1. Background
It is clear that life style and nutritional status play critical roles in general health, neuronal function, memory, and learning throughout the life span of individuals (1). It has been shown that the worldwide prevalence of obesity has been increasing and it continues to rise in developed and developing countries that can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and neurological disorders (2, 3). The increased consumption of saturated fats in high fat diets (HFD) contributes to obesity. High fat diets influence neuronal growth of the brain, disrupts cognitive function and neuronal plasticity, and finally impairs memory and learning in adult rats (4, 5).
A number of studies have reported that high fat diets impair hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) in the granular cells of the dentate gyrus and alter neurogenesis in the hippocampus (6, 7). It has been indicated that high dietary fat intake can disrupt hippocampal neurogenesis, probably through an increase in serum corticosterone levels. Park et al. reported that seven weeks of HFD significantly decreased the number of newly generated cells in the dentate gyrus and the level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus (8).
There is evidence that BDNF density decreases following HFD consumption, which leads to a decrease in neuronal plasticity and cell death (8, 9). Furthermore, BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors that promotes neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity through its interaction with Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (Trk β) (10). Also, BDNF affects neuronal plasticity by molecules, such as synapsin I and Cyclic AMP- Response Element Binding protein (CREB). Synapsin I takes a role in synaptogenesis and axonogenesis, influences synaptic vesicle exocytosis, and subsequently mediates BDNF modulation of neurotransmitter release (11, 12). Cyclic AMP-response element binding protein, as the best known transcription factor in the brain, is phosphorylated under control of BDNF and participates in learning and memory (13).
Several lines of evidence suggest that oxidative stress plays a critical role in the HFD-induced neurotoxicity (14-16). Oxidative stress is an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and internal antioxidants. Oxidative stress leads to the formation of hydroxyl radicals, lipid peroxidation, and apoptotic cell death.
It is clear that dietary enrichment with nutritional antioxidants could improve brain damage and cognitive function (17, 18). It can scavenge free radicals and protect unsaturated fatty acids from lipid peroxidation. Vitamin C and E, as an antioxidant has been reported to prevent the production of free radicals and lipid peroxidation (19, 20). Additional studies show that vitamin C and E could improve spatial memory performance and increase BDNF expression in the hippocampus (21, 22).
The hypothesis of this study was that if vitamin C and E could scavenge free radicals, an important factor in producing brain damage induced by HFD, they might be able to improve neurotoxicity related to HFD group via reduction of oxidative stress.
2. Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
A total of 15 adult Wistar male rats (250 to 300 g; 6 to 8 weeks) were used in this experimental study. The animals were kept in animal houses, according to standard laboratory conditions at a temperature of 22 ± 2°C, relative humidity of 55 ± 5%, and on a 12-hour light/12-hour dark cycle with free access to food and water. Ethical approval for all experiments was provided by the ethical committee of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences.
The rats were randomly assigned to the following groups:
1- Intact control group received a standard laboratory rodent chow diet for nine months that had a caloric density of approximately 3.0 kcal/g.
2- The HFD group received HFD (D12492) for 9 months that was designed according Furnes et al. (23) and consisted of 60.9% fat, a8.3% protein, and 2.3 % carbohydrate, with a caloric density of approximately 5.24 kcal/g.
3- The antioxidant group received HFD plus antioxidant (0.2 g/kg vitamin E, 0.2 g/kg vitamin C, and 0.6 g/kg Astaxanthin) for 9 months.
2.2. Tissue Preparation for Molecular Studies
The animals were decapitated and their brain was removed. The hippocampi were dissected out on ice, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and maintained at -80°C until use. The left hippocampi were used for real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and the right one for western blot.
2.3. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
Total mRNA of the hippocampus was extracted using the phenol-chloroform method. The hippocampus was homogenized in RNATM (1000 µL) and centrifuged (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) in chloroform at 12,000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C. Next, the RNA of the supernatant was precipitated with isopropanol and washed with 75% ethanol. A cDNA synthesis kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) for reverse transcribing of the total RNA (1 µg) to complementary DNA (cDNA) was used following the protocol outlined by the manufacturer (Bioneer, Republic of Korea).
