1. Background
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally (1). Each year, 31% (17.9 million people) of global all-cause mortalities are from CVDs. Of these, more than 75 percent occur in low- and middle-income countries (2). It is predicted that if current trends of CVD deaths continue, the annual CVD deaths will increase to 23.3 million by 2030 (mainly from heart attacks and strokes) (3). Furthermore, CVDs are the first cause of death and DALYs in Iran, responsible for 46% of all deaths and 20% - 23% of the burden of disease (4).
Although the rising CVD epidemic might be related to several individual and socio-environmental factors (5), its morbidity and mortality can be prevented by developing more precise population-based prevention programs, since most of its risk factors such as an unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia are modifiable (6). Therefore, good knowledge about CVD risk factors will help people to decrease their risk, given that it has been indicated that knowledge about CVD and its risk factors is a prerequisite for changing the health behaviors and lifestyles of individuals (7, 8). Besides, knowledge of the warning signs of heart attack and stroke will lead to an earlier presentation to the hospital, resulting in better patient outcomes (9, 10).
With the rising prevalence of NCDs and their risk factors, the IraPEN program that is based on the WHO Package of essential NCD interventions for primary health care (PEN) has been implemented into the primary health care centers for the Iranian population (11). The IraPEN uses a risk scoring tool to assess the 10-year CVD risk of individuals who referred to health centers, and then, self-care education is given to all (11). However, understanding the fundamental context of disease is required for reaching ideal health behavior (12) and succeeding in the prevention and control of these diseases, as this knowledge will teach individuals to be more proactive in reducing their exposure to modifiable risk factors for CVD (13).
Since studies on knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) increase our understanding of knowledge and behavior regarding cardiovascular health in the community (14), they can be valuable for public health to help in developing targeted educational programs (10) and assessing the effectiveness of intervention programs (15). Knowledge of CVD has been studied in various populations. Some of these studies have focused on patients (16, 17), and a few studies have been carried out in the general population (18-21). Yet, little is known about the knowledge of CVD, its symptoms, and risk factors in Iran.
2. Objectives
This study was designed to determine the level of current knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) regarding cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), CVD risk factors and symptoms in adults attending health care centers in Tehran.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design and Participants
This was a cross-sectional study that was conducted in Tehran province, Iran, between August and October 2018. The study population consisted of 300 adults aged > 20 years, selected from 10 public health care centers under the supervision of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (SBMU) in Tehran province; these centers differ culturally and socioeconomically. The sample size was calculated based on the standard deviation (SD) of the knowledge in a previous study (17) using PASS software. Considering α = 0.05 and standard deviation [SD] = 3.91 (17), a sample size of 238 was obtained, in which after considering a 20% dropout rate, we studied 300 participants. All participants provided verbal informed consent.
3.2. Questionnaire
Data were collected through a self-administered questionnaire consisting of personal questions and 29 questions related to KAP regarding CVD (CVD-KAP29). A KAP questionnaire measures the knowledge, attitude, and practice of a community regarding any given subject. Knowledge refers to a community’s understanding of this subject, CVDs, risk factors, and symptoms in this case. Attitude refers to their learned predispositional thoughts, beliefs, and feelings towards this subject. Practice refers to how they act and use preventive measures towards this subject (22).
The CVD-KAP29 was developed based on the results of the literature review and interviews with five experts in health education, epidemiology, cardiovascular disease, and nutrition. Using the content validity ratio (CVR) and content validity index (CVI), the content validity of the CVD-KAP29 was established by a multidisciplinary panel of 12 experts with experience in related fields. The CVR and CVI of the questionnaire were 0.80 and 0.91, respectively. It was also assessed for readability and comprehension of 10 individuals with different demographic characteristics; based on that, the questionnaire was simple to understand and answer. The results of the exploratory factor analysis (EFA) conducted with a four-factor solution using a varimax rotation showed that among 30 initial items, only one item (q30) had a factor loading < 0.3, and finally, 29 items were retained. The results of confirmatory factorial analysis (CFA) also established the construct validity of the CVD-KAP29 in which the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), comparative fit index (CFI), and the goodness of fit index (GFI) were 0.068, 0.94, and 0.83, respectively, indicating acceptable model fit indices. Intra-class correlation coefficients indicated a good-to-excellent test-retest reliability in knowledge and attitude subscales and poor reliability in the practice subscale. Overall, Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for knowledge, attitude, physical activity-related behaviors and nutrition, and smoking behaviors subscales were 0.856, 0.915, 0.711, and 0.509, respectively, indicating a good internal consistency.
