1. Background
Detection and characterization of focal liver lesions in patients with known primary extrahepatic are essential to define management and prognosis. Triphasic helical computed tomography (CT) - hepatic arterial phase (HAP), portal venous phase (PVP), and delayed phase (DP) - represents the standard of reference for the characterization of a wide range of focal liver lesions (1), but it results in a relevant radiation exposure.
Split-bolus multidetector-row CT (MDCT) is an innovative technique that, by splitting the intravenous (iv) contrast medium into two or three boluses and combining phase images in a single scan, can be used in cancer patients to reduce radiation dose (2-4).
2. Objectives
This study assessed the diagnostic efficacy of split-bolus MDCT technique in detecting and characterizing focal liver lesions in oncologic patients.
3. Patients and Methods
3.1. Patients
In this study, the MDCT scans of the chest-abdomen-pelvis (CAP) of the previous two years were retrospectively analysed. Written informed consent for the split-bolus MDCT protocol was obtained from each patient and the research was performed according to the world medical association declaration of Helsinki. Thirty-six oncologic patients (19 males, 17 females; 42 – 80 years of age, mean age 63.3 years, weight 56 - 77 kg, mean weight 68 kg) underwent split bolus MDCT scanning (n = 36) of the CAP as a part of their follow-up care. No patient had cardiovascular insufficiency or liver cirrhosis.
All patients had known extrahepatic primary malignant cancer histologically confirmed: colorectal cancer (n = 10), lung cancer (n = 11), breast cancer (n = 5), pancreatic cancer (n = 3), gastric cancer (n = 6), and melanoma (n = 1).
3.2. Split-Bolus Multidetector-Row Computed Tomography Protocol
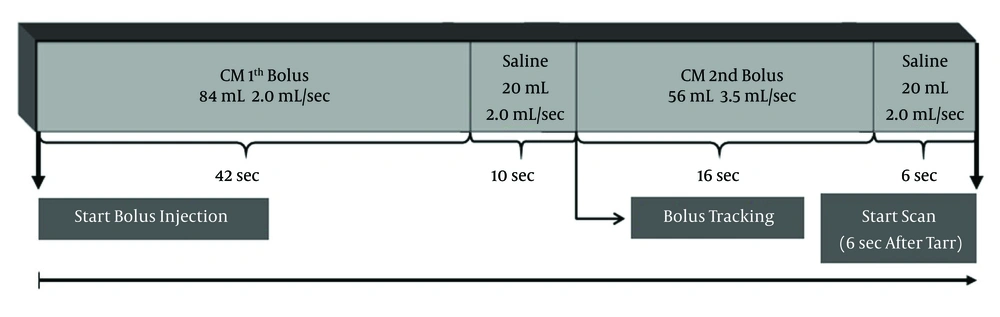
All patients were scanned with a 64-detector row scanner (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands). Our protocol consisted of unenhanced low-milliampere scans of the upper abdomen and a single scan of the CAP, after an iv injection of the of a maximum of 150 mL of contrast medium, Iopamiro 370 mgI/mL (Bracco, Milano, Italy) and Iopromide Ultravist 370 mgI/mL (Schering AG, Berlin, Germany), splitted by an automatic power injector (Medrad Stellant CT, Indianola, PA, USA) into two boli (Figure 1).
Schematic view of split-bolus 64-detector row CT technique of the chest and abdomen in a 70 Kg patient. At start of bolus injection (or time zero), first bolus of CM (84 mL at 2.0 mL/sec), followed by 20 mL of saline at the same flow rate is injected (hepatic enhancement during the PVP); second bolus of CM (56 mL at 3.5 mL/sec, followed by 20 mL of saline at the same flow rate (HAP). Approximately at the end of the second bolus injection of CM, the scan started cranio-caudally after a delay of at least 6 seconds from the arrival of the CM in the aorta. An acquisition from the pulmonary apex to the pubic symphysis was performed resulting in a simultaneous contrast enhancement of the arterial and venous systems. CM: contrast medium. PVP: portal venous phase. HAP: hepatic arterial phase. *Arrival time of contrast medium in the aorta (Tarr).
Amount of contrast medium, duration of injection, and times were established on the basis of the literature data (5-7) and broad clinical experience.
