1. Background
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder in women at reproductive age (1, 2). PCOS is diagnosed with oligomenorrhea and/or anovulation as well as clinical and/or biochemical hyperandrogenemia with/without ultrasonographic evidence of polycystic ovaries. The diagnosis is made after exclusion of other disorders including thyroid dysfunction, hyperprolactinemia, nonclassical adrenal hyperplasia, Cushing syndrome, and androgen producing tumors (3). According to Androgen Excess Society (AES), PCOS phenotypes including phenotype of hyperandrogenism and oligomenorrhea had a higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome when matched with the control subjects (4, 5); moreover, recent data support an increased incidence of cardiovascular events in women with PCOS, which are related to androgens level (6-8). PCOS is also associated with an increased risk of insulin resistance (IR), type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis (9-13). IR is also a risk factor for metabolic abnormalities and increases the risk of cardiovascular events. High mean platelet volume (MPV) might contribute to the endothelial injury by platelet activation and higher plasma concentrations of thromboxane A2 (14). Several reports have demonstrated that there is an association between MPV and cardiovascular risk factors (15) such as obesity (16), diabetes mellitus (17), hypertension (18), acute coronary syndrome (19), and stroke (20). According to AES, IR and hyperandrogenemia are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases in patients with PCOS (4, 5). Regarding the current evidences, it is reasonable to investigate the association of MPV with androgens as well as IR in patients with PCOS.
2. Objectives
To our knowledge, just one study investigated the association of MPV with androgen levels in patients with PCOS (20); however, the mentioned study included overweight and obese patients. Therefore, our study was designed to determine whether there was any association between androgens/IR and MPV in nonobese patients with PCOS.
3. Patients and Method
3.1. Study and Control Subjects
A total of 136 patients with newly diagnosed reproductive-age PCOS (regarding to criteria of new PCOS phenotypes, based on the Rotterdam criteria) (3) who were nonobese (body mass index [BMI], 20-25 kg/m2) were included. For control group, 59 healthy subjects (BMI, 20-25 kg/m2) were recruited.
All patients completed a standard questionnaire regarding their detailed history of menstrual cycles, acne, hirsutism, and medications. Oligomenorrhea was defined as menstrual cycles occurring at intervals > 35 days, with only four to nine periods in a year. BMI (kg/m2) was calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. The presence of terminal hair growth was scored using Ferriman–Gallwey Method (21); hirsutism was defined as a score > 8 (22). The presence or absence of acanthosis nigricans and acne were noted. All women had normal thyroid, renal, and hepatic function test results.
Individuals with hyperprolactinemia, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, Cushing's syndrome, and those who had taken hormonal treatment for at least three months prior to their evaluation were excluded. Furthermore, patients with hypertension and a history of angina or myocardial infarction, obesity, diabetes mellitus, diagnosed coagulation abnormalities or abnormal results of hematological parameters, any systemic disease, vascular or thyroid disorders, infection or inflammatory diseases, and malignancy were excluded. In addition, subjects who had taken any medication affecting MPV value were excluded. The control group consisted of healthy women with regular menstrual cycles, normal BMI, and no medication during preceding three months.
3.2. Biochemical Analysis
Venous blood samples for assessing FSH and LH (mIU/mL), estradiol (pg/mL), prolactin (ng/mL), total testosterone (ng/mL), androstenedione (ng/mL), and dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEAS) (μg/dL) were obtained from all participants in the morning between 08:00 A.M. and 09:00 A.M. after an overnight fast. Serum FSH, LH, total testosterone, estradiol, progesterone, and DHEAS levels were measured by the chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (paramagnetic particle, chemiluminescent immunoassay) using a Unicel DxI 800 System immune-analyzer (Beckman Coulter Ireland Inc., Ireland) with original reagents. Radioimmunoassay (RIA) with commercial kits was employed to assess serum free testosterone (BioSource, Nivelles, Belgium) and androstenedione levels (Radim, Roma, Italy). Complete blood count including MPV was assessed using Roche SYSMEX device.
3.3. Measuring Insulin Resistance
Insulin (μIU/mL) was analyzed by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) and via Roche Hıtachı Cobalt 600 device. Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) levels were measured by the Roche Hitachi T800 device. IR was calculated by the IR index as determined by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA-IR) with the following formula: fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) × fasting insulin (µIU/mL)/405; values > 2.7 were considered as IR.
3.4. Transvaginal Ultrasonography
A radiologist performed transvaginal ultrasonography examination of the ovaries in all participants. Ovarian volume was calculated by the following formula: V = (π/6) × length (mm) × width (mm) × thickness (mm). The presence of polycystic ovaries was diagnosed by the presence of 12 or more follicles in each ovary with 2-mm to 9 -mm diameter and/or increased ovarian volume (> 10 cm3).