The first section of the CVD-KAP29 included 12 items to provide information about personal questions. Section 2 consisted of 12 three-point Likert scale questions that determine the knowledge of the risk factors, symptoms, and prevention of CVD. The third section included 10 five-point Likert scale questions to provide information about the subjects’ attitude. Section 4 included two questions to explore the participants’ physical activity behaviors. Finally, section five consisted of five questions to address their nutrition & smoking behaviors. All scores were proportionally transformed to 0 - 100.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables are presented as frequency and percentages, and KAP scores are presented as the median and interquartile range (IQR). Total knowledge, attitude, physical and nutritional and smoking scores were classified into the following five categories based on the quintile scores: ≤ 20, “highly insufficient”; 21 - 40, “insufficient”; 41 - 60, “sufficient”; 61 - 80, “satisfactory”; > 80, “highly satisfactory” (8). Initially, we performed univariate logistic regression to determine the relationship of the knowledge, attitude, physical activity, and nutrition and smoking of CVD with each independent variable. Then we performed a multiple logistic regression analysis, including all variables with a P value ≤ 0.3 in the univariate analysis to determine the factors that are independently associated with CVD KAP scores. For each model, we categorized response options for the dependent variable as either “highly insufficient” or “insufficient” or “sufficient” or “satisfactory” vs. “highly satisfactory”. A P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, version 21, SPSS, Chicago, IL, U.S.A.) was used for data analysis.
4. Results
Table 1 shows the characteristics of the participants. A total of 300 adults with a mean age of 39.71 ± 12.1 years (range: 21 - 74), participated in the study. Of these, 154 were female (51.3%). The majority of participants were married (79%); 44% of participants had a university education, and 62.7% were employed. About forty-two percent indicated having a family history of chronic diseases including CVD, hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia in their immediate family members, and twenty-six percent had a self-history of chronic disease.
| Variable | Subgroups | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 146 (48.7) |
| Female | 154 (51.3) | |
| Age | < 40 years | 179 (59.7) |
| ≥ 40 years | 113 (39.7) | |
| Marital status | Singleb | 63 (21.0) |
| Married | 237 (79.0) | |
| Education level | Low-intermediate educationc | 168 (56.0) |
| University education | 132 (44.0) | |
| Occupation status | Employed | 188 (62.7) |
| Unemployedd | 112 (37.3) | |
| Residence | Rural | 133 (34.3) |
| Urban | 164 (54.7) | |
| Body mass index | < 25 | 128 (42.7) |
| ≥ 25 | 169 (56.3) | |
| Family history of chronic diseasese | Yes | 162 (42.1) |
| No | 118 (57.9) | |
| Self-history of chronic diseasese | Yes | 79 (26.3) |
| No | 202 (67.3) |
aValues are expressed as No. (%).
bIncludes never married, divorced, and widowed.
cIncludes primary school, under diploma, and diploma.
dIncludes retired, homemakers, and students.
eIncludes CVD, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia
Table 2 shows the median (IQR) and percentage distribution of the level of knowledge, attitude, and practice/behavior regarding CVD based on the quintile scores. The median (IQR) score for knowledge about CVD was 91.7 (16.7), awareness of approximately 80% of respondents was highly satisfactory. As shown in Table 3, more than 70% of the participants were aware of the fact that CVD is the main cause of death in Iran; the commonest risk factor identified was hypertension followed by obesity, and about 70% of the participants identified at least one CVD symptom.
| Scoresb | Knowledge | Attitude | Physical Activity Behavior | Nutrition and Smoking Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total score | 91.7 (16.7) | 89 (18) | 50 (25) | 80 (30) |
| Quintile scoresb | ||||
| Highly insufficient | 5 (1.7) | - | 42 (14) | 3 (1) |
| Insufficient | 2 (0.7) | 4 (1.3) | 57 (19) | 29 (9.7) |
| Sufficient | 6 (2) | 3 (1) | 152 (50.7) | 66 (22) |
| Satisfactory | 46 (15.3) | 83 (27.7) | 17 (5.7) | 96 (32) |
| Highly satisfactory | 241 (80.3) | 210 (70) | 32 (10.7) | 106 (35.3) |
aValues are expressed as No. (%) or median (IQR).
bIncludes ≤ 20, “highly insufficient”; 21 - 40, “insufficient”; 41 - 60, “sufficient”; 61 - 80, “satisfactory”; > 80, “highly satisfactory”.
