1. Background
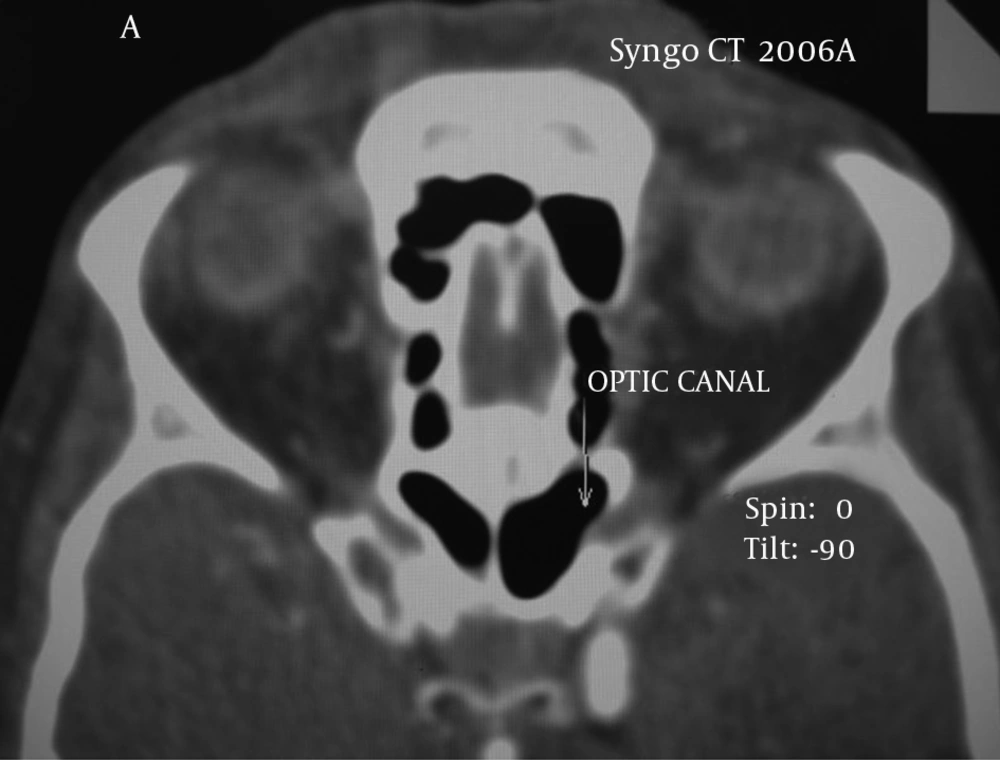
Sphenoid sinus is the most unaccessible paranasal sinus. It is surrounded by sphenoid bone and there are a lot of neural and vascular structures in its proximity. Sphenoid bone is in skull base and involved in forming anterior and middle cranial fossa. This bone comprises a body, greater wings, lesser wings and pterygoid (1). In the thick part of the body, there is a cavity full of air. It is separated into right and left halves by a bone septum. Each half is directed into the nasal cavity through an opening located in the interior part of the superior turbinate (2). Sinus pneumatization is considerably varied in different people. The walls of sinuses are covered by mucosal tissue. Its glands secrete mucoid, which is emptied into the nose through special ducts (3). There are many vital vascular and nervous structures near the sphenoid including internal carotid artery, which plays an important role in supplying the brain and eyes. From intracranial view, it passes through greater wings joint to the body. Internal carotid artery is so close to the body and forms a track on it called carotid (4). Optic nerve is close to the body of the bone and passes between two roots related to lesser wings and attached to the body from a lateral view. An artery called ophthalmic artery passes beside the optic nerve (5).
Studies showed that the internal carotid artery and optic nerve routes would change based on sphenoid sinus pneumatization, which are observed as bulging on the sidewall of the sinus. It is also possible to observe artery and nerve without bone covering in sinus wall (4, 6). Involvement of sphenoid sinus has been observed in more than 20% of patients with chronic sinusitis, besides sphenoid sinus is an appropriate route to access anterior and middle cranial fossa in surgery (e.g. pituitary gland surgery). Therefore, it is important to have adequate knowledge of the contents of sphenoid sinus and its proximity in nasal endoscopy, sinus surgeries and neurosurgeries.
