1. Background
Trichosporon asahii is a significant yeast-like fungal species found in the environment that can colonize various human organs. It can invade the human body through multiple routes, leading to infections and the development of certain diseases. With the widespread use of immunosuppressants, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and invasive treatments such as tumor radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and organ transplantation, reports of superficial and deep infections caused by T. asahii have become increasingly common (1-3). In vitro drug sensitivity testing and clinical evaluations have demonstrated that this fungus exhibits resistance to most first-line antifungal drugs, except azoles (4). Treating trichosporosis becomes particularly challenging in cases of disseminated and systemic deep infections (5), with mortality rates exceeding 77% (6).
Most studies on T. asahii have focused on understanding its drug resistance mechanisms and strategies to combat this resistance (7, 8). Trichosporon species show low sensitivity to commonly used preventive or empirical antifungal treatments. However, the combination of voriconazole or fluconazole with amphotericin B has demonstrated some therapeutic effectiveness, improving patient outcomes (9). Given the limited availability of effective antifungal drugs, gaining a better understanding of how Trichosporon evades the host's antifungal defenses is crucial for improving treatment (10).
Trichosporon asahii produces several virulence factors, including capsular polysaccharides, biofilms, and extracellular enzyme secretion (11, 12). Among these, capsular polysaccharides play a pivotal role in the fungus's ability to evade the host's immune system (13). These polysaccharides reduce the host's immune response, inhibit the antigen-presenting function of monocytes, and act as a protective barrier on the fungal cell wall, preventing effective macrophage phagocytosis and subsequent killing by the immune system (14). One key capsular polysaccharide, glucuronoxylomannan (GXM), is a high molecular weight antigenic polysaccharide. Studies on Cryptococcus neoformans have shown that GXM reduces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production in mouse glial cells, promoting apoptosis (15).
2. Objectives
This study aims to investigate the effect of GXM in T. asahii on the viability of macrophages and to examine its impact on macrophage energy metabolism by analyzing changes in ATP production under GXM intervention.
3. Methods
3.1. Source of Strain and Cells
The T. asahii strain was isolated, preserved, and provided by the Microbiology Department of Guangdong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Macrophages were derived from the THP-1 cell line through stimulation and differentiation, supplied by the Laboratory Department of Guangdong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. All experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines and approval of the Ethics Committee of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
3.2. Reagents
Alkaline peptone, absolute ethanol, isoamyl alcohol, chloroform, isopropanol, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), glucose, phenol, and sulfuric acid were all obtained as domestic pure analytical reagents. The CCK-8 kit and ATP test kit were procured from Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co., Ltd., while RPMI 1640 culture medium and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were sourced from Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
3.3. Working Fluid Configuration
To prepare the Sabouraud liquid culture medium, 2 g of peptone was dissolved in 180 mL of deionized water and the mixture was autoclaved. Simultaneously, 8 g of glucose was dissolved in 20 mL of deionized water to form the glucose solution, which was filtered using a 0.22 μm membrane and then injected into the sterilized peptone water. To make the 60% phenol solution, 0.6 mL of saturated phenol was combined with 0.4 mL of deionized water. For the 0.01 g/mL glucose solution, 0.01 g of anhydrous glucose was dissolved in 1 mL of deionized water. A 0.3% CTAB solution was prepared by dissolving 0.105 g of CTAB in 35 mL of deionized water. The CIA working solution was prepared by mixing chloroform and isoamyl alcohol in a 24:1 volume ratio. The ATP detection working solution was created by combining ATP detection reagent diluent and ATP detection reagent in a 100:1 volume ratio.
3.4. Isolation and Identification of Strains
The T. asahii strain was isolated from blood culture samples of hematological patients, cultivated as single colonies on Sabouraud medium, stained with cotton blue, and identified using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS, BIOMÉRIEUX, Vitek Ms, France). For identification through mass spectrometry, a colony was picked using a sterile pipette tip and evenly spread on the target plate. A drop of 1 μL formic acid was added, followed by 1 μL of the mass spectrometry matrix solution (VITEK MS-CHCA) after the formic acid dried. After complete drying, identification was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions and the SOP guidelines. Once identified, the strains were stored in a -80°C freezer after being cultured in bulk.
