1. Context
Echinococcus infections are the most common parasitic disease affecting the liver. Hydatid disease course is typically slow, and patients may remain asymptomatic for many years. Diagnosis of the hydatid cyst is usually incidental (1). Although the prevalence of the hydatid disease has fallen in several decades, recent data suggest that Echinococcus multilocularis is expanding its geographical range in the northern hemisphere and the infection with Echinococcus granulosus remains a major health problem in certain regions and countries in the world (2, 3). Since the medical literature lacks a bibliometric study evaluating the articles published in hydatid disease and hydatid cyst surgery, in this study, we aimed to assess the documents published in this field.
2. Evidence Acquisition
The databases we used for the evaluation of the literature in our study was provided by Thomson Reuters WoS (Thomson Reuters, New York, NY, USA), titled Web of Science Core Collection, Korean Journal Database, Russian Science Citation Index, and SciELO Citation Index. We used the keyword “hydatid cyst” to search the WoS database. Information from 1975 was provided from the WoS database. We included all documents published between 1975 to 2017 in the study. We excluded all papers produced in 2018. Documents published from England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales were included under the United Kingdom (UK) heading. Statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS (Version 22.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA; licensed for Hitit University, Corum, Turkey). We created infographics showing scientometric networks by using the VOSviewer software tool for constructing and visualizing bibliometric networks (4). We generated info maps revealing publication density of the countries throughout the world by using GunnMap free resource (5).
3. Results
3.1. Hydatid Cyst Literature
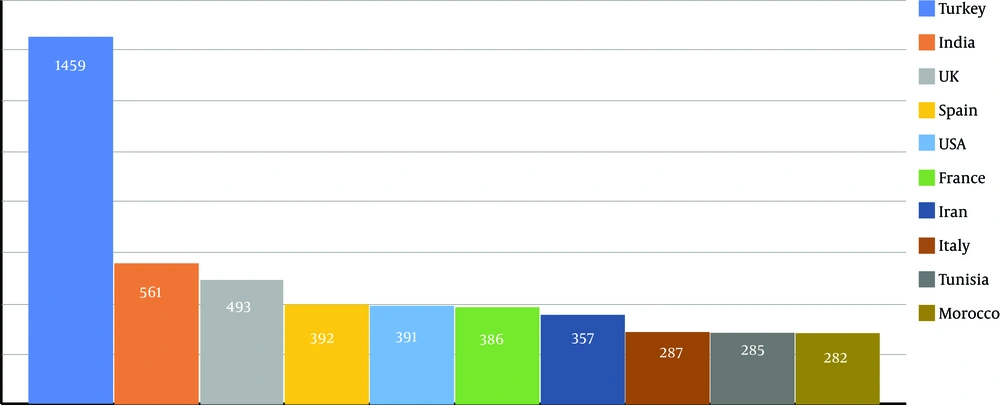
