1. Background
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies and the second cause of death in female patients worldwide. In spite of the advances in understanding many of the involved factors in breast cancer development, this type of cancer still remains as a life threatening disease in females, particularly in the western countries. According to the results of some studies, environmental factors such as diet contribute to the prevalence of breast cancer (1). Consumption of probiotics in dairy products may help the body to inhibit the growth of many types of solid tumors because of their immunomodulative property (2).
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are the most commonly used microorganisms as probiotics. They are non-pathogenic bacteria and when administered in adequate amounts, exert health benefits in their host. LAB strains can modulate the immune responses and modify the immune mechanisms (3). Different strains of LAB can also enhance both innate and adaptive immunities. Some of the modifications can promote the antitumor responses. For instance, regulation of innate immunity may be an effective means to prevent cancer. Some studies indicate that immunomodulatory properties of LAB and the pattern of immunomodulation depend on the bacterial species (4). Moreover, many studies have demonstrated the effects of dose and viable or killed probiotic administration on the immune responses (5). The results of some studies show that orally administered lactobacilli affect T-helper 1 and T-helper 2 pathways by local cytokine production like IFN-γ or TGF-β in the gut (6). In addition, it is known that oral administration of certain strains of LAB can increase not only the local immune responses in the intestine, but also the systemic immune responses (7).
2. Objectives
However, there are only a few reports about the probiotics and their capacity for breast cancer prevention. The current study aimed to evaluate the direct effect of oral administration of viable Lactobacillus acidophilus on the immune responses, particularly on cytokine production in the splenocytes of BALB/c mice bearing breast cancer tumor.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animals
The current study used thirty female inbred BALB/c mice, six- to eight-week-old and weighing 25 - 30 grams, obtained from the Pasture Institute of Iran (Tehran, Iran); they were divided into two groups of 15 each as the case and the control. The mice were kept in plastic cages, allowed for free access to water, and maintained on a 12:12 light-dark conditions in the whole period of the study. The temperature and humidity were controlled at 23 ± 1°C and 55 ± 10%, respectively. All mice were fed with standard mice pellet diet and this experiment was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee in Tehran University of Medical Science (Tehran, Iran).
3.2. Microorganism and Feeding Procedure
The L. acidophilus ATCC4356 strain used in the study was purchased from the Persian type culture collection (Iranian Research Organization for Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran). The strain was inoculated in 10 mL of DeMan-Rogosa-Sharpe (MRS) broth (Merck, Germany) and cultivated overnight at 37°C under anaerobic conditions, then centrifuged and washed three times with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) and re-suspend in PBS. After preparation of a proper amount of the suspension, it was orally administered to the mice with a gastric feeding tube. The control mice received an equal volume of PBS during the study. The probiotic group was given 0.5 mL of the suspension containing 2.7 × 108 CFU/mL L. acidophilus every day starting from two weeks before tumor transplantation, which was continued with three day intervals and seven consecutive days feeding until the day 30. The control group was given an equal volume of PBS with the same procedure similar to the controls.
3.3. Tumor Transplantation
The mice bearing breast tumor (8) were used as the tumor stock. After cervical dislocation, the tumors were removed aseptically, dissected into 0.5 cm3 pieces with scalpel and washed three times with sterile PBS. The experimental mice were anesthetized with ip injection of ketamine and xylene (10 mg/kg of body weight) and the tumor pieces were transplanted subcutaneously to the right flank of the mice.
3.4. Cytokine Determination in Spleen Cell Culture
The spleens were removed aseptically exactly after the 30th day of tumor transplantation. The experimental mice were sacrificed and their spleens were homogenized in Hanks’ balanced salt solution (Sigma, Germany). The splenocytes were sedimented by centrifugation, re-suspended in red blood cell lysing buffer (Sigma, Germany) for 5 minutes, washed and re-suspended in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco Life Technologies, Germany), supplemented with 10% FBS and 100 µg/mL penicillin and streptomycin (Invitrogen, Paisley, Germany). Then spleen cells were estimated at 2.5 × 106 cell/mL and incubated alone or treated with 20 μg/mL of tumor antigen for 72 hours in RPMI1640 (Gibco Life Technologies, Germany), then supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen, Paisley, Germany) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Sigma, Germany) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10 levels of the spleen cell cultured supernatants were detected using ELISA technique (R&D system, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendation. In order to provide the tumor antigen, one of the tumor stock mice was used and then the tumor was extracted from its body and dissected into small sections (3 mm3). After that the tumor sections were washed by sterile PBS and fragmented via sonication. Then the protein dialysis method was used in order to extract the proteins from the suspension and the protein concentration was measured by Bradford method (9).