3.5. Recovery and Cultivation of Strains
The T. asahii strain was stored at -80°C. After being thawed at room temperature, it was inoculated onto a Sabouraud dextrose agar plate, with streaks drawn in different areas. The plate was incubated for two days at a constant temperature of 28°C. A single colony was picked with an inoculation loop and transferred to a conical flask containing 200 mL of pre-prepared Sabouraud liquid culture medium. The flask was placed in a 30°C incubator and shaken at 200 rpm/min for four to five days.
3.6. Preparation and Purification of Gucuronoxylomannan
3.6.1. Separation of Capsular Polysaccharide
The protocol for separating capsular polysaccharides was performed following a previously reported method (16). The fungus was shaken for five days and then transferred into a 50 mL centrifuge tube, which was centrifuged at 4200 rpm for 10 minutes. The supernatant was carefully extracted and filtered into a clean container using a sterile filter membrane to obtain the mixed polysaccharide solution. Absolute ethanol, equal to three times the volume of the mixed polysaccharide solution, was slowly added under continuous shaking, resulting in the appearance of white turbidity in the solution. The mixture was then refrigerated at -4°C overnight. The next day, white sediment formed along the inner walls of the container. To maximize polysaccharide yield, the sediment was resuspended by shaking. The mixture was then placed in a 50 mL centrifuge tube and centrifuged again at 4200 rpm for 5 minutes. The supernatant was discarded, and the process was repeated until the mixed polysaccharide solution was fully removed. After drying the precipitate, 5 mL of deionized water was added, and the mixture was stirred to dissolve the precipitate. The solution was stored overnight in a refrigerator at 4°C, resulting in a viscous mixture of GalXM and GXM polysaccharides.
3.6.2. Determination of Polysaccharide Concentration
The concentration of polysaccharides was determined using the phenol-sulfuric acid method (17). A standard curve was first established. A 0.01 g/mL glucose solution and a 60% phenol solution were prepared, and nine clean glass tubes were used for the experiment. The prepared solutions, along with concentrated sulfuric acid and the samples to be tested, were added to these tubes. Due to the heat generated by the reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, the tubes were placed on crushed ice immediately after adding the reagents and mixing thoroughly. Then, 2.5 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid was added perpendicularly to the nozzle. After allowing the reaction to proceed for 20 minutes, the solutions from each tube were transferred into three wells of a transparent 96-well plate, with 200 μL in each well.
The optical density (OD) of each well was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using a microplate reader. The average OD value for each tube was then calculated to generate the standard curve. The polysaccharide concentration of the tested samples was subsequently calculated using the linear regression equation derived from the standard curve.
3.6.3. Precipitation of Gucuronoxylomannan by Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide
At room temperature, 2 mol/L NaCl solution was added to the polysaccharide solution to reach a final concentration of 0.2 mol/L (18). The polysaccharide-NaCl mixture was then transferred to a clean container, and 0.3% CTAB solution was added slowly, in batches. The volume of the CTAB solution was three times that of the polysaccharide solution. After thorough mixing, white turbidity, indicating the formation of the CTAB-GXM complex, was observed in the solution. The mixture was left at room temperature overnight.
The following day, the solution was centrifuged at 4200 rpm for 5 minutes to collect the precipitate. To ensure complete precipitation, additional 0.3% CTAB solution was added dropwise to check for further precipitation in the supernatant. The precipitate was washed once with 10% ethanol and centrifuged again at 4200 rpm for 5 minutes. The supernatant was discarded, and the sediment was air-dried. Next, 10 mL of 1 mol/L NaCl solution was used to dissolve the precipitate, which was allowed to dissolve overnight at room temperature. The resulting solution was the GXM-CTAB-NaCl complex.
