1. Background
The seasonal influenza A(H1N1) virus is responsible for respiratory tract infections in humans and its morbidity and mortality are increasing (1-3). During pandemic 2009, a novel influenza A virus was emerged in North America and Mexico and quickly spread to many countries across the world. Subsequently, the world health organization (WHO) enhanced phase 6 for the universal pandemic alert level urging prevention and treatment strategies through vaccination and administration of anti-influenza drugs such as adamantanes and neuraminidase inhibitors (1, 2, 4). Adamantanes block M2 ion channel protein and oseltamivir and zanamivir, which are neuraminidase inhibitors (NAIs) and block the activity of viral neuraminidase (NA). NAIs specifically inhibit viral replication by preventing virus release and allowing virus accumulation in cells (5-7).
The quick emergence and spread of resistance to oseltamivir were observed in the 2009 pandemic influenza (A(H1N1)pdm09) (4, 8). Resistance to oseltamivir can be identified by genotypic and phenotypic assays (9). Most A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses have a specific histidine to tyrosine substitution at position 275 (H275Y) of neuraminidase protein, which is responsible for resistance to oseltamivir (3, 4, 7, 8, 10). Recently, another amino acid substitution in the NA (serine to asparagines, S247N) of A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses has been identified, that designates a low-level of oseltamivir-resistance (7, 10, 11). Until February 2009, data reported from Argentina indicated that 97% of the examined European specimens were resistant to oseltamivir, which were sensitive to amantadine, rimantadine, and zanamivir (7).
2. Objectives
The goals of this study were to determine the prevalence of oseltamivir resistant influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses in Shiraz, Iran from December 2012 until February 2013, and compare the phylogenetic relationships between these viruses from Iran and other countries.
3. Patients and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
Throat swab samples from 200 patients (44.5% from females and 55.5% from males), with influenza-like illnesses were collected in Shiraz hospitals from December 2012 until February 2013. The patients aged from 2.5 months to 70 years, with the mean age of 10.01 years. The study was approved by the ethics committee of Shiraz university of medical sciences.
3.2. Cells and Virus Isolation
Madin-Darby canine kidney cell was grown in DMEM medium (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (GIBCO, Australia), containing 100 µg/mL penicillin and 100 µg/mL streptomycin. The isolation of influenza virus in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells was carried out using standard procedure described previously. After observing the cytopathic effect, the hemagglutinin assay (HA) test was performed using guinea pig erythrocytes (12).
3.3. Oseltamivir Drug Susceptibility Testing
Oseltamivir cytotoxicity was determined by growing uninfected cells in the absence or presence of various concentrations of oseltamivir for 1, 2, 3, and 4 days (Roche, UK). The cytotoxicity test was carried out using Microculture Tetrazolium assay (MTT) (Sigma, Germany) (13). MDCK cell infected with the isolated viral strains were incubated at 34°C, for 1 hour. The supernates were then replaced with medium containing various concentrations of oseltamivir carboxylate, and incubated at 34°C for 72 hours. The oseltamivir susceptibility was determined using Spearman-Karber method of measuring 50% tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) (14).
3.4. RNA Extraction
RNA extraction was carried out using Roche high pure viral RNA extraction kit (Roche, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted RNAs were kept in -80°C until further processing.
3.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Real-time PCR was carried out using SuperScript III Platinum one-step quantitative RT-PCR kit (Invitrogen, USA). Real-time runs were performed on the Corbett 6000 Rotor-Gene system. The reaction comprised 4 μL of extracted RNA combined with 16μL of master mix, including 2X reaction mix; SuperScript III RT/Platinum Taq Mix; 5.4 μL RNase/DNase-Free water; and 0.4 μL of each primer and probe with the 40 μL and 10 μL concentrations, respectively.
Each sample of RNA was tested by separate primer/probe sets for the detection of influenza universal swine (swFLuA), Swine H1, and RNase P. According to the CDC real-time PCR protocol (2009), the cycling conditions included a 30 minutes RT step at 50°C, followed by enzyme inactivation at 95°C for 2 minutes. The PCR step comprised 45 cycles at 95°C for 15 seconds, 55°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 30 seconds. Data acquisition and analyses of the real-time PCR assay were accomplished using the Rotor-Gene data analysis Software, Version 6.0A.
