1. Background
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an obligate aerobic, Gram-negative, non-fermenting, motile, and oxidase-positive bacterium that exists as a saprophyte in the environment and can be isolated from plants, animals, and humans. This microbe has a high potential for infection due to its minimal nutritional requirements and resilience to a variety of physical conditions (1). However, it is important to note that this bacterium is an opportunistic pathogen, primarily causing infections in cases of immune deficiency (2, 3). Pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause both acute and chronic infections in humans. In addition to respiratory infections, it is a major cause of nosocomial infections, including those of the urinary tract, burns, wounds, ears, eyes, and bloodstream (4). This bacterium causes extensive tissue damage and can invade the bloodstream by producing various cell-associated and extracellular virulence factors (5). These virulence factors generally include hemolysins, proteases, lipases, exotoxin A, cytotoxins, and pyocyanin. The bacterium's endotoxin can lead to sepsis and septic shock symptoms (6).
Genes involved in pyocyanin biosynthesis include the phzA1 and phzA2 operons and the phzM and phzS genes. Pyocyanin increases virulence by interfering with various cellular functions, aiding in evasion of host defense mechanisms, outcompeting other bacteria, and causing host damage (7). Alkaline protease (aprA), secreted by P. aeruginosa, leads to tissue necrosis and destruction of components of the host's immune system during infection, including proteins of the complement system, cytokines, and components of the extracellular matrix. It is especially pathogenic in corneal infections (8). Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces two types of hemolysins: The heat-sensitive phospholipase C (PLC) and the heat-resistant rhamnolipid. These highly toxic hemolysins play a critical role in tissue invasion, particularly in damaging respiratory and pulmonary epithelial cells (9, 10). The site of infection and nature of the bacteria’s action define the significance of virulence factors within the body. For instance, the bacterium can cause corneal ulcers, burn infections, and chronic pulmonary colonization using its protease factors (11).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits inherent resistance to several antimicrobial agents due to its low permeability in the outer membrane, the presence of efflux pumps, and antibiotic-inactivating enzymes (such as chromosomal beta-lactamases like cephalosporinase). Additionally, P. aeruginosa has a substantial ability to develop or acquire new antibiotic resistance mechanisms, likely due to its large genome size, adaptability, and genetic diversity (12). The proliferation of multi-drug-resistant P. aeruginosa (MDRPA) strains significantly limits antimicrobial drug options. Risk factors for MDRPA infections include prolonged hospitalization, prior antibiotic treatment, and immune system deficiency, with 27 to 72% of individuals at risk developing MDRPA over time (5). Infections caused by resistant strains are a global concern, as they are associated with a three-fold increase in mortality, a nine-fold increase in bacteremia, and a two-fold increase in hospital stay, all of which contribute to a significant rise in medical costs (12).
2. Objectives
With multidrug resistance in P. aeruginosa strains rapidly increasing and posing a serious public health threat, this study aimed to assess antibiotic resistance and identify the virulence genes (aprA, phzM, and phzS) and antibiotic resistance genes (blaGES, blaSPM, blaVIM) in P. aeruginosa strains isolated from hospitalized patients.
3. Methods
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Bacteria
In this cross-sectional study, 86 strains of P. aeruginosa were isolated from various samples, including blood, urine, wound exudates, sputum, and endotracheal tube specimens, from patients aged 1 month to 99 years who were hospitalized in different wards in Shiraz and Yasuj. The specimens were cultured for 24 hours at 37°C on blood agar and MacConkey agar media (Merck Co., Germany). The P. aeruginosa strains were identified based on Gram-staining, colony morphology, oxidase and catalase tests, motility, citrate utilization, hydrogen sulfide production, indole test, and pigment production. Molecular confirmation of the strains was conducted using the PCR method with an ExoA gene-specific primer (Table 1).
