1. Background
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligatory intracellular protozoan parasite, which infects human beings when eating undercooked meat or contaminated vegetable. Toxoplasma may cause different clinical forms such as asymptomatic or sever symptoms like abortion, congenital defects and death (1). Since the current antigens that are used for diagnosis or vaccination are contaminated with non parasitic material in which the parasite is grown, a lot of efforts are made to produce recombinant antigens to design vaccine against toxoplasmosis or make diagnostic kits (2). Choosing the type of antigen to produce recombinant vaccine or diagnostic kits is considerably important because it should be immunogene, trigger of cellular immunity response, proliferator of T lymphocytes and also presented in most of the parasite life-cycle (3).
The rhoptry protein 1 (ROP 1) is one of the excretory-secretary antigens of Toxoplasma with the above mentioned specification and it seems to bean appropriate candidate in production of recombinant vaccines and diagnostic kits (4). The gene encoding this antigen has 2122 bp (5, 6). Rhoptry protein 1 is expressed in tachyzoite, bradyzoite and sporozoite (7). It has a key role in cell invasion (8). Many studies were done on the gene cloning of other genes of Toxoplasma, although fewer studies have been done on this gene (9, 10). Previous studies have shown that the use of a DNA vaccine containing ROP1 induced protective immune responses modulated by Th1-type response elements (11-16). It is also reported that this protein could be used as a specific marker for differentiation of acute and chronic toxoplasmosis (3, 17-19).
2. Objectives
The current study aimed to produce rhoptry protein 1 from Iranian strains of Toxoplasma for further investigations.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Parasite
The RH strain of T. gondii, was provided by Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Health, Tehran Medical Sciences University. Tachyzoites of parasite were harvested from peritoneal fluid of Balb/c mice. These mice had been infected 3 - 4 days earlier.
3.2. Cloning of ROP1 Gene in Bacterial Expression Vector
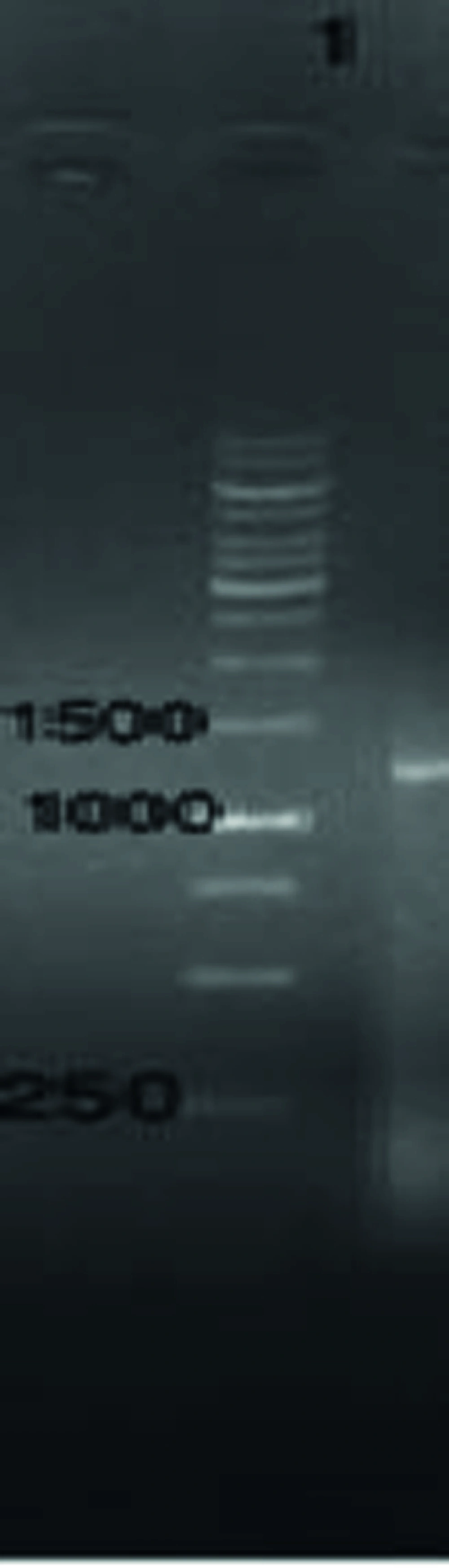
Standard methods were used for DNA extraction (20). Authors designed a pair of primers according to the ROP1 gene sequence (Accession number M71274) with EcoR1 and Sal1 restriction sites at 5` end of forward and reverse primer respectively (Forward: 5`-GGAATTCACCATGGAGCAAAGGCTG-3` and Reverse: 5`-GCGTCGACTTATTGCGATCCATCATCC-3`). The ROP1 gene of Toxoplasma was amplified by PCR. The purified PCR products were ligated into pTZ57R/T plasmid vector (20). The gene fragment was sub-cloned in a pET32a expression plasmid (prepared from Microbiology Department, School of Medical Science, Arak University).