2. Objectives
Since there is lack of knowledge regarding carotid artery variations with sphenoid sinus in Iranian cases, we aimed to study sphenoid sinus proximity with internal carotid artery and the optic nerve using computerized tomographic imaging as a precise tool in paranasal sinuses.
3. Materials and Methods
In this prospective study, 468 coronal and axial CT scan images of sphenoid sinuses of patients referred to Imam Khomeini and Apadana hospitals during 2003-2009 were assessed by a radiologist, an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist and an anatomist. CT scan machine used in this study was spiral 16 slice. The images were checked to have lumps in internal carotid artery and optic nerve, also unilateralness or bilateralness of their relationship was studied. They were also checked for having bone covering in internal carotid artery and optic nerve, unilaterally and bilaterally in sphenoid sinus. Exclusion criteria in this study were patients with damaged sphenoid sinus, patients with an earlier record of sphenoid surgery and patients younger than 12 years. Studying sphenoid sinus in patients younger than 12 years is complicated due to underdevelopment of sphenoid sinus. Hence, they were excluded from the study (7). Patients personal information including their age was collected at the time of examination. Information regarding age was only useful to determine whether the patient was older or younger than 12 years. Bulging, internal carotid artery and optic nerve in the sinus, as well as patient's age, and involved side were the study variables. If the internal carotid artery or the optic nerve had formed a bony bulging, it was categorized as bulging, and if the bulging had no bony covering, it was categorized as existence of artery or nerve in the sinus.
4. Results
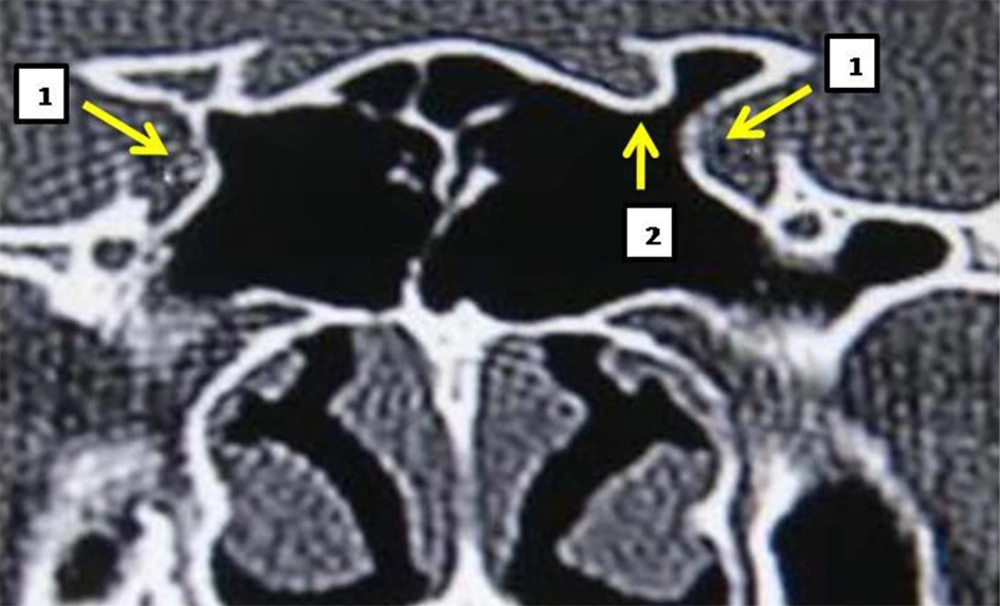
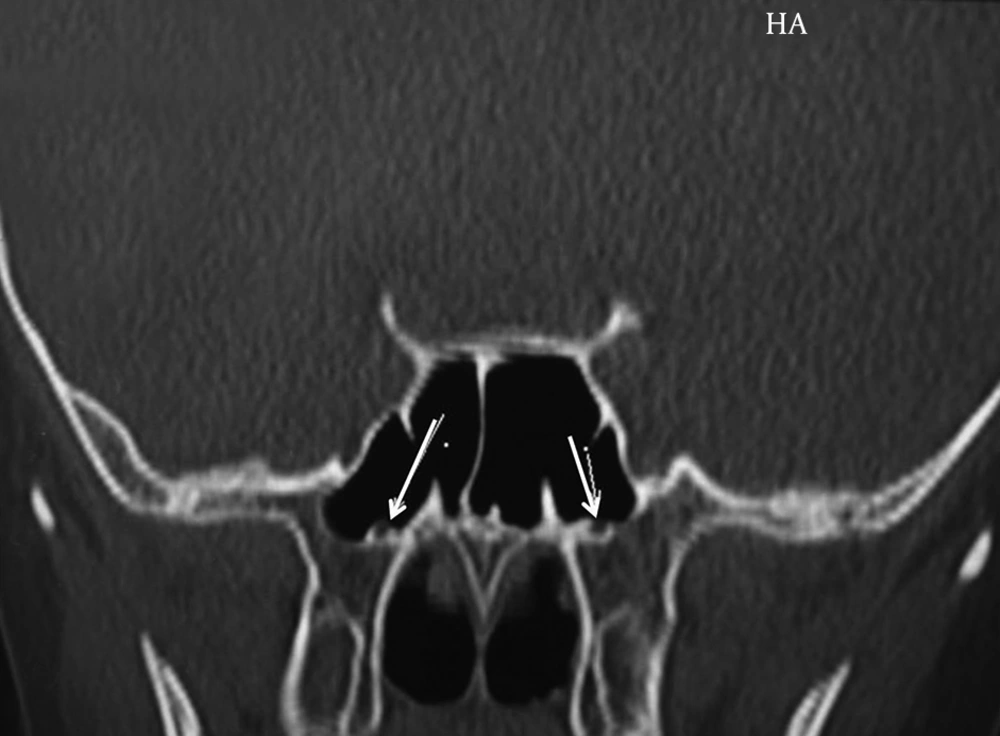
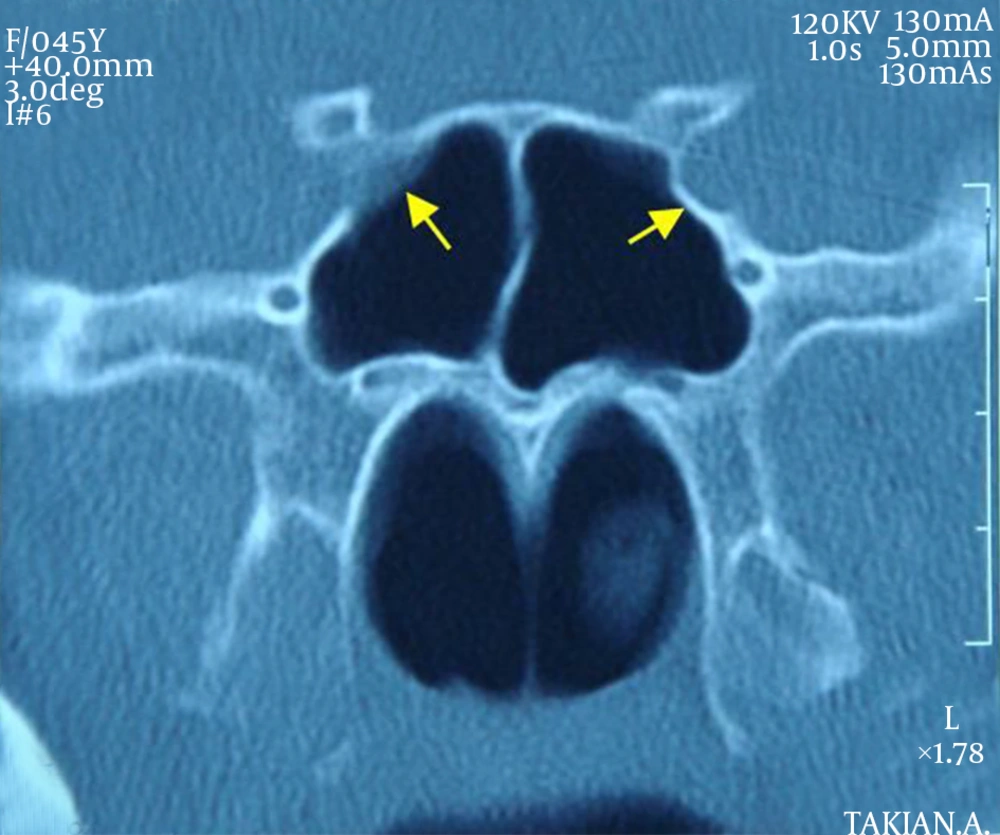
In this prospective study, 468 CT coronal scan images of sphenoid sinus were studied. The images were checked for having bulging in internal carotid artery or optic nerve, and unilateralness or bilateralness of their relationships. Among all studied scans, 365 cases (78%) showed post-sellar pneumatization and 103 (22%) presellar pneumatization. Regarding the existence of internal septa, 346 cases (74%) were reported to have multiple septation and the remaining cases had a single septum. The existence of bulging as a consequence of internal carotid artery and uncovered artery were reported to be 4.22%, and 5.8% in the right sinus, 4.9%, and 5.4% in the left sinus and 4.34% and 4.6% in both sinuses, respectively (Figures 1, 2 and 4). The existence of bulging due to optic nerve and uncovered nerve were reported to be 5.7% and 4.3% in the right sinus, 6% and 5.4% in the left sinus and 12% and 3.2% in both sinuses, respectively (Table 1) (Figure 3). In 3.36% of scans, vidian nerve was seen as a bulging under sphenoid sinus (Figure 2).