The PCR analyses were performed using QuantiFast SYBR Green PCR Kit (Bioneer, Korea) and primers (Table 1) for BDNF, Synapsin, Trk β, and CREB, and GAPDH.
| Genes | Primers |
|---|---|
| BDNF | Forward GATTAGGTGGCTTCATAGGAGAC |
| Reverse AGAACAGAACAGAACAGAACAGG | |
| Trk β | Forward TATGCCGTGGTGGTGATTG |
| Reverse TGGAGATGTGGTGGAGAGG | |
| Synapsin I | Forward CTCAGCAGCACAACATACC |
| Reverse TTCTGGACACGCACATCG | |
| CREB | Forward CCAGAAGATGAAGCGAGTC |
| Reverse TTGATGTTGAGGCAGAAGG | |
| GAPDH | Forward TTCAACGGCACAGTCAAGG |
| Reverse CTCAGCACCAGCATCACC |
Primer sequence for Quantitative Real Time-Polymerase Chain Reaction
The PCR involved initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 minutes, followed by 40 cycles at 95°C for 5 seconds, 57°C, 53.2°C, 55.1°C, and 51.6°C (BDNF, Synapsin, Trk β, and CREB, respectively) for 30 seconds and 72°C for 30 seconds with a final elongation time at 72°C for 7 minutes. The reaction was terminated by an elongation period at 72°C for 7 minutes. The same annealing temperature was used for GAPDH.
Cycle threshold (Ct) values were obtained through the auto Ct function. Following efficiency correction, the mean CT value was calculated and then normalized to the reference using delta (Δ) CT.
2.4. Western Blot
Caspase 3 was quantified using a western blot method (24). The hippocampi extract were prepared in a lysis buffer that contained Ripa buffer with protease inhibitor cocktail (2:10) and centrifuged at 12,000 g for 20 minutes at a temperature of 4°C. The supernatants were collected and protein concentration was measured using the Bradford method. The denatured protein was separated on a SDS page (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel) and transferred to a Hybond-ptm nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ, USA). Next, the membrane was blocked with 5% powdered milk and incubated with polyclonal anti body to caspase 