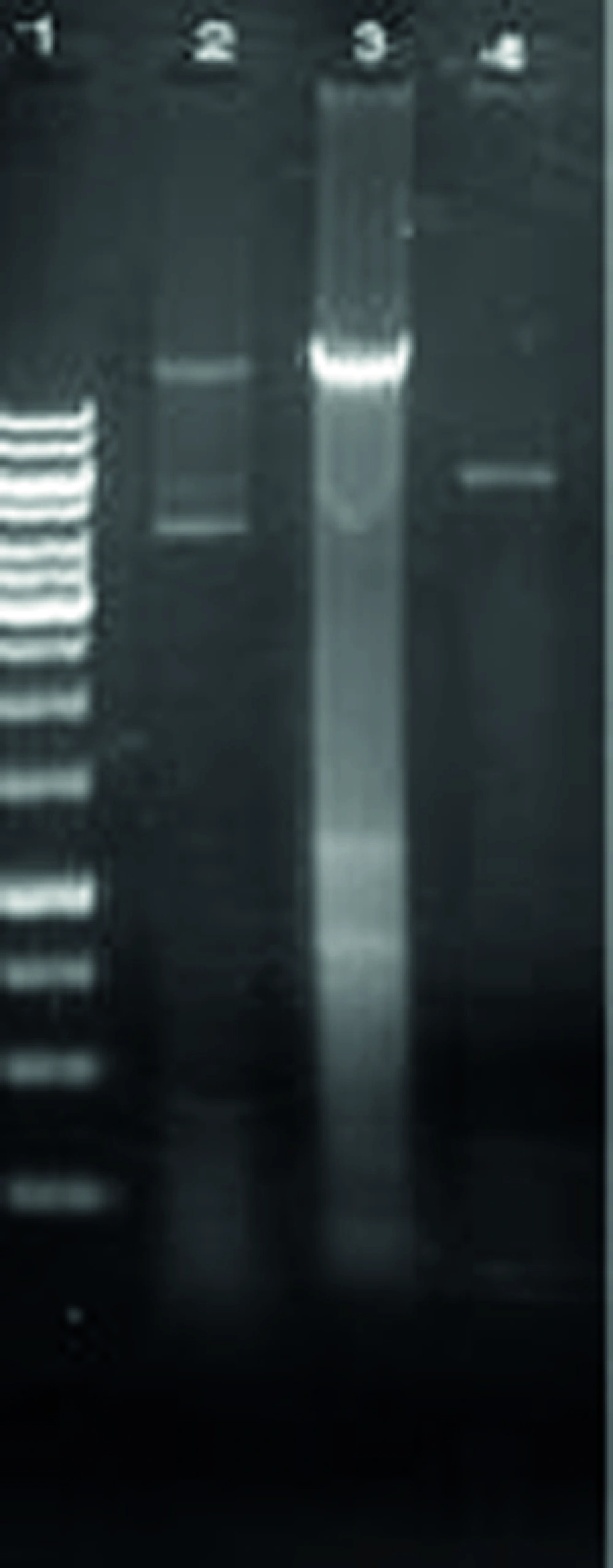
Initially, the gene fragment was separated from previous cloned plasmid by restriction cleavage and then purified using gel-extraction kit (Fermentas Inc. Canada). In addition, pET32 was cultivated in an antibiotic-containing media. After plasmid extraction, its restriction cleavage sites for EcoR1 and SaI1 were enzymatically cleaved and purified. Then, resulting plasmids were used for ligation and transformation of gene fragment. The recombinant pET32a expression vector containing ROP1 gene (pET32a-ROP1) was confirmed by PCR, restriction analysis and sequencing.
