1. Background
Organizations are social institutions (1) that, on the path to achieving organizational goals and economic success, require a suitable and healthy work environment to cultivate genius and creative skills (2) that result in the emergence and influence of creative industries in various aspects of human life (3, 4). News-oriented organizations and media are the most important creative industries that nurture and improve people's thoughts and guide their behavior and character. Therefore, considering the important role of these news organizations in today's world, it is necessary to maintain the health conditions of their work environment (5, 6).
The IRINN is one of the most important parts of the Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting as a national and public media organization. The employees of this news network are large and influential from the economic, social, and work sensitivity criteria. On the other hand, these employees need a flexible environment to perform appropriate and effective professional undertakings due to existing stress. Therefore, as a manager of creative industries, the media manager must provide a calm and stress-free environment for employees to let them create quality content-based products. Therefore, it is necessary to create a healthy working environment in the creative industry of the news network. According to the purpose of this research, to design a suitable framework that can both identify the various components of the desired theory or model and also understand the relationships of each, the paradigm model was used to identify the components of the said model and their interrelated relationships. Also, using the grounded theory method, an optimal model for the environmental health of the employees of the IRINN was designed.
The grounded theory method is an inductive approach to discovering concepts. This method provides a mechanism by which the important concepts of the research subject can be identified based on the data. When there is no theory on the topic in question, or the existing theories are scattered, and the concepts are vague, using the foundation data method, it is possible to design a conceptual model (7).
The main idea of the grounded theory method is that theorizing does not come from the available data but is created or conceptualized based on the data from the participants who have experienced the research process (8).
The three elements of concepts, components, and parameters are the main pillars of this approach. Concepts are formed after data collection and analysis, and combining several concepts creates a component. Finally, the parameters are revealed as a grounded theory paradigm model by expressing the generalized relationships between a component and its concepts (9).
In 2019, Barati identified factors affecting the development of public sports based on global approaches and presented a qualitative model using the grounded theory method (10). In 2015, Nejadmohammad Nameqi (11) identified the appropriate characteristics for the Iranian TV news staff to investigate working in a stressful environment.
In 2020, Emerson et al. (12) investigated the health promotion of the workplace and its effect on the behavior and well-being of employees. In this case, an empirical and exploratory study was conducted as a part of an occupational health initiative in an executive health service in Ireland in April 2018.
2. Objectives
Despite the importance of environmental health as one of the most influential factors in this creative industry network's environment, research has yet to be conducted to improve IRINN's current health situation. Therefore, the current study using the grounded theory method was conducted to identify the factors affecting the health status of the working environment of the IRINN news network.
3. Methods
The current research was conducted qualitatively and based on the grounded theory method in 1401 (2022 - 2023). This theory is a qualitative research approach that seeks to theorize or achieve a pattern. The grounded theory method uses the open, central, and selective coding stages for data analysis.
3.1. Study Venue: The IRINN
The statistical population of the present study at the IRINN satellite channel was launched in November 1999 with about 10 hours of programming per day to spread Iranian culture and fast, accurate, and correct transmission of news stories to Persian-speaking audiences worldwide. The channel continues to operate 24 hours a day. (Source: researcher's compilation)
3.2. Data Collection
Data collection was done through an in-depth interview method. As an important tool in data collection, the interview deals with a deeper evaluation of their perceptions, attitudes, interests, and aspirations while establishing direct contact with the interviewee. To ensure the validity of the interview questions, the triangulation method and member review were used, and the results indicated high validity of the interview questions. To measure the reliability, a judge used the auditing method, and the reliability of the questions was confirmed. In the present study, the researcher guided all interviews. Adopting this procedure allowed the researcher to use the information from the previous interviews in the subsequent ones he dealt with. The purpose of conducting the interviews was to understand and explain the effective factors on the workplace health of the IRINN staff. The interviews were conducted between 2022 and 2023 in this news network's studios and management offices. In each related department, the researcher conducted interviews and, in some cases, studied some documents. The statistical population consisted of 17 production managers and media editors with at least 10 years of work experience who were familiar with workplace health issues. Using their opinions, the causal, intervening, contextual, strategy, and consequence conditions and the model of the health status of this news network were extracted. The sensitive conditions of the news production centers and the importance of the health of the employees of this sector make it necessary to design a model to evaluate the health status of the IRINN's environment as a statistical population. The five criteria for selecting participants in the research were: (1) being an index in the news section, (2) being known by others, (3) having a theoretical understanding of the subject, (4) diversity in the job, and (5) agreeing to participate in the interview. In the current study, data collection continued until the theoretical saturation point of the main codes, and to put it more clearly, obtaining new data was no longer possible. Data analysis was done using the open, central, and selective coding methods, which finally led to the design of the proposed model.
