1. Background
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as hyperglycemia at any time in pregnancy based on defined thresholds that are lower than those considered for overt diabetes (1, 2). It is the most common metabolic disorder during pregnancy, with a total prevalence of about 7%. However, depending on the study population and diagnostic criteria, higher prevalence rates have also been reported (3, 4). Different studies have reported that a family history of type II diabetes mellitus (DM), GDM in previous pregnancies, giving birth to a child with macrosomia, body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2, idiopathic intrauterine fetal death (IUFD), and maternal age > 35 are among the risk factors of developing GDM (5).
Although most women recover after delivery, the tight control of GDM is associated with lower pregnancy and infant complications. Furthermore, the diagnosis of GDM can initiate interventions to decrease the later risk of developing diabetes or at least its early diagnose in case it occurs (6). Hence, the early detection of GDM is essential to avoid complications. Cost-effectiveness studies have shown that screening, diagnosis, and treatment of GDM can improve pregnancy outcomes and are, therefore, cost-effective, regardless of the type of treatment (7).
Different methods and time frames have been proposed for the diagnosis of GDM (Table 1), but there is still a great debate over the best approach (6). Changes in diagnostic criteria shift their sensitivity and specificity and consequently the number of pregnant women who are diagnosed with GDM. Based on the results of the HAPO study, a new method for the diagnosis of GDM has been adopted by the American Diabetes Association (ADA). The so-called International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group (IADPSG) criteria are better correlated with disease complications in the fetus, infant, and mother. This method has resulted in a 2 to 3-fold increases in the prevalence of diagnosed GDM (8-10). While some researchers have criticized this fact, others believe that due to the number of cases that can easily be controlled with lifestyle changes, the new method reduces the complications of GDM at a lower cost (11).
| Criteria | 75 g OGTT (IADPSG Criteria) | 75 g OGTT (ADA Criteria 2009) | 100 g OGTT (Carpenter and Coustan Criteria) | 100 g OGTT (NDDG Criteria) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of abnormal values needed for diagnosis | ≥ 1 | ≥ 2 | ≥ 2 | ≥ 2 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 92 | 95 | 95 | 105 |
| 1st PG, mg/dL | 180 | 180 | 180 | 190 |
| 2nd PG, mg/dL | 153 | 155 | 155 | 165 |
| 3rd PG, mg/dL | 140 | 145 |
Abbreviations: FPG, fasting plasma glucose; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus; IADPSG, International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group; NDDG, National Diabetes Data Group; OGTT, oral glucose tolerance test; PG, plasma glucose
2. Objectives
Our study aimed to evaluate the effect of IADPSG criteria on the prevalence of diagnosed GDM; we also sought to evaluate the predictive power of each risk factor of GDM.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Population
This was a cross-sectional study. The study population included pregnant women aged 18 years or older who visited the obstetrics and gynecology clinics of three university-affiliated hospitals in Tehran between October 2011 and November 2012. The exclusion criteria were an unwillingness to participate in the study, failure to complete the Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT), having an pregnancy with assisted reproductive technology, and a history of overt diabetes before the index pregnancy. Moreover, pregnant women consuming medications effective on glucose metabolism, patients with chronic liver disease, and those with endocrine disorders were excluded from the study. The University Ethics Committee approved the study protocol. All patients signed informed consent forms. Considering the GDM prevalence of 14%, α = 0.05, and accuracy of 5%, the sample size was calculated to be around 1100 women that were selected using consecutive sampling.
3.2. Data Collection
Demographic and clinical data were obtained during 10-min interviews, including age, smoking, alcohol consumption, history of hypertension, gestational hypertension, diabetes in first degree relatives or in previous pregnancies, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), having a low-birthweight infant, macrosomia, and abortion. When a clear history of PCOS was absent, we obtained the history of signs and symptoms of androgen excess (including acne or hirsutism) and ovarian dysfunction. All interviews were conducted by either of the three researchers (MA, FF, and MN). The weight without shoes and with a light dress at the first prenatal visit (before 24 weeks of gestational age) was measured by a trained nurse using a standard digital scale (Seca, Hamburg, Germany) with an accuracy of 0.1 Kg. Height was measured without shoes and with a standard wall Stadiometer (Seca) with an accuracy of 0.1 cm. Blood pressure was measured twice by trained staff after a 15-min rest, in the sitting position, using a standard mercury sphygmomanometer with an accuracy of 1 mmHg. Gestational age was calculated based on the last menstrual period. If the exact date was not specified, the time of delivery was calculated based on sonographic evaluation (between weeks 6 and 28 of pregnancy). To check the fasting glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin, a blood sample was taken from the mother after 8-h fasting in the first prenatal visit.