| Category | Values |
|---|---|
| CVD and its risk factors | |
| CVD is a leading cause of death in Iran | 211 (70.3) |
| Physical inactivity | 271 (90.3) |
| Unhealthy diet | 282 (94) |
| Positive family history | 231 (77) |
| Obesity | 294 (98) |
| Smoking | 283 (94.3) |
| Hypertension | 278 (99.7) |
| Diabetes | 238 (79.3) |
| Heart attack symptoms | |
| Chest pain or pressure or burning | 238 (79.3) |
| Pain or discomfort in arms, shoulder, jaw, neck or back | 207 (69) |
| Stroke symptoms | |
| Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg | 212 (70.7) |
Abbreviation: CVD, Cardiovascular disease.
aValues are expressed as No. (%).
Furthermore, the median (IQR) score for attitude was 89 (18); 70% of respondents had a highly satisfactory attitude about CVD, as illustrated in Table 2. Regarding physical activity and nutrition and smoking behaviors, just 10.7% and 32% had highly satisfactory behaviors, respectively (Table 2). Just 20% of participants exercised more than three times in a week; almost 21% of participants had a healthy diet (eating 2 to 4 units of fruit and 3 to 5 units of raw or cooked vegetables in their daily diet, don’t add salt to their food at the table, etc.). Nearly 20% of participants smoked regularly or sometimes.
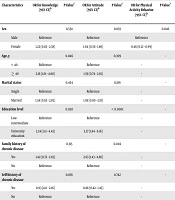
Table 4 shows the results of the multivariate logistic regression model for participants’ characteristics associated with the highly satisfactory KAP regarding CVD. In the univariate analysis, age and education were the only factors significantly associated with knowledge about CVD (P < 0.05). Factors significantly associated with attitude regarding CVD included education and family history of chronic disease. Age was the only factor significantly associated with physical activity, and finally, education was the only factor significantly associated with nutrition and smoking behaviors. These statistically significant factors, as well as factors with a P value ≤ 0.3 in the univariate analysis, were included in the multivariate logistic regression model for each response option. According to our results, the knowledge about CVD was significantly higher among participants who aged ≥ 40 years compared to those < 40 years of age (P = 0.046); participants who had a university education were more knowledgeable about CVD compared to those with lower education. Also, the attitude regarding CVD was significantly higher among participants who reported having a university education (P < 0.001) and having a family history of chronic diseases (P = 0.002) compared to those who did not. Physical activity was significantly higher among men compared to females (P = 0.046). Furthermore, education was the only factor independently associated with nutrition and smoking behavior (nutrition & smoking behavior); participants who were attending university reported better nutrition & smoking behaviors.
| Characteristics | OR for Knowledge (95% CI)b | P Valuec | OR for Attitude (95% CI)b | P Valuec | OR for Physical Activity Behavior (95% CI)b | P Valuec | OR for Nutrition and Smoking Behavior (95% CI)b | P Valuec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.558 | 0.893 | 0.046 | 0.160 | ||||
| Male | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Female | 1.22 (0.63 - 2.38) | 1.04 (0.58 - 1.86) | 0.46 (0.21 - 0.99) | 1.47 (0.86 - 2.51) | ||||
| Age, y | 0.046 | 0.309 | - | 0.337 | ||||
| < 40 | Reference | Reference | - | Reference | ||||
| ≥ 40 | 2.16 (1.01 - 4.60) | 1.39 (0.74 - 2.61) | - | 1.32 (0.75 - 2.32) | ||||
| Marital status | 0.454 | 0.189 | - | 0.485 | ||||
| Single | Reference | Reference | - | Reference | ||||
| Married | 1.34 (0.63 - 2.85) | 1.59 (0.80 - 3.18) | - | 1.27 (0.65 - 2.47) | ||||
| Education level | 0.020 | < 0.0001 | - | 0.007 | ||||
| Low-intermediate | Reference | Reference | - | Reference | ||||
| University education | 2.24 (1.13 - 4.43) | 3.37 (1.84 - 6.16) | - | 2.07 (1.22 - 3.50) | ||||
| Family history of chronic disease | 0.315 | 0.002 | - | 0.262 | ||||
| Yes | 1.42 (0.72 - 2.83) | 2.63 (1.43 - 4.86) | - | 1.38 (0.79 - 2.42) | ||||
| No | Reference | Reference | - | Reference | ||||
| Self-history of chronic disease | 0.856 | 0.742 | - | 0.194 | ||||
| Yes | 0.93 (4.0 - 2.16) | 0.88 (0.42 - 1.45) | - | 1.54 (0.80 - 2.95) | ||||
| No | Reference | Reference | - | Reference |
aValues are expressed as No. (%).
bOdds ratio (OR) and it’s 95% confidence interval (CI) for having a highly satisfactory score vs. other categories obtained from the multiple logistic regression analysis.
cThe significant level was 5%.