3.3. Data Analysis Until the Formation of the Final Theory
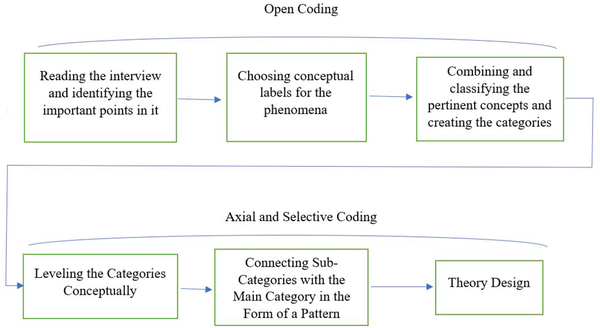
Data analysis is the main framework of the grounded theory method. This process is not done in a mechanical and step-by-step process. Analysis in this method requires the researcher's creativity, patience, foresight, and observation. The spirit of analysis in the grounded theory method's theorizing strategy is a kind of comparative data analysis, interpreted as "continuous comparison". Coding in the grounded theory method includes three steps: the first step is open coding, the second step is central coding, and the third step is selective coding.
3.3.1. First Step: Open Coding
Open coding is an analytical process through which concepts are identified, and their features and dimensions are discovered in the data. This stage of the grounded theory method is done immediately after the first interview.
After each interview, the researcher starts to find concepts, choose suitable labels, and combine related concepts. In open coding, data is broken into separate parts. The data are compared to obtain the similarities and differences, and questions are raised about the categories. Based on this, in the beginning, the phenomena were labeled, each paragraph was divided into different components, and a title was determined for each event. The next step in open coding is to discover categories. After identifying specific phenomena in the data, concepts were categorized based on them. A conceptual title was given to a category with the related codes (tags).
The definitions of code, concept, and category:
Code: Code is the basic unit (or smallest unit) of analysis. It is as if the theory is formed from the mental image and conceptualization of data, not only from the real data itself.
Concepts: In the grounded theory method, concepts are subcategories of the type of open codes whose task is to provide more details about each main category.
Categories: Compared to concepts, categories are more abstract and show a higher level. They are produced through the same analytical process of comparing to highlight similarities and differences used at a lower level to produce concepts. Classes are the "foundation" of building a theory and provide a tool by which the theory can be integrated (13).
3.3.2. Second Step: Axial Coding
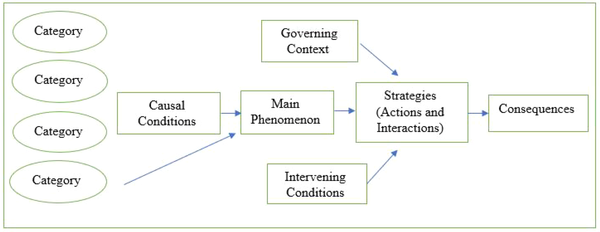
In the second stage of coding, axial coding, the researcher selects one of the categories as the central case, explores it under the title of the central phenomenon in the center of the process, and determines the relationship of other categories with it. Five core categories in the present study include causal conditions, strategies (actions and interactions), governing context, intervening conditions, and consequences (14).