For mothers whose overt diabetes was ruled out at the first prenatal visit, a standard oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation. All evaluations were performed using an enzymatic method. A blood glucose test was performed using Enzymatic Glucose Oxidase Method and the coefficient of variation (CV) was below 5%.
3.3. Diagnostic Protocols
The old ADA criteria and new IADPSG criteria were used separately for the diagnosis of GDM. Based on the old ADA criteria (2009), OGTT with 75 g of glucose was performed from 24th to 28th weeks of gestation and if two measurements were higher than the recommended cut points (FPG ≥ 95, 1hPG ≥ 180, 2hPG ≥ 155), GDM was diagnosed. In the IADPSG criteria, 75 g OGTT was performed and if only one plasma glucose reading was higher than the recommended cut point (FPG ≥ 92, 1hPG ≥ 180, 2hPG ≥ 153), the diagnosis of GDM was confirmed (1, 12). The ADA criteria (FPG ≥ 126 mg/dL or HgbA1C ≥ 6.5%) were used for the diagnosis of overt diabetes.
3.4. Statistical Analysis
All continuous variables were checked for normal distribution, using Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk tests. All normally distributed data are expressed as mean ± SD and skewed continuous variables are expressed as median (IQ 25 - 75). Categorical variables are shown as frequency (percentage). Pearson chi-square test, one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test, and Kruskal Wallis test with pairwise comparisons were used to compare between-group differences for categorical variables, normally distributed variables, and skewed continuous variables, respectively. After using the logistic regression model, clinical and demographic variables associated with GDM (according to the IADPSG criteria) with P values of less than 0.2 in univariate analysis were considered for multivariate analysis. Multivariate logistic regression with backward stepwise selection procedures was used to estimate the adjusted odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals of different variables. All analyses were performed using IBM SPSS version 20 for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA), with a two-tailed P value of < 0.05 considered significant.
4. Results
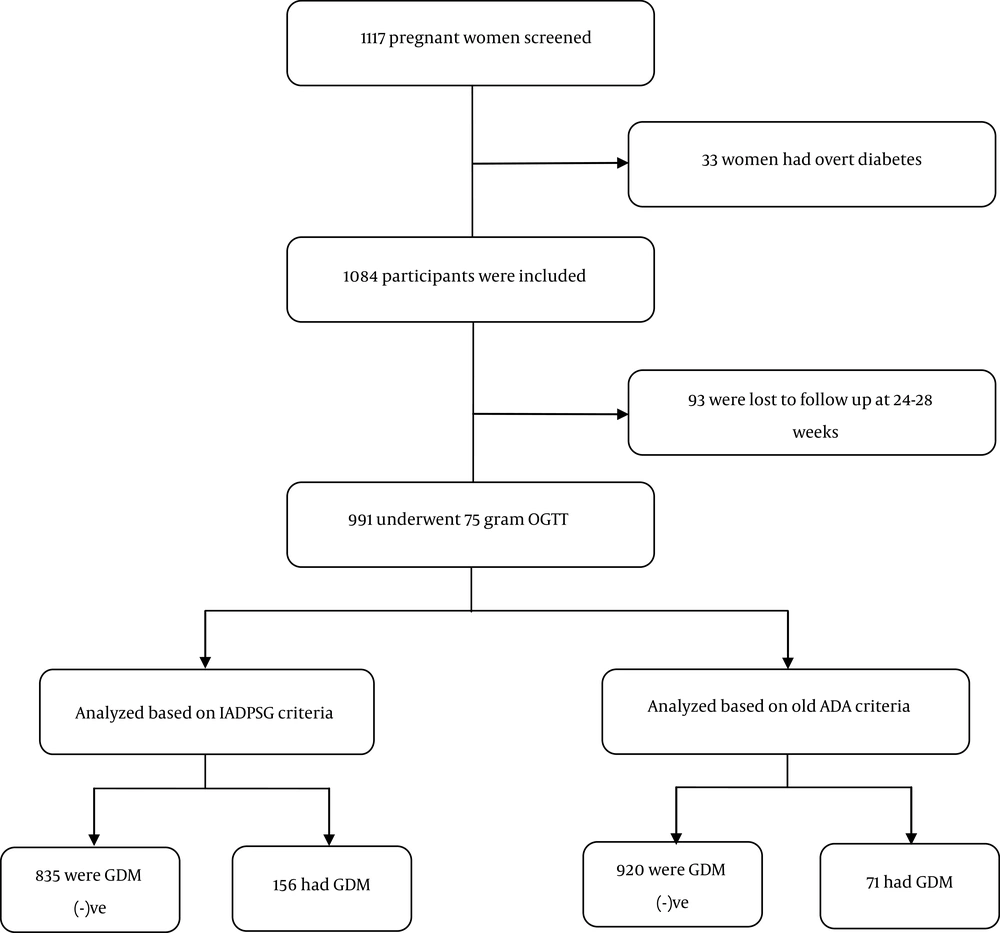
We studied a total number of 1117 pregnant women. Their mean age was 26.4 ± 4.2 years. Of them, 537 (48.1%) women were primigravid, 380 (34.1%) women were gravid 2, and 144 (12.9%) women were gravid 3. The family history of DM was positive in 108 (9.7%) women and 12 (1.1%) women had a history of impaired FPG or IGT. Table 2 shows the demographic and clinical characteristics of the study subjects. The mean gestational age at the first prenatal visit was 12.2 ± 5.9 weeks in total, and 11.5 ± 3.4, 12.4 ± 5.2, and 12.3 ± 6.1 weeks in patients with overt diabetes, those with GDM, and those without GDM, respectively.