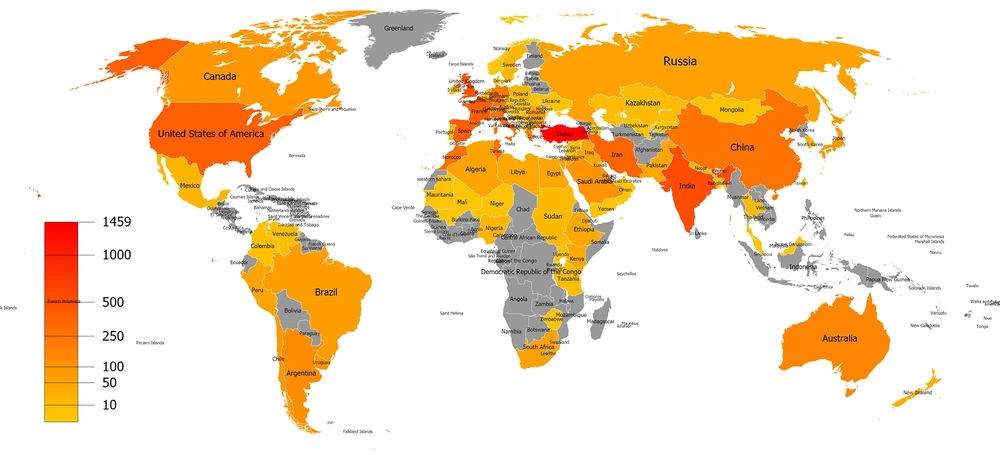
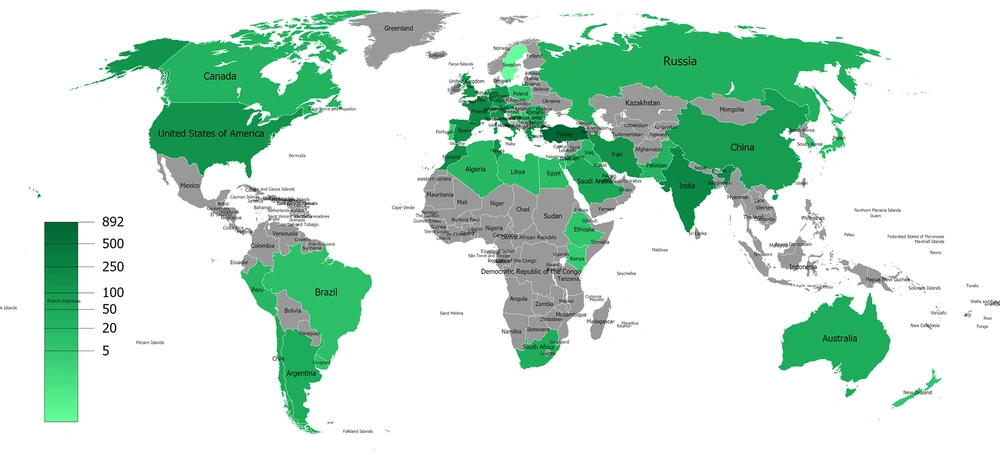
Our database search retrieved a total of 6928 documents. The keywords “hydatid cyst” and “hydatid disease” were used in the medical literature between 1975 and 2017. It was found that 89.6% of total papers were original articles (n = 6206) followed by case reports (n = 2430, 35%) (Table 1). The number of open-access documents was 1210 (17.46%). English is the primary language of the documents (n = 6172, 89.1%) followed by French (11.1%), Spanish (4.3%), German (2.7%), Russian (1.5%), and Turkish (1.1%). The top 100 countries producing HC documents were ranked by NP, and infographic showing the world of HC literature was generated (Figure 1). Turkey was found to be the most productive country on HC literature with 1459 items (21%) followed by India, the UK, Spain, and the USA (561, 493, 392, and 391 papers, respectively) (Figure 1). The distribution of density of published HC documents was shown on a generated infographic world map (Figure 2).
| Fielda/Document Types | Hydatid Cyst, No. (%) | Hydatid Cyst Surgery, No. (%) | Total, No. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original Article | 6206 (89.58) | 3194 (93.67) | 9400 (90.93) |
| Review | 527 (7.61) | 307 (9) | 834 (8.07) |
| Editorial | 341 (4.92) | 145 (4.25) | 486 (4.7) |
| Meeting | 279 (4.03) | 107 (3.14) | 386 (3.73) |
| Letter | 499 (7.2) | 213 (6.25) | 712 (6.89) |
| Case Report | 2430 (35.07) | 1588 (46.57) | 4018 (38.87) |
| Abstract | 637 (9.19) | 355 (10.41) | 992 (9.59) |
| Correction | 10 (0.14) | 1 (0.03) | 11 (0.11) |
| Clinical Trial | 69 (1) | 40 (1.17) | 109 (1.05) |
| Biography | 2 (0.03) | 1 (0.03) | 3 (0.03) |
| Unspecified/Others | 1194 (17.23) | 385 (11.29) | 1579 (15.27) |
| Book | 3 (0.04) | 1 (0.03) | 4 (0.04) |
| Totalb | 6928 (100) | 3410 (100) | 10338 (90.93) |
aSorted by total number of publications.
bTotal percentages may exceed 100% because certain items were included in more than one category.