In our patients who weighed 56-77 Kg, we obtained an adequate hepatic enhancement during the PVP by using a first bolus of contrast medium (1.2 mL/kg) at a flow rate of 1.5-2 mL/sec. The adequate liver enhanncement during PVP had been determined based on an increase, after contrast medium administration, of more than 50 Hounsfield units (HU) when compared to unenhanced CT scans of the liver (8, 9). The HAP occurs at about 35 seconds after the start of iv injection of a second bolus of contrast medium (0.8 mL/kg) at 3-3,5 mL/sec.
Using the scout film, a scan range from the pulmonary apex to the pubic symphysis was determined. Then a circular region of interest (ROI) of the bolus-tracking technique (raising the threshold value to 500 HU) was placed into the descending aorta. Near the end of the second bolus injection of contrast medium, the scan started craniocaudally after a delay of at least 6 seconds from the arrival of the contrast medium in the aorta. The inherent 6 second delay in the bolus-tracking technique is necessary to move the scan tabulation to the start of the scan and to give breath-hold instructions to the patient.
A single contrast-enhanced acquisition was obtained, resulting in a simultaneous contrast enhancement of the arterial and venous systems. To increase the diagnostic accuracy of split-bolus MDCT for lesion characterization, a delayed phase DP at 5 minutes of the upper abdomen was performed. For the split-bolus MDCT protocol, the following acquisition parameters were used: slice thickness 2.5 mm; gantry rotation speed 0.75 seconds; reconstruction index 1.25; pitch 0,935:1; and 120 kVp. The tube current was set to the automatic milliampere setting on the basis of the patient’s weight. MDCT examinations were completed with sagittal and coronal multiplanar reconstructions (MPRs).
3.3. Images Analysis
Images were transferred to an external workstation and stored in a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) (RIS/PACS, IMPAX, Agfa healthcare, Mortsel, Belgium). All CT images were independently and in consensus reviewed by two radiologists (M.S. and A.D.A. with 25 and 15 years of experience in body CT, respectively). Any discrepancies concerning the diagnosis of liver lesions in terms of detection and characterization were resolved by consensus.
Attenuation of the aorta, main portal vein, and right lobe of the liver by a circular ROI were measured at combined HAP/PVP split-bolus scans. The appearance of each lesion at split-bolus MDCT was described on the basis of the attenuation and homogeneity of the lesion in comparison with the aorta according to the typical features of triphasic MDCT (10).
After describing the state of each lesion, the pattern of enhancement over time of each one was described as a two part pattern name that incorporated the appearance of the lesion in the combined phase (HAP/hepatic enhancement during PVP) and in the DP of the split-bolus protocol (e.g. hypo-/hypo-).
For the characterization of all focal liver lesions detected by split-bolus MDCT, the features were considered in terms of the number of lesions unchanged in size during follow-up on the triphasic CT (reference standard) and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and/or ultrasound at initial evaluation, as well as the appearance of each lesion at split-bolus. The findings indicated that the enhancing pattern of focal liver lesions at split-bolus MDCT were similar to those recognized in the triphasic CT evaluation, which has also been reported in the literature (3). Furthermore, we even considered, as a reference standard, other diagnostic methods such as MRI and/or ultrasound, during a follow-up period of at least six months.
4. Results
The mean attenuation values of the aorta, the main portal vein, and liver parenchyma were 350.6±44.7 HU, 198.3±36.8 HU, 112.4±14.5 HU, respectively. These values were not significantly different from those of the standard MDCT triphasic protocol at HAP and PVP reported in the literature (3, 5 - 8).
