1. Background
The pain may be moderate to severe with serious negative consequences for the working or social life of the individual and can be changed over time. The perception of pain is highly subjective and unique, and its threshold is developed in individuals through the experiences related to injury in early life (1). Chronic pain, meanwhile, is a common disease that can change affected people’s lives, and experiencing chronic pain is one of the most common reasons to seek medical care (2). Chronic pain is a depressive condition, in which the person experiences not only the mental stress caused by the pain but also many other stressors that affect different parts of his life (2). Based on the existing research literature, long-term painful physical symptoms can lead to greater comorbidity of physical and mental illnesses, in addition to the quality of life deterioration (3). Chronic pain is one of the most common reasons adults seek medical care that has been linked to restrictions in mobility and daily activities, drug dependence, anxiety, and depression (4). The prevalence of chronic pain among adults in Tehran, Iran has been reported 24%, of which chronic low back pain (12.4%) and chronic knee pain (11.2%) were the most common complaints (5).
Despite many physical and psychological problems faced by chronic pain patients, adaptation to the disease has been reported as one of the factors contributing to disease acceptance and as an important part of participation in the treatment process, which can affect the social and physical functioning of individuals (6). Adaptation to illness is the ability to maintain a positive attitude toward oneself and the world despite having physical problems (7). Psychosocial adjustment to the disease consists of six subscales: attitude toward illness, work environment, family environment, sexual relations, development of family relationships, social environment, and psychological disorders (8). Adaptation to the process of treatment of chronic disease is an important factor in attracting a patient’s participation in treatment and assisting in the decision-making process (9). Studies have shown that psychosocial adjustment to illness is the strongest predictor of health care utilization compared with other disease variables (10). The importance of psychosocial factors as significant predictors of pain and functioning in different persons has been reported (11).
The process of coping with a chronic illness is a dynamic process that is constantly affected by psychological and social stimuli. In this process, the affected person must face individual and environmental challenges to reach an acceptable level of physical, mental and social wellbeing leading to achieve successful adaptation (12). One of the psychological challenges is being overwhelmed by the illness and its associated care. According to the interpersonal theory, when the person is overbearing, incapable of providing safety and well-being, and he does not help the group can cause the feeling of being overburdened (13). Perceived burdensomeness refers to the view that being overbearing is about friends, family, or the community comprising two dimensions: (a) selfishness means that I hate myself, and (b) I feel responsible; for example, my death will be worth more than my life to others (14). Perceived burdensomeness is also seen as a dynamic cognitive state that can be developed by risk factors, such as homelessness, unemployment, physical well-being, and low self-esteem (15). Various studies have investigated the relationship between feeling overwhelmed and different factors and have focused the effect of these variables on psychological trauma and self-harm behaviors indicating their importance in mental and physical health (16). It has shown that living with chronic pain is associated with significant emotional stress. Moreover, pain can decrease the patients’ emotional abilities and also his continuous desire to get rid of pain will often be unattainable. This ultimately weakens the patient's mood, hopelessness, and depression (17).
Pain self-efficacy can enhance coping skills and thereby increase patients’ adaptation to chronic pain by enhancing patients’ cognitive beliefs about their ability to solve problems. It has defined as patients’ beliefs in their abilities to successfully organize and control health habits, and also achieve valuable health outcomes in different situations and contexts (18). Pain self-efficacy beliefs are an important determinant of pain behaviors and indicate how much a person will try to endure distressing problems and experiences (19). Pain self-efficacy moderates the effects of hopelessness in patients. Therefore, it acts against hopelessness as a bumper and causes resistance to hopelessness and fatigue caused by illness (20-22). It has also reported that pain self-efficacy improves functional ability and reduces pain-related fear. Promoting pain self-efficacy beliefs can be a key mechanism for improving behavioral outcomes (23).
Consequences of chronic pain on the different aspects of patients' lives, such as their psychological, social, and occupational functioning (2), the importance of psychosocial adjustment of patients with chronic pain, and assessment and identification of psychological adjustment affecting the social functioning of these patients have yet been addressed in previous studies and should be more considered. Therefore, this study aimed at investigating the role of burdensomeness on psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain and whether pain self-efficacy can mediate the relationship between burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment of patients with chronic pain.
2. Objectives
The present study aimed at investigating the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment, and the mediating role of pain self-efficacy
3. Methods
The present descriptive correlational study was conducted on all patients with chronic pain referred to the orthopedic centers in Ardebil. The minimum sample size of 200 subjects was estimated for a structural equation modeling and path analysis (24). Using a purposive sampling method, 240 patients with chronic pain were selected. Inclusion criteria were having at least two years of chronic pain, no psychiatric problems, informed consent, having at least a diploma (including admission requirements). The exclusion criteria were being illiterate, unwillingness to continue the research, and having psychiatric problems.
