1. Background
Low back pain (LBP) is a prevalent and debilitating musculoskeletal disorder that can impact anyone in society. Low back pain frequently arises as a consequence of occupational factors and working conditions, making it one of the contemporary maladies affecting occupational health. The primary etiology of LBP stems from strains and sprains in the lumbar region resulting from stretching injuries inflicted upon the tendons, ligaments, or muscles in the lower back. These injuries can be precipitated by rotational movements, flexion, manual handling of heavy objects, or excessive stretching (1, 2).
In hospitals, there is a higher prevalence of work-related illnesses and injuries than in the general population (3). The high prevalence of LBP in the healthcare profession, specifically among nurses, has been documented in several studies (4-6). In a systematic study, Azizpour et al. reported the prevalence of back pain in nurses in Iran to be 63% (7).
The occurrence of LBP can significantly diminish the well-being of nurses. It can lead to limitations within the professional setting, poor attendance, and a desire to leave the nursing profession. Additionally, the efficacy of nursing practices and the ability to provide compassionate care can be negatively affected, consequently reducing the quality of care provided to patients. This, in turn, can lead to lower levels of patient and staff satisfaction and even create potential risks to patient safety (8). Low back pain is associated with the characteristics of nurses' occupations and is additionally impacted by societal and demographic variables, including age, gender, marital status, physical condition, and smoking habits, which may increase the risk for developing LBP (9, 10). Long working hours, shift work, and forced overtime can increase the risk of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) (11).
The prevalence of LBP is higher among operating room personnel compared to other healthcare workers (12). Fayzi et al. reported the prevalence of LBP among operating room personnel at 74% (13). The higher prevalence of LBP in the operating room is due to its demanding nature. The challenges of working in the operating room include long periods of standing, limited mobility, and incorrect body positioning during surgery. Additionally, performing repetitive actions over a long period and engaging in activities such as pushing, pulling, or lifting heavy equipment increases the risk of LBP (14, 15).
2. Objectives
Due to the significant occurrence of LBP among operating room staff, we decided to investigate the prevalence of LBP and the determining factors responsible for LBP in relation to demographic characteristics and working environment in educational hospitals affiliated with Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
This descriptive cross-sectional investigation was conducted during September and October 2023 to survey the personnel working in the operating rooms of five hospitals affiliated with Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (AJUMS) in Ahvaz, Iran. The hospitals included in the study were Imam Khomeini, Golestan, Abuzar, Ayatollah Taleghani, and Razi hospitals.
3.2. Population and Sample Size
The study population consisted of operating room personnel working as circulating, scrub, or anesthesia nurses. The sample size included 323 participants. This was determined based on prior research by Fayzi et al. (13), using an average prevalence of low back pain of 70%, a 95% confidence level, and a 0.05 margin of error.
Participants were selected through census sampling from the five teaching hospitals located in Ahvaz, a southwestern city in Iran. Inclusion criteria required participants to have an associate's degree or higher, at least two years of work experience in the operating room, and a willingness to participate. Exclusion criteria included osteoporosis, acquired spinal diseases, and corticosteroid consumption. Incomplete questionnaires were excluded from the analysis.
3.3. Data Collection
The data were gathered using the predisposing factors and dimensions of the low back pain questionnaire developed by Tavakkol et al. This questionnaire consisted of two parts. The first part included demographic information such as age, gender, marital status, level of education, smoking status, BMI, migration, age at first pregnancy, and number of pregnancies. The second part assessed the prevalence and dimensions of LBP. The reliability of the instrument, evaluated by Cronbach's alpha coefficient, resulted in a value of 0.77 (14).
The first stage involved counting the personnel assigned to operating rooms in each hospital. Personnel were selected for participation in the study using cluster sampling. The researcher obtained authorization from the Ethics Committee to administer surveys in hospitals during various shifts. The sampling process was conducted in accordance with the specified inclusion criteria. The questionnaires were distributed to the personnel and collected at the end of the same day.
