1. Background
Brucellosis is the most widespread zoonosis worldwide and one of the most neglected zoonotic diseases (1). More than 170 countries and regions have reported cases of brucellosis, with the highest prevalence observed within Asia, the Middle East, Sub-Saharan Africa, and the Balkans (2-7). Brucellosis is now prevalent in 31 provinces, cities, and autonomous regions in the mainland (8, 9). Moreover, obvious agglomeration has occurred, predominantly in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Regions, the Shanxi Province, Hebei Province, Jilin Province, and Heilongjiang Province (10).
Hulunbuir is a historically epidemic area of brucellosis in Inner Mongolia. According to the 2008 - 2016 brucellosis epidemic analysis of the Hulunbuir City Center for disease control and prevention, the brucellosis infection rates amongst the occupational population fluctuate from 4.94% to 18.84% (11). Previous studies have shown that changes in the incidence of brucellosis are related to increased livestock breeding, lack of immunization, and frequent trading (12, 13). At present, large-scale farms (also termed centralized animal breeding operations) are growing rapidly, increasing the risk of disease transmission (14).
Propensity score matching (PSM) has been used with increasing frequency in the analyses of non-prespecified subgroups of randomized clinical trials, and in retrospective analyses of clinical trial data sets, registries, observational studies, electronic medical record analyses, and more (15). In addition, PSM can minimize potential duplication factors and selection bias (16). In this study, to explore the risk factors of brucellosis infection in Hulunbuir, Inner Mongolia, an Autonomous Region of China, propensity score matching methods were used to analyze the epidemic characteristics and causes of disease, and to explore the risk of brucellosis infections.
2. Objectives
In this study, the PSM method was used to analyze the epidemiological characteristics of brucellosis and explore the risk factors of brucellosis infection in Hulunbuir, Inner Mongolia, China.
3. Methods
3.1. Sampling Method
This study was performed from May 2018 to December 2018, using multi-stage stratified cluster random sampling and randomly selected residents of six villages in A and B banners of Hulunbuir. According to the Diagnostic Criteria for Brucellosis (WS269-2007), a questionnaire was designed according to the actual situation (17). In total, 880 serum samples and valid questionnaires were collected.
3.2. Diagnostic Criteria for Brucellosis
According to the original Ministry of Health Diagnostic Standards for Brucellosis (WS269-2007), epidemiological history, clinical signs, and laboratory examinations, those showing positivity following Tiger Red plate agglutination assessments underwent test tube agglutination tests (SAT). SAT titers ≥ 1:100 (++) showed positivity to brucellosis antibodies (18).
3.3. Experiment Related Equipment
Biological safety cabinets were purchased from Guangzhou Ruiyang BSCIIA2. Centrifuges were obtained from HKUST Innovation KDC40. Electrical thermostats were purchased from Tianjin test HHW21. Horizontal mixers were obtained from Guangzhou Qilin Bell TS1. Incubators were purchased from DNP-9162 Shanghai Jingqi Instrument Co., Ltd. Brucella Tiger Red Plate Agglutination Antigen tests were provided by China CDC. Brucella Test Tube Agglutination Antigen assays were provided by China CDC. All the instruments and equipment are made in China.
3.4. Analytical Method
Using the PSM nearest neighbor matching method, SAT-positive case groups and negative controls were obtained at a ratio of 1:3. The Matchlt package in R software was used for propensity score matching (19). A 1:3 matching design condition logistic regression model was used to perform single-factor and multi-factor analysis and to obtain a relationship between related behavioral factors and disease outcome. The odds ratio (OR) of each factor was compared to the outcome at a credibility interval of 95% (Confidence Interval, CI).
Epidata 13.0 software was used to establish the database and to enter the questionnaire. SAS 9.4 software was used for data analysis. Data were compared using a Two-sided test at an α value of 0.05. Quantitative data were shown as the mean ± SE. Comparisons between groups were performed using an analysis of variance. For qualitative data, descriptions were described in the form of frequencies (%). Chi-square test (including continuity correction and Fisher’s exact probability methods) was used for differential analysis (20).
4. Results
4.1. Survey Population
The survey contained 892 cases and collected a total of 880 valid questionnaires. The effective response rate was 98.65%. A total of 443 males (50.34%) and 437 females (49.66%) were surveyed with a balanced male-to-female ratio. The age range of the participants ranged from 18 to 83, with an average age of 51.32 ± 11.99 years. The highest proportion of middle-aged and elderly people individuals (aged 41 to 60) was 58.64 %. In addition, statistics are also made on the ethnicity and occupation of the participants. (Appendix 1 in Supplementary File).
