Dear Editor,
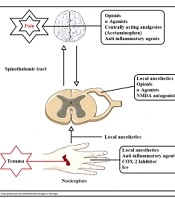
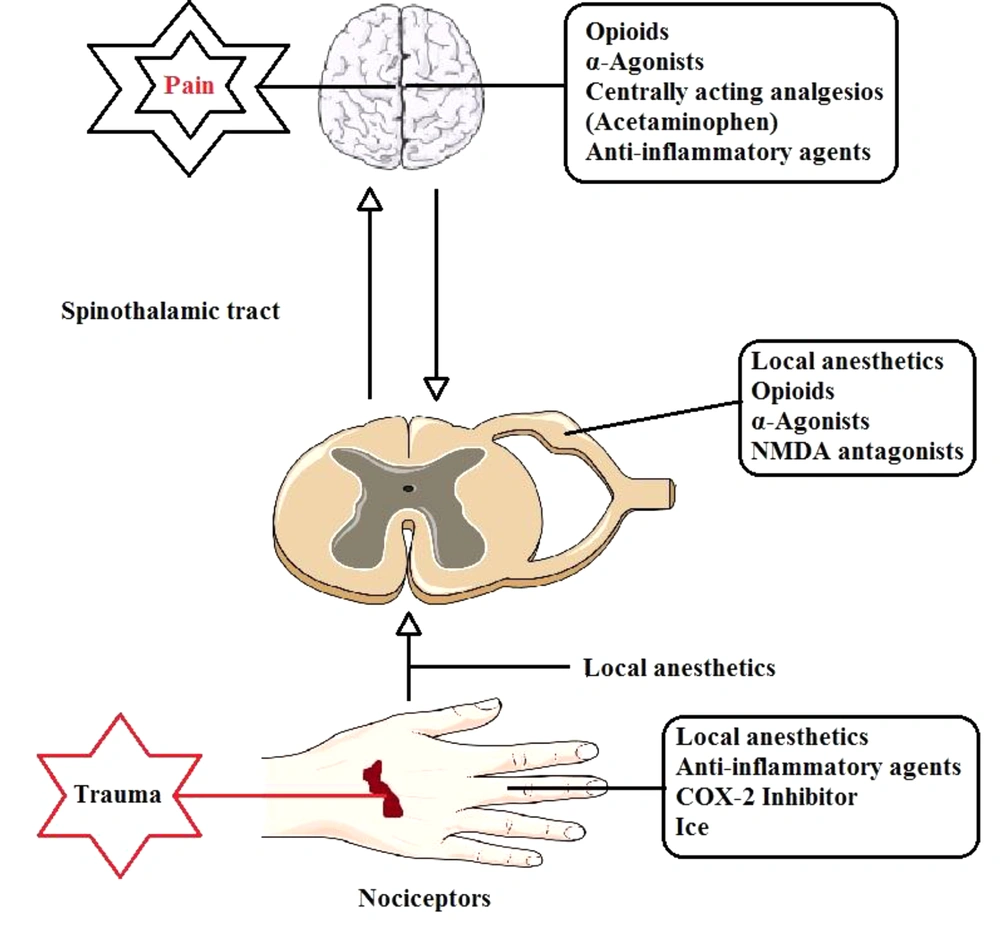
Pain occurs during TKR secondary to temperature change, trauma-triggered nerve damage, and local inflammation. TKR is often associated with pain following tissue damage and the release of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine, substance P, prostaglandins, and bradykinin (Figure 1) (1).
Several methods have been suggested for managing acute pain after TKR, including peripheral nerve blockers, multimodal or epidural analgesia, parental (IV) analgesia (eg, patient-controlled analgesia), and local infiltration analgesia (LIA) (1).
To avoid postoperative pain, it is proposed to administer analgesics or use other pain-relieving methods before introducing surgical incisions. The most effective strategy seems to be a combination of different methods or medications with different action mechanisms to prevent and alleviate pain and avoid multiple drugs (2). This is important, as the recovery of patients after TKA surgery may delay in the case of the inappropriate use of analgesics (3).
A variety of medications and methods have been proposed to alleviate severe pain after surgery, including pain-relieving agents, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, opioids, local infiltration, patient-controlled, multimodal, or epidural anesthesia, and peripheral nerve occlusion (4).
The sufficient use of analgesics after surgery can alleviate pain and obviate the need for opioid use, thus reducing the hospitalization period, drug-related complications, and patients' costs. In addition, patients' satisfaction and rehabilitation will improve. To upgrade patient outcomes, surgeons should be aware of the current anesthesia techniques and analgesia regimens used after TKA. Based on a recent meta-analysis, the femoral and sciatic nerves blockade seems to provide the best patient outcomes (5).
Therefore, it is advisable to utilize preoperative combinations of analgesics and postoperative sciatic and femoral nerve block.