Tunis El Manar University in Tunisia was found to be the most productive institution with 122 papers (1.76%) followed by Assistance Publique - Hopitaux de Paris, Istanbul University, and Hacettepe University (118, 105, and 95 documents, respectively) (Table 2). American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene had the highest publication number in this field with 161 items (Table 3). The top three authors producing HC articles were Craig PS, Wen H, and Brunetti E (n = 126, 56, and 42 papers, respectively). Cumulative citation number of all HC literature was 76178, and average citations per year were calculated as 1953.28. The most cited article was an original article titled “Ultrasound Examination of The Hydatic Liver” by Gharbi et al., published in 1981 and cited 554 times (Table 4) (6).
| Institutions | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Hydatid Cyst | |
| Tunis El Manar University, Tunis, Tunisia | 122 (1.76) |
| Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France | 118 (1.7) |
| Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey | 105 (1.52) |
| Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey | 95 (1.37) |
| Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey | 75 (1.08) |
| University of the Republic Uruguay, Montevideo, Uruguay | 75 (1.08) |
| Selçuk University, Konya, Turkey | 72 (1.04) |
| Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran | 71 (1.02) |
| University of Athens, Athens, Greece | 71 (1.02) |
| Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey | 68 (0.98) |
| Xinjiang Medical University, Ürümqi, China | 67 (0.97) |
| Gülhane Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey | 67 (0.97) |
| Ege University, Izmir, Turkey | 58 (0.83) |
| University of Salford, Salford, England, UK | 56 (0.81) |
| Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy | 54 (0.78) |
| Dicle University, Diyarbakır, Turkey | 53 (0.76) |
| Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India | 52 (0.75) |
| Inonü University, Malatya, Turkey | 49 (0.71) |
| Atatürk University, Malatya, Turkey | 48 (0.69) |
| Hospital Rabta, Tunis, Tunisia | 48 (0.69) |
| Hydatid Cyst Surgery | |
| Atatürk University, Malatya, Turkey | 85 (2.492) |
| Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France | 76 (2.229) |
| Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey | 75 (2.199) |
| Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey | 74 (2.17) |
| Tunis El Manar University, Tunis, Tunisia, | 71 (2.082) |
| Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey | 52 (1.525) |
| Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey | 50 (1.466) |
| University of Athens, Athens, Greece | 48 (1.408) |
| Selçuk University, Konya, Turkey | 39 (2.492) |
| Xinjiang Medical University, Ürümqi, China | 35 (1.026) |
| Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran | 34 (0.997) |
| Dicle University, Diyarbakır, Turkey | 33 (0.968) |
| Gülhane Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey | 33 (0.968) |
| Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey | 31 (0.909) |
| Erciyes University, Kayseri, Turkey | 30 (0.880) |
| Chu Ibnou Rochd, Casablanca, Morocco | 29 (0.850) |
| Ankara Turkiye Yuksek Ihtisas Egitim Ve Arastirma Hastanesi, Ankara, Turkey | 28 (0.821) |
| Inonü University, Malatya, Turkey | 28 (0.821) |
| All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India | 27 (0.792) |
| Ege University, Izmir, Turkey | 27 (0.792) |
| Institutions | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Hydatid Cyst | |
| American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene | 161 (2.32) |
| American Journal of Roentgenology | 124 (1.79) |
| Parasitology Research | 96 (1.38) |
| Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology | 95 (1.37) |
| Veterinary Parasitology | 91 (1.31) |
| Acta Tropica | 77 (1.11) |
| World Journal of Surgery | 73 (1.05) |
| Annales De Chirurgie | 72 (1.04) |
| Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene | 59 (0.85) |
| International Journal for Parasitology | 58 (0.84) |
| Hydatid Cyst Surgery | |
| World Journal of Surgery | 66 (1.93) |
| Annales de Chirurgie | 63 (1.84) |
| Hepato Gastroenterology | 43 (1.26) |
| Khirurgiia | 41 (1.2) |
| American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene | 39 (1.14) |
| Acta Chirurgica Belgica | 37 (1.08) |
| The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene | 37 (1.08) |
| Journal de Chirurgie | 36 (1.06) |
| Journal of Pediatric Surgery | 34 (1) |
| Annals of Thoracic Surgery | 33 (0.97) |
| Article | Author | Publication Year | Total Citation | Average Citations per Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound examination of the hydatic liver | Gharbi et al. | 1981 | 554 | 14.58 |
| Echinococcosis | McManus et al. | 2003 | 515 | 32.19 |
| Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans | Brunetti et al. | 2010 | 404 | 44.89 |
| Hydatid disease: Radiologic and pathologic features and complications | Pedrosa et al. | 2000 | 355 | 18.68 |
| Cestodes-echinococcus | Ammann and Eckert | 1996 | 298 | 12.96 |
| Personal-experience with 411 hepatic resections | Iwatsuki and Starzl | 1988 | 290 | 9.35 |
| International classification of ultrasound images in cystic echinococcosis for application in clinical and field epidemiological settings | Macpherson et al. | 2003 | 255 | 15.94 |
| Cystic focal liver lesions in the adult: differential CT and MR imaging features | Mortele and Ros | 2001 | 223 | 12.39 |
| Percutaneous drainage compared with surgery for hepatic hydatid cysts | Khuroo et al. | 1997 | 219 | 9.95 |
| Albendazole-objective evidence of response in human hydatid-disease | Morris et al. | 1985 | 210 | 6.18 |
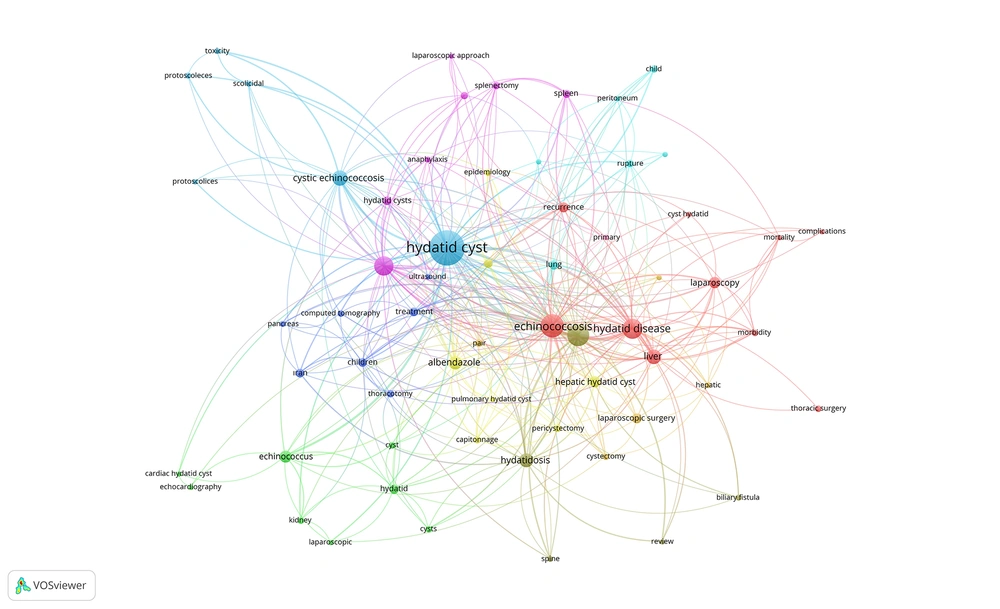
We extracted the most used keywords from the database including the most cited articles and found that “Hydatid cyst”, “Echinococcus granulosus”, “echinococcosis”, “hydatid disease”, and “liver” were the top five keywords (used 130, 57, 54, 29, and 25 times) (Table 5).
