1. Background
Otomycosis, a superficial infection of the external ear induced by fungal pathogens, is a common condition in tropical and subtropical regions (1). The similarity of the clinical symptoms of otomycosis with those of other ear infections that cause the improper administration of antifungal drugs leads to resistance to antifungal drugs (2). Some Aspergillus and Candida species, which are the main causes of otomycosis, have an inherent resistance to several antifungal drugs (3). There is evidence regarding the isolation of the multidrug-resistant Candida species, namely Candida auris, one of the most threatening fungal species, from an external ear discharge (4).
Topical forms of clotrimazole, miconazole, bifonazole, ciclopirox olamine, tolnaftate, and amphotericin B, as well as triazoles, such as voriconazole, posaconazole, and itraconazole for oral administration are instances of accessible therapies for otomycosis (5, 6). Although the causative agents of otomycosis are commonly susceptible to most antifungal drugs in vivo and in vitro, treatment is a big challenge because frequent relapses and failures are observed, particularly in cases with complete removal of these organisms, which can act as a potential risk factor leading to the gradual increase of resistant species (7, 8). Thus, alternative antifungal agents with better activity and lower side effects can help to improve the controlling of these infections. Lately, the new imidazole agents, luliconazole and efinaconazole, were approved for the treatment of onychomycosis and dermatophytosis (9). Previous studies have also shown the potent activities of these antifungal agents against different strains of fungi (10-12).
2. Objectives
As far as we know, only limited data are available on the in vitro activities of these novel imidazoles, and triazoles against Aspergillus and Candida strains isolated from otomycosis (13). Therefore, the current research was performed to compare the in vitro activities of two novel antifungal agents, namely luliconazole (LUL) and efinaconazole (EFN), with those of amphotericin B (AMB), voriconazole (VRC), fluconazole (FLU), itraconazole (ITC), ketoconazole (KTO), clotrimazole (CLO), nystatin (NYS), terbinafine (TRB), and caspofungin (CAS) against Aspergillus and Candida strains isolated from otomycosis.
3. Methods
3.1. Fungal Isolates
A total of 91 clinical Aspergillus strains (Aspergillus tubingensis [n = 57], A. niger [n = 28], A. flavus [n = 5], and A. awamori [n = 1]) and 17 Candida strains (C. parapsilosis [n = 7], C. glabrata [n = 6], C. albicans [n = 3], and C. orthopsilosis [n = 1]) obtained from patients with otomycosis, in Jahrom, Iran. The genomic DNA of these fungal strains, previously extracted by the glass-bead phenol-chloroform (6). Candida isolates were identified at the species level based on molecular methods to obtain restriction digestion of the internal transcribed spacer rDNA region using the PCR‐restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method with the MspI restriction enzyme (14). The identification of the Aspergillus isolates was also accomplished by the amplification and sequencing of a fragment of the β-tubulin gene using beta-2A and beta-2B primers, respectively (15). Randomly selected isolates were reconfirmed by DNA sequencing of the ITS rDNA and β-tubulin regions. The obtained nucleotide sequences were deposited in GenBank under the accession numbers: MT348163- MT348208 and MT303056-MT303061.
3.2. In Vitro Antifungal Susceptibility Test
In vitro antifungal susceptibility of the yeast strains and mold isolates were tested based on the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) M27-A3/M60 and M38-A3, respectively (16-19). After the dilution of the antifungal drugs in the standard RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA.) with L-glutamine and without bicarbonate, they were buffered by 0.165 M-morpholinepropanesulfonic acid (MOPS) buffer (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and using NaOH, the acidity was adjusted to pH 7.0. Drug serial dilutions were then dispensed into 96-well microdilution trays at a concentration range of 0.016 - 16 µg/mL for ITC (Janssen Research Foundation, Beerse, Belgium), VRC (Pfizer, Central Research, Sandwich, United Kingdom), CLO (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), KTO (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), TRB (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), CAS (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), and AMB (Bristol-Myers-Squib, Woerden, The Netherlands). This concentration range was determined as 0.063 - 64 µg/mL for FLU (Pfizer) and NYS (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 0.001 - 1 μg/mL for LUL (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA, and EFN (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA).