4.2. Positive Rates of Test Tube Aggregation Tests
The test tube agglutination test was performed on positive individuals. There were 152 positive patients with an infection rate of 17.27%. According to regional distribution, the number of infected people in six village was the highest, with 63 infected at an infection rate of 26.69%. There were significant differences in the infection rates between villages (2 = 42.728, P < 0.01). The infection rates of males were significantly higher than females (22.57% Vs 11.90% respectively; 2 = 16.802, P < 0.01). Infection rates were highest in those aged 21-40 years old, with an infection rate of 26.32%. Compared with other occupations, the infection rate of herders is 57.14% (Appendix 2 in Supplementary File).
4.3. Health-Related Behaviors of Brucellosis Based on Tendency Score Matching
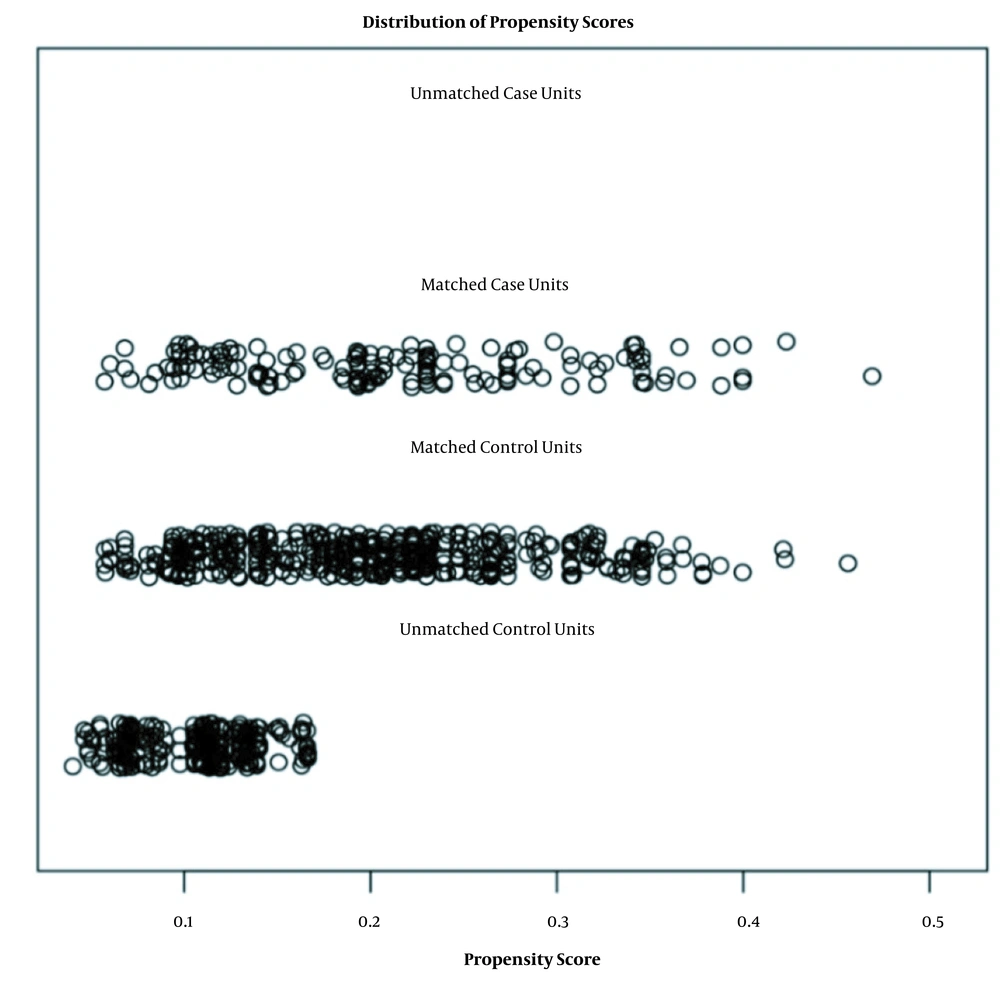
The Matchlt package in R software was used to score and match the 880 investigated individuals. Matching results were based on serum positivity. The variables included for matching analysis were village, sex, age group, nationality, occupation, marital status, educational level, economic situation, and living conditions. The nearest neighbor method was adopted, and the ratio was set to 1: 3. Caliper values were used as default values. A total of 608 respondents were selected, and a total of 152 test tube agglutination positive individuals were classified as the case group (Figure 1). Data distributions for unmatched cases were not observed. All 152 patients were successfully matched. The other 456 individuals were distributed similarly to the case group. Those not included in follow-up studies had lower scores (Figure 1). Through comparison of the average and differences of each item between the original and matched data, the closer average difference value was 0, and the equalization errors were smaller, indicating a good matching effect that met the requirements of the case/control group (Appendix 3 in Supplementary File).
4.4. Data Balance Tests Following Matching
A total of 608 sample populations were tested for balance. No significant differences were observed between the case group and control group (P = 0.001), including gender and age before matching (P = 0.126, P = 0.102). As such, the behavioral factors of the 608 sample populations were taken as the data source for follow-up case-controlled studies (Appendix 4 in Supplementary File).