3.5. MTT Spleen Cell Culture Assay
The splenocytes culture was prepared as mentioned in pervious section. The cell suspensions containing 1.5 × 106 viable cells /mL were distributed (100 µL/well) into 96-well tissue culture plates with flat-bottom wells (Costar, Cambridge, Mass.). Phytohemagglutinin (PHA), polyclonal activator, was used at 100 μg/mL as a mitogen (10). After incubation at the humidified 5% CO2 at 37°C for three days, 25 µL of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) was added to each well and the plates were incubated for four hours at the humidified 5% CO2 at 37°C; the yellow tetrazolium salt, MTT, was converted into a purple formazan substrate by the mitochondrial enzyme, succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) in the wells containing viable cells. To dissolve the dark formazan crystals, 100 µL 0f Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was added to each well and the plates were incubated for 10 minutes at 37°C under humid conditions. After incubation, the contents of the plates were thoroughly mixed for 5 minutes on a plate shaker. The optical density (OD) of each well was read at 570 nm with a 630 nm reference, and the stimulation index (SI) was calculated according to the following formula:
3.6. Survival Rate
At the end of the study, seven mice from each group were kept under the standard conditions (fed with standard diet, free access to water and maintained on a 12:12 light-dark conditions) until they died. The daily death of the mice was recorded and after the last death in both groups, the data was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier test.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses, except for the survival rate, were conducted by SPSS 15.0 using a one way ANOVA test. The values are presented as mean ± SD
3.8. Ethics Approval
All experimental procedures involving animals were accepted by the Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
4. Results
4.1. Cytokine Assay in Spleen Cell Culture
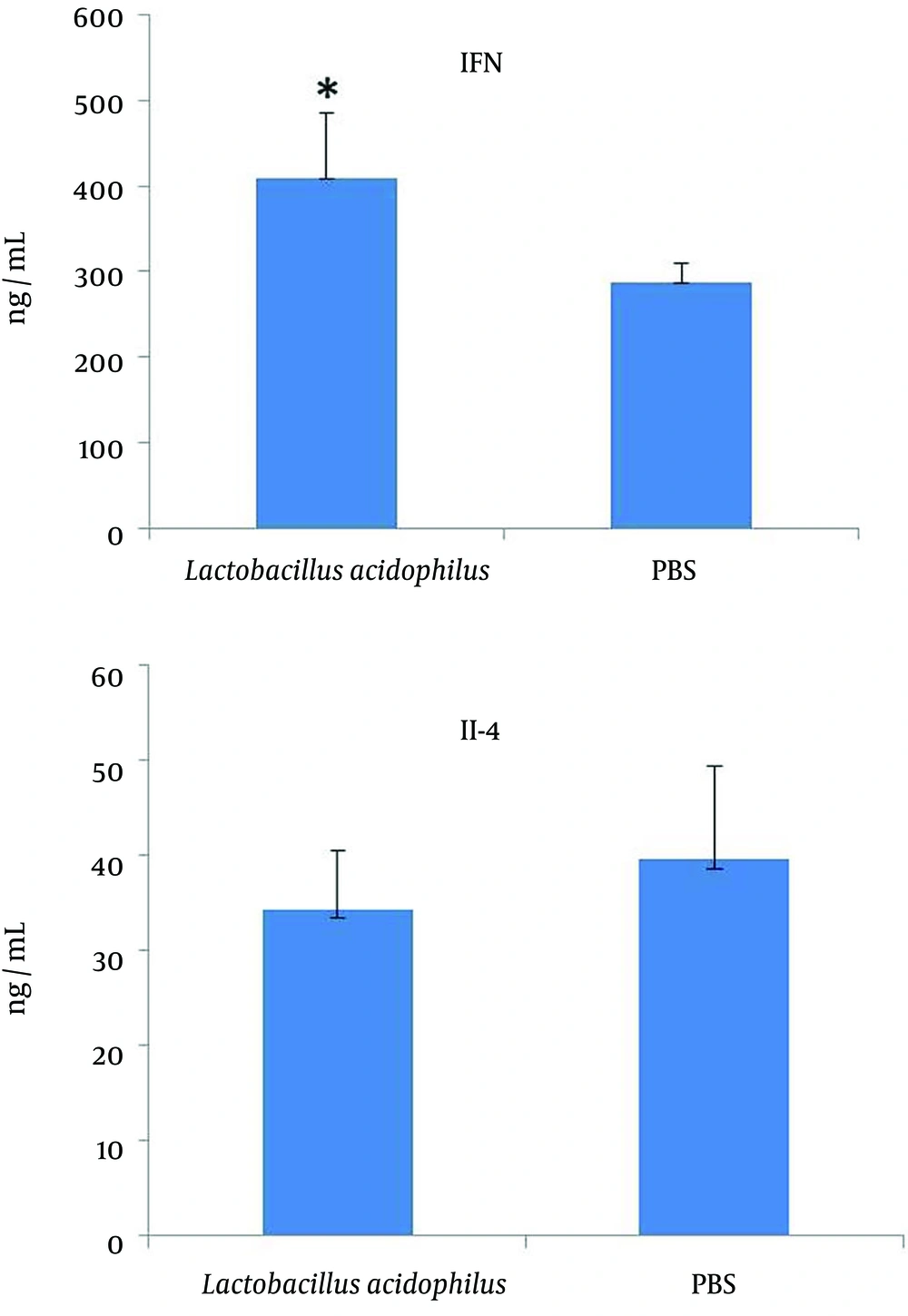
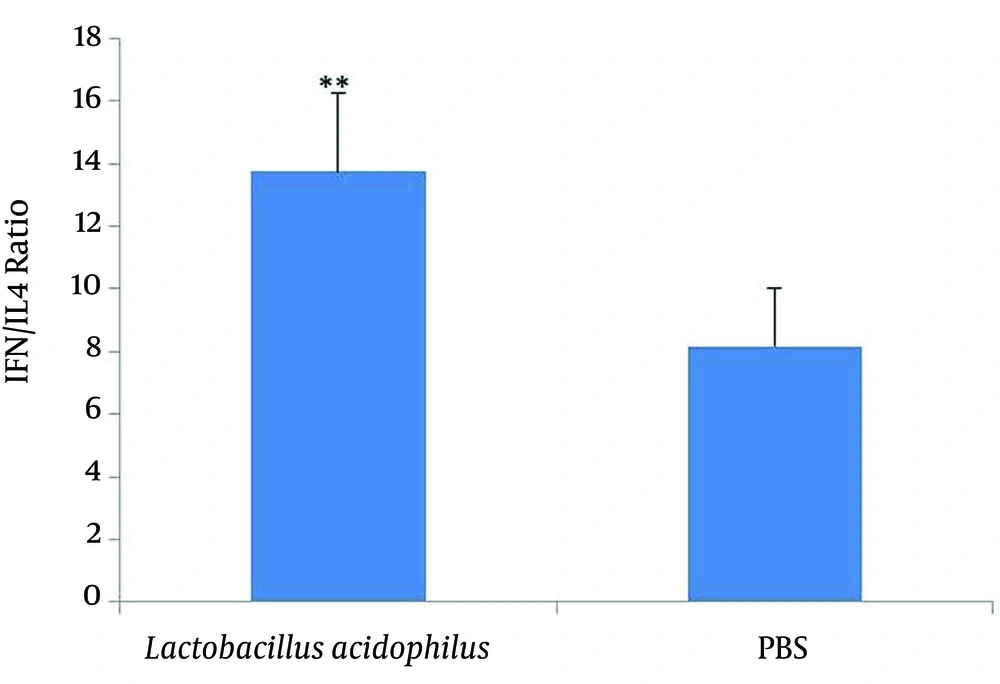