The spectrophotometric adjustment of homogeneous freshly yeast or conidial suspensions that cultured on Sabouraud dextrose agar containing chloramphenicol (50 mg/L) (SDA, Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA) was accomplished at a wavelength of 530 nm to the optical densities (ODs) of 75 - 77% and 80 - 82% for yeasts and molds, respectively. The final inocula suspension was adjusted to 0.5 - 2.5 × 103 and 0.4 - 5 × 104 conidia/mL for yeasts and molds, respectively, in RPMI-1640 with L-glutamine and without sodium bicarbonate (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and buffered at a pH 7.0 with 0.165 MOPS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
Based on CLSI guidelines (CLSI M27-A3 and M27-S4 documents), Candida species were grown at 35°C, and microdilution plates were incubated at 35°C for 24h (if no growth was observed or growth was inadequate, incubation was extended to 48 h) and read visually (16). For Aspergillus species, plates were incubated at 35°C for 24 - 72h (18). After the incubation of the microdilution plates, they were visually examined to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values. Candida krusei (ATCC 6258), C. parapsilosis (ATCC 22019), and Paecilomyces variotii (ATCC 22319) were utilized as quality controls for each new series of MIC plates.
The determination of the MIC values of the yeasts and molds was performed based on the guidelines of the CLSI M27-A3/M60 and M38-A3, respectively (16-18). The geometric mean (GM) MICs, MIC50, MIC90, and MIC ranges were estimated for all antifungals. Susceptibility and resistance to antifungal drugs for Candida species isolates was evaluated based on CLSI-S4 and MIC value of various Aspergillus species and compared with epidemiological cutoff values (ECV) for in vitro susceptibility testing using the CLSI-M59 method (19). All tests were carried out in duplicate.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
The student’s t-test was utilized to determine the differences in the mean values using SPSS software (version 16.0) at a significance level of ≤ 0.05.
4. Results
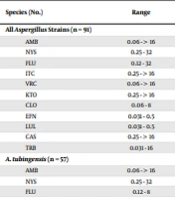
Tables 1 and 2 present the GM MIC, MIC range, MIC50, and when appropriate MIC90 of the studied antifungals. The LUL and EFN had the GM MICs of 0.098 and 0.109 μg/mL against all Aspergillus strains, respectively. These values were obtained to be 0.377, 0.777, 3.568, 3.695, 4.922, 8.311, 8.503, 0.146, and 13.739 μg/mL for VRC, CLO, ITC, FLU, AMB, KTO, CAS, TRB, and NYS, respectively. The comparison of the susceptibilities of the strains revealed a high MIC value for A. niger in all drugs, except for LUL, EFN, and TRB, which had low MICs. With regard to the Candida isolates, the GM MICs LUL, EFN, CAS, CLO, VRC, AMB, ITC, KTO, FLU, NYS, and TRB were calculated to be 0.133, 0.144, 194, 0.219, 0.475, 0.537, 0.655, 1.277, 4.905, 9.372, and 13.592 μg/mL, respectively (Table 2). A total of 7 (41.1%) and 4 (23.5%) Candida isolates were found to be susceptible-dose-dependent to FLU and VRC, respectively. Additionally, 6 (35.29%), 2 (11.7%), and 1 (5.88%) Candida isolates were resistant to FLU, CAS, and VRC, respectively (Table 2).
