1. Background
Pregnancy is widely recognized as one of the most transformative phases in a woman’s life. Prenatal screening for fetal abnormalities has become a routine part of prenatal care, with nearly 98% of pregnant women undergoing ultrasound screening around the 18th week of pregnancy (1). Most expectant mothers hold optimistic expectations about this screening and seldom consider the potential for adverse outcomes. As a result, they may be unprepared for the emotional impact of a prenatal diagnosis of fetal abnormalities, leading to a stressful period characterized by various psychological challenges. Pregnant women facing the possibility of a fetal abnormality often experience elevated levels of anxiety and stress. Research indicates that anxiety disorders affect 15% to 23% of pregnant women, with even higher rates among those coping with complications such as suspected fetal anomalies (2, 3). Studies also suggest that women diagnosed with fetal abnormalities experience two waves of heightened anxiety—first, immediately after receiving the diagnosis from a medical professional, and second, when facing the decision to terminate the pregnancy (4).
A recent study by Coppola and colleagues highlights the elevated levels of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of children with illnesses, revealing a distinct contrast with parents of healthy children. This effect is especially pronounced in mothers with children diagnosed with congenital heart diseases, who exhibit significantly elevated postpartum anxiety (5). Additionally, studies show that the severity of fetal abnormalities often correlates with the severity of maternal depression, and women who terminate a pregnancy due to fetal abnormalities frequently experience profound sadness (6).
Numerous psychological counseling methods have been proposed to alleviate psychological stress in pregnant women with anxiety, with many of these methods rooted in the cognitive-behavioral framework (7). Internet-based therapy has emerged as an effective alternative to traditional face-to-face therapy, offering advantages such as enhanced accessibility, convenience, and reduced stigma (8, 9). Research generally shows that internet-based and face-to-face therapies are comparably effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression (10, 11). A significant advantage of internet-based therapy is the ease with which partners can be included in the therapeutic process (9). This approach can be particularly beneficial for pregnant women experiencing anxiety related to fetal abnormalities, as it facilitates greater partner involvement in therapy sessions. Overall, evidence suggests that internet-based therapy can serve as a viable and effective alternative to face-to-face therapy, especially for populations like pregnant women, who may benefit from increased partner involvement in the therapeutic process (10).
Emotion-oriented cognitive-behavioral therapy (ECBT), based on the foundational work of Watson and Greenberg, emphasizes emotional awareness, enabling individuals to recognize and understand their own emotions as well as those of others. This therapeutic approach targets intense anxiety and other negative emotions (12). Emotion-oriented cognitive-behavioral therapy employs techniques that amplify emotional experiences to counteract avoidance strategies. Studies have shown that individuals with high levels of emotion dysregulation report significant improvements through emotion-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (13). In sum, empirical evidence suggests that ECBT programs addressing both emotion regulation and anxiety offer substantial benefits. This therapy incorporates emotional awareness, understanding, regulation, and a blend of cognitive and behavioral strategies to alleviate anxiety and other overwhelming negative emotions (14). Emotion-oriented cognitive-behavioral therapy has been shown to effectively reduce symptoms of anxiety, physical distress, and emotional pain in chronic conditions. Additionally, it has demonstrated substantial effects in alleviating generalized anxiety disorder, depression, and intrusive thoughts (15). Emotion-focused CBT specifically addresses protective factors, making it a valuable intervention for managing pregnancy-related stressors, including anxiety arising from concerns about fetal abnormalities (16).
Studies have shown that pregnant women who received emotion-focused CBT with their husband’s participation reported greater satisfaction and acceptability compared to those who received the therapy alone. The approach was also highly feasible for both groups, with comparable effectiveness in reducing psychological distress (17).
Despite strong empirical support for the efficacy of Internet-based emotion-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (IECBT) in treating anxiety disorders (17), there is a notable lack of research on its application for anxiety in pregnant women with suspected fetal anomalies (17). To our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate the utility of IECBT for pregnant women experiencing anxiety related to potential fetal anomalies. This research represents a critical step in addressing the unique mental health needs of pregnant women concerned about fetal anomalies, contributing to the broader field of perinatal mental health and therapeutic efficacy.
2. Objectives
The primary objectives of this research endeavor included the following key aspects:
(1) Assessing the acceptability and feasibility of implementing IECBT as a counseling intervention for pregnant women with suspected fetal anomalies.