| Variables under investigation | Right Sinus | Left Sinus | Bilateral | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lump in internal carotid artery | 105 (4.22) | 44 (4.9) | 161 (4.34) | 310 (2.66) |
| Lump in the optic nerve | 35 (5.7) | 28 (6) | 56 (12) | 119 (5.25) |
| Existence of artery in sinus | 40 (5.8) | 21 (5.4) | 30 (4.6) | 91 (4.19) |
| Existence of optic nerve in sinus | 16 (4.3) | 21 (5.4) | 11 (3.2) | 49 (5.10) |
aData are presented as No. (%).
5. Discussion
There are few researches performed on sphenoid sinus and its proximity with internal carotid artery and optic nerve. In a study by Unal, et al. 59 tomographic scans of Turkish patients were studied. According to that study, in 3.30% of patients the internal carotid artery, in 3.31% of the cases the optic nerve, and in 3.35% the vidian nerve was observed as a bulging (8) (Figure 2). In the mentioned study, there was no assessment of unilateralness or bilateralness of the bulging in the sphenoid sinus. There was no mention of the existence of artery in uncovered sphenoid sinus cavity. In the current study, 468 coronal CT scan images of sphenoid sinus were checked for existence of bulging in sphenoid sinus and uncovered internal carotid artery or optic nerve. Moreover, unilateralness or bilateralness of the relationship between them was studied.Among the studied scans, 365 cases (78%) showed post-sellar pneumatization and 103 (22%) pre-sellar pneumatization. Regarding the existence of internal septa, 346 cases (74%) had multiple septation, while the remaining cases had a single septum. Bulging in sphenoid sinus because of internal carotid artery and uncovered artery in the scans were reported to be 4.22%, and 5.8% in the right sinus, 4.9%, and 5.4% in the left sinus and 4.34% and 4.6% in both sinuses, respectively. The existence of bulging in sphenoid sinus due to optic nerve and uncovered nerve in the scans were reported to be 5.7% and 4.3% in the right sinus, 6% and 5.4% in the left sinus, and 12% and 3.2% in both sinuses, respectively. Mentioned figures are lower compared to global outbreak. Kantarci et al. studied 90 tomographic scans of patients (9). Among all cases, 16% had bilateral and 7% unilateral internal carotid lump. According to another study performed by Lin Chen et al. on 290 patients, 28% of cases had bulging in the sphenoid sinus (10). There was no mention of anatomical location of the internal carotid artery in their study. Dessi et al. in a prospective study studied computerized tomographic scans of 150 patients. They found that in 8% of patients, the optic nerve had a bulging in sphenoid sinus. It was also discovered that the optic nerve did not have a bulging in posterior ethmoid sinus in any of the observed cases. In their research, the optic nerve was studied only and there was no mention of either internal carotid artery or its proximity with sphenoid sinus (11, 12).
In conclusion due to variability of sphenoid sinus pneumatization and the separator blade of the two sinus cavities, careful attention is required during sinus surgery to avoid damage to neural and vascular structures in its proximity. A surgeon must be especially careful during operation on a carotid artery or optic nerve that does not have any bony covering to avoid possible damage to these structures. The superior turbinate is a reliable indicator for locating sphenoid sinus, especially in further surgeries, since the middle turbinate is taken out in the first operation.