3.4. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using IBM SPSS version 26. Quantitative variables were reported using mean and standard deviation, while qualitative variables were reported using frequency and percentage. Chi-square, Mann-Whitney, and Fisher's exact tests were used to evaluate the relationship between LBP and related factors.
4. Results
A survey was conducted on 323 operating room staff at five educational hospitals associated with AJMUS; eight questionnaires had to be excluded from the analysis due to data defects. Table 1 shows the distribution of population demographics in this study. 64.8% of the participants were women, 63.5% were married, and the majority (72.4%) had a bachelor's degree. Additionally, 24.4% of the participants had a history of migration, and most (87%) had no history of smoking. The average age of participants was 33.83 ± 7.02 years, with a minimum age of 23 years and a maximum age of 58 years. The average age at first pregnancy among women was 27.99 ± 3.10 years, with a minimum of 20 years and a maximum of 35 years. The average number of pregnancies was 1.54 ± 0.70, with a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 4 pregnancies.
| Variables | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 111 (35.2) |
| Female | 204 (64.8) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Marital status | |
| Single | 115 (36.5) |
| Married | 200 (63.5) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Level of Education | |
| Associate Degree | 14 (4.4) |
| BS | 228 (72.4) |
| MSc | 73 (23.2) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Smoking status | |
| Yes | 41 (13.0) |
| No | 274 (87.0) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| BMI | |
| 18.49> | 16 (5.1) |
| 18.5 - 24.99 | 180 (57.1) |
| 25 - 29.99 | 94 (29.8) |
| 30< | 25 (7.9) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Migration | |
| Yes | 77 (24.4) |
| No | 238 (75.6) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Age | 33.83 ± 7.02 |
| Age at first pregnancy | 27.99 ± 3.10 |
| Number of pregnancies | 1.54 ± 0.70 |
Table 2 shows that 41.3% of personnel work at Imam Khomeini Hospital, while 21.6% work in the general operating room. The majority of personnel (68.6%) have rotating shifts, with almost 44% of them in a standing posture in the operating room. The average work experience is 10.24 ± 5.84 years, with a minimum of 2 years and a maximum of 28 years. The average number of shifts worked is 28.46 ± 4.81 per month, with a minimum of 16 shifts and a maximum of 40 shifts per month.
| Variables | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Hospitals | |
| Imam Khomeini | 130 (41.3) |
| Golestan | 84 (26.7) |
| Taleghani | 46 (14.6) |
| Abuzar | 25 (7.9) |
| Razi | 30 (9.5) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Type of operating room | |
| General | 68 (21.6) |
| Heart | 23 (7.3) |
| Eye | 32 (10.2) |
| Obstetrics and Gynecology | 37 (11.7) |
| Urology | 34 (10.8) |
| Children | 26 (8.3) |
| Burn | 24 (7.6) |
| Orthopedics | 34 (10.8) |
| neurosurgery | 37 (11.7) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Shift work | |
| Morning | 76 (24.1) |
| Evening | 11 (3.5) |
| Shift | 12 (3.8) |
| Rotating shift | 216 (68.6) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| Body posture while working | |
| Standing | 139 (44.1) |
| Sitting | 21 (6.7) |
| Moving | 43 (13.7) |
| A combination of different modes | 112 (35.6) |
| Total | 315 (100) |
| The average number of shifts per month | 28.46 ± 4.81 |
| work experience (y) | 10.24 ± 5.84 |
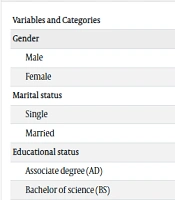
The findings of our study show that the overall prevalence of back pain is 74.3%. The chi-square test revealed a significant association between the prevalence of LBP and gender (P = 0.04), marital status (P = 0.001), and BMI (P < 0.01). The results of the Mann-Whitney test showed a statistically significant association between the prevalence of LBP and age (P = 0.001) (Table 3).