4.5. Univariate Conditional Logistic Analysis of Health-Related Behaviors to SAT-Positive Tests
Both variables and dummy variables were included for regression analysis. X10-X24 represent health-related behavioral factors, which mainly include the basic information and living habits of the respondent (Appendix 5 in Supplementary File). The above X variables were included in the conditional logistic regression model for univariate analysis. SAT positivity was used for disease outcome assessments. Among the variables involved in tendency score matching, no significant differences were observed except for villages (P values ≥ 0.1). Among the related behavioral factors of the investigated population, the OR value of raising livestock within one year was the highest, meaning that the possibility of brucellosis when raising livestock was 3.523-fold higher than not raising livestock (Appendix 6 in Supplementary File).
4.6. Multivariate Conditional Logistic Regression Analysis of Health-Related Behaviors to SAT Positivity
Eight significantly related behaviors according to univariate analysis were included as independent variables in the conditional logistic regression model for multivariate analysis. These included raising livestock, cleaning pens, picking lambs, immunizing livestock, veterinary treatment, raising young lambs indoors, watering livestock manure, and sharing one well between humans and animals. The variables selected through stepwise regression included livestock raising, enclosure cleaning, and lambing. The risk of brucellosis amongst those who raised livestock within one year was 3.119-fold higher than those that did not (95% CI: 1.50 - 6.48, P = 0.0023). However, the infection risk of individuals that cleaned the pens frequently was 0.433-fold higher than those that did not clean the pens (95% CI: 0.44 - 0.99, P = 0.0470). The risk of brucellosis infection with frequent lambing behavior was 1.684-fold higher than occasional lambing behavior and 2.836-fold higher than without lambing behavior (95% CI: 1.18 - 2.41, P = 0.0044). The results are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
| Survey Content | Regression Coefficients | χ2 | P | OR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||
| Raising livestock | 1.18344 | 9.2247 | 0.0024 | 3.266 | 1.52 | 7.01 |
| Cleaning the pen | -0.35613 | 2.5235 | 0.1122 | 0.700 | 0.45 | 1.09 |
| Lamb | 0.67137 | 10.5666 | 0.0012 | 1.957 | 1.31 | 2.93 |
| Immunize livestock | -0.21217 | 1.5725 | 0.2099 | 0.809 | 0.58 | 1.13 |
| Veterinary treatment | -0.05861 | 0.1331 | 0.7153 | 0.943 | 0.69 | 1.29 |
| Raising young lambs in the bedroom | -0.20642 | 1.7363 | 0.1876 | 0.813 | 0.60 | 1.11 |
| Livestock manure irrigating the land | 0.07621 | 0.2651 | 0.6066 | 1.079 | 0.81 | 1.44 |
| People and animals sharing wells | -0.01383 | 0.0081 | 0.9285 | 0.986 | 0.73 | 1.33 |
| Survey Content | Regression Coefficients | χ2 | P | OR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||
| Raising Livestock | 1.13737 | 9.3004 | 0.0023 | 3.119 | 1.50 | 6.48 |
| Cleaning Pens | -0.41851 | 3.9451 | 0.0470 | 0.658 | 0.44 | 0.99 |
| Lamb | 0.52089 | 8.0920 | 0.0044 | 1.684 | 1.18 | 2.41 |
4.7. Correlation Analysis of Protective Behavior, Brucellosis Infection, and Education Level
To explore methods of how to reduce brucellosis infection when raising livestock, the wearing of protective clothing, protective masks, protective gloves, and the use of disinfectant were analyzed. The results showed that all protective measures could reduce SAT positivity and brucellosis infection rates. Failing to wear protective masks, gloves and disinfectants increased the risk of illness (OR = 1.400, 1.543, 1.440). The infection rates between wearing protective clothing and not wearing protective clothing were statistically significant (OR = 1.831, 95% CI: 1.013 - 3.310, P < 0.05) (Table 3). A correlation was also observed between protective behavior and educational level. At a higher educational level, the proportion of individuals wearing protective clothing increased. The P-values for the four protective measures were ≤ 0.05 (Table 4).