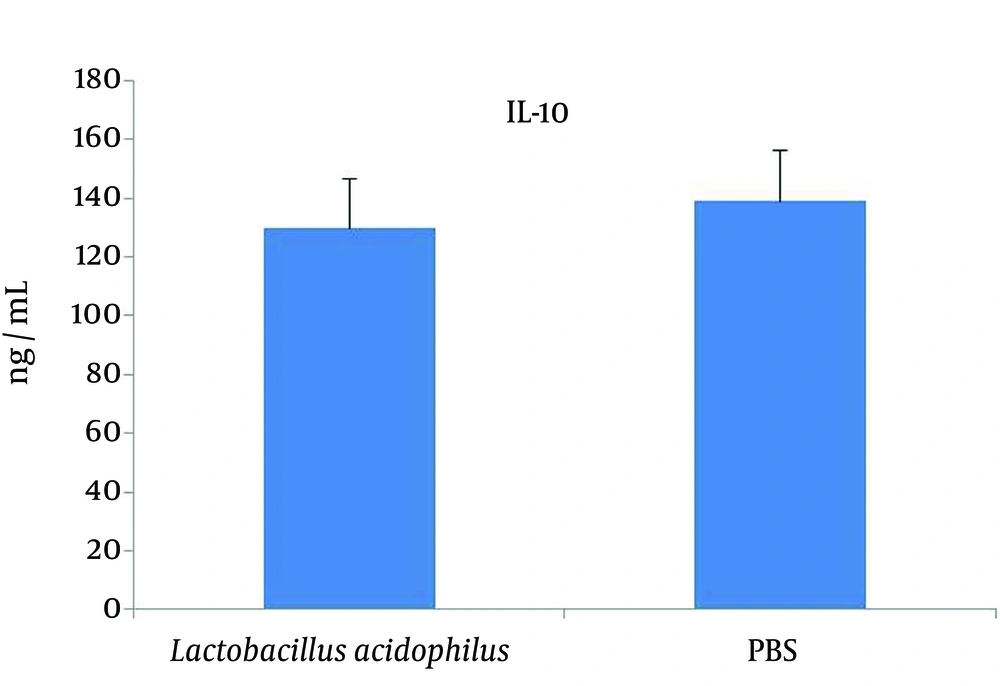
The levels of IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10 in the spleen cell culture supernatants were measured using a sandwich ELISA assay. The level of IFN-γ in the spleen cell culture supernatants was significantly (P = 0.005) higher in the L. acidophilus group compared with that of the control; while the IL-4 level was lower than that of the control, however the difference was not significant (Figure 1). The IFN-γ/IL-4 ratios are also shown in Figure 2, although the level of IL-10 (Figure 3) had no change anymore.
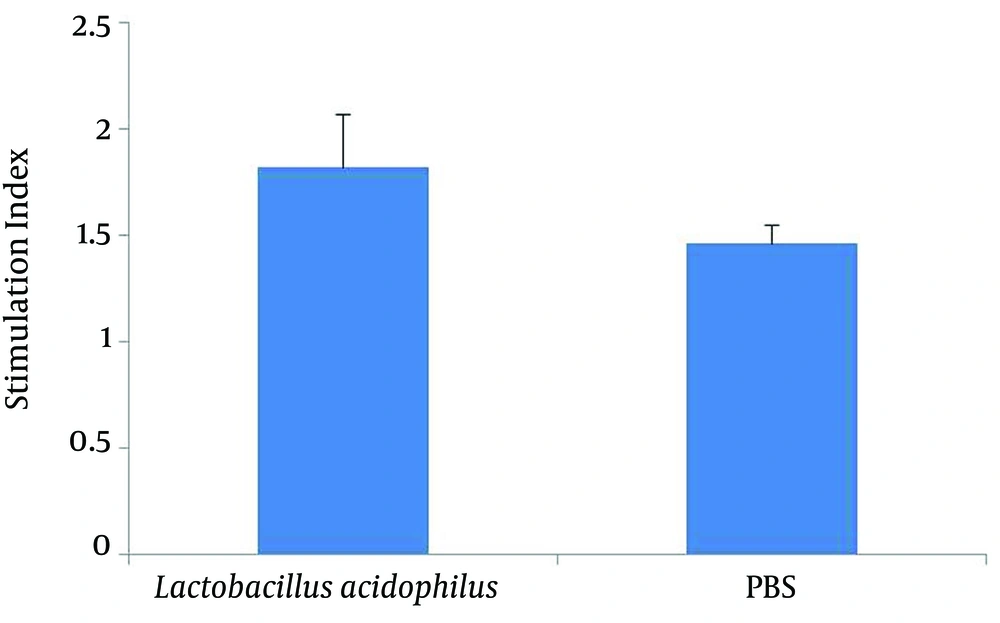
4.2. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus Administration on Splenocyte Proliferation
The results of PHA-stimulated splenocyte proliferation in both groups of mice are shown in Figure 4. The PHA-stimulated splenocyte proliferation in the L. acidophilus administrated mice was considerably higher than that of the PBS control mice. The dose of PHA used as a mitogen in this test was 5 µg/mL.