3.1. Data Collection Tools
Psychosocial Adjustment to Illness Scale (PAIS): This tool was designed in 1990 by Leonardo Derogatis to assess the quality of a patient's psychosocial adjustment to a chronic illness. It is a 46-item scale including 7 subscales: attitude toward disease (8 questions), work environment (6 questions), family environment (8 questions), sexual relationships (6 questions), family relationship development (5 questions), social environment (6 questions), and psychological disorders (7 questions). In this study, each item was scored on a 4-point Likert scale (range 0 - 3) with choices varying from "not at all" to "severe difficulties with household duties, with higher scores indicating greater impairment. The sum scores of each component were divided by the number of questions in that component and its mean was considered as the adjustment score of the component, whereas the sum of the total score of all questions was divided by the number of all questions and its mean was considered as the total adjustment score. The questionnaire was first translated by Feghhi et al. (8). It was then reviewed by 3 people fluent in English and finally reviewed and approved by an expert. Some changes were made on the scale based on the Iranian culture and it was localized. Since the majority of the subjects were housewives and retired men, the question related to absenteeism was omitted and the number of questions was reduced to 45 questions. The content validity of the questionnaire was confirmed by 10 university professors and its reliability was calculated to be 0.94 using Cronbach's alpha in 20 patients with type 2 diabetes (8).
Pain Self-efficacy Questionnaire (PSEQ): the PSEQ is a 10-item questionnaire, developed by Bandura in 1977 to assess the confidence people with ongoing pain have in performing activities while in pain, which is scored on a 7-point Likert scale (range 0 - 6). A Higher score indicates greater self-efficacy in performing and functioning despite ongoing pain. The Persian version of PSEQ has reported with acceptable reliability. The validity of this questionnaire by confirmatory factor analysis supported a one-factor solution (25).
Interpersonal Needs Questionnaire (INQ): INQ has multiple versions, of which the version 15 (INQ-15) is a self-report measure of perceived burdensomeness and thwarted belongingness that participants are asked to indicate the degree to which each item had been true for them recently. The first six statements measure perceived burdensomeness (e.g., “These days, I think I am a burden on society”), and the last nine statements measure thwarted belongingness (e.g., “These days, I feel like I belong”). INQ-15 is scored on a 7-point scale (range 1 - 7) with higher scores indicating greater thwarted belongingness and perceived burdensomeness. Internal consistency (alpha = 90%) and good reliability for this scale have been reported (26, 27). Also, in another study, confirmatory factor analysis of the two-factor model of perceived burdensomeness and thwarted belongingness provided an adequate fit for the data (28).
In this research, the ethical considerations, such as informed consent, willingness to participate in research, and confidentiality of participants' data were observed. The obtained data were analyzed by Pearson correlation and structural equation modeling using SPSS V. 19 and AMOS V. 21.
4. Results
Of the participants, 61% were female and 39% were male. Also, 33% of them had a history of surgery, 20% physiotherapy, 17% were taking and injecting drugs, and 30% of them had performed physical exercise for recovery. Table 1 represents the mean, standard deviation, and correlation matrix of the variables.
| Index | X2/df | Df | GFI | NFI | IFI | CFI | RMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 2.03 | 249 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.07 |
The results of model fit indices (after correction) are provided in Table 2. Based on the obtained results, it can be concluded that the model fits the data well and both absolute and comparative indices reached the desired level.
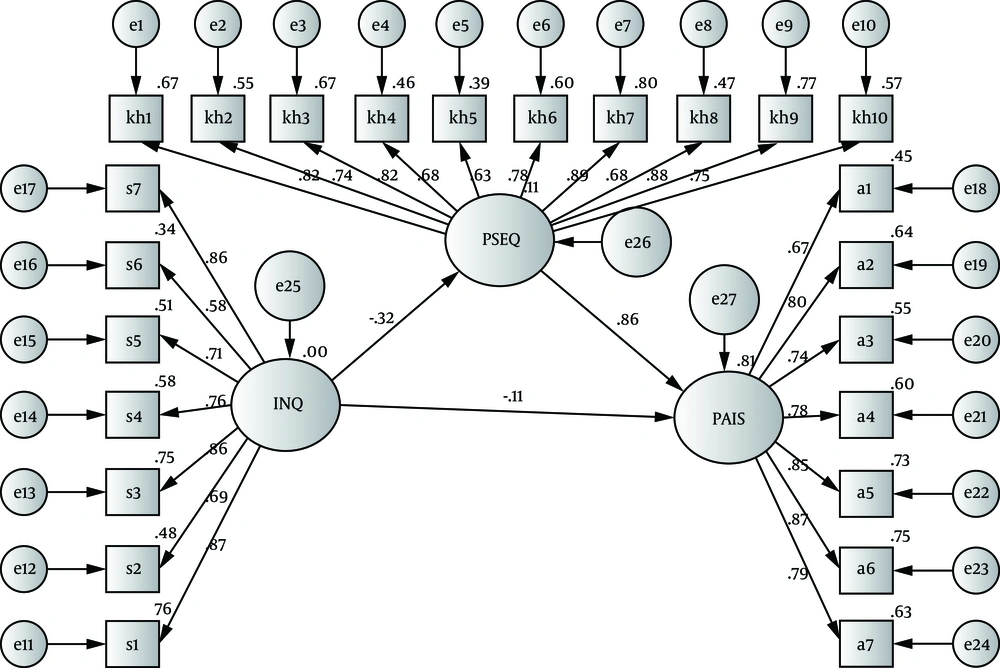
Regarding the question "Does pain self-efficacy play a mediating role in the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment?", the results indicated that pain self-efficacy had a mediating role in the research model. The detailed results of the research hypothesis are presented in Figure 1.
