1. Background
Parasitic diseases continue to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality, with more than 3 billion people infected worldwide. Many of these infections occur in the developing world, where improved measures to prevent infection require considerable investment in the public health infrastructure. The segment of the population with significant defects in the immune system continues to grow (1). Intestinal parasites still remain a major public health problem in our country.
2. Objectives
Immunocompromised patients have been susceptible to gastrointestinal parasitic infections. In Iran there have been many documents on adults but because of limitations regarding malignant children profiles we decided to collect further information on these subjects. The purpose of this cross-sectional study was determining the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections among lymphohematopoietic malignant children in Mashhad, Iran.
3. Patients and Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted at the hematology-oncology service of Dr Sheikh Children's hospital affiliated to Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, and Parasitology lab of Imam Reza Hospital of Mashhad, from October 2008 to October 2009. The research included all patients between 1 day to 18 years of age with lymphohematopoietic malignancies who were admitted to the hematology oncology department and underwent chemotherapy. Patients who had used antiparasitic or antibiotic drugs were excluded from the study. The protocol was approved by the university’s ethical committee. The parents of the patients were interviewed by a nurse to complete a questionnaire on the type of underlying lymphohematopoietic malignancies, clinical symptoms (such as diarrhea, anorexia, abdominal colic, flatulence, fever and weight loss) and duration of treatment, area of residence, contact with animals, source of drinking water, as well as information about the health status of the child.
Stool samples were collected from 89 children with lymphohematopoietic malignancies. Three fresh stool samples taken for three consecutive days were examined by direct smear, formalin-ether method, trichrome staining and ELISA test for Giardia lamblia coproantigens. All specimens were also processed according to the immunoenzymatic assay instruction guide (DRG Giardia Antigen, Germany) to detect G. lamblia specific coproantigen. The results were read using a plate reader with a 450 nm filter (Awarness, Stat fax 3200). The samples, which yielded a difference in optical density greater than or equal to 0.150 were considered positive, and those with an optical density less than 0.150 were considered negative. Statistical analyses were performed with the Chi square and ANOVA tests. The data were analyzed using the SPSS statistical software (11th version). Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
4. Results
Of the 89 patients included in the study, 53 (59.6%) were male and 36 (40.4%) female. The subject’s age ranged from 1 month to 18 years (mean 7.5 years SD = 3.8). 83 patients had acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), 4 had acute myelogenic leukaemia (AML) and 2 had non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL).
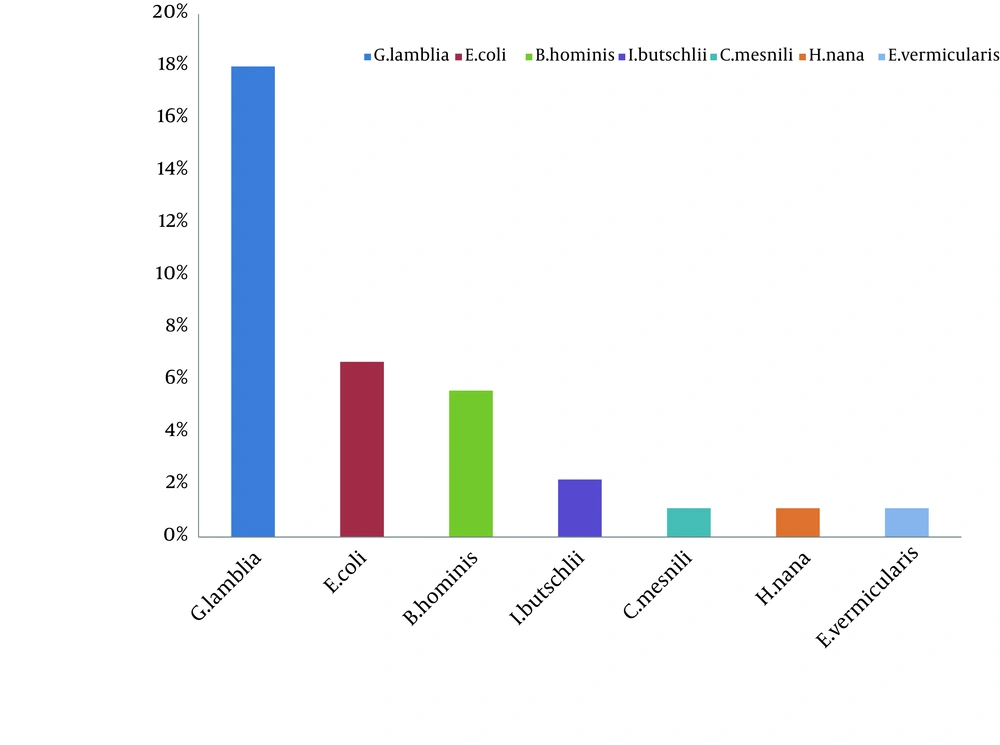