This coding method, which is called the "paradigm model" of axial coding, was presented by Strauss and Corbin, where coding is done around the "axis" of a category (Figure 1).
3.3.3. Third Step: Selective Coding (Optional)
The selection process is a major category. At this stage, creating a regular connection between this category and other categories gives credibility to the relationship. This process includes several steps:
The first step involves explaining the main line of the story. The second step is to relate supplementary categories to the main category using a paradigm (described in axial coding). The third step is to relate the categories to the next level. The fourth step is to confirm those relationships with the data. The last step is to complete the categories that need to be modified or expanded (14).
In the Figure 2, the path to conduct and complete the data analysis in the current research is given.
The path of conducting and completing data analysis (14)
4. Results
Before the interview, the research's subject and purpose were explained to the interviewees, and then they were asked to answer the research questions. Subsequently, the interviews were done, and the related notes were taken after receiving the interviewees' permission.
To avoid bias during the interviews, the researcher tried to select the statistical population from the managers and employees who were fully aware of the working health conditions in the IRINN. This was conducted because the managers of the given news channel could refuse to criticize the system's problems due to their conflict of interests, and employees, on the other hand, may have more direct and harsh criticism due to not having a position in the system. The interviewees were assured that their opinions, criticisms, and suggestions about the working health condition of the IRINN would only be used in the current research. On that basis, the interviews were conducted after the researcher clearly explained the topic and purpose of the research to the interviewees.
4.1. Open Coding Phase
After conducting the interviews, the extracted codes and concepts were written down according to Table 1.
| Coding | Key Points (Verbal Evidence) |
|---|---|
| Quiet environment; Sufficient light; Suitable ventilation and air temperature; Calm environment | In response to: What health dimensions and components are critical to the working environment of employees operating in creative industries? It can be said: Having a quiet environment without disturbing noises. Sufficient natural light in the work environment, proper ventilation, and air temperature. An environment without stress and tension, both from the sides of employees and managers during working hours. |
| Non-standard building; Failure to comply with health requirements | What obstacles does the IRINN face in implementing the workplace health model for its employees? These can be mentioned: Non-standard building and insufficient space for proper placement of employees; Difficulty in monitoring the health behavior of employees due to the physical dispersion of administrative and operational units on different floors of the IRINN building; Overcrowding of some administrative and operational units and the possibility of facing danger during possible accidents in the working environment. |
| Survey; Refer to employees; Field survey | In response to the question: How can we evaluate whether the health development of the employees' working environment is well or badly managed, it can be said: We can refer to the employees themselves, and this is the most proper and important touch point to find about the facts on the ground. It is as the employees are the main force that generates the conditions in place. Employees can point out their working environment's advantages and disadvantages better than anyone else. It should also be considered that using experts such as occupational health experts can also be very important, as the employees' information about their workplace standards may sometimes need to be corrected or completed. |
An Example of Verbal Evidence Conceptualization
In a follow-up to the coding process, by connecting the codes resulting from open coding and determining the relationship between them, axial coding was performed, and the central category and its related subcategories were selected (Table 2).
| Category and Open Coding | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Assessing the development of the health of the workplace | |
| Imperceptible inspection | 1 |
| Outsourcing the inspection process | 1 |
| Dispatching the health team to the workplace | 3 |
| Survey and field investigation | 13 |
| Obstacles to the implementation of the workplace health model | |
| Lack of sufficient funds | 3 |
| The nature of the news as a career | 1 |
| Improper building | 5 |
| Lack of proper management | 2 |
| Absence of codified law regarding health at the IRINN | 1 |
| Managers' actions regarding workplace health (managerial behaviors) | |
| Cleaning | 1 |
| Air conditioning | 2 |
| Periodic health examinations | 2 |
| Environmental disinfection | 2 |
| Distribution of sanitary items | 1 |
| Individual consequences of improving workplace health | |
| Create creativity | 3 |
| Physical health | 4 |
| Intellectual and mental health | 4 |
| Job satisfaction | 1 |
| Organizational implications for improving workplace health | |
| Reducing tension in the workplace | 1 |
| Reducing human errors | 1 |
| Increasing media productions | 1 |
| Increasing employees' organizational dependence | 1 |
| Organization growth | 1 |
| Increasing employees' productivity | 6 |
An Example of the Categorization of Related Concepts
4.2. Axial Coding Stage
At this stage, the core and sub-categories of the research are displayed in a model. This model generally helps to clarify the relationships between a phenomenon, the reasons for the emergence of the phenomenon, the strategies of interaction with the phenomenon and its consequences, the context, and the intervening conditions.