3.6.4. Purification of Gucuronoxylomannan by CIA
First, 2 mL of a chloroform and isoamyl alcohol solution (in a 24:1 ratio) was prepared and added to the GXM-CTAB-NaCl solution obtained earlier. The mixture was then shaken using a vortex oscillator for 10 minutes to ensure thorough mixing, resulting in a milky-white solution. This solution was centrifuged at 4200 rpm for 10 minutes, leading to the formation of three distinct layers. The upper aqueous phase contained GXM, while the lower organic phase was turbid, and an insoluble white substance was observed between the two layers. The upper aqueous phase was carefully transferred to a 50 mL centrifuge tube, avoiding the absorption of any other layers.
Next, three times the volume of isopropyl alcohol was added to the aqueous phase, resulting in visible white turbidity. The solution was then placed in a refrigerator at -30℃ overnight to ensure complete precipitation of the GXM. The following day, white sediment was observed on the inner wall of the centrifuge tube. The tube was centrifuged at 4℃ at 4200 rpm for 15 minutes. The supernatant was discarded, and the sediment was collected and air-dried. After air drying, the white precipitate transformed into a viscous transparent liquid.
Then, 2 mL of 1 × PBS was added to the liquid and dissolved overnight in a refrigerator at 4℃. After dissolution, the GXM solution was filtered through a sterile filter membrane. The concentration of GXM was determined using the phenol sulfuric acid method, and the remaining solution was stored in a refrigerator at -30℃ for future use.
3.7. Differentiation of THP-1 Cells into Macrophages
3.7.1. THP-1 Cell Culture
For cell resuscitation, the THP-1 cell solution, provided by Guangdong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine and stored in liquid nitrogen, was thawed by placing it into a 37℃ water bath. The vial was submerged just below the water's surface and gently shaken until fully thawed (within 1 minute). The thawed cell solution was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature, leaving the cells at the bottom of the tube. The pellet was resuspended in 1 mL of RPMI 1640 medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco, USA) supplemented with 10% FBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco, USA) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. The cell suspension was then added to a culture bottle containing 4 mL of fresh medium, mixed thoroughly, and placed in an incubator for cultivation. The culture medium was replaced every two days, and the cells were cultivated for seven days.
For cell passage, once the cells returned to normal growth conditions, passaging was performed at a 1:4 ratio. The RPMI 1640 medium was rewarmed in a 37℃ water bath. The culture bottle containing the cells was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes, and the supernatant was discarded. Next, 4 mL of fresh culture medium was added, and the cells were resuspended by gentle pipetting. The final cell suspension volume was 4 mL, with 1 mL used for cell passage, and the remaining 3 mL reserved for further use.
3.7.2. Phorbol Myristate Acetate-Stimulated Differentiation of Macrophages
First, a 1 mg/mL phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) stock solution was prepared as follows: 1 mg of PMA powder was dissolved in 1 mL of DMSO solution. This PMA stock solution was then diluted 100 times with DMSO to obtain a working concentration of 10 μg/mL. Next, 4.9 μL of the 10 μg/mL PMA solution was added to every 1 mL of the cell suspension, resulting in a final PMA concentration of 80 nmol/L. The corresponding volume of PMA solution was added to the 3 mL cell suspension and mixed thoroughly.
3.8. Detection of the Effect of Gucuronoxylomannan on THP-1 Cell Viability
After cell passage, the remaining cell suspension was measured using an automatic blood analyzer. The appropriate volume of PMA stimulator was then added to a transparent 96-well plate, and stimulation was conducted in an incubator for 16 hours. Since macrophages are adherent cells and THP-1 cells are suspension cells, after 16 hours of PMA stimulation, the suspension cells transformed into adherent cells, exhibiting stretched pseudopods. Following the stimulation, the PMA solution was discarded to stop the stimulation process. Next, 500 μg/mL of GXM medium was added, and the intervention times were set at 0 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 16 h, and 24 h, respectively. The control group received culture medium without GXM, with the same intervention time points. At the designated time, 10 μL of CCK8 working solution was added to each well, and the cells were incubated for 1 hour. A microplate reader (Tecan, Sunrise, Switzerland) was used to measure the ODat 450 nm. The OD450 value for each well was then calculated. This experiment was repeated three times.
