1. Background
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a common cardiac emergency that annually causes the death of more than 2.4 million people in Europe and North Asia and accounts for more than one-third of deaths in developed countries (1, 2). One of the main treatments for AMI is primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI), which is the treatment of choice for reperfusion of the heart worldwide (2, 3). Patients with AMI commonly report chest pain as their main complaint (4). It is common for patients to experience chest pain after PPCI. Post-PPCI, recurrent chest pain can result from sudden vessel closure, coronary vasoconstriction, focal trauma to the coronary artery, or coronary artery dilatation after stent placement (5).
Common methods to alleviate chest pain include oxygen therapy, opioid medications, nitroglycerin, aspirin, and local anesthesia. Sedatives are the most effective means of alleviating chest pain in heart patients and are a readily accessible option for nurses to manage this symptom. Because opioids can have side effects and patients respond differently to this treatment, it is crucial to offer non-pharmacological approaches along with sedatives to alleviate chest pain in patients (4, 6, 7).
The AMI patients can benefit from alternative medical treatments performed by nurses to reduce pain and improve their health conditions (8). Non-pharmacological complementary treatments can be replaced with safer options that have fewer side effects. One of the most common forms of complementary medicine, reflexology, helps in the management of many diseases and health conditions (7). By applying pressure to specific points on the hands and feet, reflexology affects the health of corresponding body parts and promotes energy circulation. The effects of reflexology treatment can differ from person to person, owing to individual variations in body systems (7, 9).
Among the various types of reflexology, foot reflexology is highly prevalent. The application of pressure on specific areas of the feet in foot reflexology can impact the corresponding areas of the body (10). Reflex points can also be found in the hands (11). In different clinical settings, reflexology is a non-invasive treatment that is utilized. The effect of hand and foot reflexology on pain in patients has been explored in several studies (4, 6-8, 12, 13). However, there is not enough data to determine whether hand reflexology or foot reflexology is more effective in reducing chest pain in patients after primary angioplasty (4, 14).
2. Objectives
While sedative drugs can alleviate pain in myocardial infarction (MI) patients, they also pose negative effects and side effects. As a result, nurses should examine the efficiency of complementary interventions in addressing patients’ pain to minimize medication usage. This study aimed to compare the effect of hand and foot reflexology on chest pain in patients after PPCI in the Coronary Care Unit (CCU) of Ayatollah Mousavi Hospital in Zanjan, Iran.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
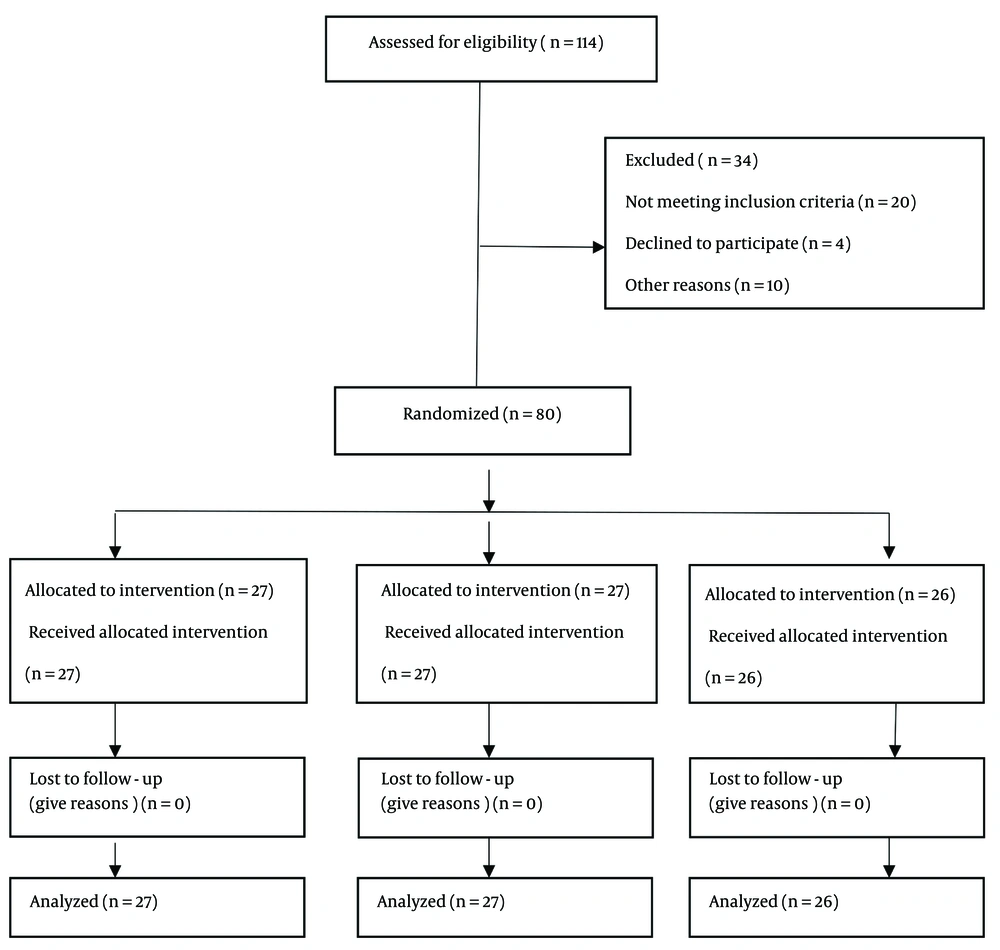
A randomized, double-blind, three-arm, parallel-group controlled trial was conducted in an urban area of Iran’s public hospital from May 2023 to December 2023. The study involved 80 patients eligible for PPCI.
