1. Background
The COVID-19 pandemic, which has caused millions of deaths, can be considered the most critical issue of the 21st century. The SARS-CoV-2 virus has infected countries worldwide in several waves, with multiple mutations in its genome and the emergence of different variants. This has resulted in more than 650 million infections and approximately seven million related deaths (1). Most patients are asymptomatic or experience mild to moderate symptoms, while a smaller proportion develop severe respiratory distress (about 20% of symptomatic patients) (2). Although classified as a respiratory virus, SARS-CoV-2 exhibits different and more aggressive behavior than other members of the coronavirus family, with a greater affinity for binding to the ACE2 receptor and affecting multiple organs and tissues (3).
Due to the presence of this receptor in various organs such as the heart, liver, lungs, kidneys, bladder, and pancreas, the effects of this virus can be observed in these tissues (4). The spread of infection, along with the unusual immune response known as the cytokine storm, has led researchers to attribute the multisystem disease to the erratic behavior of the virus (4). Liver tissue is frequently targeted by viral cytopathic effects, as several studies have shown that liver dysfunction is more common in patients with severe forms of COVID-19. Patients with liver dysfunction may also be at a higher risk of developing severe disease complications (4).
The reported incidence of liver injuries caused by the virus ranges from 14.8% to 53% (5). Therefore, evaluating liver function through various tests can be helpful in managing the disease and optimizing treatment outcomes for these patients. Common tests for assessing liver function include measuring liver enzymes such as aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin, and albumin. Abnormalities in liver function tests (LFTs) are more common and severe in intensive care unit (ICU) patients compared to those with mild to moderate disease (6).
Clinical observations have shown that in the majority of COVID-19 patients with abnormal LFTs, the abnormalities are transient, and patients recover without specific treatment. Therefore, for practical purposes, it may be useful to categorize liver involvement into two types (4). Type 1 injury refers to mild abnormalities in LFTs, which could be a non-specific reaction to the general inflammation caused by SARS-CoV-2. Type 2 injury, on the other hand, is considered a true liver injury that may require clinical management. Patients with type 2 injury typically present with ALT or AST levels that are three or more times the upper limit of normal (ULN), or total bilirubin levels that are two or more times the ULN (6, 7). Given that the liver is the main organ of detoxification, maintaining optimal liver function through all available treatment methods is essential for the treatment of COVID-19. Abnormal liver function requires clinical evaluation (8). As of the time of data collection for this study, Iran has experienced five waves of COVID-19, most of which were caused by different variants of SARS-CoV-2. The impact of specific variants on the severity of liver disease has yet to be determined through comparative-analytical assessments of LFTs across different waves.
2. Objectives
This study aimed to identify alterations in liver function parameters during the first to fifth waves of COVID-19 and compare them with demographic and clinical outcomes among patients in each wave in Yazd City, Iran.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Population and Sample Size
This descriptive, cross-sectional study targeted 1501 adult patients with a confirmed RT-PCR diagnosis of COVID-19, based on WHO criteria (9). These patients were admitted to Shahid Sadoughi Hospital in Yazd, Iran, between November 20, 2019, and November 20, 2021. This period corresponded to the first through the fifth waves of SARS-CoV-2 infection at our institution (Figure 1). The study aimed to examine the alterations in LFTs across the waves and their association with sex, age, and in-hospital outcomes. Patient information used in this study was recorded in the hospital’s health information systems (HIS). Data were collected in an Excel file format from November 20, 2019, to November 20, 2021. Liver function tests were examined at the time of admission, and the number of hospitalized patients per wave was 300.
3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Patients admitted to Shahid Sadoughi Hospital in Yazd from November 20, 2019, to November 20, 2021, were included in the study. These patients were confirmed to have COVID-19 based on WHO criteria (4). Patients undergoing treatment during the study or taking medication, as well as those with a history of liver disorders, were excluded.