3.6. Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequencing
RNA was converted to cDNA using 2-steps RT-PCR kit (Vivantis, Malaysia). NA gene was amplified and RT-PCR products were purified employing RT-PCR purification kit (Bioneer, Korea), and then sequenced applying Nested-PCR internal primers (SinaClon, Iran) (15). Chromatogram of our sequences were aligned with the consensus sequence of A(H1N1)pdm09 derived from sequences recorded in NCBI (national center for biotechnology information) by Chromas software and resistance mutations were studied using CLC Sequence Viewer 6 software.
Neuraminidase sequences obtained were deposited at GenBank database (USA) under accession numbers: KJ755333, KJ755334, KJ755335, KJ755336, KJ789325, KJ789326, KJ789327, KJ789328, KJ789329, and KJ789330. The whole NA gene alignment was performed using the ClustalW2 program.
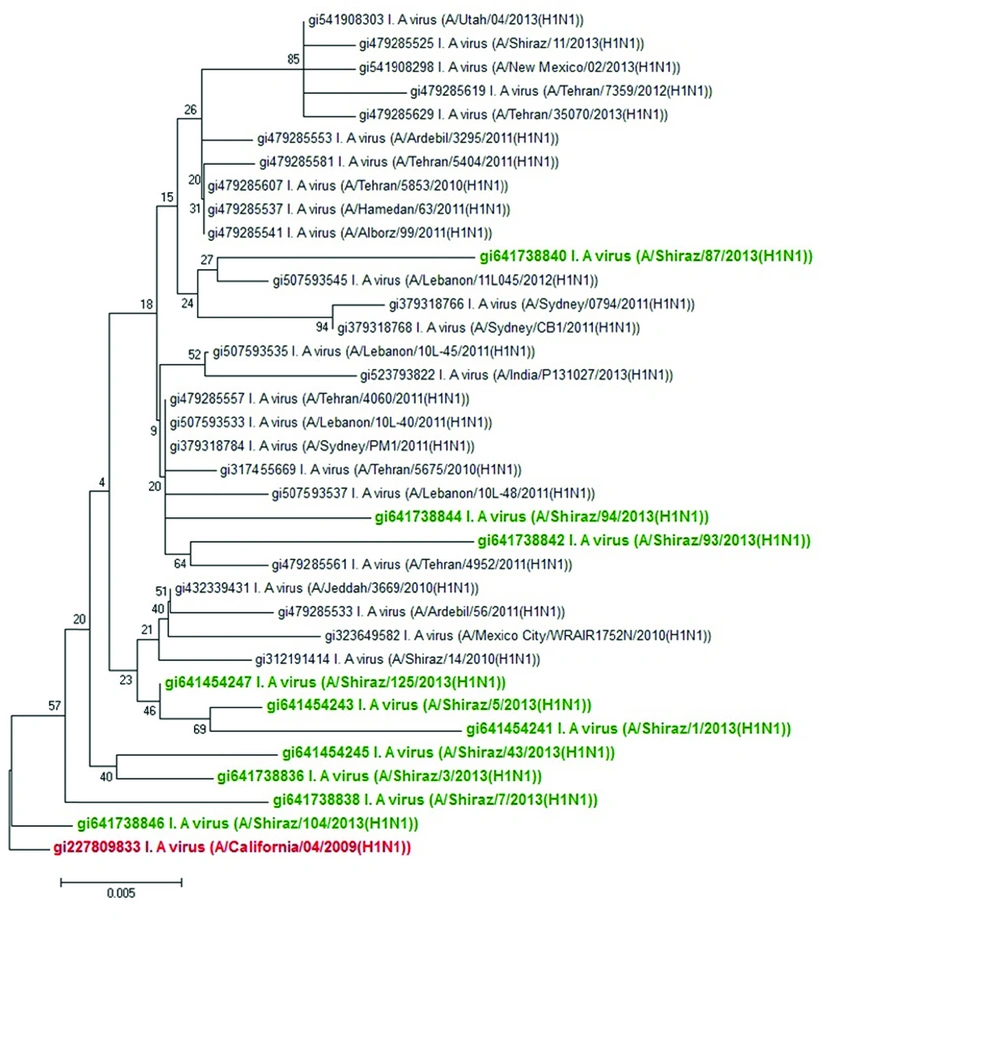
The phylogenetic tree of the NA gene was drawn using the neighbor-joining method and analyzed by the bootstrap consensus tree method with 1000 replicates. The evolutionary distances were calculated using the p-distance method. The analysis involved 36 NA gene nucleotide sequences. Evolutionary analyses were performed in the MEGA program (version 6.0) (16). The tree was rooted with a reference strain A/California/4/2009 NA sequence (GenBank accession number: FJ966084), representing the viral sequences obtained at the beginning of the pandemic.