| Keywords | N, Times |
|---|---|
| Hydatid Cyst | |
| Hydatid cyst | 130 |
| Echinoccocus granulosus | 57 |
| Echinoccocosis | 54 |
| Hydatid disease | 29 |
| Liver | 25 |
| Surgery | 23 |
| Hydatidosis | 21 |
| Albendazole | 18 |
| Echinococcus | 17 |
| Iran | 16 |
| Hydatid Cyst Surgery | |
| Hydatid cyst | 150 |
| Echinoccocosis | 64 |
| Surgery | 58 |
| Hydatid disease | 49 |
| Echinoccocus granulosus | 44 |
| Cystic echinoccocosis | 29 |
| Liver | 26 |
| Hydatidosis | 23 |
| Albendazole | 21 |
| Echinococcus | 18 |
3.2. Surgery of Hydatid Cyst Literature
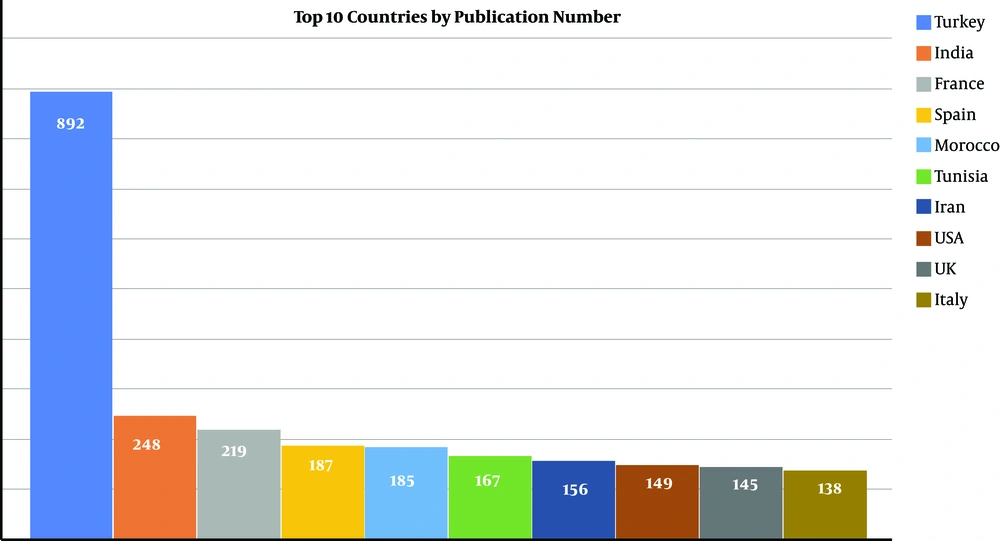
A total of 3410 documents were detected as we performed a search in the WoS database by using keywords “hydatid cyst” and “surgery”. The top 10 countries produced documents in this field was ranked by the number of publications (Figure 3). Turkey produced 26.16% of all literature with 892 items followed by India, France, and Spain (248, 219, and 187 articles, respectively) (Figure 4). We created an info map, including all countries publishing in this field (Figure 5). We found that a high majority of the documents were original articles (n=3194, 93.67%) (Table 1). English was a major language of the literature (88.36%) followed by French, Spanish, and German (13.9, 4.19, and 2.93%, respectively).
Atatürk University (Malatya, Turkey) was found to be the most productive institution with 85 items followed by Assistance Publique- Hopitaux de Paris (Paris, France), Istanbul University (Istanbul, Turkey), Ankara University (Ankara, Turkey), Tunis El Manar University (Tunis, Tunisia), Hacettepe University (Ankara, Turkey), and Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital (Ankara, Turkey), and (76, 75, 74, 71, 52, and 50 documents, respectively).
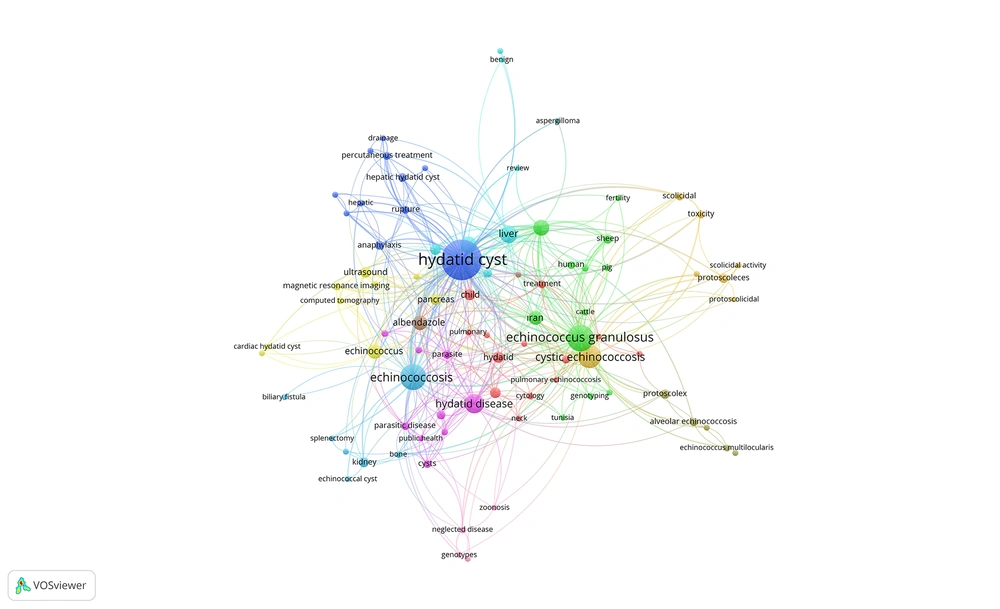
The World Journal of Surgery ranked first with the publication number in this field with 66 articles followed by Annales De Chirurgie, Hepato-Gastroenterology, and Khirurgiia (63, 43, and 41 items, respectively). We noted that 3410 articles in this field were cited a total of 39871 times. The most cited article was titled “Ultrasound Examination of The Hydatic Liver” by Gharbi, HA et al., cited 554 times (Table 6). The most used keywords in this field were hydatid cyst, echinococcosis, surgery, and hydatid disease (used 150, 64, 58, and 49). We generated a keyword network by using the top keywords (Figure 6).
| Article | Author | Publication Year | Total Citation | Average Citations per Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound examination of the hydatic liver | Gharbi et al. | 1981 | 554 | 14.58 |
| Echinococcosis | McManus et al. | 2003 | 515 | 32.19 |
| Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans | Brunetti et al. | 2010 | 404 | 44.89 |
| Personal-experience with 411 hepatic resections | Iwatsuki and Starzl | 1988 | 290 | 9.35 |