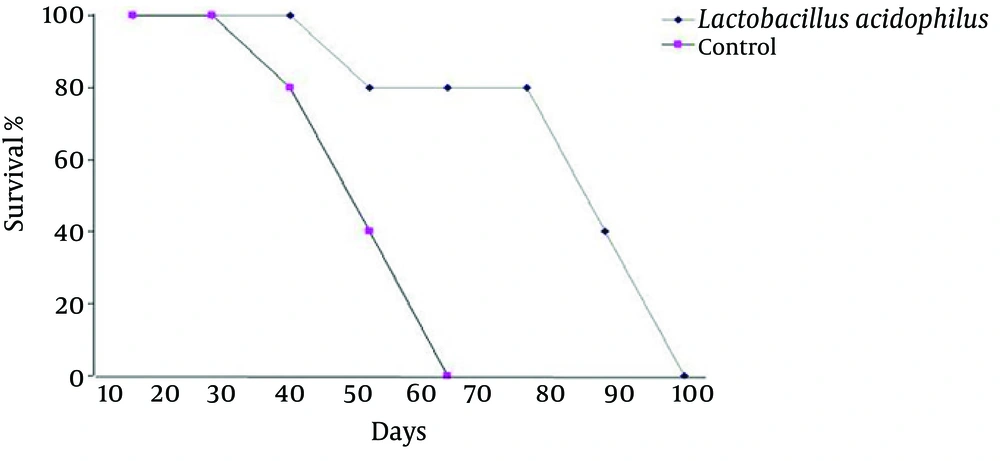
4.3. Survival Rate
The results of survival analysis showed a decrease (P = 0001) in the rate of death or in other words increase in the survival rate among the L. acidophilus group in comparison to that of the controls (Figure 5).
At the end of the study, four mice from each group were kept under standard conditions until they died. The rate of death was registered every day and the obtained data was analyzed with Kaplan-Miere Test after the last death the in both groups. P = 0.001was considered as the level of significance.
5. Discussion
Probiotics are friendly microorganisms that when administered in adequate amounts, confer health benefits in their host, according to the World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization definitions (11). Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) are the most commonly used microorganisms as probiotics. According to the results of the current study, oral administration of L. acidophilus can promote the immune responses with Th1 dominance via stimulation of the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, and inhibit the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-4 and IL-10, which can differentiate the immune responses with Th2 bias. IFN-γ is one of the most important Th1 cytokines with a key role in the activation of natural killer cells (NK cells), which are the first immune defense against the tumor cells and viral infections. IFN-γ also has an important role in Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) expression on the surface of cells.
Since MHC expression diminishes in some tumor cells, specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte (CTL) mechanisms cannot detect these cells; therefore, increasing of this cytokine may help the CD8+ T cells to campaign with this type of tumors in addition to activation of NK cytotoxicity. Moreover, high levels of IFN-γ can inhibit the intratumoral angiogenesis, which has a critical role in cancer prognosis (12). Besides the increase in the level of IFN-γ, decrease in IL-4 production in the splenocytes of L. acidophilus administered mice, as an important Th2 cytokine, also indicated the Th1 property of immune response. IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory Th2 cytokine with a key role to inhibit the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-3, TNFα and GM-CSF made by the cells such as macrophages and the type 1 T helper cells (13). IL-4 decreases macrophage inflammatory activity. It is also an important cytokine in immune regulation. Therefore, decrease of this cytokine in tumor condition may help with better prognosis. LAB are commensal bacteria in the intestine, which have close contact with Gastrointestinal Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT).
Many studies indicated the effect of these bacteria on the maturation of immune cells in GALT, and the efficacy of immune responses (14, 15). According to some other studies the effect of LAB on the development of immune responses and immunomodulation depends on two facts, first the contact of immune cells particularly the antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as macrophage and dendritic cells (DCs) with the bacterial components that are mostly peptidoglycan (PG) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) in these bacteria; and secondly on the probiotic’s metabolites specially in the fermented foods (16-18). Some investigations indicated that LAB show their effect on the immune status via toll like receptors (TLRs), particularly TLR2 that recognize LTA and PG and TLR9 that recognizes CpG like oligonucleotides, which exist in lactic acid bacteria (19-21).
These bacterial components are recognized by corresponding Toll-like Receptors (TLR), followed by cytokine secretion (20). In addition, L. acidophilus administration can affect the proliferation of immune cells in the spleen of mice via stimulation with specific tumor antigens implying that this type of LAB has immunostimulatory properties. This property can be attributed to the presence of LTA antigen as a major component in the cell walls of LAB. Some studies showed tumor-induced immunosuppression (22), and under such conditions, administration of any immunostimulator agent may contribute to the development of efficient immune defense. To confirm the other results of the current study, increase in the survival rate of the L. acidophilus and other Lactobacillus spp. administered mice supported the immunostimulatory and immunomodulatory effects of this strain (23, 24). In conclusion, the results of the study suggested that daily consumption of L. acidophilus may modulate the immune response through its antitumor property and enhance the Th1 cytokine production like IFN-γ, which is more necessary in tumor condition. But more investigations are needed to understand the other mechanisms of such effects.