1. Background
Global epidemiology of cancer in the last decade shows that prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most prevalent malignancy in men, with almost 1,276,106 new cases and 358,989 deaths (1, 2). The prostate cancer incidence rate varies across the world, and it is lower in Africa and Asia than in developed countries. Several epidemiologic studies in Iran indicate that its incidence is low (9.11 per 100,000) (3). The mortality rate alters in various parts of the world; for example, in Central America, it has the highest mortality rate (10.7 per 100,000 people), and in South-Central Asia, it has the lowest mortality rate (3.3 per 100,000 people) (2). Accordingly, increasing awareness can help develop the recognition of risk factors associated with PCa and designing prevention strategies. Studies show that several risk factors such as age, race/ethnicity, family history, cigarette smoking history, diet, and obesity have an essential role in PCa development (4).
Recent studies indicate that viral infections can lead to prostatic inflammation, which, in turn, may result in PCa development (5). Oncogenic viruses are responsible for up to 20% of all cancer cases worldwide (6). Human polyomavirus BK virus (BKV), a small (40 nm diameter) non-enveloped virus with a double-stranded DNA genome belonging to the Polyomaviridae family (7), seems to be a drastic virus in PCa etiology (8). Based on serological and molecular methods, BKV is classified into four subtypes, with subtype I seeming to be predominant in the world with a percentage of 70% - 80% (9). Transmission occurs via the respiratory system or the oral-fecal route (10). Besides, BKV induces oncogenesis via the expression of large tumor antigen (LTAg) and small tumor antigen (stAg). Large tumor antigen affects cell cycle regulation and promotes cellular transformation through disruption of tumor suppressor p53 and pRB family function. Several studies indicated that BKV might play an undeniable role in several malignancies’ development, such as bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, and oropharyngeal cancer (11-13).
2. Objectives
Due to the potential oncogenicity and genitourinary tropism of BKV, it is essential to examine its prevalence in PCa patients. Limited studies have been conducted on the prevalence of BKV among PCa patients. In this study, we assessed the prevalence of BKV in cancerous and non-cancerous prostate tissue samples taken from prostate patients referred to Imam Khomeini Hospital in Ahvaz between 2015 and 2017.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
In this study, 100 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens, including 50 cancerous and 50 benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) as the control group, were collected at Imam Khomeini Hospital between 2015 and 2017. The tissues were selected based on tissue availability and pathology reports. The diagnosis of the tissue type (PCa or BPH) was done by an expert pathologist.
Inclusion criteria were formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens of cancerous patients with registered Gleason stage for the case group and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens of confirmed BPH embedded for the control group. Exclusion criteria included formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens with other prostatic complications, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens with prostatic inflammation, damaged formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens with unknown collecting date, and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostate tissue specimens with unknown data of Gleason stage.
3.2. Deparaffinization and DNA Extraction
The DNA was extracted from 10 sections (5 µm) of the 100 paraffin-embedded blocks, which were placed in a 1.5-mL microcentrifuge tube. Briefly, the first step of deparaffinization was performed by adding 500 µL of mineral oil to a 1.5 mL tube containing tissue sections and incubated at 95°C for 10 min to dissolve the wax. The tubes were centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 10 s, and the supernatant was removed. Then, 1 mL xylene was added to the tubes and incubated at room temperature for 60 min. After the vortex procedure was done, the tubes were centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for one minute, and the supernatant was removed. Then, 1 mL absolute ethanol (96%) was added to each tube, and the tubes were centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for one minute, and the supernatant was removed. This step was repeated with 1 mL ethanol 70% again. Finally, the tubes were incubated at 65°C on a heating block for 5 min until the ethanol was completely evaporated. In the final step, 200 µL of lysis buffer and 10 µL of proteinase K were added to the tubes and incubated at 55°C for 24 h. We used the High Pure Nucleic Acid kit (Roche Applied Science, Germany) for DNA extraction according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted DNA was stored at -20°C until use. The DNA purity and concentration of all extracted samples were measured using NanoDrop (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA).
3.3. Semi-Nested PCR
Semi-nested PCR was applied for all samples to detect BKV DNA. Following primers derived from the Vgp5 (LTAg) region were used. The sequences of the outer primers were 5’-AAGTCTTTAGGGTCTTCTAC-3’ and 5’-GTGCCAACCTATGGAACAGA-3’. The sequences of the inner primers were 5’-AAGTCTTTAGGGTCTTCTAC-3’ and 5’-GAGTCCTGGTGGAGTTCC-3’. The outer and inner primers were expected to produce 176 bp and 149 bp fragments, respectively. The first-round PCR amplifications were conducted in a final volume of 25 µL including 12.5 µL 2X master mix red (PCRBIO Taq Mix Red 2×), 25 pmol/µL of each primer (0.25 µL), 3 µL template DNA, and 9 µL DNase-free water. The PCR thermal program was as follows: for the first round, initial denaturation at 94°C for 4 min, followed by 30 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 50°C for 45 s, and 72°C for one minute, with a final extension at 72°C for six minutes. For the second round, PCR mix reaction components were 12.5 µL 2X master mix red (PCRBIO Taq Mix Red 2×), 25 pmol/µL of each primer (0.25 µL), 1 µL template DNA (from the previous step), and 11 µL DNase-free water. The thermal conditions in the second round were similar to those of the first round. The PCR products were then loaded into a 3% agarose gel and visualized under UV light.