| Variables and Categories | LBP (%) | Test Statistic | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 4.05 | 0.044 | |
| Male | 75 (67.6) | ||
| Female | 159 (77.9) | ||
| Marital status | 21.78 | 0.001 | |
| Single | 68 (59.1) | ||
| Married | 166 (83) | ||
| Educational status | 2.40 | 0.301 | |
| Associate degree (AD) | 12 (85.7) | ||
| Bachelor of science (BS) | 172 (75.4) | ||
| Master of science (MSc) | 50 (68.5) | ||
| Smoking | 0.031 | 0.861 | |
| Yes | 30 (73.2) | ||
| No | 204 (74.5) | ||
| BMI | 11.72 | 0.008 | |
| < 18.49 | 8 (50) | ||
| 18.5 - 24.99 | 128 (71.1) | ||
| 25 - 29.99 | 80 (85.1) | ||
| > 30 | 18 (72) | ||
| Migration | 0.004 | 0.952 | |
| Yes | 57 (74) | ||
| No | 177 (74.4) | ||
| Age | 5942 | 0.001 | |
| With LBP | 34.73 ± 6.55 | ||
| Without LBP | 31.23 ± 7.69 | ||
| Age at first pregnancy | 364.5 | 0.952 | |
| With LBP | 27.99 ± 3.13 | ||
| Without LBP | 28.00 ± 3.00 | ||
| Number of pregnancies | 357.5 | 0.862 | |
| With LBP | 1.55 ± 0.72 | ||
| Without LBP | 1.44 ± 0.53 |
According to the findings in Table 4, Fisher's exact test shows a significant association between LBP and shift work (P = 0.001). Additionally, the chi-square test showed a correlation between LBP and body posture (P = 0.001). The Mann-Whitney results demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the prevalence of LBP and work experience (P = 0.001) and the average number of shifts (P < 0.037) (Table 4).
| Variables and Categories | No. (%) | Test Statistic | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitals | 7.03 | 0.134 | |
| Imam Khomeini | 89 (68.5) | ||
| Golestan | 63 (75) | ||
| Taleghani | 35 (76.1) | ||
| Abuzar | 23 (92) | ||
| Razi | 24 (80) | ||
| Type of operating room | 7.40 | 0.494 | |
| General | 48 (70.6) | ||
| Heart | 19 (82.6) | ||
| Eye | 25 (78.1) | ||
| Obstetrics and Gynecology | 27 (73) | ||
| Urology | 26 (76.5) | ||
| Children | 23 (88.5) | ||
| Burn | 17 (70.8) | ||
| Orthopedics | 21 (61.8) | ||
| Neurosurgery | 28 (75.7) | ||
| Shift work | 14.67 a | 0.001 | |
| Morning | 68 (89.5) | ||
| Evening | 7 (63.6) | ||
| Night | 10 (83.3) | ||
| Rotating shift | 149 (69) | ||
| Body posture while working | 15.86 | 0.001 | |
| Standing | 117 (84.2) | ||
| Sitting | 17 (81) | ||
| Moving | 26 (60.5) | ||
| A combination of different modes | 74 (66.1) | ||
| Work experience (y) | 5365.5 | 0.001 | |
| With LBP | 11.26 ± 5.77 | ||
| Without LBP | 7.30 ± 5.02 | ||
| The average number of shifts per month | 8024.5 | 0.037 | |
| With LBP | 28.22 ± 4.72 | ||
| Without LBP | 29.15 ± 5.04 |
a Exact fisher test.
5. Discussion
This study aimed to determine the prevalence of LBP among operating room personnel in hospitals affiliated with AJUMS and to assess the related factors. The findings show that the majority of the personnel were female, most were married, and a large number had a bachelor's degree. A smaller percentage had a history of migration. Most personnel had no experience of smoking. Additionally, most personnel worked in the general operating room, had rotating shifts, and worked in a standing posture in the operating room.