(2) Evaluating the effectiveness of the IECBT program in alleviating psychological distress in pregnant women with suspected fetal anomalies.
(3) Comparing the effectiveness of IECBT alone versus IECBT with spousal participation in reducing psychological distress.
(4) Measuring patient satisfaction across the two IECBT models.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design, Setting, and Definitions
This quasi-experimental research study was conducted between April and September 2022 in obstetric clinics at two prominent teaching hospitals: Ayatollah Rohani and Yahyanejad. These healthcare institutions are affiliated with Babol University of Medical Sciences in northern Iran. In addition to these hospital-based clinics, two private perinatology clinics actively participated in the research.
The study’s inclusion criteria were carefully defined to ensure the participation of relevant individuals. Eligible participants had to meet the following criteria: Pregnant women at a gestational age of less than 20 weeks, exhibiting suspected fetal abnormalities as diagnosed by a perinatologist or gynecologist, possessing Spielberger State Anxiety scores exceeding 30, expressing a willingness for both the expectant mother and her spouse to participate in the treatment, having access to a computer and internet connectivity, and demonstrating the capability to provide informed consent. Conversely, individuals meeting any of the exclusion criteria were excluded from the study. These criteria encompassed individuals experiencing acute psychological conditions during the study period, requiring medication or psychiatric intervention. Additionally, those indicated for abortion therapy within six weeks of initial study entry were also excluded.
The sample size was determined based on the methodology outlined in Hashemi et al.'s research. The required sample size was calculated using G*Power 3.1.9.2 software, with a significance level set at α = 0.05 and a statistical power (1-β) of 0.8.
The sampling method employed was simple accessibility, enrolling all women suspected of fetal abnormalities who were referred to Ayatollah Rouhani Hospital, gynecologists' offices, and cooperating perinatologists. Women with suspected fetal abnormalities included those encountering screening issues during the first or second trimester of pregnancy. The initial screening took place between the 11th and 13th weeks of pregnancy, comprising a double test with biochemical marker assessment and NT ultrasound. If abnormalities were detected, further tests such as the quad test, cell-free DNA analysis, or amniocentesis were considered, depending on the severity of the issue. Women with suspicions or positive results at this stage were eligible for participation in the study. If the initial screening showed low risk, they proceeded to the second stage, which involved a quad test and ultrasound anomaly scan at 18 weeks. In cases where issues arose in the quadruple test, further evaluations included monitoring biomarker levels from the cutoff point (typically around 16 weeks) and conducting an ultrasound anomaly scan, possibly followed by amniocentesis and cell-free DNA analysis. At 18 weeks, a detailed examination of 22 fetal organs, known as soft markers, was conducted. If two or more abnormalities were detected, cell-free DNA analysis was performed, and if critical organs were involved, amniocentesis was carried out.
A master’s degree student specializing in midwifery counseling (the first author) interviewed pregnant women and assessed their initial eligibility based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. The women were also asked to complete the Spielberger State Anxiety questionnaire. Those who met the eligibility criteria and scored above 30 on the anxiety scale were informed about the study and invited to participate. The student interviewed several pregnant women; some were subsequently excluded due to the absence of anxiety symptoms or the presence of severe mental disorders (such as suicidal ideation, psychotic symptoms, bipolar disorder, or substance abuse). From the pool of anxious women, 130 agreed to participate and provided written informed consent.
After the interviews, an independent midwife, unaffiliated with the research team, administered questionnaires to participants before and after the interventions. These assessments were conducted via the DigiSurvey® platform, with participants receiving a secure link through SMS for convenience. The research subjects were randomly divided into two groups of 65 participants each. The first group received IECBT alone, while the second group received IECBT with spousal involvement. At baseline, participants completed three specific questionnaires: The Pregnancy-Related Stress Questionnaire (NuPDQ), the Spielberger State Anxiety Questionnaire, and the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. At the end of the study, participants completed these three questionnaires again, along with the Client Satisfaction Questionnaire and the System Usability Scale.