3.9. Detection of Adenosine Triphosphate Content in Macrophages
An ATP content detection kit from Biyuntian was used to measure ATP levels. Different concentrations of ATP standard solution were prepared. As shown in Figure 1 , 100 µL of ATP detection working solution was added to each well of a transparent 96-well plate. The plate was then placed on ice for 5 minutes to ensure the complete consumption of background ATP, reducing potential errors. Afterward, 20 µL of each standard solution was added to the wells and thoroughly mixed. The ATP content was measured using the luminescence method of a microplate reader, and the standard curve was generated, allowing for the calculation of the formula.
Next, 100 µL of the cell fluid was added to each well of the 96-well plate, followed by the GXM intervention on macrophages. The intervention times were set at 0 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 16 h, and 24 h. The same time intervals were used for a blank control group without GXM. Upon completing the intervention, the cells were lysed with cell lysis buffer and left on ice for 5 minutes. Then, 20 µL of the supernatant was collected and analyzed as per the manufacturer's instructions. The test results were used to calculate the ATP content by applying the values to the linear regression equation obtained from the standard curve.
4. Results
4.1. Isolation and Identification of Strains
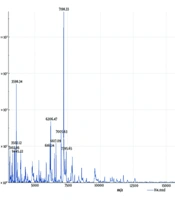
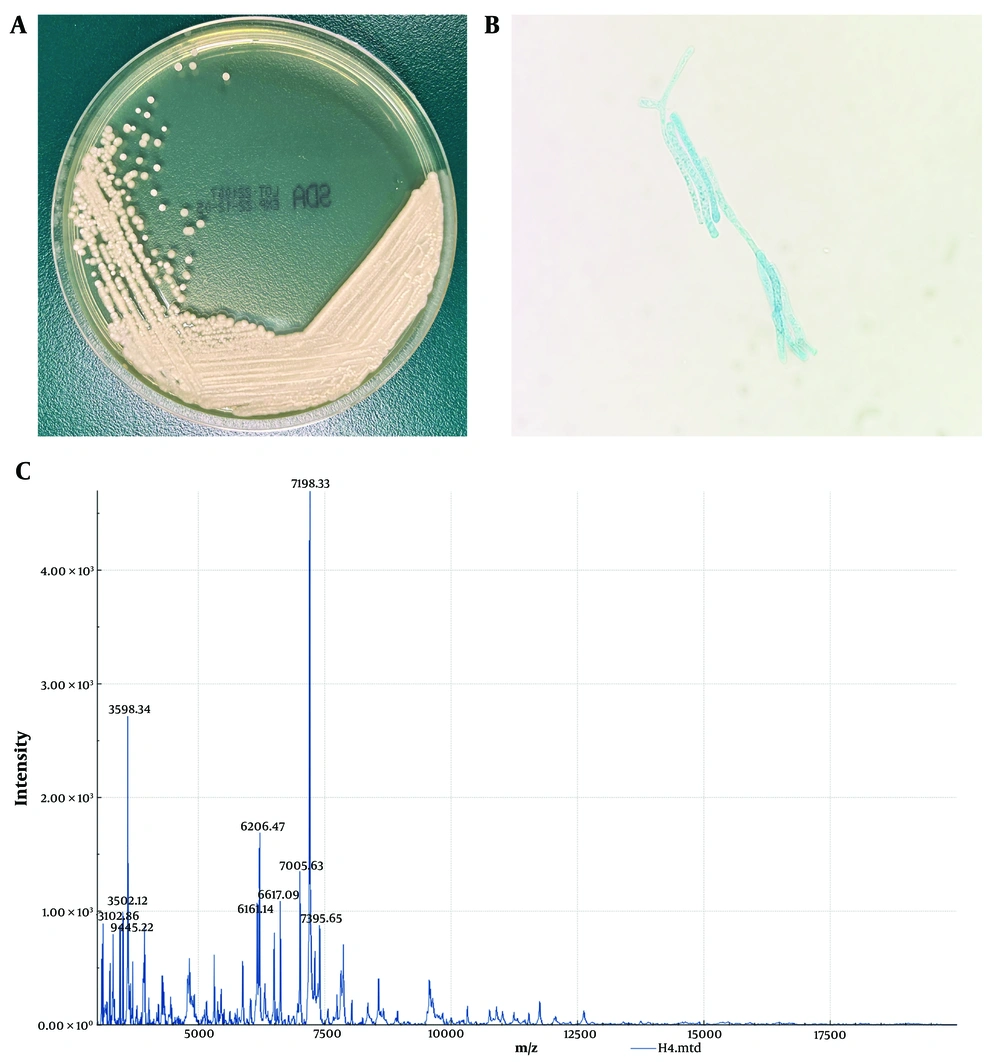