3.2. Sampling and Recruitment
The sample size was estimated to be 26 people in each group using G*Power software, considering a power of 95%, α = 0.05, and an effect size of 0.8. This study included patients aged 30 to 75 who had undergone transfemoral angiography, had a normal posterior tibial pulse, had healthy legs, were fully conscious, and reported a pain level above three on the Visual Analog Scale (VAS). The exclusion criteria comprised a history of diabetes, self-reported mental problems, deep vein thrombosis, leg wounds and scars, peripheral neuropathy, tingling sensation, use of anti-anxiety drugs, administration of thrombolytic agents after AMI, and physiological or hemodynamic instability during and after angiography, such as cardiac dysrhythmia or active bleeding at the catheter site.
The method of consecutive sampling was used to recruit participants. Initially, patients with AMI were identified and evaluated for their eligibility. Next, patients who met the inclusion criteria were briefed on the study’s objectives and participation process. Patients who expressed willingness were included in the study.
Participants were randomly assigned to three study groups (hand reflexology, foot reflexology, and control group) using randomized block designs with sextuplet blocks. The random allocation sequence was determined using the website https://www.sealedenvelope.com by NH, a member of the research team. Sealed envelopes were used for concealment. Cards with letters A, B, and C were placed in the envelopes to represent the hand reflexology, foot reflexology, and control groups, respectively. Each time, the first researcher opened one envelope until the desired sample size was obtained. Participants were then assigned to study groups based on the card found inside the envelope.
3.3. Intervention
To perform foot reflexology, the patient’s privacy was preserved. They were asked to lie on the bed, and a pillow was placed under their knee for foot relaxation. After washing their hands with warm water and removing jewelry, the masseuse applied lubricating oil to the feet. This oil was free from salt, alcohol, and essential oils, and it was clear and water-soluble. The intervention began with massaging the center of the ball of the foot, specifically where the toes connect to the rest of the foot below the third toe line, using the heel of the hand to move from the center towards the outer edge. Pressure was exerted for half a minute using the tip of the thumb on the solar plexus point located at the intersection of the foot’s ball and arch. To perform reflexology, both thumbs were rotated outward from the center of the foot. A circular motion with the thumb was applied to the heart area of the foot, using a pressure that the patient found tolerable. The duration of the procedures was 15 minutes.
This study selected the left foot and left hand for reflexology. Stimulating the reflex points on the left foot or hand can reduce pain because they correspond to the reflex areas on the left side of the body, where the heart is located (4). For hand reflexology, the patient was placed on their back. The researcher massaged the hand, starting from the sides of the palm, then the palm, the back of the hand, and finally the fingers. The process was repeated 8 - 10 times to relax the hand for reflexology. The reflexology point was stimulated after the hand massage. The cardiovascular reflex point is located on the palm, under the soft area between the ring and little fingers. The therapist applied pressure to the reflexology point without causing pain. The reflexology points were massaged 14 times in a clockwise direction. The left hand received 15 minutes of hand reflexology.