4.2.1. Causal Conditions
According to Table 3, causal conditions refer to incidents, events, and occurrences that lead to the occurrence or development of a phenomenon (15).
| General Category | Concept | Final Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Causal conditions | Obstacles to the implementation of the workplace health model | Lack of sufficient funds |
| The nature of the news as a career | ||
| Improper building | ||
| Lack of proper management | ||
| Absence of codified law for the working environment health | ||
| Lack of manpower | ||
| Reasons for the Development of the Workplace Health Model | Mental comfort | |
| Management features | ||
| Frequent changing approaches among managers | ||
| Program regarding workplace health |
Identified Categories and Concepts Related to Causal Conditions
4.2.2. Contextual Conditions
According to Table 4, contextual conditions represent specific circumstances in which action or reaction strategies occur (15).
| General Category | Concept | Final Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Contextual conditions | Workplace health issues | Non-cooperation of the IRIB Health Center with the Health Liaisons from the IRINN News network |
| Non-standard building | ||
| Improper working space | ||
| Job security issue | ||
| The issues of pressure and stress | ||
| The problem of insufficient light | ||
| The issue of unsanitary dining hall | ||
| The issue of managers' lack of knowledge about workplace health | ||
| Lack of proper temperature |
Identified Categories and Concepts Related to Contextual Conditions
4.2.3. Main Category
According to Table 5, the main category or phenomenon is the main incident or event that includes a series of mutual and related actions or interactions that control and manage the main category or phenomenon. With questions like "What does this data imply?", "What are these actions or interactions about?" It is possible to recognize the main category or phenomenon (15).
| General Category | Concept | Final Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Musts and components of workplace health | Components of workplace health | Productivity and efficiency of human resources |
| Calm and standard environment | ||
| Proper air conditioning | ||
| Standard tables and chairs | ||
| Right light and temperature | ||
| Proper dining hall and nutrition stands | ||
| Computers with low radiation | ||
| Appropriate green space and construction of a fountain | ||
| Attention to the physical health of employees | ||
| Stress-free environment |
Identified Categories and Concepts Related to the Main Phenomenon (Main Category)
The main topic of this research was the health components of the work environment; therefore, most questions are dedicated to the needs and components of the health environment.
4.2.4. Intervening Conditions
According to Table 6, intervening conditions refer to structural conditions related to action strategies/interactions related to a phenomenon.
| General Category | Concept | Final Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Intervening conditions | Actions taken by the managers concerning workplace health | Cleaning the working environment |
| Proper air conditioning | ||
| Periodic health examinations | ||
| Disinfecting the working environment |
Identified Categories and Concepts Related to Intervening Conditions
4.2.5. Action and Interaction Strategies
According to Table 7, strategies (action/interaction) are measured and purposeful actions to solve problems or shape a phenomenon. In other words, strategies are actions individuals, organizations, societies, or nations take to manage phenomena (15).
| General Category | Concept | Final Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Strategies | Assessing the development of workplace health | Inconspicuous inspection |
| Outsourcing the inspection process | ||
| Dispatching the health team to the workplace |
Identified Categories and Concepts Related to Strategies and Actions
4.2.6. Consequences
Outcomes refer to outputs or results of action/interaction (Table 8). Actions/interactions performed in response to, or the administration of, a phenomenon have consequences and results. These are not always predictable or not done on purpose. They may be for people, places, things, events, or incidents like illness. They may be potential or actual. They may happen in the present or the future (15).
