gene (16). Two well-documented polymorphisms of the Mn-SOD gene include a substitution of C to T, at nucleotide residue 339, leading to a substitution of isoleucine by threonine at amino acid residue 58 of the protein. The second is a substitution of T to C at nucleotide 47 resulting in a change of the amino acid from valine to alanine at the 16th residue of the signal sequence (Val16Ala). These two mutations are common worldwide (17, 18). The Val16Ala polymorphism in Mn-SOD is associated with increased risk of several types of cancer, namely gastric cancer (19), breast cancer (20), prostate cancer (21) and colorectal cancer (22). The effect of Mn-SOD polymorphisms as a risk factor in lymphoproliferative disorders remains unknown.
2. Objectives
The present study aimed to investigate the association of the Ala16Val polymorphism of Mn-SOD gene with the risk of lymphoproliferative disorders in a group of patients in the southeast of Iran.
3. Patients and Methods
3.1. Patients and Controls
In this single center case-control study we evaluated one hundred and three cases with lymphoproliferative malignancies (40 cases with lymphoma, 27 cases with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), 25 cases with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and 11 cases with multiple myeloma) with a mean age of 53.6 ± 11.1 years, who had been admitted to the department of hematology and oncology of Ali-Ibn Abitaleb of Zahedan. The same numbers of unrelated healthy blood donors with a mean age of 55.1 ± 10.6 years, without any type of malignancies were selected as the control group. Diagnosis and the classification of malignancies were made by histological examination of biopsied material stained using the Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) techniques. Inclusion criteria were being over 18 years of age, having lymphoproliferative malignancies. The patient exclusion criteria were having malignancies other than lymphoma or any immune disorder. The protocol was approved by the research ethics committee of the Zahedan medical sciences university and informed consents were obtained from all participants. Two milliliters of venous blood was collected in EDTA tubes from all patients and control subjects. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes using DNA blood mini kits (QIAGEN science, Germantown, MD), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted genomic DNA was stored at -20°C until use.
3.2. Genotyping of the SOD2 T/C Polymorphism (rs4880)
Polymorphism was determined using a polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method. Initially, an amplicon of the SOD2 gene containing the T/C polymorphism was amplified using the primers sod2F: (5′-CGG TGA CGT TCA GGT TGT TCA C-3′) and sod2R: (5′- CAG CAC TAG CAG CAT GTT GAG C-3′). The primers were designed using the FastPCR software according to the reference sequences in the NCBI, and then BLASTed to test them in silica specificity. The PCR reaction was performed in a 25-μL volume containing 20 pmoles of each primer, 0.2 mM of each dNTP, 2.5 μL of buffer and 0.5 U of Taq DNA polymerase, with an initial denaturation at 94°C for five minutes, followed by 32 cycles of 45 seconds at 94°C, 45 seconds at 61°C and 45 seconds at 72°C and finally 10 minutes at 72°C. Following amplification, the 490-bp PCR product was digested overnight at 60°C in a total reaction volume of 25 µL containing 2U of BsaWI restriction enzyme (New England Biolabs GmbH, Schwalbach, Germany). The resultant DNA fragments were analyzed and scored on an ethidium bromide stained agarose gel (2.5%) and visualized on a UV transilluminator.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS software (version 18). Differences between the means of the continuous variables were evaluated by the Student’s t-test. The chi-square test was used to compare the genotypes and alleles between controls and patients. Departure from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was tested among control and patient groups using chi-square (χ2) tests. The associations between SOD genotypes and lymphoproliferative disorders were estimated as odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) using logistic regression analysis. A P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
A total of 206 individuals were included in this study (Table 1). There was no significant difference in age and gender distribution in patients and controls (P = 0.43 and P = 0.89, respectively).