3.1.1. Interventions
In the IECBT alone group, participants engaged in a series of six IECBT sessions, each lasting 50 minutes, conducted via the website www.peacefulmindme.com. The therapy program's contents were comprehensively outlined in a 2023 study by Shariatpanahi et al. (17). This program offers a multifaceted approach that includes psychological education, foundational principles of IECBT, skills for identifying emotions, and guidance on recognizing and expressing emotions, as described by Watson and Greenberg in 2017 (12).
In the IECBT with spousal participation group, the program comprised twelve sessions—six sessions for the women and an additional six for their spouses. The first six sessions for women mirrored the content of the standalone IECBT sessions. The spousal sessions covered a variety of significant topics, including understanding the stages of pregnancy and related physical and psychological changes, developing empathetic skills, strengthening marital intimacy, enhancing communication strategies, learning conflict-resolution techniques, and preparing for fatherhood. Each session for spouses lasted between 20 and 25 minutes. It was mandatory for both the woman and her spouse to attend one session per week (17).
In both IECBT methods—IECBT alone and IECBT with spousal participation—participants received additional support through weekly 25-minute phone or WhatsApp sessions. A research team member, the first author, conducted these sessions to answer questions and address any issues the women and their spouses encountered during the course of treatment.
3.2. Data Collection
Data gathering was conducted using 5 questionnaires:
3.2.1. Spielberger State Anxiety Questionnaire
The Spielberger State Anxiety Questionnaire is a widely recognized tool frequently used in anxiety research (18). This comprehensive questionnaire includes 40 questions, divided into two categories: Twenty questions assessing state anxiety and 20 evaluating trait anxiety. In this study, we used the state-anxiety questions. Respondents indicate their level of agreement with each statement on a scale from 1 (indicating very little agreement) to 4 (representing very high agreement). The Persian version of the scale has demonstrated strong reliability, with a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.87 and a test-retest reliability of 0.76 (19).
3.2.2. NuPDQ (Specific Pregnancy Stress Questionnaire)
This self-report assessment is meticulously designed to gauge pregnancy-related anxiety in expectant women throughout each trimester (20). The questionnaire consists of 17 items, with participants rating each item on a scale of three response levels: 0 (signifying no anxiety), 1 (indicating some anxiety), and 2 (representing a high degree of anxiety). It includes five subscales: Medical and financial issues, physical symptoms, infant health, parenting, and childbirth. The Persian version of the NuPDQ demonstrated reliability, with a Cronbach's alpha of 0.79 (21).
3.2.3. Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
It consists of 10 questions (22), with a scoring range from 0 to 30. We used the Persian validated version of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) (23).
3.2.4. Client Satisfaction Questionnaire (CSQ-8)
The scale consists of 8 questions, employing a numerical range from 1 to 4, where 1 denotes the lowest level of satisfaction and 4 represents the highest. Sample questions include inquiries such as, "How would you rate the quality of service you have received?" and "If you were to seek help again, would you return to our program?" (1) no, definitely not; (2) no, I don’t think so; (3) yes, I think so; (4) yes, definitely) (24).
3.2.5. System Usability Scale (SUS)
This scale employs a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from "strongly agree" to "strongly disagree" (25). To compute the SUS score, the difference between the score for odd-numbered items and 1 is calculated, then subtracted from 5 minus the score for even-numbered items. Total scores range from 0 (indicating extremely poor usability) to 100 (reflecting excellent usability). Sample questions include statements like, "I think that I would like to use this website" (26).
3.3. Statistical Analysis
For data analysis, we utilized SPSS software version 24. A range of statistical tests was employed to facilitate group comparisons. The independent t-test was used for two-mode quantitative data, the chi-square test for qualitative data, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for multi-mode quantitative data. Additionally, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test assessed the normal distribution of the data. An independent t-test also compared the outcome variables within the IECBT groups, both with and without spousal participation.
To evaluate changes in outcome variables before and after the intervention, we used the dependent t-test. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was applied to compare the two groups' outcome variables post-intervention, simultaneously controlling for age and pre-intervention scores as covariates. Statistical significance was set at a P-value of less than 0.05.