| Variable | Total (N = 1117) | Overt DM (N = 33) | GDM (+) (N = 156) | GDM (-) (N = 835) | Pb | Pc | Pd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 26.5 ± 4.2 | 27.7 ± 5.1 | 28.7 ± 4.8 | 26.05 ± 3.9 | < 0.001 | 0.024 | < 0.001 |
| Gravidity | 2 (1 - 2) | 2 (1 - 3) | 2 (1 - 3) | 1 (1 - 2) | < 0.001 | 0.010 | < 0.001 |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | 27.5 ± 6.1 | 27.5 ± 3.8 | 27.3 ± 4.6 | 25.0 ± 2.8 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Pregnancy weight gain, Kg | 5.6 ± 2.0 | 9.2 ± 1.8 | 8.0 ± 2.1 | 5.2 ± 1.6 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| SBP, mmHg | 113.2 ± 10.3 | 117.5 ± 10.7 | 118.2 ± 11.3 | 112.4 ± 9.9 | < 0.001 | 0.026 | < 0.001 |
| DBP, mmHg | 71.0 ± 8.1 | 72.0 ± 9.4 | 72.8 ± 8.9 | 70.7 ± 7.9 | 0.049 | 0.490 | 0.007 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 80.4 ± 11.2 | 116.3 ± 16.5 | 93.8 ± 8.5 | 76.5 ± 5.7 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| HbA1C, % | 4.7 ± 0.7 | 6.8 ± 0.3 | 5.4 ± 0.6 | 4.5 ± 0.6 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Hemoglobin, g/L | 12.4 ± 0.9 | 12.7 ± 0.8 | 12.4 ± 1.5 | 12.4 ± 0.8 | 0.399 | 0.087 | 0.911 |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; DBP, diastolic blood pressure (during the first prenatal visit); FPG, fasting plasma glucose (during the first prenatal visit); GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus; SBP, systolic blood pressure (during the first prenatal visit)
aValues are expressed as mean ± standard deviation or median (IQR 25 - 75).
bP value among groups
cP value between overt DM and GDM (-)
dP value between GDM (-) and GDM (+)
moreover, 39 (2.95%) women had overt DM in their first prenatal visits. Of 1084 pregnant women who did not have overt diabetes at first visit, 93 did not return for further evaluation at weeks 24 - 28 of pregnancy and were not followed up. GTT was performed for the remaining 991 participants. Based on the old ADA criteria (having two plasma glucose measurements of above the specified values), 71 had GDM and the calculated prevalence of GDM was 7.1% (Figure 1).
Based on the IADPSG criteria, 156 patients were diagnosed as having GDM and the prevalence of GDM was 15.7% (Figure 1). In 84.7% of these patients, the diagnosis was made by the FPG criteria.