| Parameters | Patients | Controls | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average age | 53.6 ± 11.1 | 55.1 ± 10.6 | 0.43 |
| Female, No. (%) | 41 (48.8) | 43 (51.2) | 0.89 |
| Male, No. (%) | 62 (50.8) | 60 (49.2) | 0.88 |
Demographical Parameters of Lymphoproliferative Patients and Control Groups
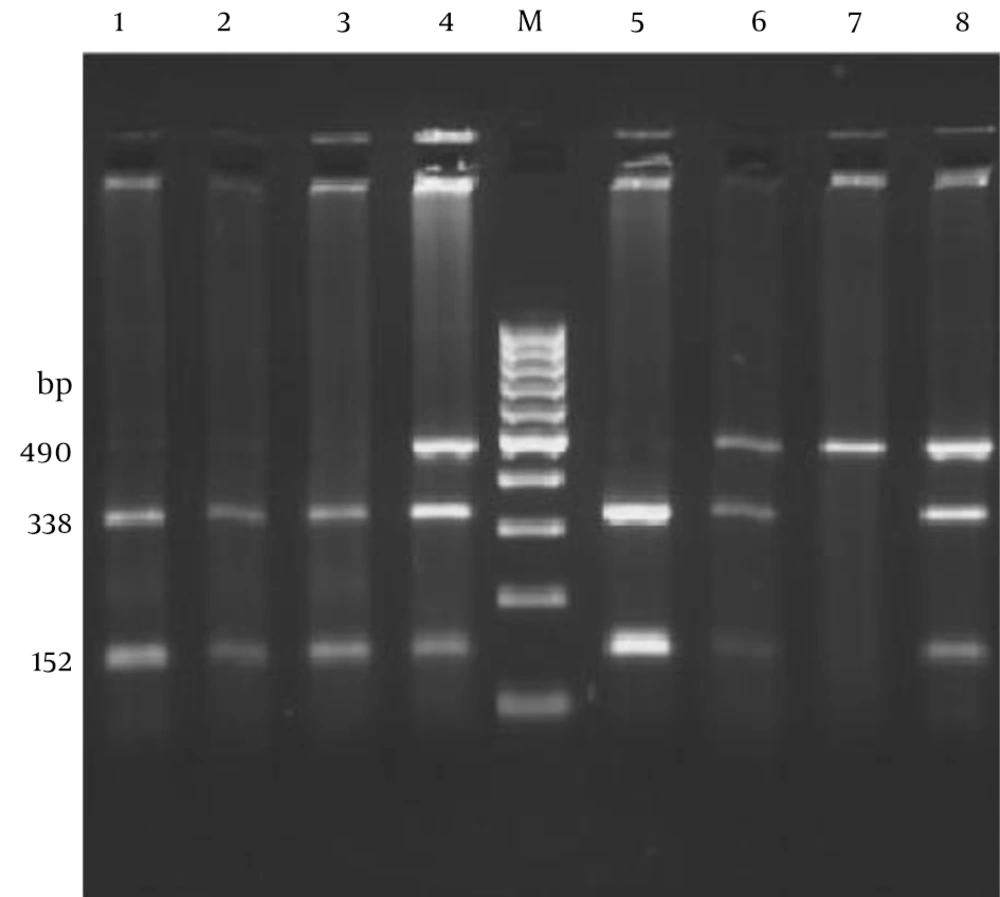
The PCR amplicon (490 bp) following digestion yielded bands of 338 and 152 bp in TT homozygotes, and 490, 338 and 152 bp in TC heterozygotes. The PCR product of CC homozygotes remained intact (Figure 1).
Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the C47T polymorphism (Rs4880) in the SOD2 gene using 2.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. A single fragment of 490 bp indicates a C/C genotype, two fragments of 338 and 152 bp indicates the T/T genotype and the appearance of all three bands represents the heterozygous C/T genotype. Lanes 1, 2 and 3 show the T/T genotype; lanes 4, 6 and 8 show C/T genotypes and lane 7 shows C/C genotype. Lane M is a 100-bp DNA ladder.
As shown in Table 2, the TT genotype of the SOD2 gene was found in 28.15% of healthy controls and 19.41% of patients, and the CC genotype was observed in 24.27% of healthy controls and 29.13% of patients. The prevalence of CT genotype in healthy controls and patients were 47.57% and 51.45%, respectively. There was no significant difference in the frequency of genotypes between patients and controls (P > 0.05).
| Frequencies | Control, No. (%) | Patient, No. (%) | OR (95%CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotypes | ||||
| TT | 29 (28.15) | 20 (19.41) | Ref | |
| CT | 49 (47.57) | 53 (51.45) | 1.62 (0.84 - 3.12) | 0.19 |
| CC | 25 (24.27) | 30 (29.13) | 1.74 (0.80 - 3.8) | 0.23 |
| Alleles | ||||
| T | 107 (52) | 93 (45.2) | Ref | |
| C | 99 (48) | 113 (54.8) | 1.3 (0.89 - 1.9) | 0.2 |
Genotype and Allele Frequencies of SOD2 C47T Polymorphism (Rs4880) in Patients With Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Healthy Controls
Using logistic regression analysis, there was no association between genotype frequency and proliferative disorders (OR = 0.637, 95%CI 0.32 - 1.27). Also, a lack of association was observed between allele frequencies and MLD (OR = 0.76, 95% CI = 0.52 - 1.12, P = 0.16) (Table 2). The distribution of SOD2 genotypes in healthy controls and patients were consistent with the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (χ2 = 0.23, P < 0.05 and χ2 = 0.16, P < 0.05, respectively).