Low back pain is the most common MSD among operating room nurses (16). A study by Cavdar et al. in Turkey showed that the prevalence of LBP among operating room nurses was 67.7% (15). Jeyakumar and Segaran reported that 84% of operating room nurses experienced LBP (17). Fayzi et al. in Shiraz, Iran, found that the prevalence of LBP was 74% among operating room personnel (13). Furthermore, a meta-analysis showed that the prevalence of LBP in the operating room is 62% (16). In our study, we found that the prevalence of LBP was high (74.3%), similar to other studies.
Age is a prominent characteristic that can affect the occurrence of musculoskeletal disorders such as LBP. The prevalence of MSDs increases with age due to age-related changes, including lower muscle mass, muscle strength, and intervertebral disc strength, leading to reduced strength and mobility (18). In the present study, there is a significant relation between the prevalence of LBP and age, similar to studies by Alemam (19) and Liu et al. (20).
Women, especially married women who adhere to cultural beliefs, are more responsible for heavy household activities such as taking care of their families, in addition to professional activities, which can increase the risk of LBP (21). The risk of LBP is higher among women due to hormonal changes, gynecological issues, and childbirth (22). Sun et al. also showed that female nurses were 1.56 times more at risk of LBP than male nurses, and married nurses were 2.06 times more at risk of LBP compared to single nurses (23). In the present study, there is a significant relationship between LBP and gender, and marital status. In our study, the number of females was greater than males, and the number of married personnel was greater than single, which can affect the results.
In a study by Kazemi et al., there was a significant relationship between BMI and LBP in nurses (24). A meta-analysis by Rezaei et al. revealed that BMI was a factor associated with LBP (3). Smoking is an important predictor of LBP (25), and studies have shown that smoking is related to LBP (26, 27). However, in our study, there was no relation between LBP and smoking, which could be due to the small number of smokers among our samples. Additionally, healthcare workers are less prone to report smoking due to their jobs.
Improper body position during activities and prolonged standing, such as in nursing care, are the most common causative factors of LBP (9). The findings of a study conducted by Negash et al. revealed that the chance of LBP in personnel who stand for a long time is 2.6 times higher than in others. They state that standing for a long time increases the immobility of the spine and the curve in the lumbar region, which leads to tightening and spasms of the lower back muscles, ultimately resulting in pain (28). In our study, LBP was related to body posture. Our finding is supported by a study conducted by Osunde (9).
According to our findings, there is a significant relationship between LBP and shift work, work experience, and the number of shifts. Chen et al. revealed a significant relationship between shift work and LBP, indicating a positive association between shift work exceeding 16 hours and LBP (29). The findings of a meta-analysis also reported that nurses who worked the night shift were 2.19 times more at risk of LBP (23). In our study, LBP was higher in personnel working the night and morning shifts. It is clear that the workload during the morning shifts is considerably higher in the operating room, and the night shift is a long-duration shift. Additionally, operating room nurses on the night shift often face heavy tasks alone, and the number of nurses on the night shift is smaller, providing less support and help.
The results of a study by Lin et al. show that the level of work experience is a predictive factor for MSDs such as LBP among nurses (30). It is reasonable that with the increase in seniority and the number of shifts, the workload increases, and exposure to risk factors also increases, affecting the incidence of LBP. Similarly, Samaei et al. found that the number of hours worked per week, engaging in shift work, and the length of time employed were statistically significant in relation to the prevalence of LBP (31).
5.1. Limitations
Our study had limitations, including a higher number of women than men working in operating rooms, the integration of multiple operating rooms into one complex in some hospitals, and a lower number of staff in single-specialty operating rooms compared to general operating rooms.
5.2. Conclusions
Our study discovered that operating room personnel have a high prevalence of LBP, which is related to both individual and occupational factors such as gender, marital status, BMI, age, shift work, body posture, work experience, and number of shifts. Based on these findings, recommendations can be proposed for nursing managers to protect personnel from LBP. A practical approach for minimizing risk factors can involve modifying work shifts and allocating less physically demanding tasks to senior staff and females. Additionally, educational programs aimed at modifying ergonomics during work and reducing physical load have the potential to alleviate LBP experienced in the operating room.