The patient’s chest pain and anxiety levels were assessed 15 minutes, 3 hours, and 6 hours post-intervention (15). Following the removal of the arterial sheath, reflexology was performed on patients in the CCU. Female patients received reflexology from a female masseur, while male patients received it from a male masseur. The patient’s chest pain levels were assessed using the VAS before, and at 15 minutes, 3 hours, and 6 hours after the intervention. The control group received reflexology treatment on the soles of their right feet.
3.4. Data Collection
Data were collected by a trained research assistant who was blinded to the participants’ group assignments. The tools used in this study included a questionnaire for gathering demographic data and the Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS-P). Initially, participants filled out a demographic information questionnaire. The patients’ pain levels were measured before, and at 15 minutes, 3 hours, and 6 hours after the intervention. The demographic questionnaire included questions about age, gender, education level, marital status, AMI type, pain medication, psychological illness history, anti-anxiety medication use, hospitalization history, high blood pressure history, and diabetes. Demographic information and a VAS Questionnaire were utilized to assess chest pain. The VAS measures chest pain on a 10 cm line from 0 (least pain) to 10 (highest pain) (16).
3.5. Ethical Considerations
The study protocol was approved by Zanjan University of Medical Sciences (IR.ZUMS.REC.1401.348). The research protocol has been registered on the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials website (IRCT20230221057475N1). The necessary permissions were acquired before entering the research area. All participants provided written informed consent. Participants’ information is kept confidential, and they have the freedom to withdraw from the study at any stage.
3.6. Data Analysis
SPSS version 22 statistical software was used for the statistical analysis. The statistician was blinded to the group assignments of participants. The data were checked for normal distribution using kurtosis and skewness, which fell within the range of -2 to 2, indicating that pain followed a normal distribution. One-way ANOVA was used to compare quantitative variables, while chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used to compare qualitative variables. ANOVA was specifically used to compare pain levels. The significance level was set at P < 0.05.
4. Results
The hand reflexology group had 26 participants, while both the foot reflexology group and the control group had 27 participants each. All participants remained in the study until the end (Figure 1).
Table 1 reveals that most participants were male, married, lived in urban areas, were employed, and had less than a high school education. The chi-square and Fisher exact tests show that there were no significant discrepancies in demographic characteristics among the three groups, as depicted in Table 1.
| Variables | Study Groups | Chi-squared/Fisher Exact Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Reflexology (n = 26) | Foot Reflexology (n = 27) | Control (n = 27) | ||
| Gender | 0.2 | |||
| Male | 22 (84.6) | 21 (77.8) | 17 (63) | |
| Female | 4 (15.4) | 6 (22.2) | 10 (37) | |
| Marital status | 0.48 | |||
| Single | 0 | 0 | 2 (7.4) | |
| Married | 24 (92.3) | 24 (88.9) | 22 (5.81) | |
| Widow | 2 (7.7) | 3 (11.1) | 3 (11.1) | |
| Residence | 0.5 | |||
| Urban | 15 (57.7) | 12 (44.4) | 16 (59.3) | |
| Rural | 11 (42.3) | 15 (55.6) | 11 (4.07) | |
| Educational level | 0.81 | |||
| Illiterate | 8 (30.8) | 7 (25.9) | 8 (29.6) | |
| High school | 8 (30.8) | 12 (44.4) | 10 (37) | |
| Diploma | 7 (26.9) | 7 (25.9) | 5 (18.5) | |
| Higher university education | 3 (11.5) | 1 (3.7) | 4 (14.8) | |
| Occupation | 0.17 | |||
| Unemployed | 0 | 0 | 2 (7.4) | |
| Retired | 4 (15.4) | 5 (18.5) | 1 (3.7) | |
| Employed | 18 (69.2) | 16 (59.3) | 15 (55.6) | |
| Housewife | 4 (15.4) | 6 (22.2) | 9 (33.3) | |
| Age | 58.85 ± 9.68 | 58 ± 8.61 | 56.88 ± 12.68 | 0.77 b |
a Values are expressed as No. (%) or mean ± SD.
b One-way ANOVA.