4. Results
4.1. Virus Isolation
The mutations linked to the drug-resistant variants of influenza viruses were studied to determine the current status of oseltamivir resistant A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses in Shiraz, Iran. Across 200 specimens, 77 (38.5%) isolates were identified as A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses using RT-PCR method, hemagglutinin assay, and NA-specific Nested PCR and genetic sequencing. The genetic sequencing then revealed that 10 of the A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses isolated during 2012 - 2013 were wild-type (H275) in the NA gene. The symptoms observed in most patients studied, were fever, chills, muscle aches, headache, cough, fatigue, and less frequently sore throat, pharyngitis, nasal congestion, digestive disturbance, and otitis.
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Neuraminidase Gene
The sequences and phylogenetic relationships of the 10 influenza viruses isolated from Shiraz, Iran during 2012 and 2013 demonstrated that they belonged to A, B, and C clusters based on their NA gene. In this phylogeny, most isolates located within A and B clusters with V13G, V106I, V241I, N248D, and N369K mutations in the NA gene. We could not detect any oseltamivir-resistant H275Y mutation in NA gene in our samples. This also indicated a close phylogenetic relationship between A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses detected from Tehran and Shiraz (Figure 1). Phylogenetic analysis of different A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses in 2013 was also consistent with isolation of A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses isolated around the world during 2013 (17). These sequences of NA gene, including those of our isolates formed a single cluster (Figure 1).
(A comparison between nucleotide sequences of A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses isolated in Shiraz, Iran in 2013 and sequences of A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses from Iran and other parts of the world, indicated by their GI numbers, also bootstrap values are shown on the branches adjacent to the tree nodes. The strains from Shiraz and a reference strain are shown in bold green and bold red respectively).
4.3. Genotypic and Phenotypic Antiviral Drug-Susceptibility
All our isolates were sensitive to oseltamivir in culture and this was evidenced by the lack of H275Y and S247N mutations and 9 substitutions (V116, I117, E119, Q136, K150, D151, D199, I223 and N295) in the NA gene as indicators of NAI resistance demonstrated by CLC Sequence Viewer 6 software (18, 19). Statistical analysis using t test showed significant differences in the frequency of oseltamivir resistance between various concentrations of the drug in 3 replicates (P < 0.001) (Table 1). All 10 oseltamivir sensitive isolates had TCID50 values between 0.49 and 5.32 (Table 1).
| Oseltamivir Concentration, mg/mL | Mean of TCID (50) Log10 Virus Yield | Effect (S or R) | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 ± 0 | - | - |
| 0.5 | 0.49 ± 0.49 | S | < 0.001 |
| 0.25 | 0.92 ± 0.51 | S | < 0.001 |
| 0.125 | 1.29 ± 0.50 | S | < 0.001 |
| 0.0625 | 1.54 ± 0.52 | S | < 0.001 |
| 0.0312 | 5.32 ± 0.58 | S | < 0.001 |
The analysis of full-length NA sequences obtained from A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses collected during December 2012 until February 2013 in Shiraz, Iran revealed close relationship between these viruses evidenced by 97% - 99.78% similarity among neuraminidase nucleotides. A comparison of these samples’ sequences showed 5 additional substitutions (V13G, V106I, V241I, N248D, and N369K) in NA protein (Table 2). These mutations were typically present in many of the 2013 sequences and were not associated with resistance pattern.