| Species (No.) | Range | MIC Parameters (µg/mL) | Ra | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-mean | MIC50 | MIC90 | |||
| All Aspergillus Strains (n = 91) | - | ||||
| AMB | 0.06 - > 16 | 4.922 | 16 | 32 | |
| NYS | 0.25 - 32 | 13.739 | 16 | 32 | |
| FLU | 0.12 - 32 | 3.695 | 4 | 16 | |
| ITC | 0.25 - > 16 | 3.568 | 4 | > 16 | |
| VRC | 0.06 - > 16 | 0.377 | 0.25 | 2 | |
| KTO | 0.25 - > 16 | 8.311 | 8 | > 16 | |
| CLO | 0.06 - 8 | 0.777 | 1 | 2 | |
| EFN | 0.031 - 0.5 | 0.109 | 0.06 | 0.25 | |
| LUL | 0.031 - 0.5 | 0.098 | 0.06 | 0.25 | |
| CAS | 0.25 - > 16 | 8.503 | > 16 | > 16 | |
| TRB | 0.031 - 16 | 0.146 | 0.12 | 1 | |
| A. tubingensis (n = 57) | - | ||||
| AMB | 0.06 - > 16 | 3.735 | 8 | > 16 | |
| NYS | 0.25 - 32 | 9.718 | 8 | 32 | |
| FLU | 0.12 - 8 | 2.477 | 4 | 8 | |
| ITC | 0.25 - > 16 | 3.374 | 2 | > 16 | |
| VRC | 0.06 - 2 | 0.276 | 0.25 | 1 | |
| KTO | 0.25 - > 16 | 7.171 | 8 | 16 | |
| CLO | 0.06 - 2 | 0.601 | 1 | 2 | |
| EFN | 0.06 - 0.5 | 0.127 | 0.12 | 0.25 | |
| LUL | 0.031 - 0.5 | 0.120 | 0.12 | 0.5 | |
| CAS | 0.25 - > 16 | 4.859 | 16 | > 16 | |
| TRB | 0.06 - 8 | 0.179 | 0.12 | 2 | |
| A. niger (n = 28) | |||||
| AMB | 0.12 - > 16 | 11.853 | 16 | > 16 | 27 |
| NYS | 8 - 32 | 23.776 | 32 | 32 | - |
| FLU | 4 - 32 | 10.247 | 8 | 16 | - |
| ITC | 1 - > 16 | 5.384 | 8 | > 16 | 18 |
| VRC | 0.25 - > 16 | 0.820 | 0.5 | 2 | 4 |
| KTO | 0.5 - > 16 | 11.888 | 16 | > 16 | - |
| CLO | 0.12 - 8 | 1.806 | 2 | 4 | - |
| EFN | 0.06 - 0.5 | 0.099 | 0.06 | 0.25 | - |
| LUL | 0.06 - 0.25 | 0.079 | 0.06 | 0.25 | - |
| CAS | 8 - > 16 | 26.251 | 16 | > 16 | 28 |
| TRB | 0.031 - 16 | 0.128 | 0.06 | 0.25 | - |
| A. flavus (n = 5) | |||||
| AMB | 0.25 - 16 | 0.758 | ND | ND | 0 |
| NYS | 16 - 32 | 27.858 | ND | ND | - |
| FLU | 0.25 - 8 | 1.149 | ND | ND | - |
| ITC | 0.25 - > 16 | 0.871 | ND | ND | 1 |
| VRC | 0.06 - 0.5 | 0.186 | ND | ND | 0 |
| KTO | 2 - > 16 | 6.063 | ND | ND | - |
| CLO | 0.06 - 2 | 0.214 | ND | ND | - |
| EFN | 0.06 - 0.031 | 0.035 | ND | ND | - |
| LUL | 0.031 | 0.031 | ND | ND | - |
| CAS | 0.25 - > 16 | 6.964 | ND | ND | 4 |
| TRB | 0.031 - 0.06 | 0.040 | ND | ND | - |
| A. awamori (n = 1) | - | ||||
| AMB | 8 | ND | ND | ND | |
| NYS | 32 | ND | ND | ND | |
| FLU | 4 | ND | ND | ND | |
| ITC | 1 | ND | ND | ND | |
| VRC | 0.25 | ND | ND | ND | |
| KTO | 8 | ND | ND | ND | |
| CLO | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | |
| EFN | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | |
| LUL | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | |
| CAS | > 16 | ND | ND | ND | |
| TRB | 0.031 | ND | ND | ND | |
Abbreviations: MIC50, concentration, at which 50% of the isolates were inhibited; MIC90, concentration, at which 90% of the isolates were inhibited; G-mean, geometric mean; FLU, fluconazole; VRC, voriconazole; ITC, itraconazole; LUL, luliconazole; EFN, efinaconazole; KTO, ketoconazole; NYS, nystatin; TRB, terbinafine; CLO, clotrimazole; AMB, amphotericin B; CAS, caspofungin
aR (resistant) based on epidemiological cutoff values for in vitro susceptibility testing of various Aspergillus spp. using the CLSI M59 method (19).