| General Category | Concept | Final Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Consequences | Individual consequences | Final codes |
| Creativity | ||
| Physical health | ||
| Intellectual and mental health | ||
| Job satisfaction | ||
| Creating motivation | ||
| Organizational implications | Personal growth and development | |
| Reducing tension in the workplace | ||
| Reducing human errors | ||
| Increasing media productions | ||
| Increasing loyalty and organizational dependence among employees | ||
| organizational growth and increased efficiency | ||
| Increasing productivity among employees |
Identified Categories and Concepts Related to Outcomes
4.3. Selective Coding Step
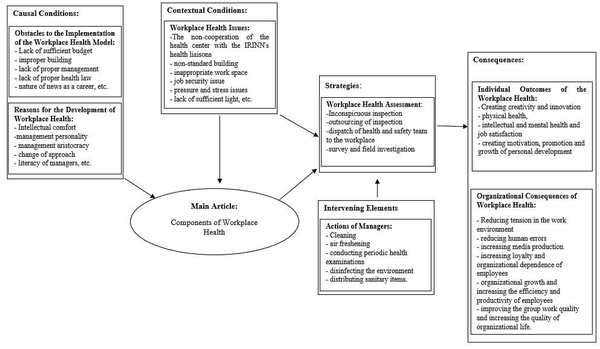
The last stage of coding in the Grounded Theory method is selective coding. In this research, taking into account the preliminary studies and the opinions of the interviewees, and the analysis of the data collected by the Grounded Theory method, the proposed model drawn in Figure 3 obtained during the analysis of the main concepts:
5. Discussion
One of the most important problems of most organizations is the health issue in the workplace, about which limited studies have been published. The present study was also conducted to identify the factors affecting the health of the working environment of the IRINN using the grounded theory model, which has not yet been conducted in the same international-level news networks worldwide.
Comparing the results of the present study with ones completed all based on the grounded theory method indicates that the grounded theory method presented in this study describes a process during which experts at the IRINN seek to identify and solve health problems in the workplace meaningfully. The participants were mostly experienced editors, and their collective perspective reflects the persistence of occupational health challenges (16).
The views of these people express their aspiration to improve the health status of the working environment to provide suitable work services.
Based on the results of this study, the causal conditions of the obstacles to implementing the workplace health model, which the interviewees emphasized, included two concepts. The concepts included the obstacles to implementing the workplace health model and, next, the causes of the development of workplace health, which, according to Table 3, each included several fixed subcategories.
The lack of sufficient budget is one of the most important sub-categories preventing the implementation of health in the workplace. According to the comments by one of the participants: "The first obstacle that we can consider for the managers of these news networks in their working tenures is the issue of the budget. Whenever you expect a manager to solve a series of issues, especially issues related to the health of the employees' working environment, they say that the organization and the network have been facing budget issues. At the same time, it is accepted that the safety of the working environment and employees should be a priority for any organization. In most executive affairs, the budget category is a key challenging issue (17, 18).
The subcategory of the nature of the news as a career has also been raised as yet another obstacle to implementing the workplace health model. Regarding nature, news as a career is stressful; therefore, it must be right in policies. The subcategory of inappropriate building is also one of the most frequent topics of the participants. Improper and unsanitary building of the IRINN in terms of light, air ventilation, and noise was the cause of health problems that require structural reforms. According to some participants in the current research: "The old and small-size building of this network has caused, and it is better to note that it has forced, some of the main editorial desks to be located in B1 and B2, which had neither enough light nor proper ventilation. The crowded and populated editorial desks are other main problems. The lack of social and physical distance between the workforce and the noise pollution by the employees and office equipment, such as laser jet printers, keyboards, speakers, etc., added to the current complications.