3.4. Sequencing of Isolated BKV DNA
We sequenced five samples out of 51 positive samples of DNA randomly in Noor Gene, a medical genetic laboratory, Ahvaz, Iran. Then, we aligned the sequenced samples with the references gene of BKV (NC-001538.1) retrieved from GeneBank using online Blast (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
3.5. Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
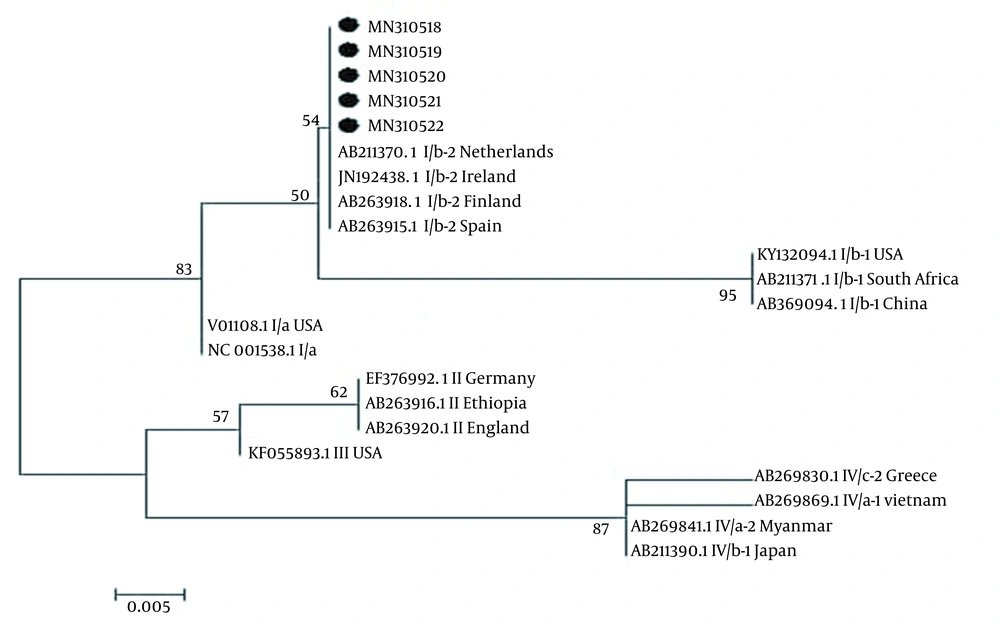
The partial nucleotide sequences of LTAg of the isolated BKV from Ahvaz were aligned with different BKV variants isolated from different regions of the world using the ClustalW algorithm method. The tree topology was built according to the maximum-likelihood method under the Kimura two-parameter substitution model with a Gamma site heterogeneity and invariant sites using MEGA 6.
3.6. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed with SPSS 22 package program (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and Fisher’s exact test was used for data analysis. A P-value below 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
The mean age of PCa patients and BPH patients was 69.38 ± 11.31 and 70.3 ± 10.51, respectively. The age range of PCa patients was between 41 and 91 years while it was between 52 and 90 years in BPH patients. The BKV DNA was found in 51% (51/100) of patients including 66% (33/50) of PCa patients and 36% (18/50) of BPH patients. There was a significant difference in the prevalence of BKV DNA between both groups of patients (P = 0.003). The characteristics of studied patients are summarized in Table 1. The patients’ age is presented in Table 2. There was no significant relationship between age and frequency of BKV DNA (P = 0.086). In the present study, the Gleason score of the tumor ranged from 5 to 10. The Gleason scores of patients with PCa are summarized in Table 3.
| Groups | No. (%) | BKV DNA Positive, No. (%) | BKV DNA Negative, No. (%) | P-Value | OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCa | 50 (100) | 33 (66) | 17 (34) | 0.003 | 3.45 (1.51 - 7.85) |
| BPH | 50 (100) | 18 (36) | 32 (64) |
Frequency of BKV DNA Among Groups (PCa and BPH)
| Age Groupsm y | No. (%) | BKV DNA Positive, No. (%) | BKV DNA Negative, No. (%) | P-Value | OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 - 60 | 21(100) | 11 (52.4) | 10(47.6) | 0.4 | 0.894 (0.329 - 2.43) |
| 60 - 80 | 58 (100) | 32 (55.2) | 26(44.8) | ||
| > 80 | 21 (100) | 8 (38.1) | 13(61.9) | ||
| Total | 100(100) | 51(51) | 49(49) |
Frequency of BKV DNA Among Different Age Groups of Patients (PCa and BPH)
| Gleason Score Classes | Number | BKV DNA Positive, No. (%) | BKV DNA Negative, No. (%) | P-Value | OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 7 | 5 (73.6) | 2 (26.4) | 0.094 | 1.78 (0.52 - 6.11) |
| 6 | 7 | 4 (57.14) | 3 (42.86) | ||
| 7 | 15 | 10 (66.66) | 5 (33.34) | ||
| 8 | 7 | 4 (57.14) | 3 (42.86) | ||
| 9 | 7 | 4 (57.14) | 3 (42.86) | ||
| 10 | 7 | 6 (85.7) | 1 (14.3) | ||
| Total | 50 | 33 (66) | 17 (34) |
Frequency of BKV DNA in Different Classes of Gleason Score
The BKV DNA was reported positive in the specimen with a Gleason score of 7 (30%) but not in PCa specimen (P = 0.094). (P = 0.094).