Univariate analysis showed that a history of abortion (P < 0.001), macrosomia (P < 0.001), history of GDM (P < 0.001), impaired FPG or IGT (P = 0.01), family history of DM (P = 0.004), and history of hypertension (P < 0.001), BMI and weight (P < 0.001) were the factors associated with GDM (Table 3). In addition, the FPG level had a significant correlation with the risk of developing GDM (P < 0.001) (Table 3).
| Variable | GDM (%) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No (N = 848) | Yes (N = 156) | ||
| Past history, No. (%) | |||
| History of abortion | 74 (8.7) | 42 (27.1) | < 0.001 |
| History of macrosomia | 0 (0.0) | 7 (4.5) | < 0.001 |
| History of congenital malformation | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0.845 |
| History of GDM | 1 (0.1) | 9 (5.8) | < 0.001 |
| History of IFG or IGT | 0 (0.0) | 5 (3.2) | < 0.001 |
| Family history of DM | 68 (8.0) | 27 (17.4) | < 0.001 |
| History of HTN | 1 (0.1) | 3 (1.9) | 0.013 |
| Biochemical characteristics, mean ±SD | |||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 12.4 ± 0.8 | 12.4 ± 1.4 | 0.953 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 76.5 ± 5.7 | 93.9 ± 8.5 | < 0.001 |
| Weight gain, kg | 5.2 ± 1.6 | 8.0 ± 2.0 | < 0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.0 ± 2.8 | 27.3 ± 4.6 | < 0.001 |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; DM, diabetes mellitus; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; IFG, impaired fasting glucose; IGT, impaired glucose tolerance
Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age at pregnancy, BMI, family history of diabetes, and history of macrosomia in previous pregnancies were independent predictive factors of GDM after adjusting for other factors. Among these factors, the history of macrosomia in previous pregnancies was associated with an increased risk of GDM (Table 4).
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | P Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.09 (1.04 - 1.13) | < 0.001 |
| BMI | 1.2 (1.11 - 1.25) | < 0.001 |
| History of macrosomia | 6.78 (1.73 - 26.6) | 0.006 |
| Family history of DM | 2.01 (1.18 - 3.41) | 0.01 |
| History of GDM | 1.07 (0.31 - 3.68) | 0.9 |
| History of PCOS | 1.72 (0.67 - 4.40) | 0.25 |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; DM, diabetes mellitus; OR, odds ratio; PCOS, polycystic ovarian syndrome
5. Discussion
This study aimed to assess the prevalence of GDM based on the IADPSG and old ADA criteria simultaneously. We found that the prevalence of GDM was 2.2 times higher based on the IADPSG criteria than based on the old ADA criteria (7.1%). In addition, it was shown that pregnancy at an older age, high BMI, family history of diabetes, and history of macrosomia in previous pregnancies were predictive factors for developing GDM.
The prevalence of GDM varies in different societies and ranges from 1% to 14% (13). This variation in prevalence mainly results from geographic and demographic factors, as well as differences in diagnostic criteria (3). Two studies in Brazil and Norway, using IADPSG criteria, reported a prevalence of 18% and 31.5%, respectively (14, 15). Reports of the prevalence of GDM in Iran have also shown different results (16-19). In a systematic review of studies between 1992 and 2007, the prevalence of GDM in different areas of Iran was reported to be between 1.3 and 8.9% (20). None of these studies applied the IADPSG criteria. In 2012, a single-center small study in Iran reported a prevalence of 31% based on the IADPSG criteria (16).
Different criteria are used for the diagnosis of GDM, each having its own accuracy and sensitivity, leading to variations in the reported prevalence of GDM (3). The WHO criteria for the diagnosis of GDM are more sensitive than the National Diabetes Data Group (NDDG) and ADA criteria (6). Other studies also suggest that the ADA criteria are more sensitive than NDDG for the diagnosis of IGT (21). In a multicenter study of 25,000 pregnant women using the IADPSG criteria, the GDM prevalence was reported as 17.8% (22). In a study by Agarawal et al. in the United Arab Emirates in 2010, the GDM prevalence based on the new criteria showed a 3-fold increase (10). In a study by Sacks et al. in 2012, the GDM prevalence at 15 centers was evaluated. They showed that the prevalence was 17.8%, ranging from 9.3% to 25.5% (23). In another study in Australia on 1,275 pregnant women by Moses et al., the GDM prevalence was reported as 9.6% and 13% based on the old and new criteria, respectively (24). In 2011, in another study of 607 Indian pregnant women, the GDM prevalence was 7.1% based on the old criteria and 10.8% based on the new criteria (25).
