1. Introduction
It is almost the 3rd year of the Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic; first, the virus appeared in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, and has caused more massive critical outbreaks than prior severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) or Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) (1). Although it's been almost three years, it is yet to be known whether angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor expression or drugs used to suppress the infection resemble the multi-organ involvement of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (1, 2). SARS-CoV-2 progression depends on multiple factors, including the compromised immune system and underlying diseases (3, 4). Reactivation of opportunistic pathogens such as herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) and varicella zoster virus (VZV) secondary to immunosuppression associated with COVID-19 infection may worsen patients' prognosis (5, 6). In this case report, we present two COVID-19 cases with the manifestation of herpetic eye disease and their prognoses, one with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and one with diabetes.
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Case 1
A 61-year-old man was diagnosed with COVID-19 by real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (real-time qRT-PCR) and was managed with favipiravir, naproxen, dextromethorphan, and zinc plus. After six days, he presented to the general hospital of Arak province with dyspnea, dry cough, fever, weakness, diarrhea, and SpO2 < 90%. Other clinical manifestations are mentioned in Table 1. The patient reports a history of insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Laboratory tests on admission followed by a heart rate of 82 and positive C-reactive protein (CRP) (Table 2). A chest CT-scan revealed nearly 20% COVID-19 infection involvement in the lungs. The patient was admitted; 5,000-unit Vit D, serum N/S 1000 cc, IV (checking output and urination), and tab prednisolone 20 mg were administered daily. Subcutaneous injection of Amp ReciGen 44 mcg (12,000,000 IU) was considered every three days. The daily dose of prednisolone decreased to 10 mg after four days. By the 7th day of admission an improvement in respiratory symptoms and a rise in O2 saturation (without O2 mask 94); the only complaint was right eye redness and blurry vision. Ophthalmologist observed dendritic using slit-lamp, and HSV-1 infection was confirmed. The ophthalmologist confirmed herpetic eye disease. Using conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods, HSV-1 infection was confirmed (7). Other major ophthalmologic findings were pterygium, hyperemia, and conjunctivitis (Table 3).
| Variables | Case 1 | Case 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 61 | 54 |
| Gender | Male | Male |
| Hospitalization status | Inpatient | Inpatient |
| Blood pressure | No | Yes |
| Diabetes | Yes | No |
| CVD | No | No |
| Asthma | No | No |
| Allergy | No | No |
| Chronic kidney | Yes | No |
| Immune deficiency (HIV) | No | Yes |
| Malignancy | No | No |
| Fever | Yes | Yes |
| Skin rash | No | No |
| Diarrhea | Yes | No |
| Dyspnea | Yes | Yes |
| Headache | No | No |
| Muscle pain | Yes | No |
| Abdominal pain | No | No |
| Fatigue | Yes | Yes |
| Dry cough | Yes | Yes |
| Chills | No | No |
| Final patient condition | Discharge | Expire |
Abbreviation: CVD, cardiovascular disease.
| Laboratory Test | Case 1 | Case 2 |
|---|---|---|
| D-dimer | 210 ng/mL | 600 ng/mL |
| Platelet count | 322 103/μL | 101 103/μL |
| C-reactive protein | Positive | Positive |
| Vitamin D | 21 ng/mL | 32 ng/mL |
| White blood cell | 5.3 103/μL | 3 103/μL |
| Serum creatinine | 1.9 mg/dL | 1 mg/dL |
| Interleukin 6 | 4 pg/mL | 45 pg/mL |
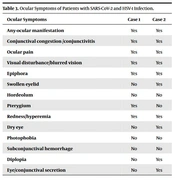
| Ocular Symptoms | Case 1 | Case 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Any-ocular manifestation | Yes | Yes |
| Conjunctival congestion /conjunctivitis | Yes | Yes |
| Ocular pain | Yes | Yes |
| Visual disturbance/blurred vision | Yes | Yes |
| Epiphora | Yes | Yes |
| Swollen eyelid | No | Yes |
| Hordeolum | No | No |
| Pterygium | Yes | No |
| Redness/hyperemia | Yes | Yes |
| Dry eye | No | Yes |
| Photophobia | No | No |
| Subconjunctival hemorrhage | No | No |
| Diplopia | No | Yes |
| Eye/conjunctival secretion | No | Yes |
2.2. Case 2
A 54-year-old man with a history of HIV and hypertension presented to the ED of the general hospital of Tehran province (related to Tehran University of Medical Sciences) with dyspnea, fever, general weakness, and drowsiness (Table 1). The patient was immediately admitted to ICU due to low SpO2 (under 80%) and 130 heart rate. Real-time PCR results were positive. The patient complained of blurred vision, ocular pain, and diplopia and was suspicious of mucormycosis or HSV-1 infection. (other ocular manifestations: conjunctivitis, epiphora, swollen eyelid, red dots on the lower eyelid) (Table 3). Further assessment and laboratory sampling for detecting HSV-1 infection using the PCR method were done (7). The ophthalmologic evaluation confirmed herpetic eye disease. After 24 hours, due to a drop in SpO2 saturation, deterioration of respiratory symptoms, high levels of IL-6 (45 pg/mL) and D-dimer 600 ng/mL (other laboratory results showed in Table 3), and loss of consciousness, the patient was intubated. Also, 200 mg of remdesivir as a loading dose (then 100 mg daily for 3 days) and 5000 units of heparin (IV, every six hours) were administered. The patient expired three days after intubation.
3. Discussion
As mentioned, SARS-CoV-2 may involve multiple organs through various mechanisms (1, 2). Regardless of multi-organ involvement, COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory symptoms and a higher level of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines due to compromised immune response and suppression secondary to “cytokine storm” or immunosuppressive therapy are more likely to have a poor prognosis (6, 8). So viral, bacterial, and fungal-associated superinfection should be considered, mentioning HSV-1 reactivation as an opportunistic pathogen (6, 7, 9, 10).
As we reported, both cases presented with mild to severe respiratory symptoms, both had medical histories of background disorders including diabetes and HIV, respectively and in both patients, HSV-1 infection caused ocular manifestations. The cytokine storm only occurred in the 2nd case (45 pg/dL). To date, diplopia has not been reported as a neurological symptom of COVID-19, and encephalitis has been rarely reported in patients with COVID-19 (11, 12); diplopia reported in the 2nd case may resemble HSV-1’s neuropathy, and a low level of consciousness may favor HSV-1 encephalitis. According to recent studies, the probability of HSV-1 infection’s acute hepatitis has also been reported (7, 13). Nonspecific cutaneous manifestations have been reported on COVID-19 infection, likely related to HSV-1 and VZV (14, 15). However, our study showed HSV-1 ocular manifestation among two immunocompromised COVID-19 cases. So, the recurrence of HSV-1 infection probably is related to immune responses during COVID-19 pathophysiology.