3.3. Protein Expression and Purification
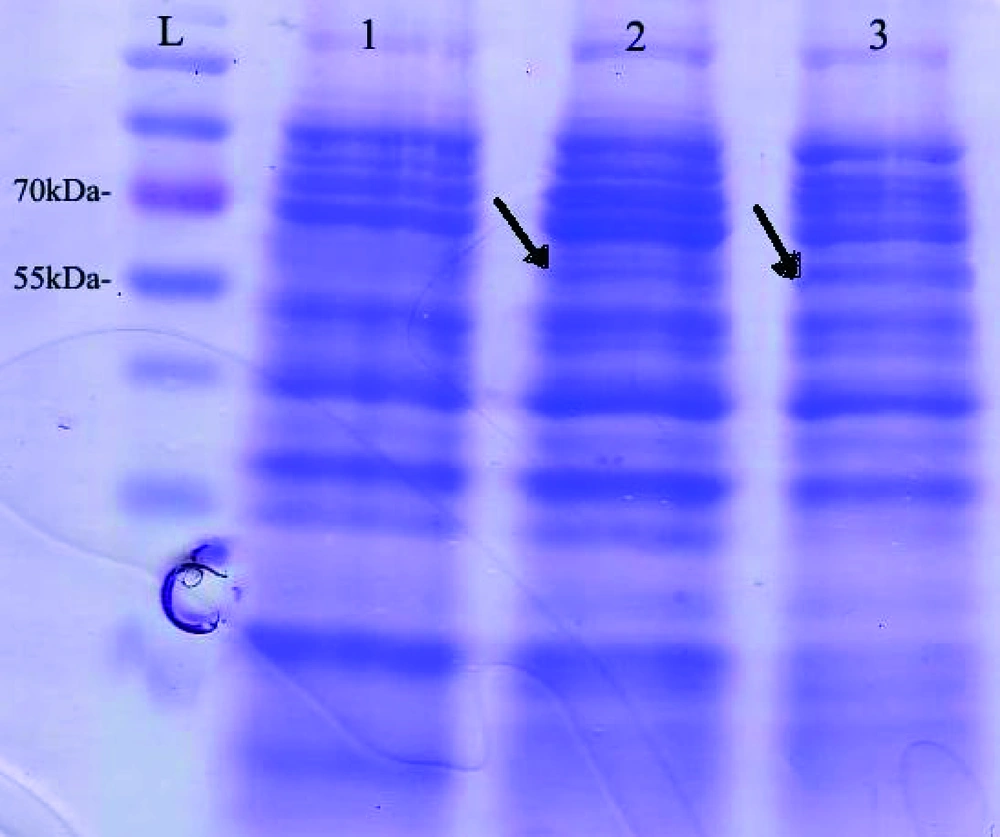
Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS was transformed with pET32a-ROP1 and grown in LB broth supplemented with ampicillin (100 µg/mL) and chloramphenicol (34 µg/mL) (Invitrogen ,USA) and shaken at 200 rpm at 37˚C. Also E. coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS was not transformed grown as control. The plasmid promoter was induced by 1 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) for 6 hours. Sampling was done before and after induction in 2- hour intervals. The bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 5 minutes. The expressed protein was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting (12).The expressed protein was purified using Ni-NTA column according to manufacture instructions (Qia-gen, Germany)
3.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
Recombinant protein was assayed by 12% gradient SDS-PAGE and western blot. SDS-PAGE was performed according to the method of Laemmli (21). Western blot was performed by Ni-NTA conjugate. At first, SDS-PAGE gel was blotted on to Polyvinyli dinedi fluoride (PVDF Membrane, Roche Diagnostic, Germany) membrane using transfer buffer (12). Membrane was incubated 1 hour in 1% skimmed milk and washed 3 times with washing buffer (Tris-buffer-saline and tween 20 or TBS-tween). Membrane was incubated 1 hour in TBS-tween buffer containing a 1/1000 dilution of Ni-NTA conjugate. The blots were then washed three times with TBST and reactions were developed by diaminobanzidine (DAB) Solution (Roche Diagnostic Germany).
4. Results
The genomic DNA of T. gondii was prepared and used as template for amplification of the gene encoded ROP1. The amplified fragment had the expected size of 1183 bp comparing to Molecular weight marker (Figure 1).
The recombinant plasmid was analyzed by restriction enzyme and the resulting fragments were compared with molecular weight marker (Figure 2).