| Survey Content | Regression Coefficients | χ2 | P | OR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||
| Without protective clothing | 0.605 | 4.013 | 0.045 | 1.831 | 1.013 | 3.310 |
| Do not wear a protective mask | 0.337 | 1.901 | 0.168 | 1.400 | 0.868 | 2.259 |
| Do not wear protective gloves | 0.434 | 3.282 | 0.070 | 1.543 | 0.965 | 2.468 |
| No disinfectant | 0.365 | 2.386 | 0.122 | 1.440 | 0.907 | 2.287 |
| Survey Content | Elementary School and Below | Junior High School | High School and Above | P-Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protective clothing | < 0.0001 | |||
| Wear | 38 (52.78) | 29 (40.28) | 5 (6.94) | |
| Not wearing | 187 (75.40) | 57 (22.98) | 4 (1.61) | |
| Protective masks | 0.0017 | |||
| Wear | 77 (61.60) | 41 (32.80) | 7 (5.60) | |
| Not wearing | 148 (75.90) | 45 (23.08) | 2 (1.03) | |
| Protective gloves | 0.0060 | |||
| Wear | 90 (63.38) | 45 (31.69) | 7 (4.93) | |
| Not wearing | 135 (75.84) | 41 (23.03) | 2 (1.12) | |
| Disinfectant | < 0.0001 | |||
| Use | 95 (60.90) | 53 (34.97) | 8 (5.13) | |
| Not using | 130 (79.27) | 33 (20.12) | 1 (0.61) |
5. Discussion
Inner Mongolia Autonomous is an endemic area of animal and human brucellosis in China. Reports indicate that a total of 22,848 human brucellosis cases were reported in a certain area of Inner Mongolia from 2004 to 2019, with an average annual incidence of 87.2 per 100,000. Human brucellosis exhibited a significant increasing trend, and Brucella melitensis is the main pathogen responsible for human brucellosis in this region (21). For the prevention of brucellosis, it is necessary to frequently open windows for ventilation, avoid contact with animals that have not been quarantined, and strictly disinfect the environment where the animals are raised. On the other hand, effective vaccines can also effectively prevent the spread of brucellosis.
Of the 880 individuals included in the study, 152 were RBPT- and SAT-positive, with an infection rate of 17.27%. In key epidemic areas, the infection rates between villages significantly differed. Brucellosis prevention and control in most areas of Inner Mongolia has been successful, with the overall incidence declining. However, within the Hulunbuir Area, success should be based on effective intervention and local situation. The source of infection of brucellosis in these areas has not been eliminated or controlled. From the demographic characteristics of the survey data, the prevalence of brucellosis in males was significantly higher than that in women. The differences observed may be related to a higher number of males engaged in grazing and breeding (22).
In terms of age, the infection rates were the highest in young adults aged 21 to 40 years (30.26%). Although brucellosis showed no preference for age groups, those who were young and middle-aged (21 - 40 years) are the most able-bodied group and are mainly engaged in livestock breeding and slaughter, increasing the infection rate (23, 24). From the perspective of ethnicity and consistent with previous studies, the Mongolian population had the lowest infection rates (25-27). The highest infection rates of other ethnic minorities can be explained by living habits and breeding methods (28, 29). Amongst the survey population, herders and veterinarians were occupational groups with the highest infection rates. Although these data were related to sample size, the results were consistent with previous studies. Herders and veterinarians represent the key occupational groups (30).
In this study, each behavioral factor was taken as an independent variable and included for single and multi-factor conditional logistic regression analysis. Multi-classification data adopts a dummy variable method, and meaningful variables of single-factor analysis were added to the multi-factor model. In addition to raising livestock, the population in rural areas grows crops at home. The survey subjects used cattle and sheep dung as fertilizer to irrigate the land. The excrement of sick animals and contaminated water represents the major source of infection. The behavior of sharing wells between humans and animals increases the risk of brucellosis. For these individuals, brucellosis training and education should be strengthened. The Lembel Area belongs to the high-cold area. Outdoor enclosures in the winter increase the risk of disease and death of livestock.
The survey subjects had young lambs that were raised indoors. Living in the same room increases the risk of contracting brucellosis. In actual situations, it is impossible to restrict herders from raising livestock and not to treat them when sick. However, sharing wells with animals and raising young lambs indoors should be restricted and explained. These easily changeable behaviors can reduce the risk of brucellosis infection. The survey was performed on the protective behaviors of those raising livestock. Among the 320 respondents with breeding behaviors, regardless of the protective equipment used, the infection rate of the population was reduced. These data suggest that the major cause of brucellosis infection in this area is caused by direct contact between humans and livestock, and infections are transmitted through the air (31, 32). Considering the actual situation in pastoral areas, lamb deliveries were primarily performed through self-delivery in the absence of a strong awareness of protection.
5.1. Conclusions
In summary, this study reveals that A and B flags within Inner Mongolia Autonomous regions show a high incidence of brucellosis infection, and timely and effective control of the spread of infection is required (33). Research results show that feeding livestock, carrying lambs regularly, and raising livestock without protective measures all increase the risk of contracting brucellosis. This may strengthen preventive measures and provide healthy behavior training for key populations (34). Moreover, this may change the habits of local residents, reduce exposure, improve the knowledge of public health, and enhance self-protection awareness. Such practices may reduce the occurrence and spread of brucellosis within the region.