3 (1:1000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and anti-actin (1:1000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 2 hours followed by alkaline phosphatase conjugated secondary antibody (1: 10,000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 1 hour. Bands were detected by chromogenic substrate 5- bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate in the presence of nitroblue tetrazolium and analyzedusing densitometric measurements by an image analysis system (UVIdoc, Houston, TX, USA).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses of the results were carried out using the SPSS version 16 software. Data was presented as mean± SEM and analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey post-hoc comparison. Values of P < 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
Effects of HFD and antioxidants on expression of BDNF, Synapsin I, CREB, and Trk- B in the hippocampus in the real time-polymerase chain reaction
Following electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gel at 100 volts, one single band was detected for quantification of all genes (Figure 1).
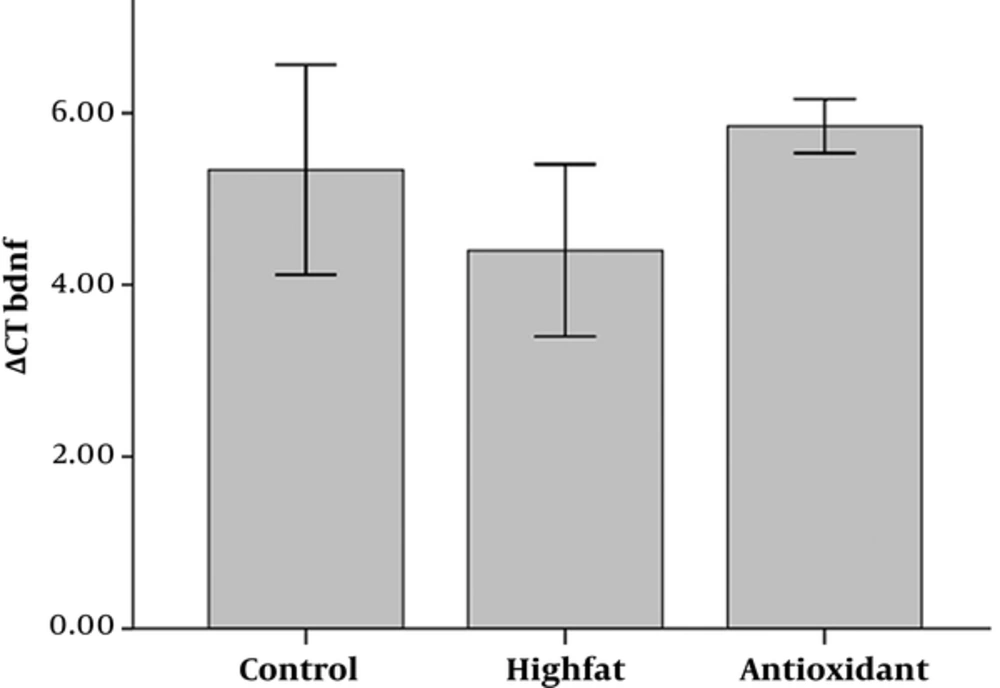
Figures 2 to 5 show the delta CT (ΔCT) values of BDNF, Trk β, Synapsin I, and CREB, respectively. Analysis of variance of data showed that HFD causes upregulation of BDNF, which was insignificant when compared to the control group (Figure 2). There was no significant difference between antioxidant and HFD groups.
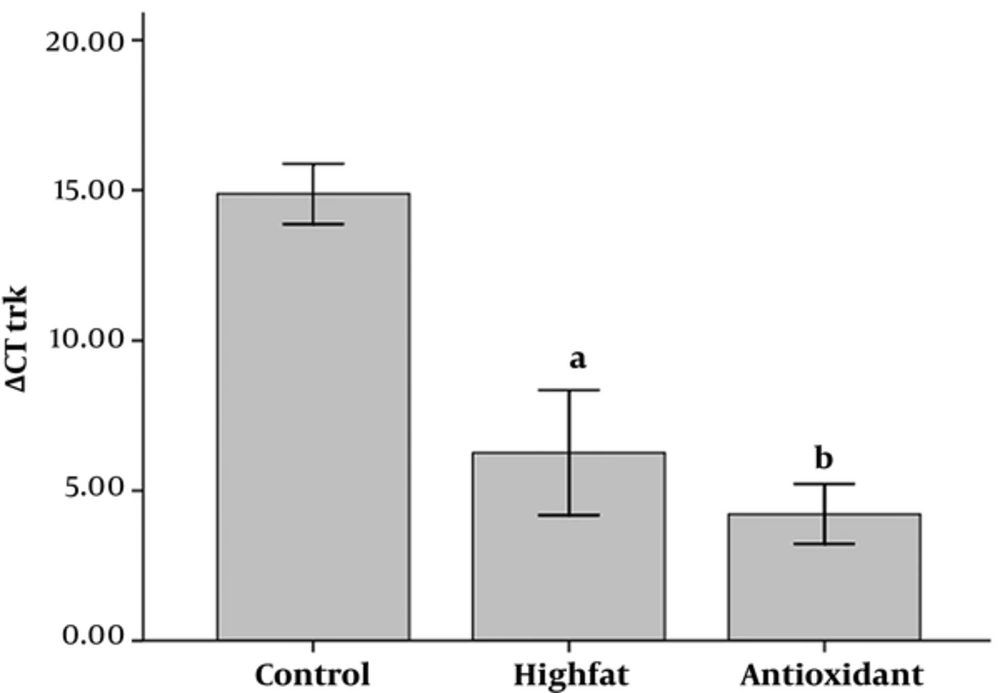
Analysis of ΔCT values of Trk β showed that there was a significant difference between control and other groups (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001 for HFD and antioxidant, respectively, Figure 3) and the control group expressed less Trk β than others. Furthermore, administration of antioxidant insignificantly increased Trk β when compared to the HFD group.