| Species (No.) | Range | MIC Parameters (µg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-mean | MIC50 | MIC90 | S | SDD | R | ||
| All Candida strains (n = 17) | |||||||
| AMB | 0.06 - 8 | 0.537 | 0.5 | 4 | - | - | - |
| NYS | 0.06 - 32 | 9.372 | 16 | 32 | - | - | - |
| FLU | 0.25 - 64 | 4.905 | 4 | 32 | 4 | 7 | 6 |
| ITC | 0.12 - 16 | 0.655 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - |
| VRC | 0.031 - > 16 | 0.475 | 0.25 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 |
| KTO | 0.5 - 8 | 1.277 | 1 | 4 | - | - | - |
| CLO | 0.031 - 4 | 0.219 | 0.25 | 0.5 | - | - | - |
| EFN | 0.06 - 1 | 0.144 | 0.06 | 0.5 | - | - | - |
| LUL | 0.06 - 0.5 | 0.133 | 0.06 | 0.5 | - | - | - |
| CAS | 0.031 - 4 | 0.194 | 0.12 | 2 | 15 | - | 2 |
| TRB | 0.25 - > 16 | 13.592 | >16 | >16 | - | - | - |
| C. parapsilosis (n = 7) | |||||||
| AMB | 0.06 - 8 | 0.403 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| NYS | 0.06 - 32 | 4.819 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| FLU | 0.25 - 64 | 2.972 | ND | ND | 4 | - | 3 |
| ITC | 0.12 - 16 | 0.244 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| VRC | 0.031 - 32 | 0.075 | ND | ND | 5 | 2 | - |
| KTO | 0.5 - 8 | 2.208 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CLO | 0.031 - 4 | 0.136 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| EFN | 0.06 - 1 | 0.247 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| LUL | 0.06 - 0.5 | 0.203 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CAS | 0.031 - 4 | 0.606 | ND | ND | 7 | - | - |
| TRB | 0.25 - > 16 | 6.563 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| C. glabrata (n = 6) | |||||||
| AMB | 0.5 - 8 | 0.794 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| NYS | 0.06 - 16 | 8.979 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| FLU | 4 - 64 | 4.489 | ND | ND | - | 6 | - |
| ITC | 0.12 | 2 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| VRC | 0.06 - 4 | 3.564 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| KTO | 0.5 - 1 | 0.561 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CLO | 0.031 - 4 | 0.397 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| EFN | 0.06 - 0.5 | 0.085 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| LUL | 0.06 - 0.25 | 0.076 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CAS | 0.031 - 2 | 0.069 | ND | ND | 5 | - | 1 |
| TRB | > 16 | 32 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| C. albicans (n = 3) | |||||||
| AMB | 0.06 - 8 | 1 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| NYS | 0.06 - 32 | 32 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| FLU | 0.25 - 64 | 10.079 | ND | ND | - | 1 | 2 |
| ITC | 0.12 - 16 | 1.243 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| VRC | 0.031 - 32 | 0.783 | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| KTO | 0.5 - 8 | 1.259 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CLO | 0.031 - 4 | 0.249 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| EFN | 0.06 - 1 | 0.097 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| LUL | 0.06 - 0.5 | 0.122 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CAS | 0.031 - 4 | 0.124 | ND | ND | 2 | - | 1 |
| TRB | 0.25 - > 16 | 12.699 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| C. orthopsilosis (n = 1) | |||||||