| Primer Sequence | Primer Name | Gene | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Amplicon Size, pb | Refrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-GACAACGCCCTCAGCATCACCAGC-3 | ExoA-F | ExoA | 72 | 396 | (13) |
| 5-CGCTGGCCCATTCGCTCCAGCGCT-3 | ExoA-R | ||||
| 5- ATGCGCTTCATTCACGCAC-3 | blaGES -F | blaGES | 54 | 863 | (14) |
| 5- CTATTTGTCCGTGCTCAGG-3 | blaGES -R | ||||
| 5- AAA ATC TGG GTA CGC AAA CG-3 | blaSPM -F | blaSPM | 52 | 271 | (15) |
| 5- ACA TTA TCC GCT GGA ACA GG -3 | blaSPM -R | ||||
| 5- GATGGTGTTTGGTCGCATA-3 | blaVIM -F | blaVIM | 52 | 390 | (16) |
| 5- CGAATGCGCAGCACCAG-3 | blaVIM -R | ||||
| 5- TGTCCAGCAATTCTCTTGC -3 | aprA-F | aprA | 51 | 1017 | (17) |
| 5- CGTTTTCCACGGTGACC -3 | aprA-R | ||||
| 5- TCGCCATGACCGATACGCTC-3 | phzS-F | phzS | 60 | 1752 | (18) |
| 5- ACAACCTGAGCCAGCCTTCC-3 | phzS -R | ||||
| 5- CGGCGAAGACTTCTACAGCT -3 | phzM-F | phzM | 58 | 330 | (19) |
| 5- AGGTAGATATCGCCGTTGGA-3 | phzM -R |
Nucleotide Sequences of Primers Used in the Study
3.2. Determination of Antibiotic Susceptibility
Following the CLSI guidelines, antimicrobial susceptibility testing was conducted using the disk diffusion method (20). The isolates' responses to antibiotics—ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 µg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 µg), piperacillin-tazobactam (PTZ, 100/10 µg), gentamicin (GM, 10 µg), cefepime (CPM, 30 µg), imipenem (IMP, 10 µg), tobramycin (TB, 10 µg), and meropenem (MEM, 10 µg) were assessed. P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 was used for quality control.
3.3. Metallobetalactamases Phenotypic Test
Test isolates were cultured on Mueller Hinton agar plates, following CLSI recommendations. A 0.5 M EDTA solution was prepared by dissolving 18.61 g of EDTA in 100 mL of distilled water and adjusting the pH to 8.0 using NaOH. This mixture was sterilized via autoclaving. Two 10 μg imipenem disks were placed on the MHA plate, with 10 μL of the EDTA solution added to one disk to achieve a concentration of 750 μg. After incubation in air at 35°C for 16 to 18 hours, the inhibition zones around the imipenem and imipenem-EDTA (IMP-EDTA) disks were compared. In the combined disk test, an increase in the inhibition zone of ≥ 7 mm with the imipenem-EDTA disk compared to the imipenem disk alone was interpreted as metallobetalactamase (MBL)-positive (21).
3.4. Modified Carbapenem Inactivation Method
In the modified carbapenem inactivation method (mCIM) test, a 10-μL loopful of an isolate from an overnight culture (grown on a blood agar plate) was emulsified in 2 mL of tryptic soy broth (TSB). A 10 μg meropenem disk was added to the tube, ensuring the disk was completely submerged in the suspension. The tube was then incubated for 4 hours ± 15 minutes at 35°C. Shortly before the end of the TSB-meropenem disk incubation, a 0.5 McFarland suspension of E. coli ATCC 25922 (a meropenem-susceptible strain) was prepared and inoculated onto a Mueller Hinton agar plate following standard disk diffusion procedures.
After incubation, the meropenem disk was removed from the TSB-meropenem suspension and placed on the Mueller Hinton agar plate previously inoculated with E. coli ATCC 25922. The plate was then incubated at 35°C for 18 - 24 hours. Following incubation, the zone of inhibition was measured and interpreted according to CLSI guidelines. A zone diameter of 6 to 15 mm, or the presence of pinpoint colonies within a 16 - 18 mm zone, indicated a carbapenemase-positive (mCIM-positive) result. A zone diameter of ≥ 19 mm was considered carbapenemase-negative (mCIM-negative). A carbapenemase-producing strain of P. aeruginosa served as the positive control, while P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 was used as the negative control (22).