The isolated colonies from the Sabouraud medium plate appeared white, dusty, with a centrally dry colony and fine wrinkles (Figure 1A). The colony was smeared and stained with cotton blue. Under the microscope, rectangular arthrospores of varying lengths and round or oval spores with rounded ends were observed, some budding and others not (Figure 1B). The isolate was then sent to the Clinical Laboratory of Guangdong University Town Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine for identification via matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS), which confirmed the species as Trichosporon asahii (Figure 1C).
4.2. Determination of Gucuronoxylomannan Content
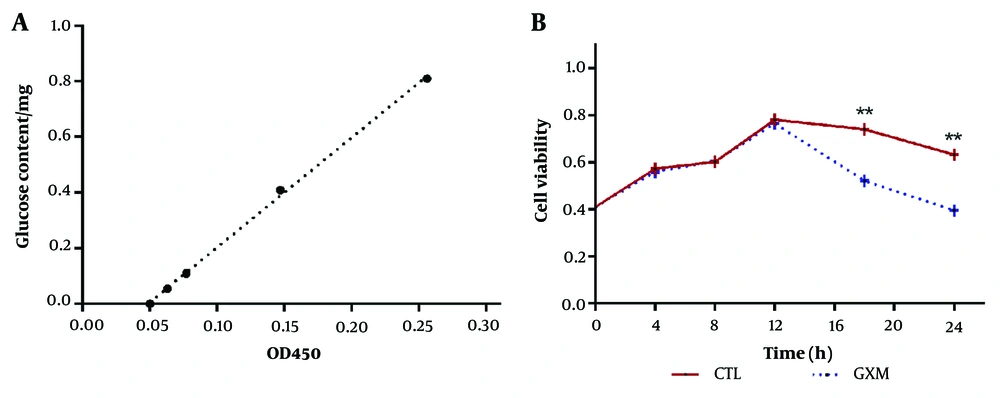
The phenol sulfuric acid method was used to measure the OD value of various glucose concentrations at a wavelength of 450 nm, and a standard curve was generated, as shown in Figure 2A. The average concentration of mixed polysaccharides was approximately 19.478 mg/mL, and with a mixed polysaccharide solution volume of 5 mL, about 97.39 mg of mixed polysaccharides were obtained. The average concentration of GXM was approximately 13.670 mg/mL, and with a GXM solution volume of 2 mL, around 27.34 mg of GXM were collected. The GXM yield was 28.1%.
4.3. Determination of Macrophage Cell Viability
A CCK-8 test kit was used to monitor changes in macrophage cell activity over time under GXM intervention, as shown in Figure 2B. During the first 12 hours, no significant differences were observed between the experimental group and the control group. However, after 12 hours, a noticeable divergence in cell viability between the two groups began to emerge. By 18 and 24 hours, the viability of macrophage cells in the GXM group was significantly lower than that of the control group (P < 0.01).