The present study of GDM used the old ADA and new IADPSG criteria simultaneously, making it possible to compare the prevalence of GDM based on these criteria with high accuracy. The IADPSG criteria are more sensitive to the screening of GDM. As an example, Shang and Lin reported a prevalence of 37.7% for GDM based on the IADPSG criteria and a prevalence of 12.9% based on the old ADA criteria. GDM, as diagnosed by IADPSG, had a greater association with the complications of the disease (9). In some studies, the results of IADPSG for the diagnosis of GDM were similar to diagnostic methods approved by the WHO (26). However, most studies have shown that using the IADPSG criteria, there would be a 2 to 3-fold increases in the GDM prevalence (9, 10). A recently published meta-analysis showed that studies that used the IADPSG criteria reported a significantly higher prevalence of GDM (6-11 folds) compared to other studies (3).
Various risk factors have been suggested for the development of GDM in previous studies. BMI has been reported in prior studies to be a predictive factor for GDM. In the present study, we also found that higher BMI at the beginning of pregnancy and more weight gain during pregnancy were the risk factors for GDM. The reduction of insulin sensitivity among obese pregnancies can justify this relationship. This obesity-related insulin resistance increases the normal glucose levels (27). This finding emphasizes the importance of weight control strategies, especially during pregnancy. In addition, our study showed the family history of diabetes, history of macrosomia, history of GDM in previous pregnancies, abortion, and impaired GTT to be the independent risk factors for GDM. Moreover, there was a significant correlation between age and onset of GDM. Macrosomia during index pregnancy may indicate poor maternal diet or GDM severity. This, in turn, predisposes the mother to recurrent GDM (28). The predisposing effect of a history of GDM may result from a “shared risk factor” in repeated pregnancies (29). Miscarriage during index pregnancy may point to the presence of various endocrine pathologies or poor blood glucose control. These may affect the normal metabolism of insulin, hence predisposing the mother to GDM (30). In line with the findings of this study, Teh et al. reported that a history of GDM and BMI of above 35 are two independent risk factors for GDM (31). However, Teede et al. reported that a history of GDM, higher maternal age and BMI, and a family history of diabetes were the most important risk factors for GDM (32). Four previous studies have shown that a family history of diabetes, history of GDM, higher maternal age, and BMI are the main risk factors for GDM (33-35).
In addition, although pregnant women at risk of GDM often receive training on lifestyle change and diet to control their weight, studies have shown that the diagnosis of GDM is an important factor in reaching the desired weight for these mothers (36). The awareness of diabetes creates a motivation to take more serious measures to adjust the lifestyle (37). Thus, early diagnosis and quick management of GDM is of great importance. Using IADPSG criteria, which are more sensitive for the diagnosis of GDM, is a better screening test for this purpose.
Our study faces some limitations. We did not evaluate the clinical outcomes of GDM in this study. Furthermore, due to its observational nature, the complete elimination of biases including “referral bias” was not possible. We did not have access to the pre-pregnancy weight of the participants and thus we assumed that this measurement was the best estimate of their pre-pregnancy BMI that we could have under study conditions. Moreover, the diagnosis of PCOS was mainly based on self-report.
However, our study, applied both criteria for the diagnosis of GDM simultaneously, which made it possible to compare the prevalence of GDM based on these criteria with high precision. The sample size was also large (> 1,000 participants).
Using the IADPSG criteria, a higher number of mothers who would otherwise be considered as healthy by the old criteria were diagnosed with GDM and received early treatment for the prevention of its complications. This may render this set of criteria more favorable. However, medicalization of pregnancy due to the higher rate of GDM is one of the disadvantages of using IADPSG criteria. In addition, our study did not evaluate the effect of criteria on feto-maternal and neonatal outcomes. Thus, we cannot recommend one of the criteria over another. The study of different risk factors and analysis of the effect of each factor on the prediction of GDM development can help us diagnose at-risk individuals for whom the GTT is either not available or not feasible. In addition, this study may be considered a start for the recognition of the power of each risk factor in GDM incidence.
According to the findings of the present study, the prevalence of GDM showed a 2.2-fold increase when the IADPSG criteria were applied in lieu of the old criteria. It was also shown that increased maternal BMI and age, family history of diabetes, history of GDM, and macrosomia in pregnancies are the risk factors for GDM.