1. Background
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) integrase EC 2.7.7.49 is a key enzyme responsible for integration of viral DNA into the host cell DNA; the process that is mandatory for viral replication and host cell infection (1-3). Unlike protease and reverse transcriptase of HIV-1 virus, integrase has no analogue in host cells; therefore, viral infection is highly dependent on integrase activity. Accordingly, integrase deactivation could be considered as an effective way for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) treatment (4-9).
Integrase is a single stranded 32 kDa protein with 288 residues encoded by the 3' end of the POL gene. The structural analysis of integrase protein revealed that it has three distinct domains, each with specific functions (10, 11) These domains include the N-terminal domain (NTD), residues 1 - 50, with zinc binding motif of HHCC that takes part in enzyme multimerization i.e. formation of functional multimeric assemblies as tetramers or octamers (12-14); and the catalytic core domain (CCD), residues 51 - 212, that contains a conservative catalytic motif of DD35E, which is composed of Asp64, Asp116 and Glu152. This domain with the aid of two magnesium ions (Mg+2) catalyzes the integration of viral DNA into host cell genome. The first magnesium ion is placed between Asp128 and Asp185 (A-site) and the next magnesium ion is placed between Asp128 and Glu221 (B-site).
The magnesium ion of the B-site makes a pentahedral complex with the two carboxyl groups of Asp128 and Glu221, hydroxyl group of 3’-OH of dA nucleotide and two H2O molecules. This complex activates the 3’-OH group for a nucleophilic attack on host cell DNA. In this context, the A-site stabilizes the pentahedral complex of the B-site and guarantees the integration process. Moreover, it has been shown that the CCD domain facilitates DNA binding to the enzyme binding site (15, 16). The last domain of integrase, residues 213 - 288, is called the C-terminal domain (CTD), which is believed to act as a non specific binding site for DNA (12, 14, 17-19).
The integration catalyzed by integrase could be divided into two distinct processes. The first process is called 3’-OH processing, in which integrase in the host cell cytoplasm binds to the CAGT sequence at both ends of the viral DNA, hydrolyzes G and T nucleotides and leaves the naked 3’-OH on the last nucleotides (20, 21). The next process is called the strand transfer process, in which integrase in host cell nucleus uses Mg2+-activated 3’-OH groups of B-site to attack host cell DNA to integrate viral DNA (22, 23).
Based on this mechanism, there are two classes of inhibitors designed against these two processes: 1-inhibitors against the 3’-OH process at the DNA binding site, known as integrase binding inhibitors (IBIN) and 2-inhibitors against the integrase-DNA (or pre-integration) complex. These inhibitors, which bind to Mg2+ ions of the binding site and prevent DNA transfer to the host cell genome, are called integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTI) (24-28).
Even though the full-length crystal structure of integrase from prototype foamy virus (PFV) in complex with DNA is available to model HIV-1 integrase in bioinformatics methods for drug design, there is an essential need for the full-length coordinate structure of HIV-1 integrase (29-39).
2. Objectives
In the present work, we attempted to construct a full-length coordinate structure for HIV-1 integrase using the PFV integrase as the starting structure in a bid to obtain more effective drugs. Finally, we decided to simulate, in parallel experiments, the new HIV-1 integrase and an intact copy of PFV integrase to compare them, from a structural point of view, to see whether the two structures show similar dynamic behaviors. This, presumably, helps identify which of the structures is more representative of viral HIV-1 integrase.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Crystal Structures Used
The crystal structure of wild type PFV in the protein data bank (PDB) (ID number 3L2T) with no mutation, was used as a native structure for PFV throughout this study. The structure, which was obtained by the X-ray diffraction method and refined at the resolutions of 2.0 Å, was retrieved from the protein data bank (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb) (40).
3.2. Sequence Alignment
The sequence of wild type HIV-1 integrase in FASTA format was obtained from http://www.bioafrica.net/ as presented in Figure 1. This sequence was then aligned with the PFV sequence on the http://fasta.bioch.virginia.edu/ server to match their sequence similarity (Figure 1 B).
3.3. Constructing a New Structure for HIV-1 Integrase
To construct a coordinate structure for HIV-1 integrase based on the PFV structure, we used a copy of the 3L2T.PDB file and renamed it HIV-1.pdb. This file was opened in the text editor software and 59 residues from the N-terminal and 15 residues from the C-terminal were deleted to provide a protein with appropriate length for HIV-1 integrase. The file was then opened in the Swiss-Pdb Viewer software (http://www.expasy.org/) and the residues were mutated according to alignment results presented in Figure 1 B to match the HIV-1 integrase sequence (41, 42). In this process, the constructed structure was energy-minimized.