3.3. Data Collection
Demographic characteristics (age, sex), pandemic wave, AST, ALT, ALP, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, albumin, and in-hospital outcome data were extracted from the Excel file. The units and reference values of the investigated liver function parameters are presented in Table 1. The data were cross-referenced for each patient, and cases with missing critical information were excluded.
| Parameter | Unit | Reference Value |
|---|---|---|
| AST-SGOT | U/L | Male < 37; female < 31 |
| ALT-SGPT | U/L | Male < 41; female < 31 |
| ALP | U/L | Child: 180 - 1200; adult: 64 - 306 |
| Total bilirubin | mg/dL | Adult: 0.1 - 1.2 |
| Direct bilirubin | mg/dL | ≤ 0.3 |
| Albumin | g/dL | 3.4 - 5.4 |
Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase.
3.4. Statistical Analysis
Patient characteristics were described using mean (SD)/median (IQR) or frequency (percentages) for numeric and categorical variables. Since the numeric variables did not follow a normal distribution, the Mann–Whitney U test and Kruskal–Wallis test were used to compare differences in age and liver parameters of patients across pandemic waves. The chi-square test was used to examine the association between categorical variables and in-hospital outcomes during the pandemic waves. The data were analyzed using SPSS 26 software with an alpha level of 0.05.
4. Results
Out of 1501 hospitalized patients during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, males (816, 54.3%) were more likely to be admitted compared to females (685, 45.7%). However, there was no significant difference between male and female patients across the pandemic waves (Table 1). Most of the patients were elderly, with a median age of 66 years. The mean age of infected individuals varied between pandemic waves. We observed an increase in age during the first and second waves, followed by a decrease during the third and fourth waves, and another increase during the fifth wave.
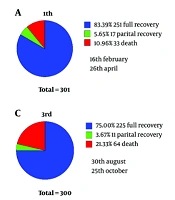
The median age of hospitalized patients was higher in the second wave and lower in the fourth wave compared to other waves (Table 1). Males were more affected than females in all pandemic waves; however, there was no significant relationship between sex and pandemic waves. In-hospital mortality increased significantly from the first to the third wave, decreased during the fourth wave, and increased again during the fifth wave. In the third and fourth waves, which had the highest and lowest number of deaths, respectively, the proportion of males was highest at 57% and lowest at 53% between the two waves (Table 2 and Figure 1).
| Variables | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | < 0.001 b | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 59.8 ± 24.86 | 65.83 ± 17.13 | 62.14 ± 24.19 | 56.24 ± 21.57 | 61.5 ± 19.75 | |
| Median (interquartile range) | 70 (35.25 - 82) | 67.5 (48 - 80) | 72 (38 - 81) | 59 (37 - 74) | 65 (46.75 - 77) | |
| Age (y) a | 0.012 b | |||||
| < 65 | 137 (45.5) | 150 (50) | 121 (40.3) | 163 (54.3) | 146 (48.7%) | |
| ≥ 65 | 164 (54.5) | 150 (50) | 179 (59.7) | 137 (45.7) | 154 (51.3) | |
| Gender a | 0.87 | |||||
| Male | 161 (53.6) | 160 (53.3) | 171 (57) | 159 (53) | 165 (55) | |
| Female | 140 (46.4) | 140 (46.7) | 129 (43) | 141 (47) | 135 (45) |
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
b P < 0.05.
The results of investigating the effect of different SARS-CoV-2 strains on liver parameters across different waves suggest varying behaviors of these strains. Among the strains, the dominant strain in waves one and three had the most significant impact on increasing liver parameters. The effects of different strains on liver parameters are summarized in Figure 2. Statistically, the highest and lowest significant differences were observed between waves one and three, and waves four and five, respectively. The Kruskal-Wallis test revealed significantly higher increases in the median levels of ALP, total bilirubin, and direct bilirubin in the first wave; AST and ALT in the third wave; and serum albumin in the second wave (P < 0.001). Among the liver parameters, a significant relationship was observed between albumin, SGPT (ALT), total bilirubin (bilirubin T), and direct bilirubin (bilirubin D) with the age of the patients Figure 3).