5. Discussion
This study has been done to demonstrate the current level of public knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding CVD, its risk factors, and symptoms. According to our findings, most of the participants had a highly satisfying knowledge and attitude about CVDs. This is consistent with some previous studies conducted in Shiraz, Tabriz, and Tehran provinces (16, 18, 21). However, inconsistent with our findings, some other studies have reported a low level of knowledge in their populations (16, 18, 21, 23). In this study, respondents’ knowledge regarding the CVD risk factors was better than that of the warning symptoms of heart attack and stroke, which is consistent with some other studies (5, 8). Hypertension was the most frequently identified risk factor of CVD, followed by smoking that was in the same line with the findings of other previous studies (8, 18, 24, 25). Although our study participants showed less knowledge related to positive family history and diabetes as risk factors, it is higher in comparison with previous studies from Kuwait, Northern Ireland, Canada, Jordan, and Nepal (8, 10, 26-28). Furthermore, the commonest CVD symptom recognized by respondents was chest pain, pressure, or burning for heart attack followed by sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg for stroke; these findings were higher compared to that reported in Australia, Canada, and Kuwait (10, 27, 29).
The high level of knowledge and attitude about CVD among our participants might be due to the implementation of the IraPEN program in primary health care centers. IraPEN is a modification of the WHO Package of essential NCD (PEN) interventions for the Iranian population launched in 2014 by the Ministry of Health and Medical Education. IraPEN uses a risk scoring tool according to a laboratory-based WHO risk score that assesses the 10-year CVD risk of individuals who referred to health centers based on various risk factors. In this system, health workers show people how to deal with their conditions, provide access to affordable medicine, and guidance on practicing healthy habits, like regular exercise and a healthy diet (11, 30).
Despite the high level of knowledge and attitude, almost one-fifth of our participants reported exercising more than three times a week or having a healthy diet, and nearly one-fifth are smokers.
Consistent with our findings, a review study reported that the Middle East has one of the worst physical activity profiles globally (31). Based on the result of this review, physical inactivity, especially in women, and an unhealthy diet are the most prevalent metabolic risk factors in almost all countries in this region (31).
Based on our results, higher educated individuals have significantly higher knowledge, attitude, and nutrition and smoking behaviors compared to those with low to intermediate education, similar to other studies, which observed a consistent link between better KAP scores and higher education (8, 10, 24, 25). It seems that it is reasonable to assume higher CVD KAP scores in higher educated individuals since more education can result in more exposure to information about diseases.
Besides, Similar to some previous studies, which reported a significant association between age and CVD knowledge (23, 25), the current study showed that participants more than 40 years old were more knowledgeable about CVD compared to those aged less than 40 years. This is in contrast to other studies, which reported no significant difference in CVD knowledge among different age groups (23, 26, 28). This might be due to middle-aged people usually getting more medical care and having more intention to access information about diseases.
Nevertheless, the current study did not find a significant difference among females and males regarding CVD KAP, which is consistent with other studies conducted in a different population (8, 16, 26, 28). However, this is in contrast with some other findings of previous studies, which reported a significant association between sex and CVD knowledge (8, 10, 25). Also, the current findings did not find better knowledge and behavior regarding CVD in participants who reported having a positive family history of chronic disease, including CVD, hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia; but their attitude was significantly better in comparison to those who did not have such a family history. Furthermore, participants who have CVD or diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia did not have a higher CVD KAP score in comparison to those who did not, which is consistent with the study conducted by Awad and Al-Nafisi (10). It may be because of high knowledge in all participants that we could not find any difference.
The strength of this study is using a validated questionnaire. However, the main limitation is that participants were selected from 10 centers in only one province of Iran, which may limit the generalizability of the results, and further investigations of other Iranian populations are recommended.
5.1. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the current level of public knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding CVD, CVD risk factors and symptoms. Although more than half of the current study participants had high knowledge and attitude about CVD, their behavior is not satisfied. Therefore, it is necessary to establish more effective educational interventions aimed at promoting positive health behaviors and explaining to the public that knowledge and action regarding the reduction of risk factors are linked to reduced CVD and mortality.