3.4. Systems Preparation
The final constructed structure for HIV-1 was placed in the center of a rectangular box with the following dimensions, 8.15 × 9.06 × 9.58 nm, for further experimentation. An intact copy of 3L2T.pdb was used as an intact PFV integrase and placed in the same box with 9.44 × 9.26 × 10.63 nm dimensions. The two boxes were then filled with SPCE solvents using the genbox command of GROMACS package so that the proteins were covered by a water shell of 1.0-nm thickness.
3.5. Molecular Dynamic (MD) Simulation
The experiments were performed using the double-precision MPI version of GROMACS 4.5.5 installed on the UBUNTU version 12.10 with amber 99sb force field (43). The net charges of simulated systems were analyzed by the preprocessor engine of the GROMACS package. System neutralization was done by adding equivalent numbers of positive sodium ions. Energy minimization was performed for hydrogen atoms, ions and solvents in 1500 steps, using the steepest descent method to minimize the system energy to at least 300 kJ/mol. Linear constraint solver (LINCS) algorithm was used to apply constraint on bonds lengths. The SETTLE algorithm was also used to constrain the geometry of solvents.
The systems were then subjected to a short molecular dynamic with all-bonds restrains for a period of 500 ps, before performing a full MD without any restrains (44). All simulations were carried out for 10 ns at 37°C and one atmospheric pressure. Berendsen, and Thermostat and Barostat, were used for temperature and pressure coupling, respectively and the Particle Mesh Ewald (PME) method for electrostatic interactions. The time steps of one femtosecond were applied to all simulations. All of these simulations were done at neutral pH (Asp, Glu, Arg and Lys ionized) (45, 46).
3.6. Docking Experiments
Binding energy of DNA to each integrase was calculated using the Hex software version 5.1 (http://www.loria.fr/) (47). The default-shape only mode of correlation was used to study the physical fitness of DNA to their binding site in HIV-1 and PFV integrase. Docking results were scored based on their energy and the first 100 solutions were averaged to obtain the binding energy of DNA to integrase.