The results of the Mann-Whitney test showed that older hospitalized patients with COVID-19 experienced a significant decrease in serum albumin levels compared to younger patients (P < 0.0001) (Figure 3). SGPT levels were significantly higher in younger patients compared to older patients (P < 0.0001). Additionally, serum levels of total bilirubin (bilirubin T) and direct bilirubin (bilirubin D) were significantly increased in older patients compared to younger patients (P < 0.0001) (Figure 3). Furthermore, significantly more patients aged 65 and older (171, 78%) died compared to younger patients (48, 22%) (P < 0.001).
The results of the Mann-Whitney test showed that in men, the median values of SGOT (AST), SGPT (ALT), bilirubin T, and bilirubin D were significantly higher than in women (P < 0.001). In contrast, the mean values of albumin were higher in women than in men (P = 0.713). Moreover, more males (127, 58%) died compared to females (92, 42%), but there was no significant relationship (P > 0.05) (Table 3). The results of the Mann-Whitney test showed that the median albumin values in deceased patients were significantly lower compared to fully recovered and partially recovered patients (P < 0.0001). The median values of SGOT (AST), SGPT (ALT), ALP, bilirubin T, and bilirubin D in deceased patients were significantly higher compared to fully recovered and partially recovered patients (P ≤ 0.005) (Table 4).
| Parameters | Male (n = 816) | Female (n = 685) | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin | 3.97 ± 0.56 (3.9 - 0.8) | 3.98 ± 0.55 (3.9 - 0.8) | 0.713 |
| SGOT | 54.03 ± 66.2 (39 - 32) | 46.8 ± 94.9 (35 – 25) | < 0.0001 |
| SGPT | 48.02 ± 57.3 (33 - 31.0) | 38.6 ± 80.9 (26 - 23.5) | < 0.0001 |
| ALP | 214.4 ± 186.5 (181.5 - 90.0) | 199.1 ± 106.6 (181 - 88.0) | 0.543 |
| Bilirubin T | 0.88 ± 1.1 (0.7 - 0.3) | 0.71 ± 0.75 (0.6 - 0.3) | < 0.0001 |
| Bilirubin D | 0.28 ± 0.61 (0.2 - 0.2) | 0.21 ± 0.24 (0.2 - 0.1) | < 0.0001 |
Abbreviation: ALP, alkaline phosphatase.
a Values are expressed as mean ± SD (median IQR).
| Parameters | Full Recovery (n = 1220) | Partial Recovery (n = 62) | Death (n = 219) | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin | 4 ± 0.55 (4 - 0.8) | 4.1 ± 0.62 (4.2 - 0.6) | 3.7 ± 0.51 (3.7 - 0.70) | < 0.0001 |
| SGOT | 48.6 ± 80 (36 - 28.00) | 39 ± 26 (35 - 37) | 66 ± 87 (46 - 21.25) | <0.0001 |
| SGPT | 42 ± 67 (29 - 27.75) | 34 ± 33 (26 - 32) | 54 ± 83 (33 - 20.75) | 0.005 |
| ALP | 201 ± 139 (179 - 84.00) | 204 ± 92 (182.5 - 117) | 240 ± 233 (195 - 67.00) | 0.003 |
| Bilirubin T | 0.77 ± 0.96 (0.6 - 0.30) | 0.7 ± 0.5 (0.72 - 0.4) | 1 ± 1.3 (0.7 - 0.30) | < 0.0001 |
| Bilirubin D | 0.23 ± 0.5 (0.2 - 0.10) | 0.22 ± 0.17 (0.2 - 0.12) | 0.32 ± 0.5 (0.2 - 0.10) | < 0.0001 |
Abbreviation: ALP, alkaline phosphatase.
a Values are expressed as mean ± SD or (median- IQR).
5. Discussion
In this study, we investigated LFT findings in COVID-19 patients, considering the timeline of the disease. From November 2019 to September 2021, our country experienced five waves of the disease, each caused by different strains resulting from multiple mutations in the virus genome (10). Mutations in the viral genome can occur due to various factors, including viral replication enzymes, host enzymes, recombination events, spontaneous nucleic acid damage, and specific genetic elements responsible for the production of new variants (9). Although SARS-CoV-2 has fewer mutations compared to most RNA viruses due to its error-correcting enzyme, it still undergoes mutations to evade the immune response, develop drug resistance, and adapt to its host (9, 11). Several mutations, such as B.1.1.7 (alpha), B.1.351 (beta), P.1 (gamma), and B.1.617.2 (delta), have been reported as strains that spread from their original countries (e.g., the UK, South Africa, Brazil, and India) to other nations (12).