3.5. Identification of Virulence Factors
Molecular PCR was utilized to detect the pathogenic genes (aprA, phzM, and phzS) and antibiotic resistance genes (blaGES, blaSPM, blaVIM) in the isolates. For this purpose, the strains were cultured on TSA medium (Merck Co., Germany) and incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. To extract bacterial DNA, 1.5 mL of the cultured bacterium in TSB was centrifuged for 5 minutes at 7000 g, after which the supernatant was discarded, and the resulting pellet was resuspended in 500 μL of deionized water. The microtubes were then heated at 95°C for 10 minutes, followed by centrifugation at 13,000 g for 5 minutes. The supernatant was stored at -20°C and used as the DNA sample in the PCR reaction.
The primers listed in Table 1 were used for the genes studied in P. aeruginosa isolates. Each PCR reaction cycle included an initial pre-denaturation step at 94°C, denaturation at 94°C, annealing at the optimal temperature for each primer, and a final extension step at 72°C for 5 minutes, over a total of 35 cycles (Table 1). The PCR products were electrophoresed using 1% agarose gel in a 0.5X TBE buffer on an electrophoresis device (Bio-Rad Co., USA) and analyzed under UV light. P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 was used as a positive control.
4. Results
In the current research study, 86 P. aeruginosa isolates were obtained from 52 (62.8%) male and 32 (37.2%) female patients. Among these, 39.5% of patients were in the 1 - 30-year age group, and 39.5% were bedridden in the ICU. Wound samples were the most common specimen source, with 71.9% of strains isolated from wound samples (Table 2). The results of disk diffusion antibiotic susceptibility testing are shown in Table 3. P. aeruginosa strains exhibited the highest resistance to imipenem, meropenem, and cefepime at 90.7%, 65.1%, and 61.6%, respectively. Additionally, resistance to ciprofloxacin was observed in 57% of