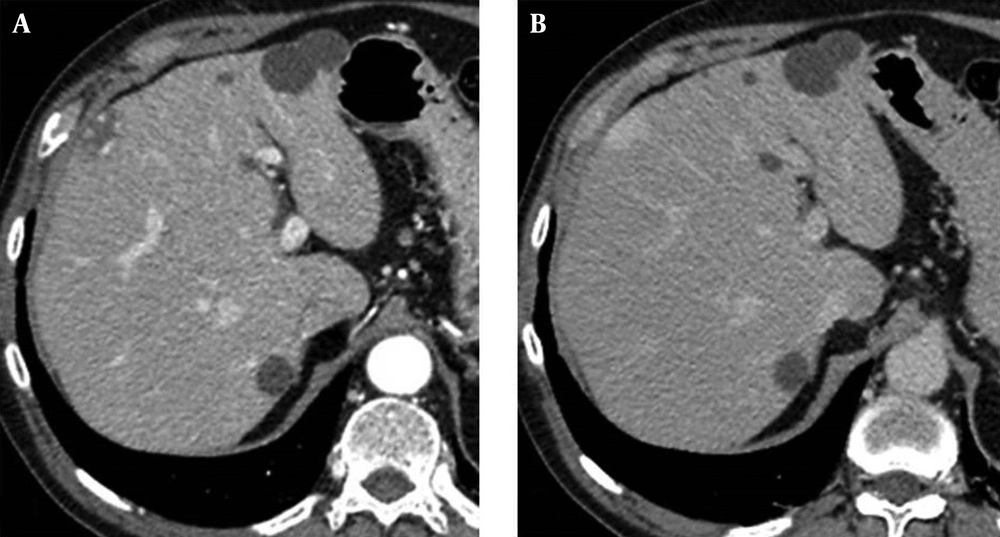
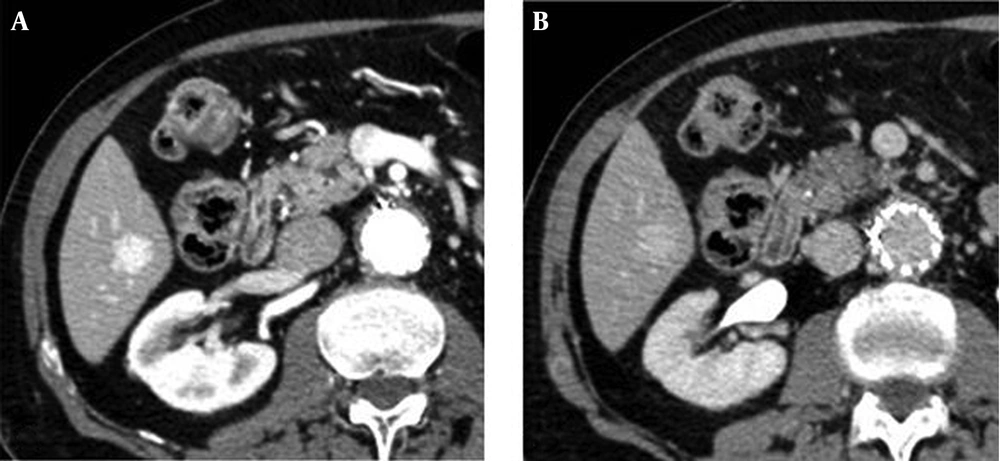
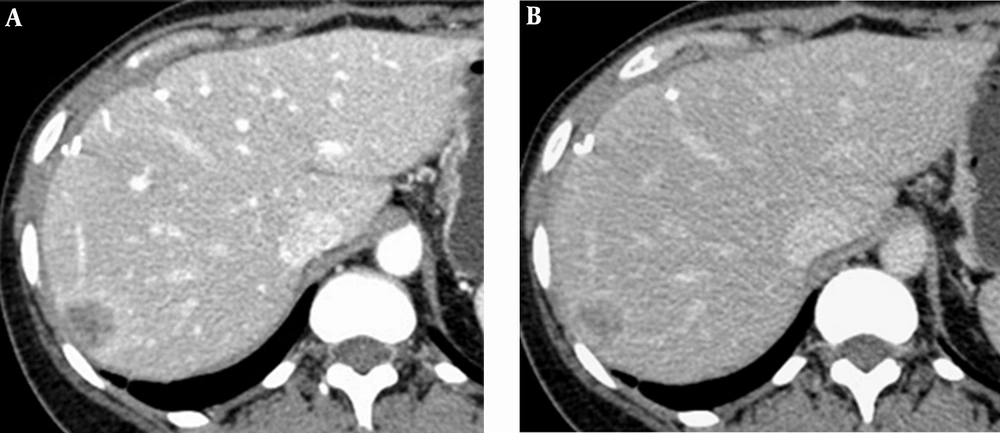
On 208 focal liver lesions, split-bolus MDCT protocol characterized 186 (89.4%) benign and malignant lesions: typical hemangiomas (n = 9), atypical hemangiomas (n = 3), cysts (n = 78), hypovascular (n = 93) and hypervascular (n = 3) metastases. Twenty two (10.6%) hypodense lesions were categorized as indeterminate (≤5 mm).