3.5. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was performed using PASW 18 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Quantitative data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation or median (range). Frequency (percentage) was used for categorical variables. When comparing the continuous variables Student’s t test was used for the normally distributed subset and Mann-Whitney U test was used for the otherwise distributed subset. Pearson Chi square or Fisher's exact tests were used for categorical variables. Linear regression analysis was performed for statistically significant data in correlation test. P value < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3.6. Ethic Committee
The approval of the study protocol was obtained from Institutional Review Board and each participant signed an informed consent regarding the principles in the Declaration of Helsinki.
4. Results
There were no significant differences between patients and controls with respect to age (P = 0.07) and BMI (P = 0.312) (Table 1).
| Groups | Number of Patients | Mean ± SD | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.070 | ||
| Controls | 59 | 26.91 ± 4.92 | |
| Patients With PCOS | 136 | 25.39 ± 5.51 | |
| BMI | 0.312 | ||
| Controls | 57 | 22.07 ± 2.13 | |
| Patients With PCOS | 106 | 21.52 ± 3.84 |
aAbbreviations: BMI, body mass index; and PCOS, polycystic ovary syndrome.
Total testosterone, free testosterone, androstenedione, DHEAS, LH, and estradiol levels and LH/FSH ratio were significantly higher in patients than in controls (P < 0.05) (Table 2).
| Control Patients | Patients With PCOS | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estradiol | 0.016 | ||
| N | 57 | 130 | |
| Mean | 60.77 | 78.84 | |
| Median | 52.00 | 55.00 | |
| SD | 37.90 | 62.24 | |
| Minimum | 22.56 | 17.00 | |
| Maximum | 225.00 | 355.00 | |
| Free testosterone | < 0.001 | ||
| N | 55 | 125 | |
| Mean | 1.38 | 2.50 | |
| Median | 1.40 | 2.41 | |
| SD | 0.65 | 1.03 | |
| Minimum | 0.30 | 0.25 | |
| Maximum | 3.00 | 4.71 | |
| Total testosterone | < 0.001 | ||
| N | 59 | 135 | |
| Mean | 0.38 | 0.68 | |
| Median | 0.34 | 0.66 | |
| SD | 0.20 | 0.32 | |
| Minimum | 0.12 | 0.13 | |
| Maximum | 0.94 | 1.65 | |
| Androstenedione | < 0.001 | ||
| N | 45 | 102 | |
| Mean | 1.00 | 3.07 | |
| Median | 0.84 | 2.57 | |
| SD | 0.60 | 2.19 | |
| Minimum | 0.20 | 0.23 | |
| Maximum | 2.50 | 10.00 | |
| DHEAS | |||
| N | 58 | 134 | < 0.001 |
| Mean | 171.87 | 317.50 | |
| Median | 162.36 | 316.21 | |
| SD | 76.93 | 155.09 | |
| Minimum | 53.00 | 50.30 | |
| Maximum | 351.00 | 726.00 | |
| FSH | |||
| N | 58 | 129 | 0.103 |
| Mean | 6.10 | 5.52 | |
| Median | 6.20 | 5.64 | |
| SD | 2.70 | 2.00 | |
| Minimum | 1.21 | 1.46 | |
| Maximum | 19.90 | 12.56 | |
| LH | 0.006 | ||
| N | 58 | 128 | |
| Mean | 7.10 | 9.41 | |
| Median | 6.28 | 7.28 | |
| SD | 4.06 | 7.17 | |
| Minimum | 1.37 | 0.51 | |
| Maximum | 19.45 | 36.44 | |
| LH/FSH | 0.025 | ||
| N | 58 | 128 | |
| Mean | 1.36 | 1.75 | |
| Median | 1.09 | 1.26 | |
| SD | 0.92 | 1.40 | |
| Minimum | 0.26 | 0.13 | |
| Maximum | 4.58 | 9.84 |
aAbbreviation: PCOS, polycystic ovary syndrome; N, number of the all subjects, SD, standard deviation; DHEAS, dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate; LH, luteinizing hormone; and FSH, follicular stimulating hormone.