| Accession Number | 13 | 106 | 241 | 248 | 275 | 369 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FJ966084 | V | V | V | N | H | N |
| KJ755333 | G | I | - | D | - | K |
| KJ755334 | G | I | - | D | - | K |
| KJ755335 | G | I | I | - | - | K |
| KJ755336 | G | I | - | D | - | K |
| KJ789325 | G | I | I | - | - | - |
| KJ789326 | G | - | I | D | - | - |
| KJ789327 | G | I | I | D | - | K |
| KJ789328 | - | I | I | D | - | K |
| KJ789329 | - | I | I | D | - | K |
| KJ789330 | - | - | I | - | - | - |
5. Discussion
In April 2009, a new influenza A(H1N1) virus emerged in Mexico that quickly spread all over the world (20). This pandemic virus was first reported in June 2009 in Iran and became predominant during the 2009 influenza seasons (21). Increasing resistance of influenza A viruses to oseltamivir has recently been reported around the world (3). It is usually believed that oseltamivir resistant viruses emerge under the selective pressure of antiviral drug, but they are less pathogenic or transmissible than sensitive viruses (6). Resistance to oseltamivir in the A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses is associated with two mutations (H275Y and S247N). However, strains with H275Y mutation have the important advantage of rapid replication, which leads to a more widespread circulation (15). This study highlighted the prevalence of oseltamivir resistant A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses from 2012 to 2013 in Shiraz, Iran. This variant exhibited 5 mutations in NA gene, including V13G, V106I, V241I, N248D, and N369K.
Our study showed that V106I, V241I, N248D, and N369K mutations are most common substitutions in NA gene of A(H1N1)pdm09 virus. These 4 mutations in resistant and sensitive isolates occurred at the specific sites of NA in positions 106, 241, 248, and 369. Phylogenetic analysis showed that genetic features of A(H1N1)pdm09 variants isolated in Shiraz and other cities of Iran during 2012 and 2013 were also associated with A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses isolated from our patients. On the other hand, the A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses collected in this study revealed high homology to viruses of cluster B isolated in Shiraz in 2010.
The results showed that all of our isolates were sensitive to oseltamivir and phylogenetically close to the reference strain (A/California/4/2009). The results of the analysis of molecular test were consistent with those of phenotypic tests performed in cell cultures. Oseltamivir resistance to A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses with H275Y mutation was detected in 4 patients in 2009 in Tehran, Iran. In this study, A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses isolated from some patients, who did not consume oseltamivir and infected with these viruses were resistant to this drug. Thus, the results showed that the resistant virus could have emerged in the presence or absence of selective drug pressure (4). In 2009, another study performed in Shiraz, Iran showed no oseltamivir resistant A(H1N1) pdm09 viruses with H275Y mutation (21). In a similar study conducted in Beijing, China, all of the A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses isolated in 2012 - 2013 were sensitive to oseltamivir (22). However, studies conducted in the United States, Australia, Brazil, Italy, and the Asia-Pacific showed a significant increase in the oseltamivir resistant A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses with H275Y mutation (2, 15, 17, 18, 23-25). Experiments conducted in cell cultures in Greece showed resistant variants with H275Y, to be the dominant population. This finding shows that the H275Y substitution does not compromise with the replication of A(H1N1)pdm09 virus in vitro (8).
The analysis of oseltamivir resistance test results requires knowledge about the present laboratory procedures and their restrictions. Optimal testing procedures are different depending on the influenza virus type/subtype and drug testing. Therefore, commentary on antiviral sensitivity testing for clinical goals is complicated, and the results obtained may also vary with respect to different laboratories. The combination of applied and genotypic methods would be the most instructive and provide optimal testing method in connection with newly emerging oseltamivir resistant strain (9).
There is growing concern that A(H1N1)pdm09 virus strains resistant to oseltamivir may appear and spread in a similar fashion to oseltamivir resistant A(H1N1) seasonal virus (26). Our information about identification and transmissibility of oseltamivir resistant variant is still limited, and requires in vivo and in vitro studies. In addition, A(H1N1)pdm09 virus must be carefully monitored to identify the emerging of drug resistant variants. Results of in vivo research in ferret and mice models in Lebanon revealed that oseltamivir resistant A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses are pathogenic and can be effectively transmitted via close contact, but not through respiratory droplets. Inefficient transfer of droplets of oseltamivir resistant A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses could account for extremely low frequency of these viruses (2). In the present situation, the correct use of oseltamivir followed by careful surveillance is essential to identify drug-resistant A(H1N1)pdm09.