strains. The lowest resistance was noted with piperacillin-tazobactam at 47.7%, and ceftazidime at 57%. The susceptibility profile of MDR strains is presented in Table 4. The results of MBL and mCIM phenotypic tests indicated that 82.6% (n = 71) of isolates were MBL-positive, and 74.4% (n = 64) were mCIM-positive (Table 5).
| Categories | Results |
|---|---|
| City | |
| Shiraz | 43 (50) |
| Yasuj | 43 (50) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 32 (37.2) |
| Male | 52 (62.8) |
| Hospital wards | |
| Burn | 24 (27.9) |
| ICU | 34 (39.5) |
| General internal medicine | 3 (3.5) |
| Outpatients | 7 (8.1) |
| Surgery | 8 (9.3) |
| Pediatric | 8 (9.3) |
| Nephrology | 1 (1.2) |
| NICU | 1 (1.2) |
| Sample | |
| Blood | 15 (17.4) |
| Wound | 32 (37.2) |
| Urine | 33 (38.4) |
| Stool | 2 (2.3) |
| Sputum | 4 (4.7) |
Patients Infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Demographic characteristics (N = 86) a
| Antibiotics | Resistance | Intermediate | Sensitive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceftazidime (30 μg) | 57 | 1.2 | 41.9 |
| Imipenem (10 μg) | 90.7 | 8.1 | 1.2 |
| Cefepim (5 μg) | 61.6 | 4.7 | 33.7 |
| Gentamicin (10 μg) | 58.1 | 3.5 | 38.4 |
| Ciprofloxacin (5 µg) | 57 | 5.8 | 37.2 |
| Piperacilin/tazobactam (100/10 µg) | 47.7 | 4.7 | 47.7 |
| Tobramycin (10 µg) | 61.6 | 1.2 | 37.2 |
| Meropenem(10 µg) | 65.1 | 5.8 | 29.1 |
Resistance of Strains to Different Antibiotics by Disk Diffusion Method (N = 86) a
| Number of Isolates | MDR + (N = 57, 66.3%) |
|---|---|
| City | |
| Shiraz | 28 (65.1) |
| Yasuj | 29 (67.4) |
| Hospital wards | |
| Burn | 19 (79.2) |
| ICU | 21 (61.8) |
| General internal medicine | 3 (100) |
| Outpatients | 2 (28.6) |
| Surgery | 4 (50) |
| Pediatric | 6 (75) |
| Nephrology | 1 (100) |
| NICU | 1 (100) |
| Sample | |
| Blood | 10 (66.7) |
| Wound | 23 (71.9) |
| Urine | 22 (66.7) |
| Stool | 1 (50) |
| Sputum | 1 (25) |
The Susceptibility Profile of MDR Pseudomonasaeruginosa Isolate (N = 86) a