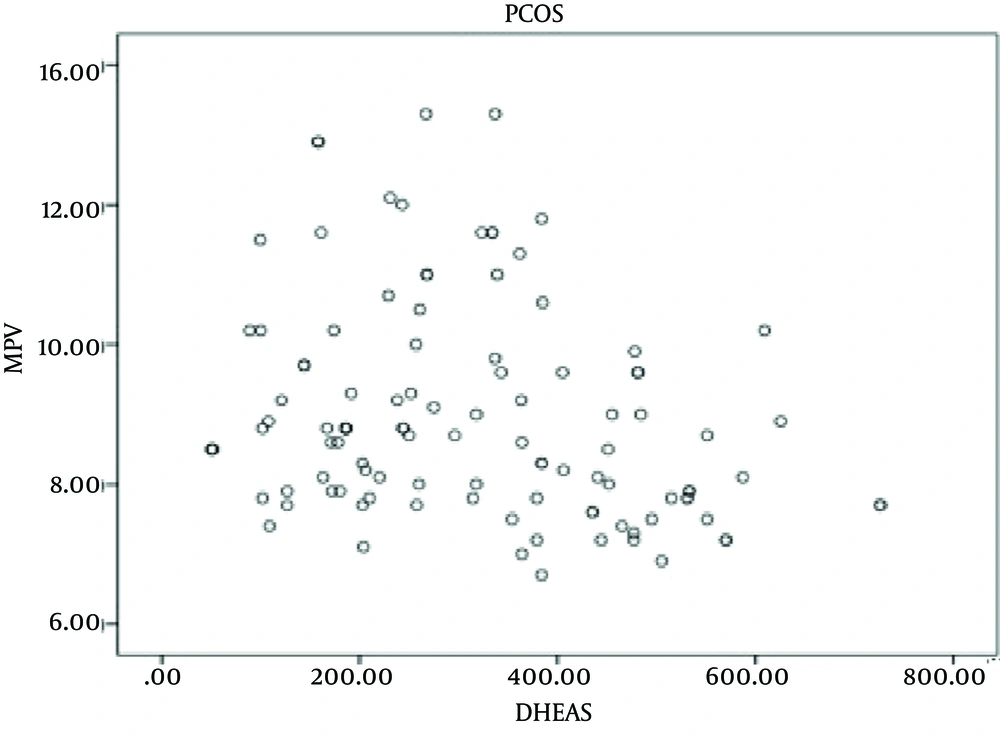
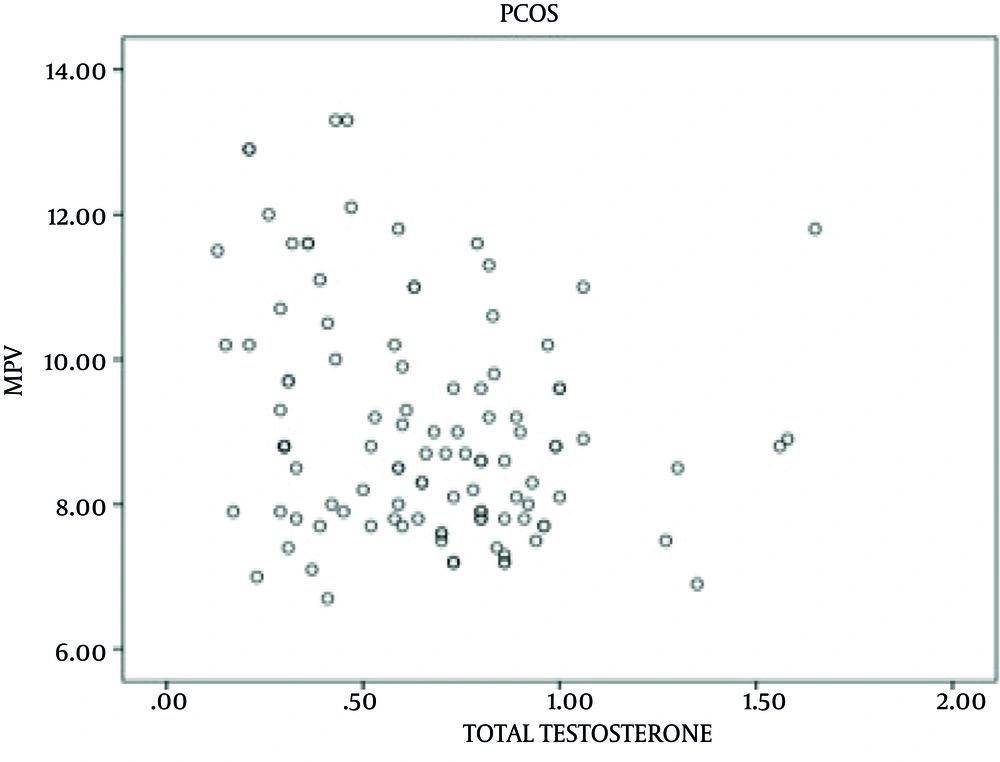
HOMA-IR was significantly higher in patients than in controls (44.9% and 19%, respectively; P = 0.001). When patients were divided into two group regarding their HOMA-IR status, patients with IR showed no significant differences with those without IR in BMI (P = 0.117) and levels of total testosterone, androstenedione, and DHEAS (P = 0.514, P = 0.602, P = 0.484, and P = 0.502, respectively). No significant differences were observed in mean MPV value between patients and controls (mean, 9.02 fL (8.5-10.1) and 8.9 fL (7.7-9.1), respectively; P = 0.777). MPV values were also similar between controls and patients without IR (P > 0.05). There was difference in MPV values between patients with high androgen levels (mean, 8.7 fL (7.1-11.9) and patients with normal levels (mean, 9.5 fL (6.9-13.2), P = 0.012) as well as between patients with high androgen levels and controls (mean, 8.9 fL (7.7-9.1), P = 0.04). No difference was observed between patients with normal androgen hormones levels and controls in MVP values (P > 0.05). There was a negative correlation between total testosterone and DHEAS with MPV (P = 0.016, r = -0.229; and P = 0.006, r = -0.261, respectively) (Table 3 and Figures 1 and 2). Multiple logistic regression analyses confirmed the independence of these associations (Table 4).
