1. Background
Bordetella pertussis is a human pathogen, Gram-negative bacteria causative agent of whooping cough. It secretes several virulence factors including adhesins which consist filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA), pertactin (PRN) and toxins such as tracheal cytotoxin, pertussis toxin (PT), and adenylate cyclase-hemolysin (AC-Hly), allowing it to multiply and colonize the human respiratory epithelium (1). Among them, adenylate cyclase toxin (CyaA) is a major virulence factor of B. Pertussis and anti-CyaA antibodies are present in sera from convalescent patients and patients vaccinated with WCVs (2, 3). CyaA is a 177 kDa protein endowed with adenylate cyclase (AC) activity and with the ability to invade and intoxicate mammalian cells (4).
Upon entry into the cell, the N-terminal AC enzymic moiety is activated by host calmodulin to produce supraphysiological levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). In immune effector cells, it impairs their phagocytic and bactericidal capabilities and induces apoptosis, features which are assumed to assist survival of the bacteria in the initial stages of respiratory tract colonisation (5). At high concentrations, CyaA forms pores or channels which make the toxin cytolytic (4). Anti-CyaA antibodies have been shown to enhance phagocytosis of B. Pertussis through neutralisation of CyaA which, normally inhibits phagocytosis by neutrophil polymorphonuclear leukocytes (6, 7). An immune response to this toxin might therefore be useful to prevent colonisation of the host by B. Pertussis. Immunisation with CyaA, purified from B. Pertussis or in recombinant form from Escherichia coli, protected mice against intranasal challenge with virulent B. Pertussis (8-10). In addition, co-administration of CyaA or CyaA*, a derivative lacking AC enzymic activity, with an ACV indicated the enhancement of the protective effects of an ACV in mice (11).
2. Objectives
The aim of the work reported here was to formulate CyaA by a method that is applicable to large-scale manufacture but which would still allow retention of the enzyme activity and immunogenicity of the protein.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Recombinant CyaA From E. coli