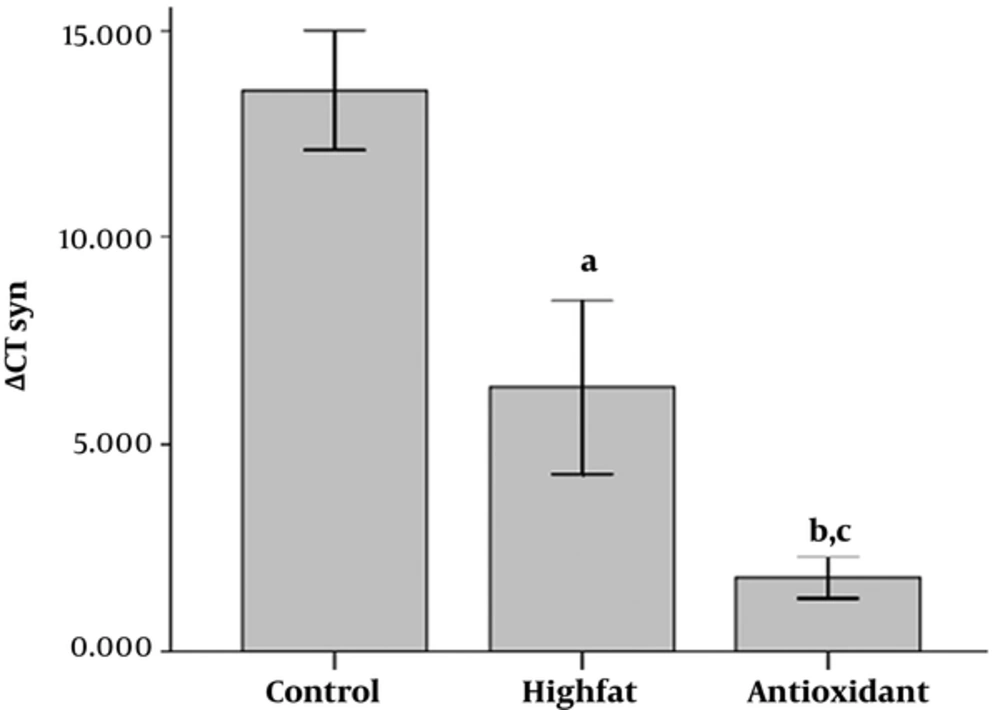
As shown in Figure 4, there was a significant increase in synapsin I expression in the HFD, and antioxidant-treated groups compared with the control group (P < 0.05 and P < 0.001 for HFD and antioxidant, respectively). Administration of antioxidant increased synapsin I expression compared to HFD groups, significantly (P < 0.05).
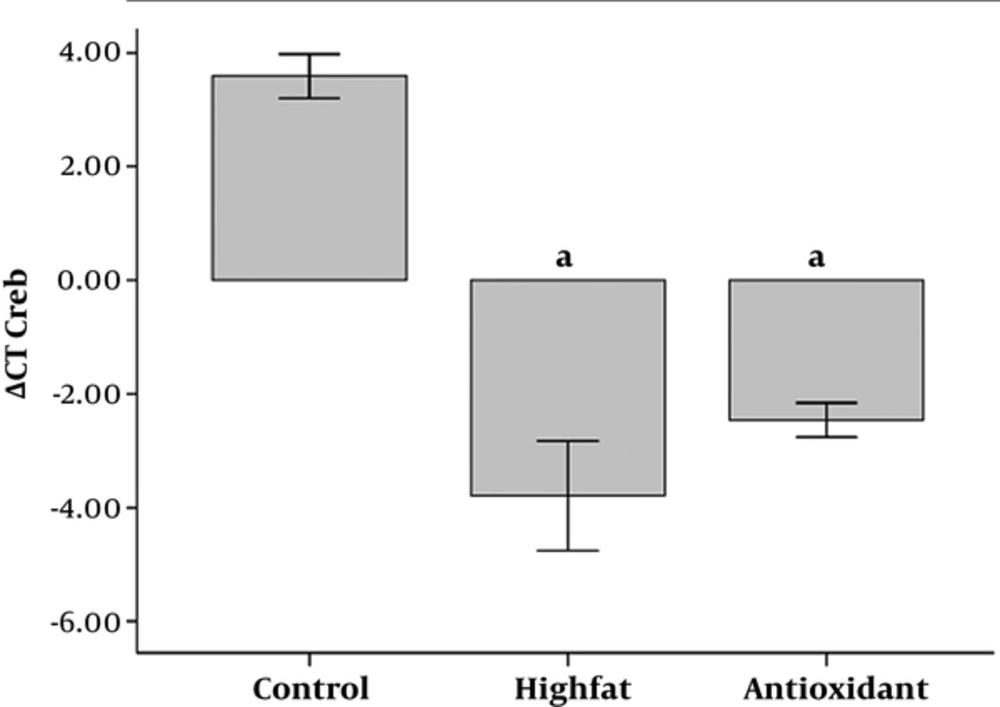
Furthermore, expression of CREB increased in HFD and antioxidant groups (P < 0.001 for both groups, Figure 5) in comparison to the control group.