4. Results
As summarized in Table 1, the detailed demographic information shows no statistically significant differences between the two study groups. These non-significant variations include factors such as education, age, husband's age, and other relevant demographic parameters, as illustrated in Table 1 below.
| Variables | IECBT Alone | IECBT with Spouse | P-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education | 0.817 | ||
| Less than a Diploma | 8 (44.4) | 10 (55.6) | |
| Diploma | 29 (52.7) | 26 (47.3) | |
| Academic | 28 (49.1) | 29 (50.9) | |
| Job | 0.475 | ||
| Housewife | 53 (48.6) | 56 (51.4) | |
| Employed | 12 (57.1) | 9 (42.9) | |
| History of disease | 0.144 | ||
| No | 56 (47.9) | 61 (52.1) | |
| Yes | 9 (69.2) | 4 (30.8) | |
| Hospitalization history | 0.612 | ||
| No | 55 (49.1) | 57 (50.9) | |
| Yes | 10 (55.6) | 8 (44.4) | |
| Current drug | 0.128 | ||
| No | 53 (47.3) | 59 (52.7) | |
| Yes | 59 (51.3) | 56 (48.7) | |
| Inhabitation | 0.857 | ||
| City | 40 (50.6) | 39 (49.4) | |
| Village | 25 (49) | 26 (51) | |
| Smoke or alcohol | 0.576 | ||
| No | 42 (48.3) | 45 (51.7) | |
| Yes | 23 (53.5) | 20 (46.5) | |
| Husband's education | 0.455 | ||
| Less than a Diploma | 16 (53.3) | 14 (46.7) | |
| Diploma | 23 (56.1) | 18 (43.9) | |
| Academic | 26 (44.1) | 33 (55.9) | |
| History of husband's disease | 0.052 | ||
| No | 59 (48) | 64 (52) | |
| Yes | 6 (85.7) | 1 (14.3) | |
| History of husband's hospitalization | > 0.999 | ||
| No | 57 (50) | 57 (50) | |
| Yes | 8 (50) | 8 (50) | |
| Husband's smoke or alcohol | 0.033 | ||
| No | 56 (54.9) | 46 (45.1) | |
| Yes | 9 (32.1) | 19 (67.9) | |
| Age | 28.68 ± 5.71 | 31.06 ± 5.73 | 0.019 |
| BMI | 26.93 ± 4.38 | 27.94 ± 4.02 | 0.177 |
| Husband's age | 33.20 ± 4.87 | 34.77 ± 5.21 | 0.079 |
Abbreviation: IECBT, internet-based emotion-focused cognitive behavioral therapy.
a Values are expressed as No. (%) or mean ± SD.
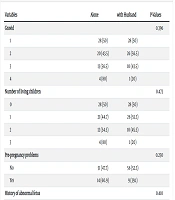
Table 2 presents the frequency distribution of various factors within the IECBT groups, as well as the average gestational age for both the IECBT group with spousal participation and the IECBT group without spousal participation. This table shows no significant differences in these variables between the two groups, one including spousal involvement and the other without.
| Variables | Alone | with Husband | P-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gravid | 0.396 | ||
| 1 | 28 (50) | 28 (50) | |
| 2 | 20 (43.5) | 26 (56.5) | |
| 3 | 13 (56.5) | 10 (43.5) | |
| 4 | 4 (80) | 1 (20) | |
| Number of living children | 0.473 | ||
| 0 | 28 (50) | 28 (50) | |
| 1 | 21 (44.7) | 26 (55.3) | |
| 2 | 12 (54.5) | 10 (45.5) | |
| 3 | 4 (80) | 1 (20) | |
| Pre-pregnancy problems | 0.250 | ||
| No | 51 (47.7) | 56 (52.3) | |
| Yes | 14 (60.9) | 9 (39.1) | |
| History of abnormal fetus | 0.410 | ||
| Yes | 6 (40) | 9 (60) | |
| No | 59 (51.3) | 56 (48.7) | |
| Under the supervision of a psychiatrist | 0.300 | ||
| Yes | 6 (66.7) | 3 (33.3) | |
| No | 59 (48.8) | 62 (51.2) | |
| Abnormal fetus in spouse's family | 0.571 | ||
| Yes | 43 (48.3) | 46 (51.7) | |
| No | 22 (53.7) | 19 (46.3) | |
| Gestational age | 15.92 ± 2.20 | 15.86 ± 2.24 | 0.875 |
a Values are expressed as No. (%) or mean ± SD.