| Categories | MBL + (N = 71, 82.6%) | mCIM + (N = 64, 74.4%) |
|---|---|---|
| City | ||
| Shiraz | 37 (86) | 35 (81.4) |
| Yasuj | 34 (79.1) | 29 (67.4) |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 25 (78.1) | 25 (78.1) |
| Male | 46 (85.2) | 39 (72.2) |
| Sample | ||
| Blood | 11 (73.3) | 13 (86.7) |
| Wound | 31 (96.9) | 27 (84.4) |
| Urine | 25 (75.8) | 19 (57.6) |
| Stool | 1 (50) | 2 (100) |
| Sputum | 3 (75) | 3 (75) |
The Metallobetalactamase and Modified Carbapenem Inactivation Method Phenotypic Tests Results in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates a
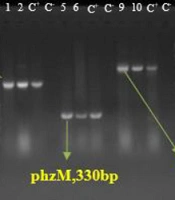
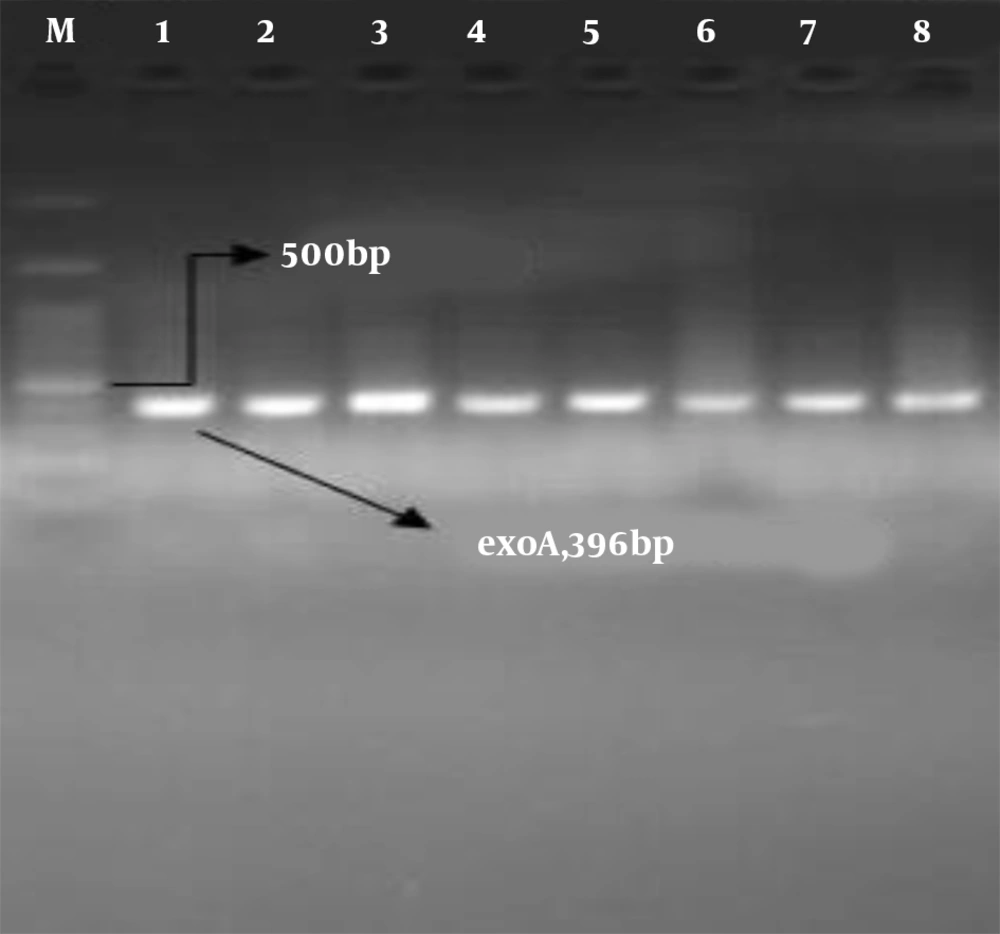
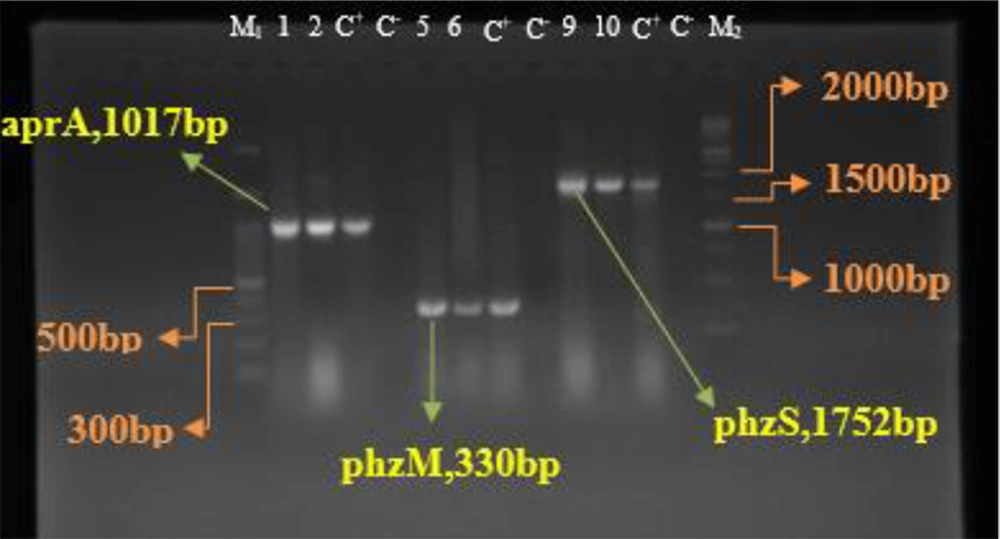
All isolates identified as P. aeruginosa by morphological and biochemical assays contained the exoA gene (Figure 1). The PCR results for the amplification of aprA, phzM, and phzS genes in all P. aeruginosa isolates showed the highest frequency for the aprA gene at 98.8%. The frequencies of the phzM and phzS genes were 96.5% and 91.9%, respectively (Figure 2). No blaGES, blaSPM, or blaVIM genes were detected in the isolates in this study.
5. Discussion
The proliferation of MDRPA strains has become a global concern (12). In fact, patients increasingly suffer from infections caused by MDR strains, leading to a rise in mortality worldwide. Treatment options for bacterial infections, some of which are serious and life-threatening, are becoming increasingly limited due to various drug resistance mechanisms. These include low cell wall permeability, a high genetic capacity for resistance mechanism expression, gene mutations regulating resistance genes, natural competence, and horizontal gene transfer via transposons, plasmids, and bacteriophages (1). A critical antibiotic resistance mechanism in P. aeruginosa strains is active efflux pumps, which facilitate the excretion of antibiotic molecules (23-25).