Twenty mL of an overnight culture of E. coli BL21/DE3 containing the relevant plasmids were diluted into 500 mL of LB containing appropriate antibiotics, incubated at 37C with shaking at 200 rpm until an OD600nm of between 0.4-0.45 was obtained (~3 h). Isopropyl-1-thio--D-galactoside (IPTG) was added to a final concentration of 1 mM and shaking continued at 37C for 3 h. Finally, cells were harvested at 10,000 xg for 25 min and the supernatant discarded. Cells pellets could be stored at -20C if necessary.
3.2. Expression and Purification of CyaA
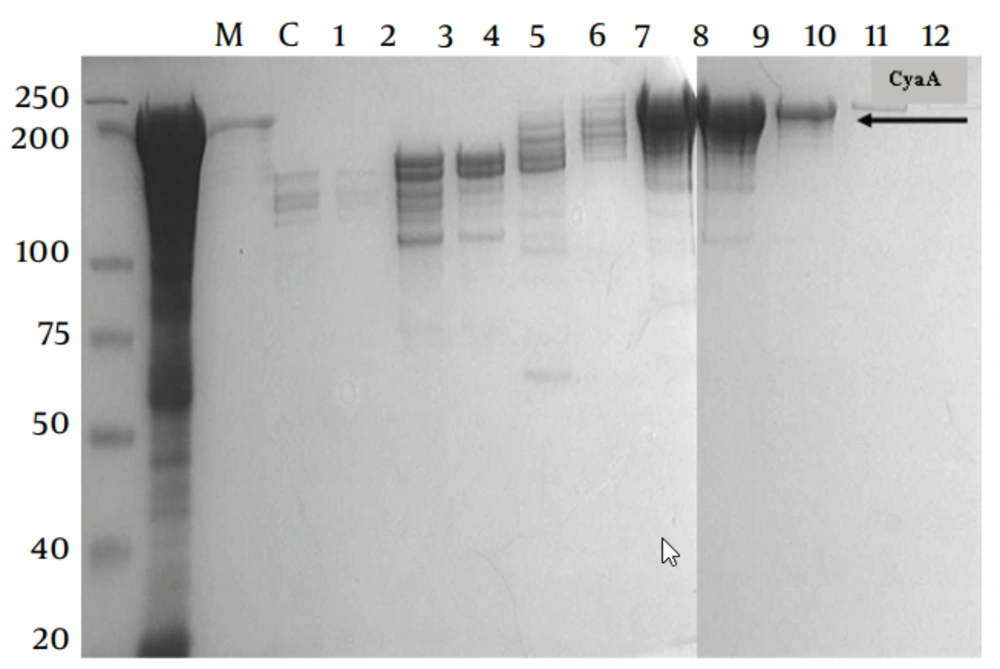
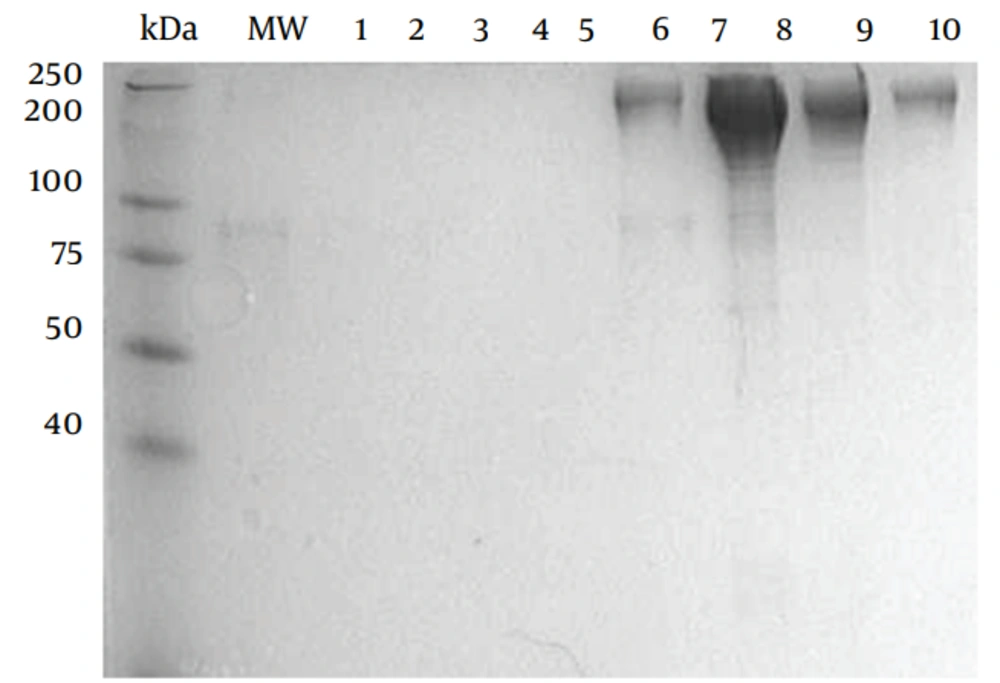
E. coli BL21/DE3 (F− ompT rB− mB−) was used as the host strain for production of CyaA. The source of plasmids used in this study ( pGW44 and pGW54) was described previously (12, 13). Co-expression of pGW44 with pGW54 generates fully active acylated, invasive CyaA , pGW44-188, pGW54 generates Non-active AC/ invasive (CyaA*). The recombinant proteins were purified as described previously with the following modifications; the CyaA inclusion bodies were washed twice with 1% (w/v) N-octyl -d glucopyranoside (Sigma, Sweden in 20mM histidine buffer (pH 6.0), twice with 2M urea in 20mM histidine buffer (pH 6.0) and once with pyrogen-free water before solubilisation in 8M urea, 20mM histidine buffer (pH 6.0). The solubilised crude CyaA was purified by QSepharose, Germany Amersham) and phenyl-Sepharose chromatography ( Figures 1 and 2).
3.3. Oxidative Burst Procedure
The oxidative burst component of the phagocytic process was measured in leukocytes using the commercial flow cytometric-based BurstTest kit (OPREGEN Pharma; BD Biosciences, U.S.A) according to the manufacturer’s instruction for E.coli bioparticles. The BurstTest assay relied on unlabelled IgG opsonized E.coli bacteria as the particulate stimulus and dihydrorhodamine (DHR) 123 as a fluorogenic substrate of oxidative activity. Briefly, both heparinised whole blood, and J774.2 mouse macrophages and U937 human monocytes were incubated (120 minutes, 37ºC, 5% CO2) with either recombinant CyaA or CyaA* in urea, 20mM histidine diluted to 0.05, 0.1 or 0.2 g protein/mL or with PBS, then incubated for another 15 minutes at 37ºC in 5% CO2 with opsonized E. coli cells (6 cells per leukocyte).