| Percutaneous drainage compared with surgery for hepatic hydatid cysts | Khuroo et al. | 1997 | 219 | 9.95 |
| Albendazole-objective evidence of response in human hydatid-disease | Morris et al. | 1985 | 210 | 6.18 |
| Diagnosis and management of hydatid-disease of the liver-a 15-year north-american experience | Langer et al. | 1984 | 186 | 5.31 |
| Laparoscopic liver resection of benign liver tumors-results of a multicenter european experience | Descottes et al. | 2003 | 180 | 11.25 |
| Surgical-treatment of hydatid cysts of the lung-report on 1055 patients | Dogan et al. | 1989 | 180 | 6 |
| Albendazole as a potential treatment for human hydatidosis | Saimot et al. | 1983 | 180 | 5 |
4. Discussion
The greatest prevalences of hydatid disease in humans has been noted in temperate zones of the world such as Mediterranean countries, southern and central parts of Russia, central Asia, China, South America, and Australia (3). Hydatid cyst is an increasing health concern in many regions of the world and it is currently considered as an endemic zoonosis in the Mediterranean region (7, 8). The most endemic areas have been reported to be Mediterranean countries, and we found that six of the top ten countries publishing in hydatid disease literature were from the Mediterranean region (Figure 1). According to the WHO database, the annual incidence of hydatid disease is 4.4 in a 100000 population in Turkey, which was found in our study to be the most productive county of the world in this field. Although certain regions of Spain, Italy, and Cyprus had greater prevalences of hydatid disease than Turkey, the sum of publication numbers of these countries could not reach the document number of Turkey (6.2, 8, and 5.7, respectively). Although Turkey ranked first in the publication number, no article from Turkey was in the top 10 cited documents. The most cited articles in this field were from Tunisia and were published by Gharbi et al. As we evaluated the most cited items of the literature, we detected that the countries that produced these articles were Tunisia, Australia, Italy, France, Germany, Spain, Switzerland, the USA, and India.
4.1. Limitation
Our study had two limitations. First, we used only one database, WoS, since it has been considered as the most reliable database in the academic literature. Second, we could not reach the documents before 1975 because WoS provided access to items published since 1975.
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first bibliometric study in the literature related to hydatid disease and hydatid cyst surgery. Researches from the regions and countries having a high prevalence of hydatid disease should be encouraged and funded to carry out novel studies. Physicians from the countries with a high publication number in this field should produce more citable articles.