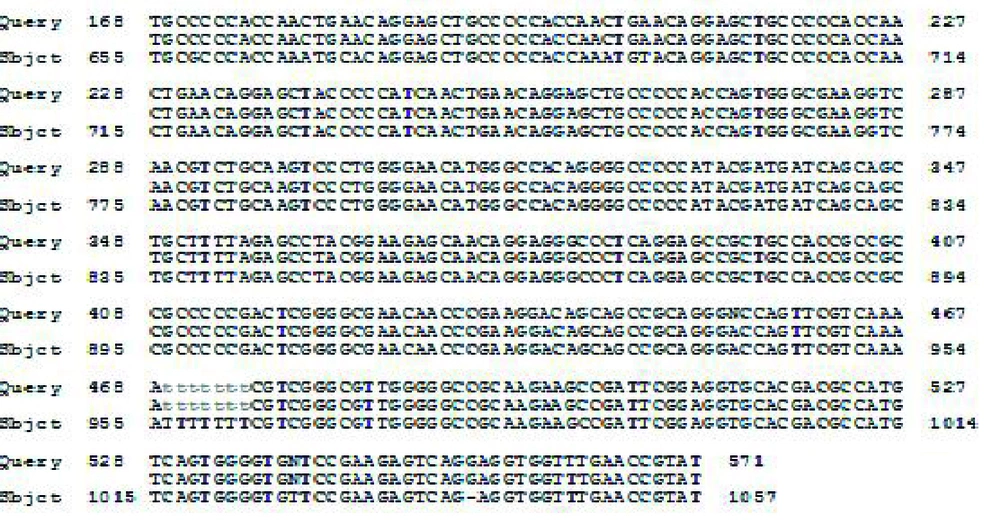
The recombinant plasmid (pET32a-ROP1) was sequenced .The sequencing result was confirmed by comparing with the databases and using basic local alignment search tool (BLAST) Software (Figure 3).
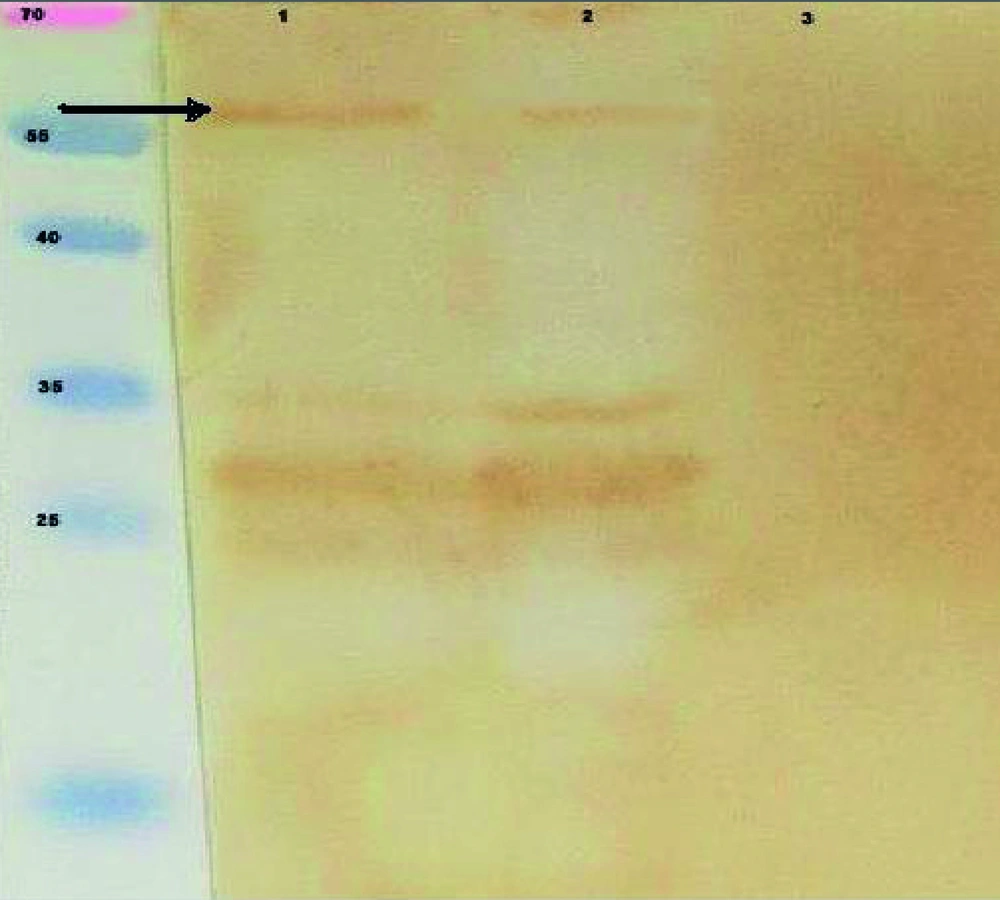
Expression of pET32a-ROP1 in E. coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS was induced and the expressed protein was purified by Ni-NTA column. SDS-PAGE and western blot analyses showed the expected molecular mass near 60 kDa recombinant protein (Figures 4 and 5).