The Argus-Lab 4.0.1 Software (http://www.arguslab.com) was used to extract binding site residues that participate in DNA binding to integrase (48).
4. Results
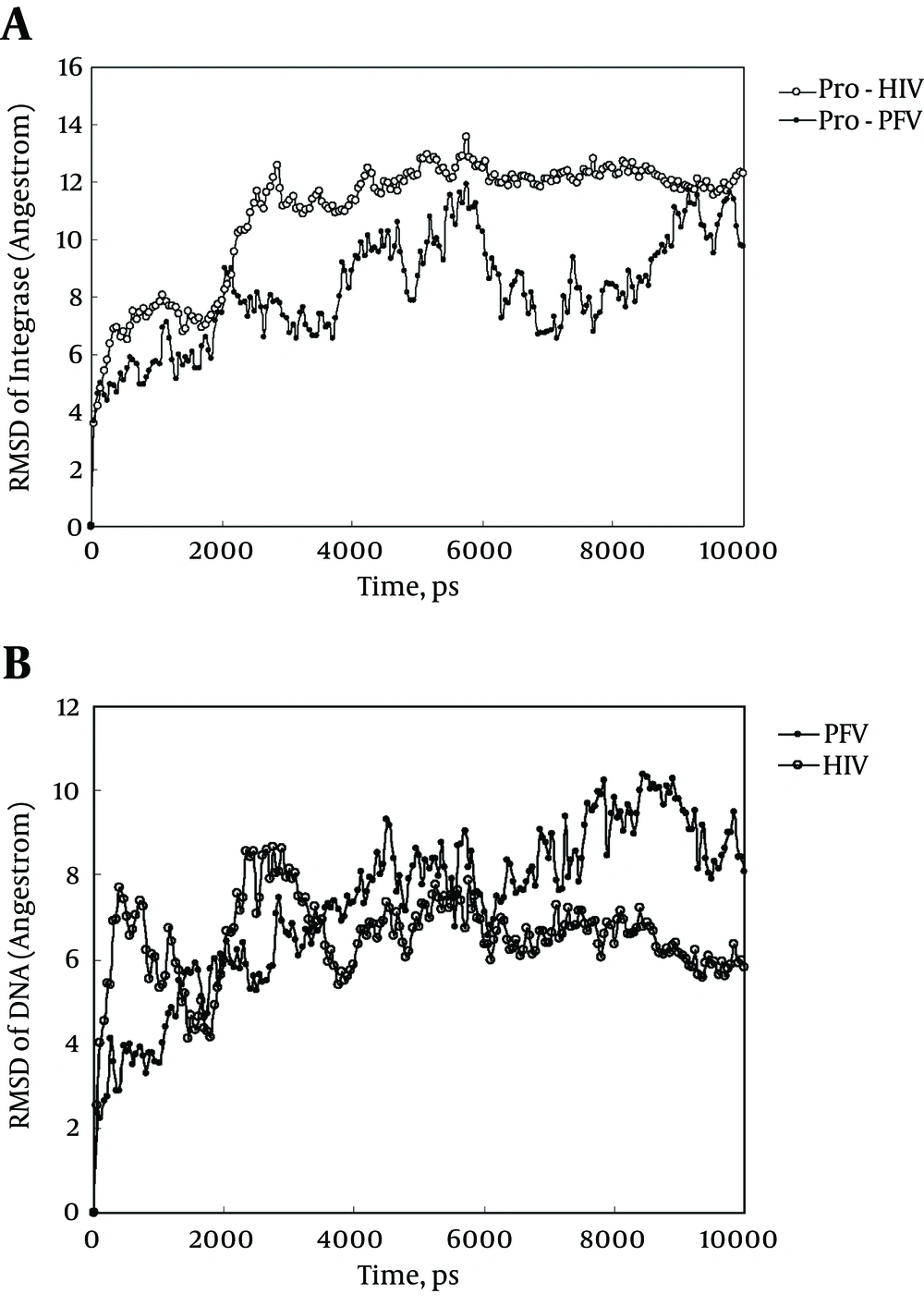
As indicated in Figure 2 A, HIV-1 undergoes more structural alterations than PFV upon simulation with a greater increase in the Root Mean Square Displacement (RMSD) curve. This means that HIV-1 integrase experiences extensive changes in its tertiary structure while attaining its equilibrated structure at about 3000 ps. On the other hand, in equilibrated states, at 5000 - 10000 ps, the RMSD curve of PFV shows more variation than that of HIV-1 integrase. The less fluctuating RMSD is an indication of a more stable and less flexible structure for the HIV-1 integrase. Figure 2 indicates that DNA- HIV-1 integrase complex is tighter and less flexible.
A, Root mean square displacement plot of HIV-1 and prototype foamy virus integrase backbone against their initial state obtained at 37°C and one atmospheric pressure in SPCE water box; B, root mean square displacement plot of DNA of HIV-1 and prototype foamy virus integrase-DNA complex against their initial state obtained at 37°C and one atmospheric pressure in SPCE water box and shows the RMSD progression of complexes of DNA with HIV-1 and PFV in comparison to their initial state.
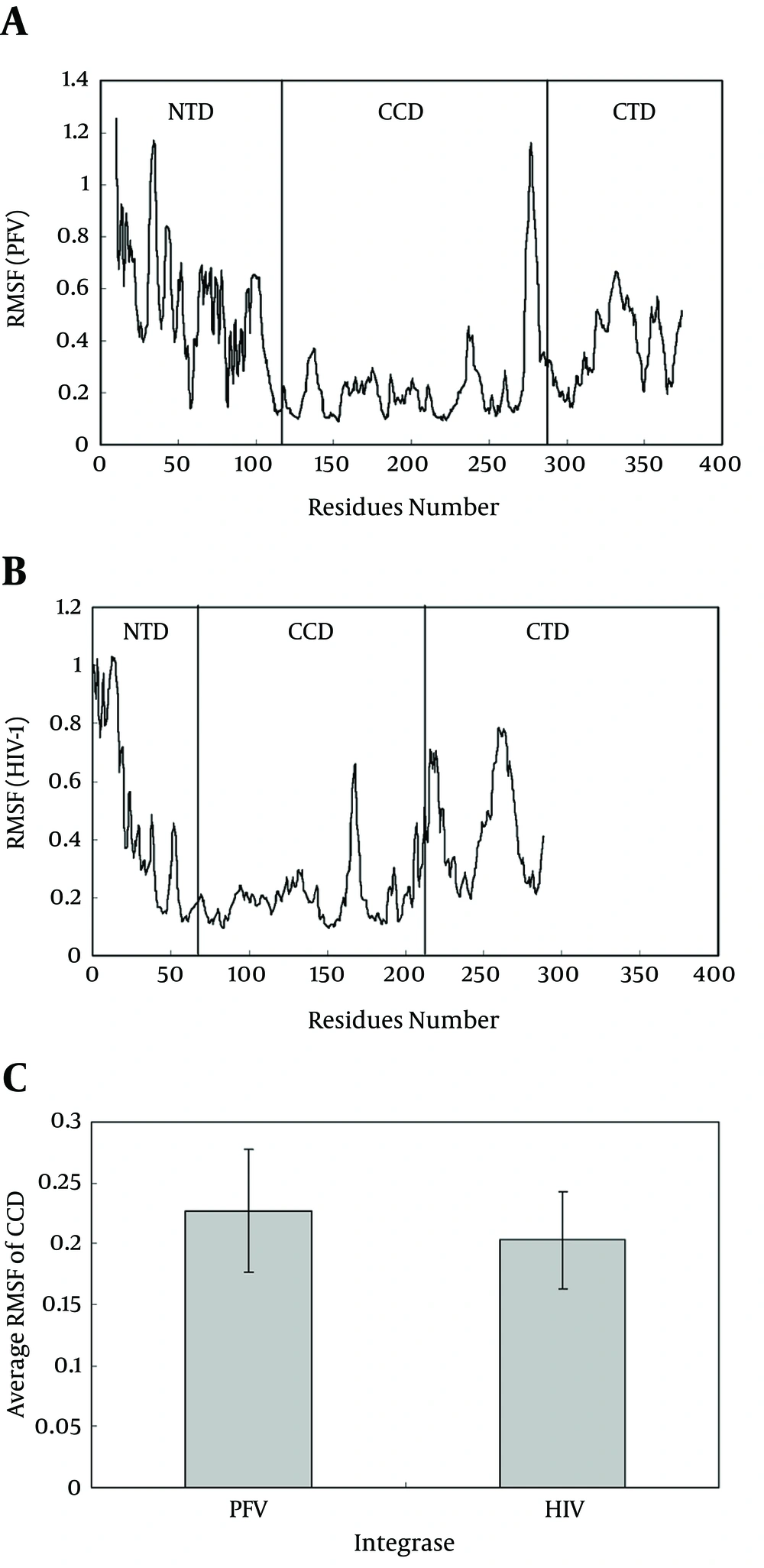
Figures 3 A and B show root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) plots for alpha carbons of HIV-1 and PFV during simulation, respectively. As depicted, the RMSF of each domain of N-terminal domain (NTD), catalytic core domain (CCD) and C-terminal domain (CTD) from HIV-1 (Figure 2 A) could be compared to their counterparts on the PFV system, separately (Figure 2 B). These drawing show that CCD domains of both systems in contrast to NTD and CTD domains, show lower RMSF values and lower flexibilities during simulation.