The majority of participants with anterior and inferior infarctions had no prior hospitalizations, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or smoking habits. Fisher’s exact test and chi-square analysis confirmed that the clinical characteristics of the three groups were not significantly different (Table 2).
| Variables | Study Groups | Chi-square Test/Fisher’s Exact Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Reflexology (n = 26) | Foot Reflexology (n = 27) | Control (n = 27) | ||
| Type of myocardial infraction | 0.6 b | |||
| Anterior | 11 (42.3) | 13 (48.1) | 10 (37) | |
| Lateral | 0 | 3 (11.1) | 2 (7.4) | |
| Inferior | 12 (46.2) | 9 (33.3) | 13 (48.1) | |
| Extensive | 3 (11.5) | 2 (7.4) | 2 (7.4) | |
| Diabetic | 0.82 | |||
| Yes | 5 (19.2) | 4 (14.8) | 6 (22.2) | |
| No | 21 (80.8) | 23 (85.2) | 21 (77.8) | |
| Sedative | 0.1b | |||
| Morphine | 2 (7.7) | 1 (3.7) | 0 | |
| Pethidine | 3 (11.5) | 0 | 1 (3.7) | |
| Do not give sedation | 21 (80.8) | 26 (96.3) | 26 (96.3) | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.8 | |||
| Yes | 10 (38.5) | 8 (26.6) | 9 (33.3) | |
| No | 16 (61.5) | 19 (70.4) | 18 (66.7) | |
| Previous hospitalization | 0.96 | |||
| Yes | 13 (50) | 13 (48.1) | 12 (44.4) | |
| No | 13 (50) | 14 (51.9) | 15 (55.6) | |
| Smoker | 0.7 | |||
| Yes | 9 (34.6) | 7 (25.9) | 8 (29.6) | |
| No | 17 (65.4) | 20 (74.1) | 19 (70.4) | |
| Hypertension | 0.29 | |||
| Yes | 14 (53.8) | 9 (33.3) | 14 (51.9) | |
| No | 12 (46.2) | 18 (66.7) | 13 (48.1) | |
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
b Fisher’s exact test.
ANOVA indicates that there is no significant difference in chest pain before the intervention among the three groups (P < 0.05). After the intervention, there were no significant differences found among the three groups at 15 minutes, 3 hours, and 6 hours (P < 0.05) (Table 3).
| Variable and Time | Hand Reflexology | Foot Reflexology | Control | ANOVA b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | ||||
| Baseline | 4.46 ± 1.02 | 4.44 ± 0.97 | 4.74 ± 1.22 | 0.5 |
| Fifteen minutes after the intervention | 4 ± 0.77 | 4 ± 0.88 | 4.51 ± 1.22 | 0.73 |
| Three hours after the intervention | 3.5 ± 0.75 | 3.36 ± 0.74 | 3.89 ± 0.79 | 0.2 |
| Six hours after the intervention | 3.3 ± 0.77 | 3.37 ± 0.74 | 3.52 ± 0.85 | 0.8 |
a Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
b One-way analysis of variance.
5. Discussion
This study aimed to compare the effect of hand and foot reflexology on chest pain in patients after PPCI. According to the study results, there was no significant distinction in chest pain between the three groups before and after the intervention. Samadi et al. discovered that foot reflexology effectively relieved pain in patients with acute coronary syndrome, which contrasts with the findings of the current study. The pain scores of the intervention group exhibited a notable disparity before and after the therapy (6). The discrepancy between Samadi et al.’s studies and ours was due to the different research communities. We included patients with AMI who underwent PPCI in our study. There were variations in the severity and strength of chest pain among the two groups being studied.
Contrary to Sayari et al.’s research, our study found no reduction in chest pain in AMI patients through reflexology (4). Sayari et al. analyzed patients who underwent thrombolytic therapy for MI. The study discovered that removing the arterial sheath led to a decrease in patient pain, possibly because of variations in the research community. Lee et al.’s systematic review found that reflexology effectively reduces fatigue and improves sleep quality, although its impact on pain control is limited (17). Our findings are in line with what Lee et al. discovered. Therefore, it is recommended to study the impact of reflexology on individuals suffering from acute coronary syndrome.
5.1. Conclusions
The present study found that hand and foot reflexology did not decrease chest pain in patients who had PPCI, and there was no significant difference between the three groups. An intervention was carried out in the study to mitigate the impact of the arterial sheath on post-removal pain. The patients attained a state of relative stability in terms of pain, likely because the hand and foot reflexology did not influence this investigation. Therefore, it is important to assess the efficacy of reflexology in acute pain by comparing it to other therapeutic interventions rather than PPCI.
5.2. Limitations
The patients’ attentiveness prevented them from being blinded. Both the researcher (who measured the dependent variables) and the statistician were kept blind to the group allocations of the participants.