4.4. Determination of in Adenosine Triphosphate Content in Macrophages
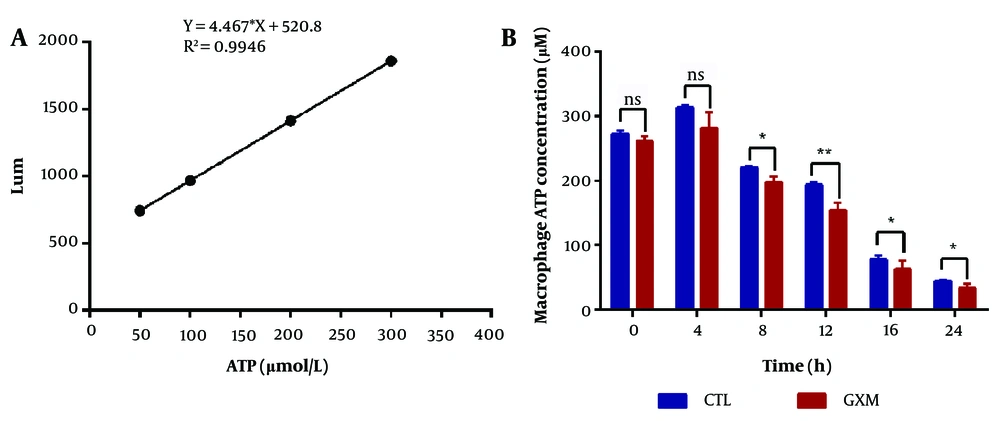
The standard curve was generated based on the Lum values of the tested samples, with the Lum value plotted on the Y-axis (ordinate) and ATP content on the X-axis (abscissa), as illustrated in Figure 3A. As shown in Figure 3B, the ATP production capacity of macrophages at 8, 12, 16, and 24 hours in the experimental group was significantly lower compared to the control group (P < 0.05).
5. Discussion
Monocyte macrophage-mediated innate immunity plays a crucial role in defending against fungal invasion. Research indicates that the phagocytosis of human peripheral blood monocytes and neutrophils on Trichosporon is significantly weaker compared to Candida albicans (19). Glucuronoxylomannan is present only in the cell wall of Trichosporon and the capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans (20, 21). Gucuronoxylomannan is a secreted polysaccharide that sheds into the culture medium as the fungi grow (22), and it serves as the primary pathogenic factor of capsular polysaccharides (23). The GXM of T. asahii shares the same antigenic determinant and anti-phagocytic properties as that of Cryptococcus neoformans. However, compared to C. neoformans GXM, T. asahii's GXM has a smaller diameter and carries a lower negative charge (13). Gucuronoxylomannan can influence macrophage immune phagocytosis by altering glucose metabolism (24).
In this study, we successfully extracted GXM from T. asahii using CTAB precipitation and CIA purification methods. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of GXM being extracted from T. asahii. Additionally, we investigated the effect of GXM on macrophage cell viability, revealing that after 12 hours, the viability of macrophage cells exposed to GXM was significantly lower than in the control group. This is the first report linking T. asahii GXM to macrophage cell viability.
Adenosine triphosphate is crucial for maintaining normal physiological functions, and changes in ATP levels affect many cellular functions. When C. neoformans infects a host, its GXM influences host cell energy metabolism, reducing host effector cell activity and allowing the pathogen to evade immune killing (15). Since T. asahii GXM shares the same antigenic determinant and anti-phagocytic properties as C. neoformans GXM, we hypothesized that T. asahii could also affect host cell energy metabolism through GXM, enabling it to evade immune responses.
The results of this experiment support our hypothesis: Under GXM intervention, macrophage ATP levels decreased over time and were consistently lower than in the control group. Gucuronoxylomannan appears to impair the ability of macrophages to produce ATP. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to report an association between T. asahii GXM and macrophage ATP content.
5.1. Conclusions
This preliminary study explored the effect of T. asahii on the energy metabolism of host cells. Our findings suggest that T. asahii can reduce immune cell killing by affecting the energy metabolism of macrophages through GXM, which may contribute to its pathogenicity. These findings provide potential new directions for the clinical treatment of T. asahii infections and offer theoretical support for future studies on the drug resistance mechanisms and pathogenesis of T. asahii.