Administration of antioxidant significantly increased CREB expression compared to the HFD group.
Effects of HFD and antioxidants on expression of caspase 3 in the western blot
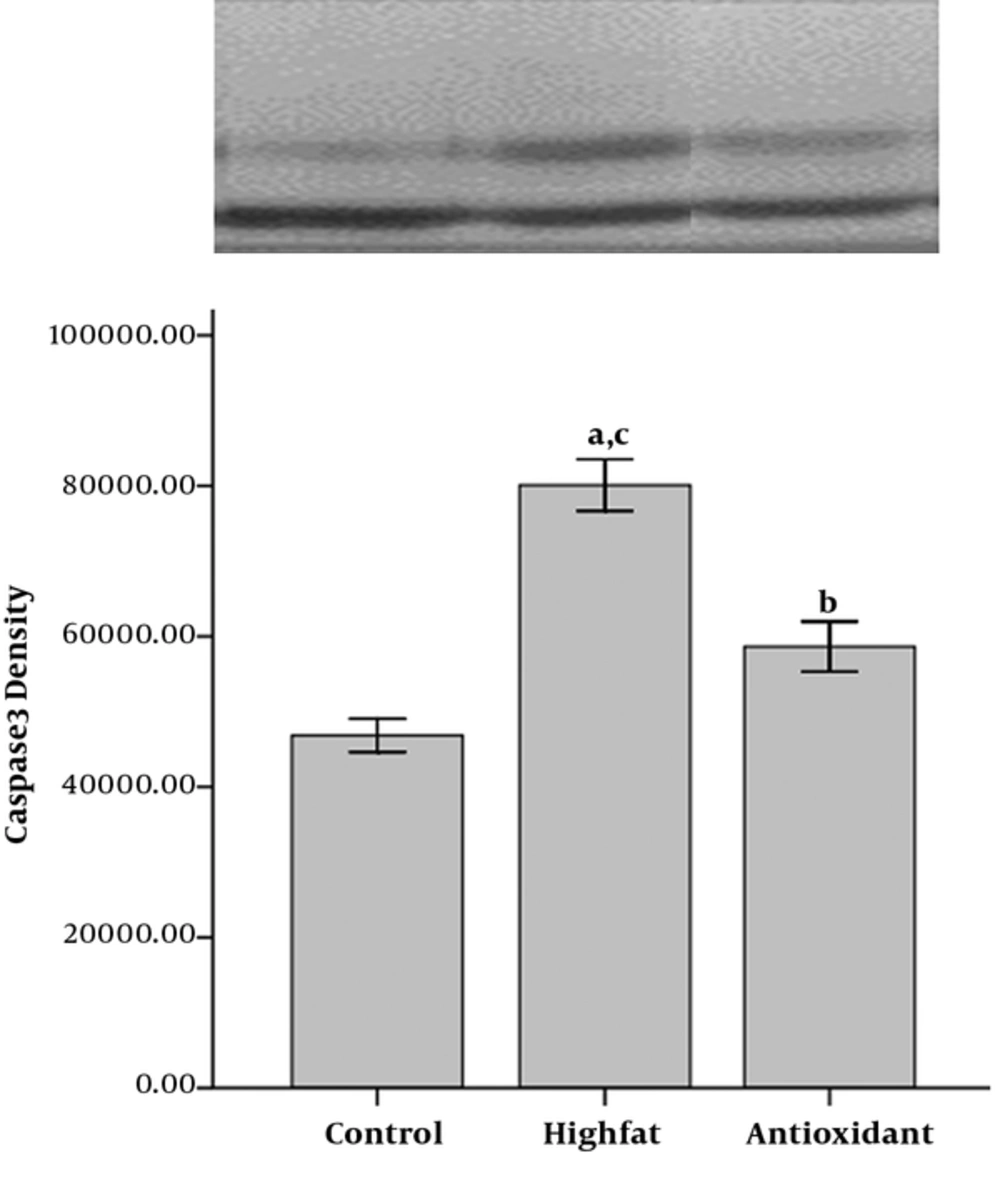
Densitometry from the membranes showed significantly less expression of caspase 3 in the control group compared to the other groups (P < 0.001 for HFD and P < 0.05 for antioxidant group, Figure 6). There was a significant difference in caspase 3 expression between the antioxidant and the HFD groups (P < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Several studies using rodent models have addressed the relationship between HFD and neurotrophic factors in the brain. Yu et al. Showed that BDNF and Trk β decreased following HFD in the hippocampus and ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus of male rats (25). Furthermore, consuming a high fat refined sugar diet for 2 month decreased hippocampal BDNF and performance in the Morris water maze. They reported that the downstream effectors for the action of BDNF on synaptic plasticity, including synapsin I, CREB, and growth-associated protein 43 mRNA were reduced proportionally to BDNF levels (7).
Inconsistent to the mentioned studies, the present study showed that administration of HFD for 9 months led to an increase in BDNF, Trk β (BDNF receptor), synapsin I (important for neurotransmitter release), and CREB (required for various forms of memory and is under regulatory control of BDNF). Furthermore, the results showed that the antioxidant could exaggerate HFD-induced increase in BDNF, Trk β, CREB, and synapsin I. It has been reported that vitamin C and E could exert protective effects by enhancing BDNF expression in stressed rats (26). A study by Coskun et al. showed that vitamin C supplementation failed to protect the brain tissue against exercise-induced oxidative damage and behavior as a pro-oxidant (27). In another study, vitamin E ameliorated the ethanol-induced changes on secretion of BDNF and neurotrophin-3 (28).