Table 3 presents the results of the covariance analysis for intra-group and inter-group changes due to the two interventions. The within-group comparison shows that both the IECBT intervention alone and IECBT with spousal participation significantly reduced pregnancy-specific stress, depressive symptoms, and anxiety symptoms among the women by the end of the intervention (P < 0.001). When comparing the two groups, IECBT with spousal participation proved to be notably more effective in reducing pregnancy-specific stress (Eta = 0.055, P = 0.007) and depressive symptoms (Eta = 0.480, P < 0.001) compared to IECBT alone. However, there was no significant difference between the two counseling methods, IECBT alone and IECBT with spousal participation, in their impact on reducing anxiety symptoms in women (Eta = 0.001, P = 0.787).
| Variables | IECBT Alone | IECBT with Spouse | Between Two Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Diff | P | Before | After | Diff | P | P | Eta | |
| Pregnancy-Specific Stress | 21.08 ± 6.45 | 12.65 ± 3.21 | -8.43 ± 7.21 | > 0.001 | 20.93 ± 5.45 | 11.08 ± 3.02 | -9.85 ± 6.89 | > 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.055 |
| Depression | 16.86 ± 2.63 | 12.86 ± 5.60 | -4.00 ± 5.66 | > 0.001 | 17.09 ± 2.96 | 5.43 ± 0.80 | -11.66 ± 3.05 | > 0.001 | > 0.001 | 0.480 |
| Anxiety | 54.98 ± 2.16 | 34.35 ± 7.30 | -20.63 ± 7.80 | > 0.001 | 55.14 ± 7.31 | 34.14 ± 7.31 | -21.0 ± 7.97 | > 0.001 | 0.787 | 0.001 |
Abbreviation: IECBT, internet-based emotion-focused cognitive behavioral therapy.
a Variables are expressed as mean ± SD.
b Results of Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) tests.
The findings in Table 4 indicate no significant difference in the acceptability and feasibility between the two IECBT approaches: IECBT alone and IECBT with husband participation.
| Variables | IECBT Alone | IECBT with Husband | P-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acceptability | 29.42 ±1.96 | 29.29 ± 1.88 | 0.716 |
| Feasibility | 81.50 ± 5.03 | 81.04 ± 5.55 | 0.620 |
Abbreviation: IECBT, internet-based emotion-focused cognitive behavioral therapy.
5. Discussion
This quasi-experimental study aimed to evaluate the acceptability, feasibility, and effectiveness of IECBT involving the spouse of pregnant women suspected of having fetal anomalies. The findings demonstrated that both groups—those receiving IECBT alone and those with spousal participation—experienced reductions in stress, anxiety, and depression. Regarding the effectiveness of IECBT, Roslan et al. noted that mothers informed of fetal abnormalities often experience heightened psychological distress during pregnancy, such as depression, anxiety, and stress (27). Similarly, Afshari et al. compared the effectiveness of ECBT and CBT in alleviating anxiety symptoms in anxious children and reported that ECBT, relative to CBT, effectively improved emotion regulation strategies in children suffering from separation anxiety (28). Additionally, Suveg et al. compared ECBT with traditional CBT in children with primary anxiety disorders, finding that both approaches yielded similar improvements in emotion regulation, with no significant impact of initial emotion regulation disorder levels on outcomes (29).
Emotion-focused cognitive behavioral therapy, a novel counseling approach incorporating emotion regulation elements, is thought to influence the entire cognitive-emotional model during treatment. Consequently, delivering sessions tailored to the unique needs of pregnant women with psychological distress may significantly reduce these symptoms, as Penner and Rutherford’s 2022 study suggests (30). In support, Bastani et al. emphasize that specific training for pregnant women enables them to identify cognitive distortions and irrational thoughts, equipping them to better control their thought patterns (31).
Moreover, involving spouses in counseling may further alleviate psychological symptoms, as their presence can provide essential support and reassurance, especially during pregnancy (32, 33). One study found that cognitive-behavioral counseling involving the spouse had a positive effect on reducing stress, anxiety, and postpartum depression compared to a control group that received routine care (34). Additionally, a review during the COVID-19 pandemic recommended psychological counseling for pregnant women and advocated for spousal training to support the psychological well-being of expectant mothers (35). Overall, the evidence supports that spousal involvement in counseling sessions can enhance the reduction of psychological disorders in pregnant women.