According to health studies, an inappropriate building causes sick building syndrome (SBS) and various diseases for residents and increases job burnout (19-22).
Therefore, in the grounded theory method, the researcher analyzes and scrutinizes the event and phenomenon using the supervision and information of the most knowledgeable people about the research. In other words, the type of sampling is accrual and judgmental (23).
Therefore, the first step in improving the health conditions of the workplace is the structural modification of the building; as mentioned, this requires an appropriate budget. In addition to all the above, the sub-category of weakness in managerial roles and positions was also one of the main obstacles in not implementing the health model of the working environment of the IRINN. According to one of the participants: "The first and biggest obstacle is the managers of this network because they do not care about our dignity and self-esteem, let alone the implementation of the workplace health model!". Management and employees have the most important role in improving the organization. The manager is a dynamic element in a complex organization with different working areas (24).
The sub-category of lack of codified law regarding health in the IRINN was also raised. By reforming the management structure and familiarizing the managers with workplace health-related rules, this problem can be solved (25, 26). The researchers provided the relevant health instructions and documents to the managers, which is a strength of this study.
Therefore, the mentioned events as causal conditions cause the creation of situations, discussions, and issues related to the phenomenon and explain to some extent why and how individuals and groups engage in this phenomenon. Causal conditions are the events that affect this phenomenon and lead to its occurrence (13).
In addition to the obstacles, finding the cause of the development of workplace health also includes sub-categories such as mental comfort, management characteristics, changing the approach of managers, and having a plan regarding workplace health that originates from obstacles and based on scientific documentation, the establishment of health management in the work plans of managers, the holding of training courses, as well as the justification of managers and their familiarity with scientific health documentation, have a significant impact on the development of the health environment of the IRINN (27-29).
According to Table 4, several background conditions have been stated as limitations for the establishment of the correct environmental health model of the Islamic Republic of Iran News Network (IRINN), which include subcategories such as non-cooperation of the health center of the Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting (IRIB) with the health liaisons of the IRINN, non-standard building, inappropriate work environment, lack of job security, the issue of pressure and stress, the issue of lack of sufficient light, the issue of the unsanitary dining hall, the issue of managers few knowledge about the health of the work environment, and the issue of the lack of proper temperature. In this context, the non-cooperation of the IRIB Health Center with the health liaisons of the IRINN is one of the major problems of this news channel, which is largely related to its in-house method of management; the one that suffers a variety number of drawbacks including managers' lack of knowledge, the incorrect attitude of relevant experts and the lack of familiarity of senior managers with the importance of health in administrative organizations. To remove the above shortages, training and culture-building, as well as modification of the management programs, are required (30, 31).
The sub-categories of non-standard buildings and the inappropriateness of the working space are important contextual factors influenced by the budget and managers' personal views. These factors cause the emergence of the subcategory of lack of sufficient light, lack of suitable temperature, and inadequate ventilation, and as a result, the occurrence of the subcategory of pressure and stress, which, according to scientific documentation, is the most important environmental health factor for any organization (32, 33).
Based on Table 5, several components were expressed as the main category, which shows the organization's faulty structure and unsanitary equipment. These cases are raised as an important challenge in most health and safety management studies of organizations and industries. Based on this, it is necessary to standardize the environment of the IRINN based on the concepts and guidelines of national environmental and professional health (24).
Intervening conditions facilitate or limit strategies, which include space, time, culture, economic status, technological status, profession, history, and individual biography, requiring basic educational interventions (34).
Based on the present research results (Table 6), the managers' actions regarding the health of the work environment (managerial behaviors) were identified as intervening conditions. The participants in this research believed that the managers of the IRINN, except for a few measures, do not have the desire to take basic health measures in the working environment. The most important measures needed in this field are proper cleaning, air conditioning, periodic health examinations, disinfecting the environment, and distributing sanitary items. Considering that the component of intervening conditions outlines how to design and manage the organization's processes to improve the main idea, it is necessary to explain the concept of workplace health in the organization's policy and strategy (35).