In this study 35.9% of our patients had parasitic infections and the prevalence of infection according to the type of parasite is shown in Figure 1. The most common parasite was G. lamblia 16 (18%) and the other parasites were identified as follows: Entamoeba coli 6 (6.7%), Blastocystis hominis 5 (5.6%), Iodamoeba butschlii 2 (2.2%). Chilomastics mesnili 1 (1.1%), Hymenolepis nana 1 (1.1%) and Enterobius vermicularis 1 (1.1%). The age group of 7 - 8 years showed maximum frequency of Giardia infection, followed by 5 – 6 years. Although the frequency of Giardia was more in females than in males, there was no significant difference between them (P = 0.144). 64.3% of patients with giardiasis had no symptoms and 35.7% had clinical symptoms. The most common clinical symptoms were as follows: recurrent abdominal discomfort (35.7%), diarrhea (16.3%), flautness (15.8%), weight loss (50%) and anorexia (10%).
In this study some factors such as water supply and contact with animals was documented, our findings showed that 44.4% of children with giardiasis use unsanitary water supply (wells or water containers) and 22.2% had contact with animals. 14 cases (87.5%) of giardiasis were detected with the ELISA method. The sensitivity and specificity of this method were 98.6% and 81.3%, respectively.
5. Discussion
Parasitic gastrointestinal infections have been variably reported among immune compromised adults in Iran while data on children have been limited. This prospective cross-sectional study aimed to assess the clinical profile of intestinal parasitic infections among lymphohematopoietic malignant children in Mashhad, Iran. Our study demonstrated a prevalence of 35.9% for parasitic infection in lymphohematopoietic malignant children. In Turkey, Aksoy et al. found parasitic infections in 42% of children with neoplasm (1) but in Mexico City Rivera-Luna et al. found parasitosis in 12.9% of childhood acute leukemia (2).
In India, Rudrapatna et al. in a retrospective study found intestinal parasitic infections in 16.5% of patients with malignancy (3). Menon et al. found intestinal parasites in 42% of a group of Malaysian children with cancer (4). Our study shows that the high prevalence rate of parasitic infections may be due to three factors: first, the type of malignancy (lymphohematopoietic malignancies versus other malignant neoplasms); second, immunocompromising effect of the chemotherapy for cancer (all the patients in our study underwent chemotherapy), and third (the most important factor), use of two different diagnostic methods (ELISA in addition to microscopic examination) which led to a higher sensitivity for detection of intestinal parasites.
According to our findings, 18% of patients had giardiasis so that Giardia is the most frequently identified enteric parasite in our study; Aksoy et al. found giardiasis in 14% of children with neoplasm (1). However, Rudrapatna et al. reported giardiasis for 3.1% of malignant patients (3). Infection with G. lambliais caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with cysts. It has worldwide distribution and occurs in developed and developing country (5). G. lamblia transmission can be from person to person but is more commonly waterborne, a result of the relative resistance of G. lamblia cysts to chlorination. Clinical features of giardiasis vary from the asymptomatic carrier to a severe malabsorption syndrome. Many factors could affect this variation of clinical effects like virulence of the Giardia strain, age, host immune system condition and number of cysts swallowed (6).