| Correlation Between Serum Concentration of Androgen Hormones and Mean Platelet Volume | |
|---|---|
| Free Testosterone | |
| r | -0.164 |
| P value | 0.102 |
| N | 100 |
| Total Testosterone | |
| r | -0.229 |
| P value | 0.016 |
| N | 110 |
| Androstenedione | |
| r | 0.040 |
| P value | 0.732 |
| N | 77 |
| DHEAS | |
| r | -0.261 |
| P value | 0.006 |
| N | 109 |
aAbbreviations: MPV, mean platelet volume; r, correlation coefficient; N, number of the patients with PCOS; and DHEAS, dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate.
| Coefficient of Regression | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | Std. Error | ||
| DHEASa | 15.102 | 1.609 | < 0 .001 |
| Total Testosterone | -1.214 | 0.436 | 0.007 |
aAbbreviations: DHEAS, dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate.
5. Discussion
PCOS leads to developing inflammation and atherosclerosis. Many recent studies have demonstrated the close relationship between atherosclerosis and increased MPV (8-12). Our study revealed that MPV did not differ between nonobese women with PCOS and controls. In contrast, a previous study reported an increased MPV in women with PCOS in comparison to non-PCOS controls (20). The discrepancy between the findings of two studies could be due the inclusion of obese patients with PCOS in the previous study and increased MPV in this population might occur as a consequence of obesity, which is known to causes increased MPV (15). A recent study including nonobese and obese patients with PCOS demonstrated that MPV did not correlate with PCOS except in patients with obesity (23). According to AES (4, 5) and a review (24, 25), growing evidence links androgens with pathophysiology of PCOS and metabolic derangements. Moreover, a recent study has announced that hyperandrogenism might be the progenitor of inflammation, which is independent of obesity in the patients with PCOS. The authors declared that further studies are needed to evaluate the effect of androgen hormones on metabolic abnormalities in patients with PCOS (26). In this regard, a recent study has reported a positive correlation between MPV and DHEAS levels in PCOS (20). In contrast, our study showed that high levels of androgens were associated with the low MPV values in the nonobese patients with PCOS. This contrast might be due to enrolling obese patients and a smaller sample size of the former study. Thus, we suggest that the studies that aim to investigate the association between MPV and any hormonal/metabolic parameters in patients with PCOS must exclude the patients with risk factors of atherosclerotic such as obesity, which may affect MPV. In addition, recent studies support an increased incidence of cardiovascular events related to IR and/or obesity in patients with PCOS (27). In our study, IR was higher in nonobese women with PCOS than in healthy controls. Our study showed no differences in MPV values among patients with and without IR. Additionally, we did not detect any association between IR and MPV. All these findings suggest that IR might not be an independent risk factor for MPV changes in nonobese patients with PCOS.
Finally, if the result of our study could be confirmed by prospective studies including four groups, namely, obese women with PCOS, nonobese women with PCOS, nonobese healthy women, and obese healthy women, the effect of obesity on MPV could be better understood. Our study showed that MPV values did not change in nonobese women with PCOS. Additionally, IR, which is one of the most common features of PCOS, was not related to MPV in nonobese patients with PCOS. Lastly, we showed that elevated androgen levels caused a decrease in MPV in the same population.