According to Table 7, the premeditated strategies in this study are measured, and purposeful actions are presented to solve problems and issues (15). In this research, the evaluation of the development of workplace health is expressed as strategies of action and interaction, which includes four subcategories: intangible inspection, outsourcing of evaluations, sending the health and safety team to the workplace, and surveying and field investigation.
According to scientific sources, invisible control and inspection increase the possibility of fact-checking, while its results are closer to reality. A clear example is health and safety inspections by the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Labor.
Outsourcing the evaluation and use of health evaluators of health centers are also useful for control and, as a result, better performance in the field of workplace health offices. This will improve the work environment. This sub-category can be done in coordination with the health centers to dispatch the health team to the workplace to assess the employees' health and the working environment periodically.
Based on scientific documentation, management should try to attract external and governmental resources and facilities and use information technologies to improve environmental health conditions. In this regard, if experienced and expert personnel and appropriate resources and facilities are used, and detailed planning is done to achieve organizational goals, it can lead to employee satisfaction and increase the health of society (23).
The highest frequency in open coding is related to the survey and field investigation subcategory. This case indicates that the employees are aware of the effective corrective strategies for the study. This case is mentioned in various studies as a factor to improve the organization's position. Therefore, using the existing potential and receiving effective opinions on the goal and its modification through field investigation and scientific documentation can significantly improve the existing situation.
According to the present study, the final consequences discussed in Table 8 were classified into two dimensions: individual and organizational. In its first stage, the individual effects and consequences of workplace health improve the physical health of the employees. In the next steps, it brings about the mental and psychological comfort of the employees and, as a result, creates job satisfaction and the emergence of creativity and talents and the development and progress of the organization (36).
The organizational consequences of improving the health of the work environment include reducing tension in the working environment, reducing human errors, increasing media production, increasing the organizational dependence among employees, growing the organization, and increasing productivity among employees. In various studies, these cases have been repeatedly stated as the final results of establishing the health system in organizations and industries (37).
Based on what was stated, achieving a suitable health condition in the workplace requires having a suitable model in which managers understand the workplace conditions better. They consider important and necessary components such as leadership, human resources, strategy, resources, and facilities and processes to establish proper health management of news networks and increase the productivity and satisfaction of employees (38).
According to the interviewed managers and editors, a news network's leadership and management component plays the most important role in improving the health of the work environment. According to scientific documentation, the senior manager of each organization, with detailed planning to provide better and more favorable services, explain health issues in organizational goals, outline the role of employees in achieving these goals, and provide the necessary facilities in line with the goals and environmental health strategies plays an important role in improving the health of the work environment of any organization (39, 40).
5.1. Research Limitations
• The shallow knowledge of the managers and the employees and their weak beliefs in health issues caused some in-depth non-cooperation in this field.
• Also, according to the type of this research and the need to refer to employees for conducting the interviews, the most important limitation was the possibility of conducting interviews as some employees couldn't join the interview due to their working time limits. It should be mentioned, however, that a huge effort was made to find and use the highest possible capacity of the IRINN's employees to complete this task of conducting in-depth interviews.
• Another limitation related to this research was the fear of interviewing and providing accurate information. Some employees did not participate in the interview as they believed that this may jeopardize their profession.
• Managers' lack of knowledge about workplace health took a long time for the interviewer to explain the contents and brief the experts.
5.2. Conclusions
The results of the present study showed that qualitative research based on the grounded theory method or foundation data theory is suitable for theorizing about the studied phenomenon, especially when the research literature on the subject does not have the necessary depth and richness. Therefore, it leads to the presentation of a new theory that has not been proposed in the research communities. Accordingly, the current study of the occupational health situation at the IRINN led to the identification of the main categories and subcategories affecting the current health status of this news channel. Hence, it was determined that this news channel needs fundamental reforms and improvements concerning its building, management structure, approaches, routine, and common functions.