5. Discussion
We examined associations between polymorphisms in the gene encoding Mn-SOD and risk of malignant lymphoproliferative (MLDs) disorders in a case-control study. Our results demonstrate that the Mn-SOD Val16Ala polymorphism (rs4880) is not a risk factor for MLDs. The Mn-SOD is encoded by the nuclear genome and after translation in the cytoplasm it is transported into the mitochondria via an N-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence containing 24 amino acids. The substitution of T to C (rs4880) changes a Val to Ala at the 16th position of the mitochondrial targeting signal peptide and this can alter the secondary structure of the enzyme (23). As a result of this substitution, transportation of the Ala variant of the Mn-SOD protein into the mitochondria decreases and the mitochondrial enzymatic activity is reduced when compared to the Val variant (24). Superoxide dismutase has an important role in ROS detoxification, thus protecting the cell from damage and carcinogenicity, particularly among individuals with a higher level of oxidative stress or who are deprived of other anti-oxidative protection, such as low levels of antioxidant intake (25).
Free radicals of oxygen could damage the cell and change cell proliferation, cell division and programmed cell death. As a result of oxidative damage caused by reduced function or inappropriate targeting of SOD2, the activity of tumor suppressor genes can be decreased and oncogenes may be activated (19). One downstream effect of ROSs production in cells is intensified DNA damage. Age-dependent increases in the level of damaged DNA have been commonly assessed through biomarkers such as the formation of 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine (oxo8dG) (26) and it is thought that there is a correlation between ROSs production in cells and DNA damage. Although our findings do not support the role of SOD2 polymorphism in the etiology of MLDs, reduction in activity of this enzyme has been reported in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders (27).
Our study compared polymorphism of superoxide dismutase type 2 (SOD2) in a healthy population compared to patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and showed a lack of association between the polymorphism and any of the disease states. This research was the first study, which reported these results. However, several studies have been performed to explore the relationship between SOD polymorphisms and human cancers. For instance, Woodson et al. showed that the Val/Ala polymorphism in the SOD2 gene increased the risk of prostate cancer by approximately 70% (28). One meta-analysis evaluation of polymorphisms in SOD, in relation to the risk of prostate cancer, showed a significant increase in cancer formation without any apparent change in the aggressiveness of prostate cancer (18). Blein and co-workers in a cohort study reported that the rs4880 Val16Ala polymorphism within the SOD2 gene was associated with increased risk of malignant breast and prostate cancers (29). Therefore, it seems that the polymorphisms within the SOD gene can be considered as risk factors for prostate cancer. Additionally, increased risk of breast cancer in Chinese women with high stress life style and low antioxidant intake was also shown (30). The positive correlations between the polymorphisms and other kinds of cancers have been reported by previous researchers. For example, in recent studies on Chinese populations, the association between SOD2 polymorphisms and the risk of gastric cancer and its progression revealed a positive association (19, 31). In contrast with the mentioned studies, there are several reports, which failed to confirm any association between SOD polymorphisms with the onset of malignancies. For example, Sutton et al. demonstrated that this polymorphism decreased the risk of lung cancer (18). Lightfoot et al. also reported decreased incidence of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in homozygotes for the SOD2 16Ala allele in the UK population (27). Additionally, studies on bladder cancer were unable to indicate a positive correlation between polymorphisms within SOD gene and the occurrence of this form of cancer (32, 33). According to the results presented by our study and other investigators, it may be concluded that the correlation between SOD2 polymorphisms is dependent on the kinds of cancers, for example, prostate and breast cancers appear to a have positive correlation, while, bladder and hematological malignancies, like lymphoproliferative disorders, are not associated with the polymorphisms of SOD2. The limitation of this study was the small sample size, so it seems that more investigations on Val16Ala polymorphism in larger samples and even other polymorphisms of the SOD gene can improve our knowledge regarding the role of SOD polymorphisms and incidence of lymphoproliferative disorders.