Metallobetalactamases hydrolyze all beta-lactams, including carbapenems, except monobactams like aztreonam. Infections caused by MBL-producing P. aeruginosa are associated with a high incidence of disease and mortality. Metallobetalactamase production in P. aeruginosa was first reported in Japan in 1991 and has since spread globally. Integrons, which are mobile gene cassettes, encode MBLs. Metallobetalactamase-producing strains are resistant to various antimicrobial agents, especially carbapenems in P. aeruginosa (25). Studies have reported contradictory findings on the drug resistance of P. aeruginosa strains, likely due to differences in the origin of the strains and increased resistance in recent years (26). In the present study, P. aeruginosa isolates showed the highest antibiotic resistance to meropenem and imipenem, similar to findings by K.G. Makedou et al., where there was also high resistance to these antibiotics (27). Conversely, in T.L. Pitt et al.'s study, ciprofloxacin resistance was recorded at 29.7%, significantly lower than in the current study (28). In contrast, imipenem resistance was 7.13% in Azargon et al.'s study, compared to 90.7% in the present study (29).
Patients with cystic fibrosis or cancer are particularly vulnerable to life-threatening infections caused by P. aeruginosa. Infections from this microorganism can impact various body systems, including the cardiovascular system, central nervous system, respiratory system, ears, eyes, urinary tract, skin, bones, and joints (30-32). The Quorum Sensing (QS) mechanism, a cell-to-cell communication system, regulates gene expression responsible for disease production in bacteria, including P. aeruginosa and Salmonella. This mechanism enables the recipient to respond, influencing transcription and translation processes (33). The elastase enzyme acts on various substrates, including connective tissue elements such as collagen, elastin, fibronectin, and laminin. The plcH gene encodes PLC, which hydrolyzes phospholipids. Rhamnolipid is a glycolipid biosurfactant containing rhamnose with a detergent-like structure that dissolves phospholipids in lung surfactants, facilitating degradation by PLC (34).
As different strains of P. aeruginosa cause various infections, evaluating the frequency of bacterial virulence factors is essential. In this study, the aprA gene was the most prevalent, observed in 98.8% of isolates, followed by the phzM gene at 96.5% and the phzS gene at 91.9%. Fakhkhari et al. also reported a high frequency of the aprA gene (98%) in their study (35). Similarly, Wang et al. reported a frequency of 99.5% for aprA (36). In a 2021 study, Bogiel et al. found that the phzM and phzS genes were present in 100% of samples (17). Another study by Bogiel et al. in 2022 recorded an 88.7% frequency for the aprA gene and 77.5% for phzM (18). In 2021, Sonbol et al. (5) also reported a 100% frequency for the phzM gene, aligning with the findings of this study. The distribution of pathogenic genes in P. aeruginosa populations may vary, enabling specific strains to better adapt to particular infection sites (37). In the present study, a relatively high percentage of virulence genes aprA, phzM, and phzS were observed in P. aeruginosa isolates. Given the pathogen's resistance to many antibiotics, clinicians should exercise caution in prescribing antibiotics, particularly for infections caused by this bacterium. Panahi et al.'s study in Iran detected the exoA, phzM, and phzS genes in 96%, 98%, and 92% of isolates, respectively, results that closely match those of this research (38).
In this study, the MBL and mCIM phenotypic tests revealed that 82.6% of isolates were MBL-positive, while 74.4% were mCIM-positive. In a study by Mirbagheri et al. in Mashhad, northeast Iran, 88.8% of imipenem-resistant isolates were phenotypically MBL producers (39). Another study in Ahvaz, southwest Iran, found that 90% of imipenem-resistant isolates were MBL producers (40). The higher frequency of MBL-producing isolates in these studies compared to our findings could be due to differences in sample isolates, the geographic distribution of MBL genes, and the methods used for phenotypic detection.
5.1. Conclusions
The results of this study indicate a relatively high prevalence of pathogenic genes in P.aeruginosa strains, reflecting the bacterium’s substantial capacity for colonization and pathogenicity. The observed antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa to multiple antibiotics, particularly carbapenems, may be attributed to factors such as the diversity of isolation sources, variations in research methodologies and sample types, sensitivity differences, and the overuse of antibiotics. Physicians should exercise caution when prescribing antibiotics, especially for infections caused by this bacterium. A long-term study spanning at least 10 to 20 years is recommended to gather comprehensive information on the trends of P. aeruginosa drug resistance and pathogenicity in Iran.