64.3% of our patients with giardiasis had no symptoms and 35.7% had clinical symptoms. The most common clinical symptoms were recurrent abdominal discomfort (35.7%), diarrhea (16.3%), flautness (15.8%), weight loss (50%), and anorexia (10%). Although, in our study giardiasis was more frequent in females (56.25%) than males (43.75%) it was not statistically significant (P = 0.144).
The age group of 7 – 8 years showed maximum frequency of Giardia infection, followed by 5-6 years. This infection is particularly high in poor and developing countries due to the use of contaminated drinking water, inadequate sanitary conditions and poor personal hygiene (7). In this study, some factors such as water supply and contact with animals have been documented; our findings show that 44.4% of children with giardiasis use unsanitary water supply (wells or water containers) and also 22.2%of children with giardiasis had contact with animals that shows unsanitary conditions. This may indicate that immune compromised children and their parents need health education about prevention of parasitic infections and must also have access to sanitary conditions and good water supply.
Routine stool examinations are normally recommended for the recovery and identifications of intestinal protozoa. However, in the case of G. lamblia, because the organisms are attached so securely to the mucosa by the means of a sucking disk, a series of five or six equal stool samples may be examined without recovering the organisms. The organisms also tend to be passed in the stool on a cyclical basis (8). The most important thing about these parasites is that the appearance of Giardia in the stool is not so regular and frequent tests are required in order to detect cyst shedding and one direct smear that uses small amounts of sample cannot detect Giardia parasites; therefore we need three rounds of stool examination that can increase the chances of diagnosis.
In our study three fresh stool samples taken for three consecutive days were examined by three methods for diagnosis of parasitic infections; direct smear, formalin-ether method, trichrome staining and ELISA test for G. lamblia coproantigens. Many serological assays have been introduced to detect serum antibodies but because of the lack of appropriate antigens of Giardia, the sensitivity of serological tests remains poor. Besides, detection of coproantigen has been successful and commercial kits are available which have been reported to be more sensitive than microscopic diagnosis of giardiasis (9). Procedures involving the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) have also been developed to detect Giardia antigen in feces. The ELISA is at least as sensitive as microscopic wet examinations (8).Comparison of ELISA test and formalin ether in our study shows that from 16 cases of giardiasis 14cases can be detected with the ELISA method. The sensitivity and specificity of this method was 98.6% and 81.3%, respectively.
In this study, formalin – ether test considered as a gold standard test and other parasitologic diagnostic methods like direct method and trichrome staining were used and ultimately ELISA for G. lamblia antigen detection was tested. It is known that fecal examination to detect G. lamblia cysts or trophozoites produces a high percentage of false-negative results. Rocha et al. showed that the assay was able to identify all 30 positive patients (sensitivity = 100.0%). The assay seems to be a good alternative for giardiasis diagnosis, especially when the fecal examination was repeatedly negative and the patient presents symptoms similar to that of giardiasis (10).
The coproantigen-ELISA is especially advantageous in situations where only a single stool sample can be examined. It should not, however, replace microscopic examination of stool specimens for ova and parasites since other potential pathogens would otherwise escape (11). Routine microscopic detection of parasite is inexpensive, but needs expert technicians. Methods for antigen detection can be carried out more quickly and without proficient technicians (12). We highlight the importance of diagnosis and the skills of the laboratory of parasitology, since most parasitic infections responsible for diarrhea in lymphohematopoietic malignant children can be treated. We conclude that because of irregular shedding of Giardia and time consuming methods for detection of Giardia cysts and trophozoites, it is recommended to use sensitive methods like fecal antigen detection instead of routine methods.