1. Background
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), are chronic relapsing-remitting conditions primarily driven by immune dysregulation, though their exact etiology remains unclear. In recent decades, there has been a marked increase in the incidence of IBD (1, 2). A meta-analysis of population-based studies recently assessed the global incidence and prevalence of IBD, revealing a rising trend worldwide, particularly in North America and Europe. Additionally, a long-term analysis over several decades showed a consistent increase in the incidence and prevalence of both CD and UC across various countries (3, 4).
When patients with IBD present with symptoms of active inflammation, infectious etiologies of bacterial, viral, or parasitic nature are routinely explored prior to the initiation of steroids or changes in other immunosuppressive treatments (5). Moreover, some authors have concluded that stool examination for infectious etiologies should be conducted with each IBD flare; however, this remains controversial (2, 6-8). Numerous studies have highlighted an elevated risk of Clostridium difficile infection in patients with active IBD, emphasizing the vulnerability of this population to such infections. However, despite the well-documented association between IBD and C. difficile, the burden of other commonly tested infectious agents in the context of active IBD remains poorly understood (1, 8, 9).
2. Objectives
This study aims to evaluate the yield of stool pathogen testing in IBD flares to clarify the role of infections and associated risk factors.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design and Setting
A retrospective review of medical records for patients admitted with an IBD flare, including UC, CD, and IBD unclassified (IBDU), was conducted at Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, between October 2018 and August 2019.
3.2. Patient Selection
A computer-generated list of patients diagnosed with UC, CD, or IBDU was used to identify potential cases. Manual chart reviews were performed to confirm that the admission was related to an IBD flare. Patients with unclear IBD diagnoses or those admitted for reasons other than a flare were excluded from the study.
3.3. Data Collection
The following variables were recorded during the chart review: Patient demographics, concurrent and previous IBD therapy, prior use of antibiotics, steroid use, presenting symptoms, vital signs, initial laboratory workup [including complete blood count (CBC) with white blood cell (WBC) differentials, C-reactive protein (CRP), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)], type of stool samples sent, endoscopic inpatient procedures, and endoscopic scores.
3.4. Stool Exam
Stool samples were collected and analyzed for the presence of C. difficile toxins A and B using the ARIES®C. difficile Assay. This assay employs Multi-Code® real-time PCR chemistry in conjunction with ARIES® Systems, which facilitate automated nucleic acid extraction, purification, and real-time PCR-based detection of target nucleic acid sequences. The assay specifically targets and detects the C. difficile toxin A gene (tcdA) and toxin B gene (tcdB), ensuring accurate identification of toxigenic C. difficile strains. For patients who did not respond to steroid treatment and underwent endoscopic evaluation, tissue samples were collected for histopathological analysis. The biopsy specimens were examined using histopathological techniques, including hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical staining for Cytomegalovirus (CMV) antigens to confirm viral presence. This comprehensive approach enabled the identification of characteristic cytopathic changes, such as enlarged cells with intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of CMV colitis.
3.5. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was conducted using the statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS) software. Chi-square tests were employed to assess the relationships between categorical variables, determining the statistical significance of associations between patient characteristics and outcomes.
4. Results
4.1. Demographics and Disease Characteristics
A total of 96 adult patients were included in this study, with a mean age of 34 years. Approximately half of the population were male (n = 51). Regarding disease classification, 43 participants (45%) were diagnosed with UC, 51 (53%) with CD, and 2 (2%) with inflammatory bowel disease-unclassified (IBD-U). The median disease duration was 9.5 years. In patients with UC, the distribution of disease was as follows: Proctitis was observed in 2 patients (5%), left-sided colitis in 18 patients (42%), and pancolitis in 23 patients (53%). Among those with CD, 11 patients (22%) had colonic involvement, 34 patients (67%) had ileocolonic disease, and 6 patients (11%) presented with small bowel disease. At the time of flare, around half of the population, 48 patients (50%), were on biologic therapy. Additionally, 34 patients (35%) were receiving steroids, while 17 patients (18%) were on immunomodulatory treatment.
4.2. Clostridium difficile Infection
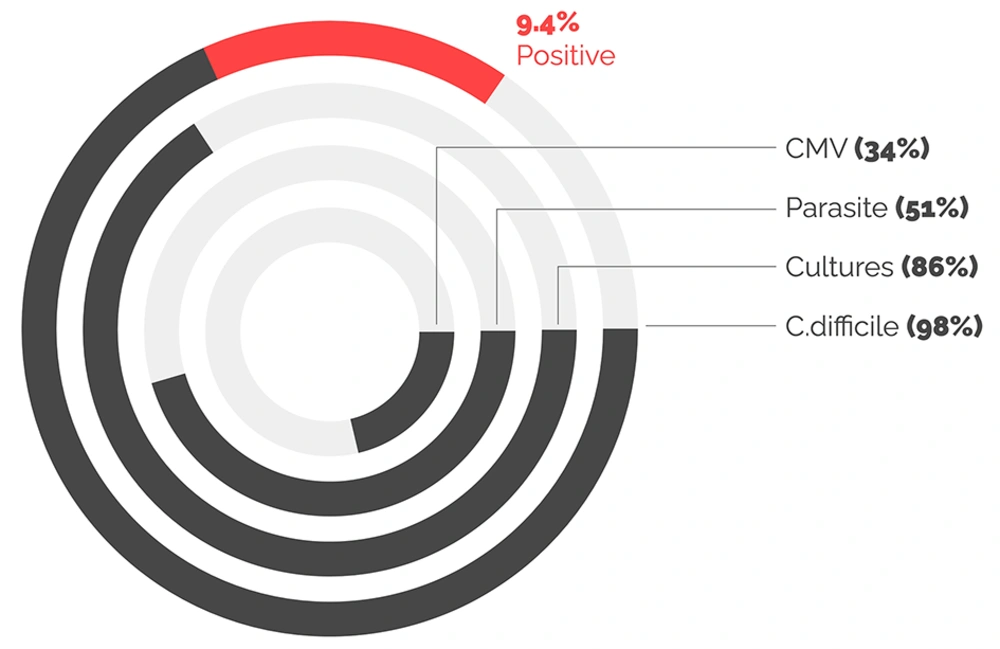
Testing for C. difficile was performed among 94 (98%) of the study participants, with 9 (9%) testing positive. Of those who tested positive, six patients were diagnosed with UC and three with CD. All results are illustrated in Figure 1.