The follow-up split-bolus MDCT protocol demonstrated similar results in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions with respect to the triphasic protocol according to our experience and as reported in the literature (1, 3) (Table 1).
| Focal Liver Lesion | Enhancement Patterns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triphasic Technique | Split-Bolus Technique | |||||
| HAP | PVP | DP | HAP/PVP | DP | ||
| Cysts | Hypo- | Hypo-(cyst) | Hypo- | Hypo-(cyst) | Hypo- | |
| Typical hemangioma | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | |
| Hypo- | Hypo- | Hyper- | Hypo- | Hyper | ||
| A | A | A | A | A | ||
| Hyper- | A | A | Hyper- | A | ||
| Atypical hemangioma (10) | ||||||
| 1a | Hyper-b | Hyper-(no THAD)b | Iso | Hyper-(no THAD)b | Iso | |
| 1b | Hyper- | Hyper-(THAD) | Iso | Hyper-(THAD) | Iso | |
| 2a | Hypo- | Hypo-(homogeneous) | Iso | Hypo-(homogeneous) | Iso | |
| 2b | Hypo- | Hypo-(inhomogeneous)c | Iso | Hypo-(inhomogeneous)c | Iso | |
| 3 | Hypo- | Hypo-(inhomogeneous)d | Iso | Hypo-(inhomogeneous)d | Iso | |
| Metastases | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | |
| Hyper-(rim) | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hyper-(rim) | Hypo- | ||
| Hypo- | Hypo- | Hyper- | Hypo- | Hyper- | ||
| Hyper- | A | A | Hyper- | A | ||
| Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | ||
| Indeterminate lesions (≤ 5 mm) | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | Hypo- | |
Abbreviations: A, arterial; DP, delayed phase; HAP, hepatic arterial phase; PVP, portal venous phase; THAD, transient hepatic attenuation difference.
aHypo-, iso- and hyperattenuating refer to relative attenuation in comparison to that of the surrounding liver parenchyma.
bLess hyperattenuating than the aorta.
cHypoattenuating area with bright-dot sign in the HAP or PVP; the bright-dot sign was defined as a tiny enhancing dot within a hemangioma that did not progress to globular enhancement.
dHypoattenuating area with central enhancing area (centrifugal enhancement pattern) in the PVP.
Representative cases by split-bolus MDCT are shown in Figures 2 - 4.
5. Discussion
In oncologic patients, the rationale for an appropriate use of the CT is to optimize and standardize protocols to reduce radiation dose and to ensure diagnostic efficacy.
In this study, we implemented an innovative split-bolus MDCT protocol that combined the HAP and hepatic enhancement during PVP in a single acquisition, allowing the identification of hypo-, hypervascular, and mixed focal liver lesions. A DP at 5 minutes of the upper abdomen further helped in the characterization of the lesions.
The split-bolus technique consists of splitting the iv contrast medium into two boluses and performing MDCT acquisition in a single-pass. The rationale is similar to that of the CT urography protocol (4, 11) with the same goal of reducing the radiation dose.
In our study, using a flow rate of 1.5-2 mL/sec for the first bolus of contrast medium, an adequate attenuation in HU of the main portal vein and the liver parenchyma (more than a 50 HU increase of the liver enhancement during PVP, in comparison to unenhanced CT scan) was obtained (8, 9). The second bolus of 45 - 60 mL of contrast medium at 3 - 3.5 mL/sec ensured an adequate enhancement of the aorta during HAP.
The main goal of this innovative technique in oncologic patients, is to ensure a reproducible protocol and an imaging quality of diagnostic efficacy. Instead of obtaining two scans separately at the HAP and hepatic enhancement during PVP, as it occurs in bi- or triphasic CT techniques, it is possible to obtain a single combined phase scan. This results in reduction of the radiation dose, especially over the long-term and, moreover, in a decrease in the number of images to be analyzed and the amount of data stored on the PACS, in comparison to the triphasic CT technique.
The split-bolus MDCT technique by combined HAP and hepatic enhancement during PVP, in addition to 5 minutes DP, allowed an accurate characterization of focal liver lesions similar to those of a triphasic CT (3).
Our study has some limitations: the small number of the patients, and the retrospective study design. In oncologic patients, the designed technique can be proposed alternatively to bi- or triphasic MDCT and in a single-pass to PVP in the initial staging and in the follow-up respectively.