A sample without stimulus served as negative background control. DHR 123 was then added and the cells incubated (10 minutes, 37ºC, 5% CO2). The reaction was stopped by the addition of lysing buffer, which partially fixes leukocytes and lyses erythrocytes in case of whole blood. After washing steps (250 x g, 5 min, 4 oC) erythrocytes were removed by hypotonic lysis. Finally, to exclude aggregation artefacts of bacteria or platelets, a DNA staining solution was added immediately prior to flow cytometric analysis. Cells were analysed by flow cytometry (FACS.Calibur, BD Biosciences, U.S.A) and 5000 granulocyte or diploid cell events acquired to obtain the percentage and number of cells ingesting bioparticles, as well as their mean fluorescence intensity (enzymatic activity) using Cellquest Pro software (BD Biosciences, U.S.A).
Nucleated cells were discriminated by setting in the red fluorescence channel (DNA staining FL2), on those events which had the DNA content of a human diploid cell (to exclude bacteria aggregates). The nucleated events were then discriminated; in to lymphocytes, monocytes and polymorphonuclears by combined measurements of the forward angle light scatter (FSC) and side angle light scatter (SSC). The granulocyte cluster or U937 or J774 in different tests was then gated in the analysis program in the scatter diagram (FSC vs. SSC) and its green fluorescence histogram (FL1) was analysed. The SSC vs. FL-1 diagram also was set to make sure that the appropriate cell population data were collected.
4. Results
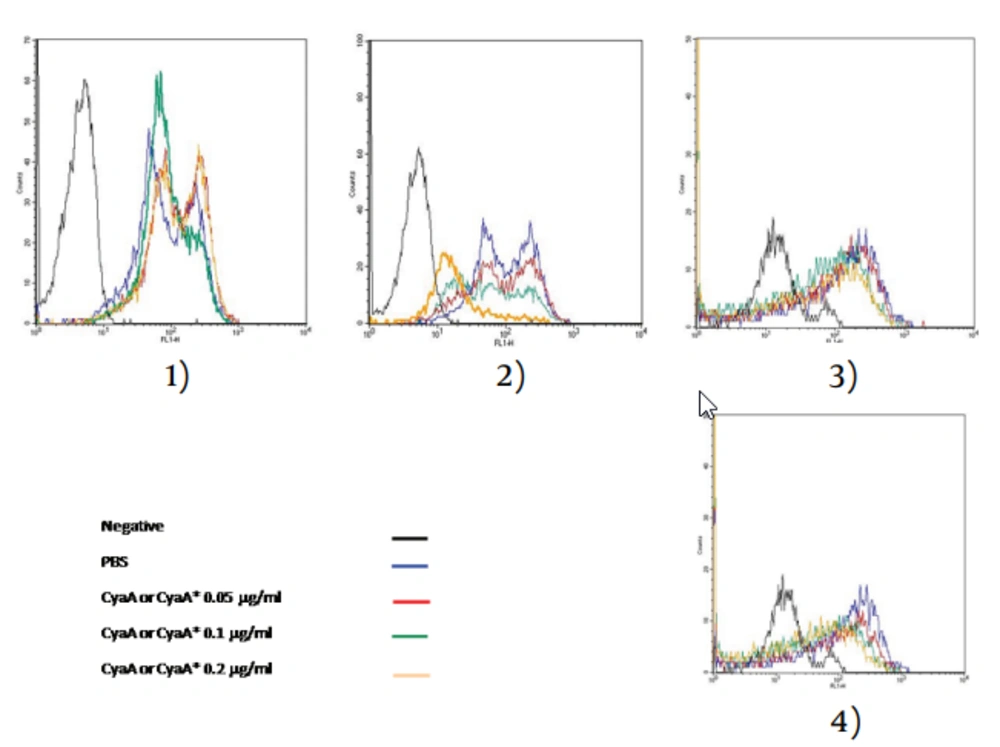
Flow cytometry assays for the measurement of the oxidative burst were based on the conversion of a non-fluorescent molecule to the fluorescent form under the influence of intracellular reactive oxygen intermediates. This conversion reflected the amount of oxidative burst induced by various stimuli. The substrate used was dihydrorhodamin-123 (DHR-123), which entered the cells as a freely permeable dye and was converted to rhodamine 123. It was used as an indicator of oxidative burst and was found to be more sensitive than other substrates. The cells (human granolocytes, J774.2 and U937) were treated with CyaA and CyaA* (0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 g protein/mL final concentration) for two hours and then incubated with opsonised E. coli for 15 min. In addition, some of the cells were incubated with PBS instead of CyaA, as controls. Cells were washed and then read by flow cytometry at a wave length of 488 nm.