| AMB | 0.06 | 0.06 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| NYS | 32 | 32 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| FLU | 32 | 32 | ND | ND | - | - | 1 |
| ITC | 0.12 | 0.12 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| VRC | 0.25 | 0.25 | ND | ND | - | 1 | - |
| KTO | 4 | 4 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CLO | 0.12 | 0.12 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| EFN | 0.25 | 0.25 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| LUL | 0.25 | 0.25 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| CAS | 0.12 | 0.12 | ND | ND | 1 | - | - |
| TRB | 16 | 16 | ND | ND | - | - | - |
Abbreviations: G-mean, geometric mean; FLU, fluconazole; VRC, voriconazole; ITC, itraconazole; LUL, luliconazole; EFN, efinaconazole; KTO, ketoconazole; NYS, nystatin; TRB, terbinafine; CLO, clotrimazole; AMB, amphotericin B; CAS, caspofungin; R, resistant; S, susceptible; SDD, susceptible-dose dependent.
5. Discussion
The present research assessed the in vitro susceptibility testing of 108 molecularly well-characterized Aspergillus, and Candida isolates recovered from otomycosis patients to LUL, a novel imidazole, and EFN, a novel triazole, and comparing them with other antifungal drugs. The LUL and EFN are new imidazole and triazole agents, which their efficacy in the management of dermatophytosis and onychomycosis has been recently confirmed. The literature is indicative of the potent activities of these antifungals against dermatophytes, C. albicans, dematiaceous fungi, Malassezia, and azole-resistant and azole-susceptible A. fumigatus strains (7, 12, 20-22). However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no report regarding the resistance of these species to these drugs. As the results of the current research indicated, LUL (0.098 μg/mL) and EFN (0.109 μg/mL) had the lowest GM MICs against Aspergillus strains. The MIC ranges of LUL against A. niger and A. tubingensis isolates were 0.06 - 0.25 and 0.031 - 0.5 μg/mL, respectively. These values for EFN were 0.06 - 0.5 and 0.06 - 0.5 μg/mL, respectively (Table 1).
In a study performed by Hivary et al., the MICs of LUL against A. niger and A. tubingensis, as the predominant agents of otomycosis, were in the ranges of 0.00024 - 0.125 μg/mL and 0.00024 - 0.125 μg/mL, respectively (20). In addition, the MIC value presented by Tupaki-Sreepurna et al. demonstrated that EFN was more potent than other azoles against different non-dermatophytic fungi (21). The EFN MIC values was estimated at < 0.25 μg/mL for Aspergillus (12, 21, 23). Our results revealed low MIC values for EFN and LUL against Aspergillus, which is in line with other reports (12, 21, 23). In the current research, TRB had the GM MICs of 0.040, 0.128, and 0.179 μg/mL against A. flavus, A. niger, and A. tubingensis, respectively. The TRB (Lamisil) is a safe allylamine antifungal used both topically and orally for the management of infections, such as pityriasis versicolor, cutaneous candidiasis, and dermatophytosis (24). Based on a study by Mosquera et al., this drug had potent activities against Aspergillus species (25). In the present study, TRB had a lower GM MIC against A. flavus and A. niger compared to the values reported by Moore et al. (26). The VRC and CLO are other antifungal agents utilized for the treatment of Aspergillus-induced infections.