5. Discussion
T. gondii is an obligatory intracellular parasite which has a complicated life cycle and attacks almost all nucleated cells. The high incidence and severe or lethal damages of toxoplasmosis clearly indicate the need for the development of a more effective vaccine (22). Moreover, in recent years, researchers are trying to improve the serological diagnosis of toxoplasmosis using recombinant proteins. Therefore, it is critical to generate specific antigens. Recombination is an easy method to access this specific protein (23).
Available commercial tests to detect anti-Toxoplasma antibodies were usually prepared based on whole antigens derived from tachyzoites of parasite. This stage of parasite must be harvested from infected mice or cell cultures because antigens prepared by the traditional method are not composed of defined parasite antigens. They are inevitably contaminated with at least some host tissue, thus could result in false-positive reactions and reducing the clinical value of serological test (24). Many researchers have emphasized the detection of specific antibodies against excreted-secreted antigens (ESA) of Toxoplasma. in diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis is worth (24). T. gondii ESA constitutes 90% of the circulating antigens in infected humans, thus this parasite is one of the first targets of the host immune response (24).
ROP1 gene is one of the major antigens of T. gondii with unusual gene structure. The major part of this gene has similar sequence in genomic DNA, cDNA and mRNA so it is possible to directly isolate gene fragment from DNA (11). This protein is presented in tachizoytes, bradizoytes and sporozytes forms of parasite and plays a role in invasion to host cells. The ROP1 is expressed in many phases of parasitic life cycle, it confers a suitable target for production of clinical diagnostic kits and recombinant vaccines (2). Gue et al. cloned a 760bp ROP1 gene fragment into pBV220 expression plasmid and assessed the immune responses of Balb/c mice vaccinated by this plasmid (13). In another study carried out by this group, encoding plasmids for a 760bp fragment of ROP1 gene and a 600bp fragment of IFN-δ gene were generated and immunologically assessed in Balb/c mice (15).
Chen et al. cloned a 750bp fragment of T.gondii ROP1 gene into pUC18 plasmid and then transferred it to pcDNA3 eukaryotic expression plasmid (11). Another group directed by Chen constructed a fusion-based recombinant plasmid consisting of two fragments of ROP1 (760bp) and SAG1 genes (pSAG1-ROP1). Recombinant plasmids were injected to Balb/c mice via liposome-entrapped particles and immune responses were analyzed (16). Eslamirad et al. cloned a 760bp fragment of T. gondii ROP1 gene into eukaryotic expression plasmid. In the study, the used vector was pTZ57R, which was different from vectors used in other studies. Also the used gene fragment could only encode part of ROP1 protein that was expressed at very low levels in eukaryotic CHO cells and was hardly traceable in vivo. However, the results reflected relatively satisfactory immunogenicity of plasmids in animal models (20).
Aubert et al. produced a number of T. gondii antigens such as ROP1 in fusion with cks protein of E. coli and used these recombinant antigens to identify anti-toxoplasmosis specific IgM and IgG antibodies in human serum (17). Meek et al. cloned fragments of ROP1 and SAG1 genes into pRP261 expression plasmid and used the resulting expressed proteins to serological diagnosis of toxoplasmosis in patients suffering from acute and chronic toxoplasmosis (18).
In brief, the current study expressed recombinant ROP1 in E. coli expression system as full length. This protein was produced alone. It was prepared for use in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis by ELISA system and for evaluation as a recombinant vaccine. In the current study, unlike other studies, the goal was to express full length of ROP1. Also this protein was produced alone not fused with other proteins. This will provide the chance to design future studies to evaluate the diagnostic value of this protein in human toxoplasmosis. One can also evaluate the ability of this protein to induce host immune response.