| Direct Effects | Estimate d Value | Standard Value | S.E. | C.R. | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived burdensomeness on psychosocial adjustment | -1.64 | -0.11 | 0.59 | -2.77 | 0.001 |
| Perceived burdensomeness on pain self-efficacy | -0.29 | -0.32 | 0.06 | -4.76 | 0.001 |
| Pain self-efficacy on psychosocial adjustment | 13.78 | 0.86 | 1.31 | 10.49 | 0.001 |
Based on the results of Figure 1 and Table 3, the negative and direct effect of perceived burdensomeness (β = -0.11, P < 0.01) on psychosocial adjustment, as well as the positive and direct effect of pain self-efficacy (β = 0.86, P < 0.001) on psychosocial adjustment were also confirmed. On the other hand, perceived burdensomeness (β = -0.32, P < 0.01) had a negative and direct effect on pain self-efficacy.
To investigate the mediating role of pain self-efficacy in the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment to the disease, Bootstrap was used and the results are summarized in Table 4.
| Variable | Upper Value | Lower Line | Significant Line | Estimation Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictor Variable | Intermediate Variable | Criterion Variable | ||||
| Perceived burdensomeness | Pain self- efficacy | Psychosocial adjustment to illness | -0.27 | -0.16 | -0.38 | 0.01 |
According to the results of Table 4, the indirect effect of exogenous variable perceived burdensomeness on pain self-efficacy and psychosocial adjustment to illness was confirmed.
5. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment, and the mediating role of pain self-efficacy in chronic pain patients. The result of this study showed that the feeling of being overburdened had a negative and significant relationship with psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain. The findings are consistent with the results of other relevant studies, such as Vahidi and Shaker Dioulagh study (29), in which stress had a significant and negative relationship with mental adjustment to the disease. In line with the results of the present study, it has found that the caregiver's perception of the burden makes them susceptible to some personal and marital problems (30).
Since patients' attitudes, beliefs, and expectations about themselves and their problems affect the level of pain, disability, and response to treatment (31), they indicate the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and low psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain. It can be said that when a patient with chronic pain develops a negative attitude toward himself and his illness and blames himself for it and suffers from his family members, a cycle of negative thoughts can be formed that motivates and frustrates the patient by providing the backgrounds for the development of depression. It also leads to separation from the job and social position in the patient, which gradually results in psychosocial adjustment. This cycle has defined as a process of maintaining a positive attitude toward yourself and the world despite having physical problems (32). Therefore, it is clear that feelings of perceived burdensomeness by developing a negative attitude toward yourself will decrease the psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain.
In addition, the findings of the present study showed that pain self-efficacy -despite having a positive relationship with psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain- can mediate the negative relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment. This finding is in line with the results of a relevant study indicating a positive and significant relationship between self-efficacy and psychosocial adjustment (33). It has also shown that self-efficacy plays a mediating role in the relationship between happiness and pain self-management in patients (22).
According to the social cognitive theory in explaining the meditating role of pain self-efficacy in the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain, it can be said that people with high levels of pain self-efficacy utilize desirable levels of pain relief and discomfort management, and consequently pain control (24), while reducing emotional distress and disability (34). They can not only increase their ability to cope with the disease by reducing their negative emotions and anxiety, but also improve their overall functioning levels. Such factors can reduce the feeling of helplessness and overburdened in these people. In this regard, it has believed that people who are more adaptable than their less-adapted counterparts are more optimistic about themselves and others focusing more on their life priorities, and consequently on intimate family relationships. They are more likely to cope easily with their physical conditions and increase their physical activities and are optimistic about their diseases leading to faster recovery (35). Also, regarding the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment of patients with chronic pain, it has reported that perceived burdensomeness and the resulted negative attitude of the patients towards themselves can decrease their mental functioning by creating negative and depressive thoughts. To explain the mediating role of pain self-efficacy in the relationship between these two variables, it is important to conduct a study on the mediating role of pain self-efficacy on the relationship between depression and suicidal ideation in patients with chronic pain indicating a significant relationship between depression and suicidal ideation through pain self-efficacy (36). The present study had some limitations. The used subjects were selected from the patients with chronic pain in Ardabil city, which can affect the generalizability of the results and was the most important limitation of this research.
5.1. Conclusions
The purpose of this study was to investigate the mediating role of pain self-efficacy in the relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain. The findings of the present study showed that despite the negative and significant relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain, pain self-efficacy can play a mediating role in the relationship between these two variables so that pain self-efficacy can mediate the negative relationship between perceived burdensomeness and psychosocial adjustment in patients with chronic pain.