The susceptibility of Aspergillus species to these antifungals was also investigated in the present study. The comparison of VRC and CLO with ITC, FLU, KTO, and AMB revealed a lower GM MIC for VRC and CLO against Aspergillus species. The results of previous studies are indicative of the resistance of this species to VRC (27). Sutton et al. suggested VRC as an agent that can be used clinically for the treatment of refractory invasive aspergillosis and should be prioritized over the conventional AMB treatment (28). There are reports regarding the growing resistance of ITC to A. fumigatus (29). On the contrary, black aspergilli (MIC > 16 µg/mL) showed resistance to ITC in more than 50% of cases, without any clear mechanisms explaining this resistance (30). Our results showed that the common black aspergilli species (e.g., A. niger and A. tubingensis) showed higher ITC resistance.
Ototopical FLU is used for the management of otomycosis, especially against Aspergillus (31). The GM MICs of FLU against A. niger, A. tubingensis, and A. flavus were obtained to be 10.2, 2.47, and 1.14 μg/mL, respectively (Table 1). Our results revealed FLU resistance in 6 isolates (35.29%), which is in line with other reports indicating in vitro FLU resistance (32). Evidence is suggestive of the higher susceptibility of A. niger and A. tubingensis accounting for mild to systemic aspergillosis to AMB under in vitro conditions. However, these cases undergo frequent relapses and failures in spite of using antifungal therapy; accordingly, their therapeutic values are challenging (33).
In the present study, AMB MICs ranged between 0.06 and > 16 μg/mL for Aspergillus species, which is similar to the results reported by Oakley et al., but in contrast to those obtained by Kaya et al. (34, 35). Among the tested antifungal agents, KTO, CAS, and NYS had higher GM MICs against Aspergillus species compared to other drugs. Our data showed that A. flavus was more susceptible to LUL and EFN than A. niger and A. tubingensis. Nevertheless, aspergilli recovered from the external auditory canal demonstrated higher susceptibility to LUL, EFN, and TRB. Therefore, these topical agents can be considered as effective treatments for aspergillosis. In this study, the susceptibility of Candida isolates recovered from otomycosis was tested for the eleven drugs. The LUL (GM = 0.133μg/mL) and EFN (GM = 0.144 μg/mL) had the lowest MICs for Candida isolates. The LUL and EFN have an unclear sensitivity, dose dependence, or resistance range because of the lack of an acceptable breakpoint for Candida species.
The GM MICs of LUL and EFN for C. glabrata were obtained to be 0.076 and 0.085 μg/mL, respectively. These values were 0.122 and 0.097 μg/mL for C. albicans and 0.203 and 0.247 μg/mL for C. parapsilosis, respectively. Our results revealed that C. glabrata had lower MICs for LUL and EFN than C. parapsilosis and C. albicans strains. Niwano et al. (36) and Koga et al. (37) were the first researchers reporting a very low MIC for LUL and EFN (MIC range: 0.031 - 0.13 and 0.031 - 0.25 µg/mL, respectively) against C. albicans. Niwano et al., comparing oral LUL and FLU in a murine model of systemic candidiasis, reported the lower efficacy of LUL compared to that of FLU (36, 38). In the current study, CAS had a GM MIC of 0.194 μg/mL against Candida species. The previous studies have also confirmed the potent in vitro activity of this drug against Candida strains (39). Based on our results, NYS and TRB had the highest MIC values against Candida isolates, which is consistent with the results reported in the literature (40). However, Candida isolates also showed resistance to FLU, VRC, and CAS.
5.1. Conclusions
Our findings revealed that LUL and EFN had the highest in vitro activities against Aspergillus (GM MICs of 0.098 and 0.109 μg/mL, respectively) and Candida (GM MICs of 0.133 and 0.144 μg/mL, respectively) strains. In most of the cases, the novel topical triazoles and imidazoles (EFN and LUL) appeared to show good antifungal activities. The findings of the present research could be useful in promoting the significance of antifungal susceptibility testing for appropriate treatment.