A, Root mean square displacement plot of prototype foamy virus integrase obtained for 10 ns Simulation at 37°C and one atmospheric pressure in SPCE water box; B, root mean square displacement Plot of HIV-1 Integrase Obtained for 10 ns simulation at 37°C and one atmospheric pressure in SPCE water box; C, average root mean square displacement for catalytic residues of prototype foamy virus (Residues 120 - 282) and HIV-1 (Residues 50 - 212) calculated from data of Figure 4 A and B as average ± SD (P < 0.05)
Figure 3 C illustrates the average RMSF values for HIV-1 and PFV CCD domain. Higher values of RMSF for PFV (P < 0.001) may be attributed to its longer domains of NTD and CTD with extra 59 and 15 residues, respectively, in contrast to HIV-1 integrase. Longer flexible tails of PFV provide a source for more flexibility and instability in its tertiary structure and leads to a loosely folded conformation.
The MSD curve of DNA displacement inside integrase during simulation showed more tightly bound DNA to HIV-1 with retained propagation in contrast to PFV integrase (data not shown). In other word, the Figure 3 indicates that DNA was held more strongly by HIV-1 integrase via its binding site than by PFV integrase.
The first hydration layer of macromolecules is described as a dense layer of solvents arranged at a distance of 3 - 5 angstroms from the macromolecule backbone. This layer plays an important role in structure-function cooperation of macromolecules. To show the difference of thickness in the hydration layer of HIV-1 and PFV, we calculated the first hydration layers for both simulated systems. These calculations (data not shown) indicated that the population of solvents in the first hydration layer of PFV was two times more than that of HIV-1 integrase. These findings, being in accordance with our results, confirm that PFV integrase has a more extended structure with more extended hydration layer compared to HIV-1. The data was interpreted as a more extended structure for PFV-DNA complex with a loosely folded structure in contrast to HIV-1-DNA complex.