The results of our study revealed that the third wave of the disease, caused by the B.1.1.413 variant, which was initially observed in Western countries, Australia, and Canada (12), was the most severe among the five waves. It had the greatest impact on disease severity, liver function parameters, and mortality. In contrast, the fourth wave, associated with the B.1.36 variant (originating in China and spreading from west to east) (12), was the mildest wave, with minimal impact on patient outcomes. However, since the exact variant infecting each patient was not documented in this study, any conclusions regarding the impact of different variants on liver outcomes or the mechanisms underlying these differences will require more in-depth evaluations in future studies.
Although men were more affected than women in all waves, this gender disparity was more pronounced in the stronger waves (waves three and five). Most deaths occurred during waves three, two, and five, in that order. Several studies have reported that men are more susceptible to severe COVID-19 infection and adverse outcomes, including mortality (13, 14). This gender difference can be attributed to factors such as higher expression of the ACE2 enzyme in men, the influence of male hormones and the X chromosome, lifestyle choices like smoking and alcohol consumption, and women's tendency to adhere more strictly to hygiene practices to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection (14).
Age, a well-established risk factor in COVID-19, showed a statistically significant relationship with various parameters in our study. The direct association between increasing age and higher mortality rates in COVID-19 patients has been consistently observed in previous studies (15, 16). In our study, we found that the third wave, which had the highest average age among patients, also had the highest mortality rate. Conversely, the fourth wave had the lowest average age and the lowest mortality rate. Despite most patients being elderly in our study, the average age of patients in the last two waves showed a greater decrease compared to the first two waves. This decrease may reflect factors such as increased virus strength due to mutations, lower vaccination coverage among younger populations, reduced adherence to quarantine and health measures among younger individuals, and a higher susceptibility of younger people to the virus due to their healthier immune systems.
Albumin is a liver-produced protein, and a low level of albumin in serum (below 3.4 g/dL) can indicate liver or kidney dysfunction or other diseases (15, 16). Although albumin levels were within the normal range in our study across different waves, we observed a greater decrease in albumin levels during the first three waves compared to the last two waves (P < 0.0001). Furthermore, the second and third waves showed the greatest decrease in albumin levels, which also coincided with the highest mortality rates (P < 0.0001). Hypoalbuminemia (albumin below 35 grams per liter) has been reported in 74% of COVID-19 patients in previous studies, with even higher percentages observed in critically ill patients (15, 16). Similar to our findings, Xu et al. reported hypoalbuminemia in patients with severe COVID-19 infection and suggested it as a predictive factor for infection severity (15, 16). Reduced albumin synthesis by the liver due to viral proliferation and inhibition of albumin transport-binding sites by SARS-CoV-2 virions are possible explanations for the decreased albumin levels observed during COVID-19 infection.
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced from the breakdown of hemoglobin and is an indicator of liver blockage and inflammation when improperly processed by the liver. It is divided into direct and indirect types based on its binding to glucuronic acid (17). In our study, we investigated bilirubin as a marker for determining liver status in COVID-19 patients. We observed a relationship between increasing age and male gender with bilirubin levels, as well as an association between higher bilirubin levels and increased mortality rates. The first wave had the highest increase in total and direct bilirubin levels. The high expression of ACE2 receptors in bile duct epithelial cells, similar to type 2 alveolar cells, may explain the liver damage caused by the virus and the subsequent elevation of liver parameters such as bilirubin (18).