In this study, HFD was used for 9 months, and longer than other studies. Such changes may be long-lasting changes, in which neurotrophic factors increase compensatory. Consistent with the current study, BDNF expression in the ventral tegmental area was increased by cocaine and they suggested that this may be essential for modulating cocaine-rewarding effects (29).
In another study, rats, fed a diet rich in sugar, exhibited increased hippocampal inflammation (TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA) and oxidative stress, as indicated by an upregulation of NRF1 mRNA compared to control rats. In contrast, these markers were not significantly elevated in rats that received the cafeteria diet without added sucrose. Hippocampal BDNF mRNA was similar across all groups (30), which confirms the current results.
The other finding of this study was attenuation of apoptosis following antioxidant administration in the HFD group. It has been reported that consumption of a fat-rich diet blunts leptin and insulin orexigenic signaling by a mechanism dependent on in situ activation of inflammation that could induce apoptosis of neurons and a reduction of synaptic inputs in the arcuate nucleus and lateral hypothalamus (31, 32). Wang et al. showed that apoptotic hepatocytes were significantly greater in livers of rats fed HFD, and these were associated with a higher level of cleaved caspase-3 (33). Caspase- 3 is one of the key executioners of apoptosis that is synthesized as inactive performs, which upon receiving an apoptotic signal, is cleaved and forms the active enzyme (34). The ability of vitamin C or vitamin E to reduce cell damage elicited by various apoptotic stimuli has also been well studied (35, 36). Vitamin C is an effective scavenger of hydroxyl radicals, and vitamin E is a lipid radical chain breaker that scavenges oxygen radicals and alkyl radicals. Taken together, it is possible that vitamin E and C inhibit ROS generation and might be implicated in the protection of HFD-induced neurotoxicity.
In conclusion, the current findings demonstrate that administration of vitamin E and C significantly attenuated HFD-induced neurotoxicity in the rat hippocampus. Therefore, it is likely that they may be useful as a potential treatment for the adverse effects associated with HFD.