4.1. Results of Sequencing
The results of alignment sequencing of partial BKV DNA for five positive samples by NCBI and BK Virus database (https://hbvdb.ibcp.fr/HBVdb/HBVdbGenotype) revealed that the detected BKV DNA sequences belonged to subtype I (Figure 1). The nucleotide sequences were recorded to GenBank with accession numbers MN310518 to MN310522.
5. Discussion
Cancer is one of the major global health problems (14), and PCa, which comprises 7.1% of all cancers in men, is the most frequent cancer in men (2). In Iran, PCa is the third most frequent cancer in men and the sixth most prevalent cancer (15). Several shreds of evidence indicated that viral infection-induced inflammation of the prostate might increase the risk of PCa, so it is suggested that viruses may associate with prostate carcinogenesis (16). The carcinogenic effect of BKV is proven in rodent and animal models, and according to the research of IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer), BKV is “possibly carcinogenic to humans” (7). There is strong evidence that BKV is involved in PCa development. It is interesting to know that in two studies conducted by Das et al. (17) and Russo et al. (18), BKV LTAg expression was observed merely in cancerous prostate tissues but not in normal tissues. Additionally, immunohistochemistry analysis in Russo et al. (18) study indicated that in cancer cells, which were LTAg positive, p53 was located in the cytoplasm, while in LTAg-negative cells, p53 was located in the nucleus, emphasizing the role of BKV as a cofactor in the pathogenesis of PCa.
Das et al. declared that the BKV DNA was confirmed in 79% (11/14) of cancerous prostates but just in 27% (4/14) of non-prostate cancers, and LTAg expression was detectable in 47% (13/28) of cancerous prostates, and 14% (4/29) of non-prostate cancer subjects. Based on this study, there was a significant difference in the expression of BKV between normal and cancerous prostates (P = 0.008) (17). Zambrano et al. (19) demonstrated that the BKV DNA was presented in 25% (3/12) of prostate specimens by the PCR method and Lau et al. (20) confirmed the existence of BKV DNA in tumor cells in 7% (2/30) of prostate specimens using in situ hybridization (ISH). In four studies conducted in Italy, the BKV DNA was found in 23% (6/26) (21), 85% (22/26) (18), 32% (18/56) (22), and 44% (31/71) (23) of cancerous prostate tissues. Balis et al. (24) (Greece) revealed that the percentage of BKV DNA in PCa tissue was 19% (8/42). In a study by Akgul et al. (25) in Germany, the presence of BK virus was verified in only 1.17% (1/85) of PCa tissues.
Our results, which are parallel with previous studies, indicated that there are significant differences in the BKV DNA between positive cancerous prostate tissues and non-cancerous prostate tissues (P = 0.003). Our results are parallel with Mischitelli et al. (23), Delbue et al. (22), Russo et al. (18), and Das et al. (17). They indicated that the BKV DNA positivity was more frequent in malignant than in normal prostatic tissue. Whereas, some studies, in contrast, did not find a significant difference in BKV DNA positivity between malignant and benign tissue specimens (21, 26). Discrepancies among these studies may be due to different methods of virus detection, differences in sample size, type of samples (fresh or paraffin-embedded tissue samples), differences in the prevalence of the virus in different populations, and the ability of the virus to have latency and reactivation state (7).
In this study, the Gleason score of the tumor ranged from 5 to 10. Out of 33 cases who were positive for BKV DNA, the highest frequency of 30% BKV DNA positivity was found in cancerous prostate tissues with Gleason score 7, and the lowest frequency of BKV DNA was found in Gleason scores 6, 8, and 9 (4/33, 12%) (P = 0.094). However, this result contradicts the results of a study performed by Anzivino et al. (21) that indicated the highest frequency of viral positivity within Gleason scores 8 and 9. Considerably, Delbue et al. (22) reported that the highest frequency of viral positivity was observed in Gleason score 6 (12/18, 66%).
5.1. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study indicated the coexistence of BKV DNA in 51% (51/100) of tissue samples including 66% (33/50) of PCa tissues and 36% (18/50) of BPH tissue. Taghavi et al. (26) conducted a study in (Iran) on the BKV genome, and concluded that 28% (17/60) of patients with PCa and 15% (9/60) of patients with BPH were BKV-positive. According to the recent study, higher BKV infection was confirmed in PCa patients than in BPH patients (P = 0.003). The results of our study and other studies provide insight into further studies of BKV pathogenesis and its association with PCa. Moreover, plenty of investigations are necessary to understand the molecular mechanism underlying BKV oncogenic activities in PCa.