Although relatively few studies have been conducted on bilirubin levels in COVID-19 patients, a study by Paliogiannis, which conducted a pooled analysis of six studies, found that five of the studies indicated an increase in bilirubin levels in severe COVID-19 patients compared to those with an intermediate form of the disease (19). Another study by Liu investigated bilirubin levels as potential indicators of disease severity in COVID-19 patients and found that the death rate among patients with high bilirubin levels was 5.8%, compared to 0.6% among those with normal levels. These patients also tended to have more severe pneumonia and longer recovery durations. Additionally, the increase in conjugated bilirubin (CB) and the ratio of conjugated to unconjugated bilirubin (CB/UCB) were directly associated with disease severity, hospitalization duration, and mortality risk (20). Therefore, it is important to pay special attention to bilirubin levels in the clinical management of COVID-19 patients.
Aspartate aminotransferase and ALT are essential enzymes found in the heart, liver, kidneys, and muscles. Measuring the levels of these enzymes is crucial for assessing liver health (21). An increase in these parameters indicates liver damage, and in our study, we observed higher levels of these enzymes in men compared to women. Age did not have a significant effect on AST, but it had a significant inverse relationship with ALT. The third wave had the greatest impact on increasing the levels of these enzymes, and it was also associated with the highest mortality rate. Wang et al.'s meta-analysis study reported an increase in AST and ALT levels associated with patient mortality. Furthermore, the increase in these parameters can serve as a predictive tool for disease recurrence (22).
The increase in ALT and AST levels is observed in liver damage, which can be attributed to factors such as increased expression of ACE2 receptors in cholangiocytes, cytokine storms caused by an excessive immune response, drug toxicity, and liver failure in patients with multiple organ dysfunction. ACE2 expression is higher in cholangiocytes compared to liver cells, and these cells play a crucial role in liver regeneration and immune response (23, 24). Liver biopsies from deceased COVID-19 patients have previously shown moderate macrovesicular steatosis and mild globular and portal activity, indicating liver damage (25). Previous studies on SARS-CoV-2 patients also observed an increase in mitotic cells, along with eosinophilic bodies and ballooned liver cells. The exact cause of these liver injuries is not fully understood but could be attributed to COVID-19 infection, severe inflammatory responses, or drug-induced damage. Similar associations between SARS-CoV and MERS viruses and liver damage have been reported (23, 24).
Alkaline phosphatase is another enzyme that reflects liver or gallbladder function. Although it is also found in bones, intestines, pancreas, and kidneys, the liver is one of its main sources (26). In our study, we observed increased levels of ALP among COVID-19 patients, especially in the initial waves (the first and third waves). Although there was no significant relationship between ALP levels and demographic factors (age and sex) in this study, its levels were higher among deceased patients compared to those who had fully or partially recovered. Overall, ALP had weaker associations with other variables compared to the other factors investigated in this study. Hwaiz's study on liver enzymes in COVID-19 patients found that ALP had the lowest percentage increase among other enzymes, at 20.3% (27). Kumar's study also reported an increase in ALP levels with disease progression (28), which aligns with the findings of our study, where higher levels were observed among deceased individuals.
Our study faced limitations, such as not evaluating other markers of liver injury or inflammation, such as gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as the lack of data regarding the ethnicity, socioeconomic status, dietary habits, and alcohol use in the studied cases. These limitations were due to the retrospective nature of the study. Future research with a prospective study design could help provide a more comprehensive understanding of how multiple variables and confounding factors impact the effects of the SARS-CoV-2 virus on liver health. Moreover, future longitudinal investigations of variant-specific changes and how mutations in the viral agent influence liver outcomes and immune responses in COVID-19 patients could significantly contribute to a deeper understanding of the relationship between COVID-19 and liver injury.
5.1. Conclusions
The results of this study showed that the liver is one of the main targets of the coronavirus, and certain mutations of SARS-CoV-2 have increased its cytopathic effect, which has played a significant role in increasing patient mortality by elevating liver enzymes and parameters. Our descriptive study found that older patients and males were more likely to be hospitalized than females. Our findings showed that liver parameters differed between pandemic waves, suggesting varying behaviors of different coronavirus strains. Among these strains, the dominant strain in wave three had the greatest effect on increasing liver parameters, followed by waves one, two, five, and finally, four.