4.3. Cytomegalovirus Infection Testing
Testing for stool cultures was performed in 83 (86%) of patients, while testing for ova and parasites was conducted in 49 (51%). Only 33 (34%) of patients underwent biopsies with CMV staining; 24 (74%) of these biopsies were from patients with UC. No stool cultures, parasite testing, or CMV testing yielded positive results in this population.
4.4. Associations with Clostridium difficile Infection
There was no significant association between disease phenotype, therapy (biologic, steroid, or immunomodulator), or smoking history and the risk of C. difficile infection. Neither clinical evaluation nor routine laboratory tests, including CRP levels, neutrophil, and eosinophil counts, were predictive of infectious causes. The presence of rectal bleeding was also not associated with positive C. difficile results. All results are depicted in Table 1.
| Risk Factor | Total Number | Positive Cases | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.65 | ||
| Male | 51 | 5 | |
| Female | 45 | 4 | |
| Disease type | 0.32 | ||
| UC | 42 | 6 | |
| CD | 51 | 3 | |
| IBD-Unclassified | 2 | 0 | |
| Under biologic therapy | 48 | 5 | 0.09 |
| Under steroid therapy | 34 | 2 | 0.76 |
| Under immunomodulator therapy | 17 | 1 | 0.54 |
| Prior antibiotic use | 9 | 2 | 0.20 |
| Smoking history | 40 | 3 | 0.55 |
| CRP level | 96 | 9 | 0.71 |
| Elevated neutrophil count | 96 | 7 | 0.83 |
| Elevated eosinophil count | 96 | 8 | 0.79 |
| Rectal bleeding | 96 | 5 | 0.21 |
Association Between Different Risk Factors and Clostridium difficile Infection
5. Discussion
The association between IBD flare-ups and infectious colitis has been documented previously. It is common for the symptoms of infectious colitis to mimic those of an IBD flare. As a result, it has become standard clinical practice to perform extensive stool testing before diagnosing a presumed IBD flare. However, the risk of infectious diarrhea varies by geographic region, and the primary objective of the current study was to measure the positivity rate in the institution as well as the region (8, 10). Many studies have demonstrated that IBD increases the risk of C. difficile infection, with prevalence rates ranging from 0.4% to 32%, depending on the region in which the study was conducted. In the current study, 9.4% of suspected flare-ups were associated with positive C. difficile infection. Among these, approximately 66% of patients had underlying UC, while 33% had CD. Notably, all Crohn’s patients with C. difficile infection had underlying colonic involvement. These findings highlight the importance of conducting C. difficile testing for all IBD phenotypes (4, 6-8, 10, 11).
Previous studies have also shown that C. difficile infection is more likely to occur following antibiotic use. However, the current study did not reveal a positive correlation with prior antibiotic use (P = 0.20). We believe this may be due to the study being underpowered for such correlations, owing to underreporting and a small sample size (5). On the other hand, the rate of non-C. difficile infections in IBD flares varies considerably across studies (12, 13). In general, the incidence of non-C. difficile infections during an IBD flare is rare. A study conducted in 2018 by Hanada et al. recruited 9,247 patients with IBD flares (13), concluding that less than 3% of stool samples tested positive for non-C. difficile infections. In the current analysis, none of the stool samples tested positive for bacteria (other than C. difficile) or parasitic organisms. This supports the hypothesis that stool testing for non-C. difficile infections during IBD flares yields a low positivity rate in the current study population. Clostridium difficile was the only pathogen routinely identified in relapsing IBD patients, and routine stool testing generally has a low yield, as confirmed by different reports (5, 7).
Cytomegalovirus is another potential pathogen in IBD flare-ups. In humans, CMV is a common infection with a seroprevalence exceeding 70% (14). In healthy individuals, CMV is typically asymptomatic but establishes a lifelong latent infection. The prevalence of CMV-associated colitis in IBD patients varies in the literature, with rates ranging from 4.5% to 16.6%. In the current study, CMV was not detected in any of the tested samples. However, it is believed that this is an underestimation of CMV colitis prevalence due to the low testing rate, as only 35% of flare-admission patients were tested for CMV (15-17).
The strength of the current study lies in its direct results. However, the large number of exclusions led to a smaller study population, limiting the ability to evaluate correlations or identify risks for developing C. difficile infections. Larger studies are needed to better assess these correlations. Additionally, the study was limited by the lack of viral testing aside from CMV, and the retrospective nature of the study resulted in insufficient data on CMV testing during all IBD flare admissions. Although this study was conducted at a tertiary referral hospital, the single-center design limits its generalizability.
5.1. Conclusions
The current study found that in relapsing IBD patients, pathogens other than C. difficile were not routinely identified. Routine stool testing is unlikely to detect bacterial or parasitic pathogens other than C. difficile, except in regions with a high prevalence of parasitic infections. Larger studies are needed to further investigate the association between IBD flare-ups and infectious colitis and its risk factors.