Our detailed investigation revealed that stress and depression scores in the IECBT group with spousal involvement were significantly lower than those in the IECBT alone group. However, it is notable that no statistically significant difference was observed in anxiety scores between these two groups. This study is a pioneering effort, representing the first exploration of IECBT's feasibility and acceptability among pregnant women. Due to the limited number of comparable studies in this specific demographic, we referenced research conducted in other populations, which, while not specifically involving pregnant women, used similar emotion-focused approaches to CBT. For example, Sun et al. demonstrated that a support intervention significantly reduced stress, anxiety, and depression in pregnant women dealing with fetal abnormalities (36). Similarly, Motakeffar et al. (2022) reported positive outcomes from emotion-focused cognitive counseling in addressing psychological disorders (37). These studies align with our findings due to their similar focus on both population and intervention method.
Additionally, a study by Bayat et al. examined the impact of psychological intervention on anxiety in pregnant women with fetuses affected by chromosomal disorders, finding a substantial reduction in psychological symptoms post-intervention (38). The similarity between their study and ours is evident, particularly regarding the population and variables explored. Goetz et al. also reported reductions in depression and anxiety by implementing a web-based mindfulness intervention for mothers with a history of high-risk pregnancies (39). Bright et al. conducted an internet-based psychotherapy study that showed significant reductions in mental health issues among pregnant mothers (40). These studies are consistent with our findings, as they address anxiety using digital health interventions.
Moreover, studies have shown that anxiety, stress, and depression in pregnant women experiencing severe fear were significantly reduced through cognitive-behavioral therapy with their spouses present (41). Another study highlighted the significant reduction of anxiety, stress, and depression in women with unwanted pregnancies through psychological interventions involving their spouses (42). Dafei et al. also emphasized the beneficial impact of a spouse's presence in psychological sessions, which contributed to reducing stress and depression in pregnant women (34). These studies support our findings and emphasize the positive role of spousal involvement in treatment.
It is essential to note that anxiety, unlike stress and depression, often requires consideration of external factors to achieve effective relief. Consequently, differences between individuals in groups with and without spousal involvement may not be as apparent, as previous studies have shown (43-45).
Another significant finding of our study is that the acceptability and feasibility scores did not differ significantly between the two groups receiving IECBT, whether with spouses or alone. These results suggest that IECBT is equally acceptable and feasible for participants, regardless of spousal presence. This flexibility can be particularly valuable in societies where women face economic and social constraints that limit their ability to attend therapy sessions (46).
The absence of significant differences in acceptability and feasibility between the two groups may be attributed to the favorable outcomes participants experienced concerning the time and effort they invested in the program. This success is largely due to the use of digital health methodologies (47). A 2023 study by Shariatpanahi et al. also reached similar conclusions, indicating that IECBT, whether delivered individually or with spousal involvement, shows varying participant perspectives but not feasibility differences. Their findings suggest that acceptability levels may increase when group or couple treatments are utilized (17). The variations in research outcomes across studies may likely stem from differences in the predisposing factors related to psychological disorders.
5.1. Limitation
Nonetheless, certain limitations of this study should be acknowledged. Firstly, our IECBT intervention included both therapist support and an internet-based framework, making it difficult to isolate the impact of IECBT alone. Future investigations should aim to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of IECBT without therapist support to understand its standalone efficacy. Secondly, this study was conducted with a relatively modest sample size and lacked longitudinal follow-up data. To strengthen the robustness of these findings, future research should consider larger sample sizes and include extended follow-up periods.
Lastly, the generalizability of our findings is limited to married women. Future studies should examine how societal, cultural, and religious factors may influence outcomes. Additionally, a broader, multicenter study that includes diverse cultural contexts is recommended to comprehensively assess the role of spousal support for anxious women with suspected fetal anomalies.
5.2. Conclusions
In summary, both counseling methods, IECBT alone and IECBT with spousal participation, are feasible and effective in addressing stress and anxiety among pregnant women with suspected fetal anomalies. Our research additionally revealed that IECBT alone is less effective in alleviating pregnancy-related stress and anxiety compared to IECBT with spousal participation. However, further research is required to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of adding six sessions of spousal support to IECBT. The findings of this study significantly contribute to the advancement and efficacy of IECBT with spousal participation, and future research should aim to replicate these results across diverse populations globally through randomized controlled trials.