The statistically significant results obtained with CyaA were substantiated by the flow cytometric histograms (Images 2 and 4 in Figure 3). Images 1 and 3 showed that CyaA* had little effect on J774.2 and or granulocytes only at the highest concentration. Similar experiments were carried out with undifferentiated and differentiated U937 human monoblast treated with CyaA at 0.1 g/mL. As Table 1 shows, only differentiated cells were affected by CyaA.
| Toxin conc, g/mL | Inhibition of Oxidative Burst in J774.2 Cells (Mouse Macrophages) ,% | Inhibition of Oxidative Burst in Granulocytes (Human Peripheral Blood), % | Inhibition of Oxidative Burst in U937 Cells (Human Monocytes) (Without PMA), % | Inhibition of Oxidative Burst in U937 Cells (Human Monocytes) (With PMA), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CyaA a (0.05) | 18 | 35 | 0 | 15 |
| CyaAa(0.1) | 38 | 55 | 0 | 40 |
| CyaAa(0.2) | 80 | 70 | 0 | 53 |
| CyaA* b(0.05) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CyaA*b(0.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CyaA*b(0.2) | 0 | 21 | 0 | 0 |
| PBS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
aCyaA = This toxin has both invasive and enzymatic activity
bCyaA*= This toxin has invasive property, but no enzymatic activity
These tests are a flow cytometeric assay which relays on unlabelled IgG opsonized E.coli bacteria as the particulate stimulus and dihydrorhodamine (DHR) 123 as a fluorogenic substrate of oxidative activity.
5. Discussion
The first line of defence against microbial infection was provided by neutrophils. Upon phagocytosis of bacteria, a respiratory burst occurred; initially reducing oxygen to form superoxide, with secondary formation of H2O2, OH- and other oxygen-derived molecules that participated in bacterial killing (14). An early report showed that culture medium and bacterial extract from B. Pertussis, containing adenylate cyclase of high specific activity, were able to inhibit the chemiluminescence (CL) response of human alveolar macrophages and neutrophils to zymosan (15).
Others have reported the role of CyaA in the inhibition of this response. CyaA toxin produces high levels of intracellular cAMP in human monocytes and inhibits the oxidative response to a variety of particulate or soluble stimuli (16). Other researchers demonstrated that B. Pertussis can survive intracellularly within various leukocyte cell types, including human macrophages and polymorphonuclear cells (17, 18). It is possible that the inhibition of oxidative burst in these cells would benefit from the intracellular survival of the bacteria which may be an important evasive strategy for B. Pertussis.
The results of oxidative burst experiments in the current study suggested that CyaA inhibits the oxidative burst of J774.2 macrophage-like cells and human granulocytes as it induced a decrease in mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) as measured by flow cytometry. Although the concentration of CyaA used in the assay caused appreciable cell killing of J774.2 cells, as determined by the MTT assay, it should be emphasised that the effect of CyaA on oxidative burst was measured only in viable cells, by the flow cytometric method, here in contrast, CyaA* did not appear to inhibit the oxidative burst when it was compared with CyaA at the same concentrations. The results indicated that the AC enzymic activity of CyaA toxin was necessary for the inhibition of oxidative burst in these cells. This result is in line with Steed et al. (18) who indicated that CyaA inhibited respiratory burst activity in human PMNL.
A similar experiment, preformed on U937 human monocytes in the presence and absence of PMA, showed that CyaA inhibited the oxidative burst by approximately 15%, 40% and 53% when tested at 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 μg/mL final concentrations on PMA-activated monocytes respectivly, but were ineffective on non-differentiated cells. Thus, PMA could stimulate the immature cells to differentiate, which CyaA then affected. These data suggested that the activity of CyaA on these cells were best seen when they differentiated, possibly to express high level of receptor for CyaA.