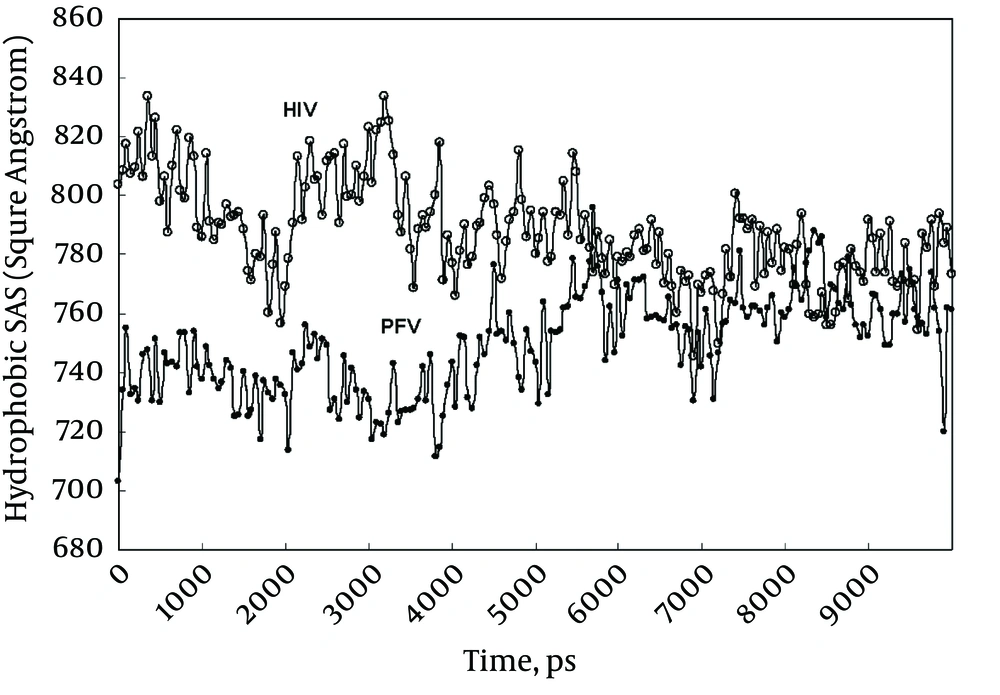
Figure 4 shows the hydrophobic part of accessible solvent area (ASA) for HIV-1 and PFV integrases during simulation periods. Since HIV-1 integrase structure used in this experiment does not equilibrate before simulation, it is expected to express higher ASA during the early phase of simulation (Figure 4). Progress in ASA for HIV-1, gradually pushes integrase toward its native state with decreased ASA. Ultimately, HIV-1 integrase reaches its equilibrated structure with similar ASA as PFV.
Intra-molecular hydrogen bonds include bonds formed between secondary or tertiary structure elements. Time course determination of these hydrogen bonds for our simulated systems provide valuable information about our systems.
Given that the counts of bonds are proportional to residue numbers, we calculated the intra-molecular bonds formed per residue to make a reasonable comparison between HIV-1 integrase and PFV. We found that about 1.8 and 1.5 hydrogen bonds formed per residue in HIV-1 integrase and PFV integrase, respectively. This finding indicates that the more hydrogen bonds are formed, the more stable conformation for HIV-1 integrase will be.
Binding site hydrophobicity of integrase for DNA is another useful index to structurally compare HIV-1 with PFV. Hydrophobicity could be calculated for a binding site by summation of hydrophobic indices of residues comprising of enzyme active site. In order to calculate hydrophobicity, we first extracted residues of active site for each integrase by the Argus-Lab 4.0.1 software (http://www.arguslab.com). Our data showed that PFV binding site includes residues Asp128, Tyr129, Asp185, Phe190, Tyr212, His213, Pro214, Gln215, Glu221, Asn224 and Arg326, and HIV-1 binding site includes Ile60, Trp61, Gln62, Leu63, Asp64, Asp116, Phe121, Gln148, Glu152, Asn155 and Lys159. Then, using the Kyte-Doolittle scale for hydrophobicity, we calculated the total hydrophobic index for active site residues of HIV-1 and PFV. The total hydrophobic index of HIV-1 and PFV were calculated as -14.7 and -28.3, respectively (48). The more hydrophobic index for HIV-1 integrase (more positive) indicates its stronger hydrophobicity compared to PFV, which means that DNA makes a more stable complex with HIV-1 than PFV.
This finding encouraged us to calculate the direct binding energy of DNA to both integrase, HIV-1 and PFV, by performing docking experiments. Using the Hex software version 5.1 (http://www.loria.fr/), we performed docking experiments for DNA with both HIV-1 and PFV. Our results indicate that the binding energy of DNA to HIV-1 integrase and to PFV integrase are-662 KJ/Mol and -658 KJ/Mol, respectively. The higher binding energy of DNA to HIV-1 (about 14 KJ/mol higher) confirmed again the higher stability of DNA-HIV-1 complex compared to DNA-PFV complex.
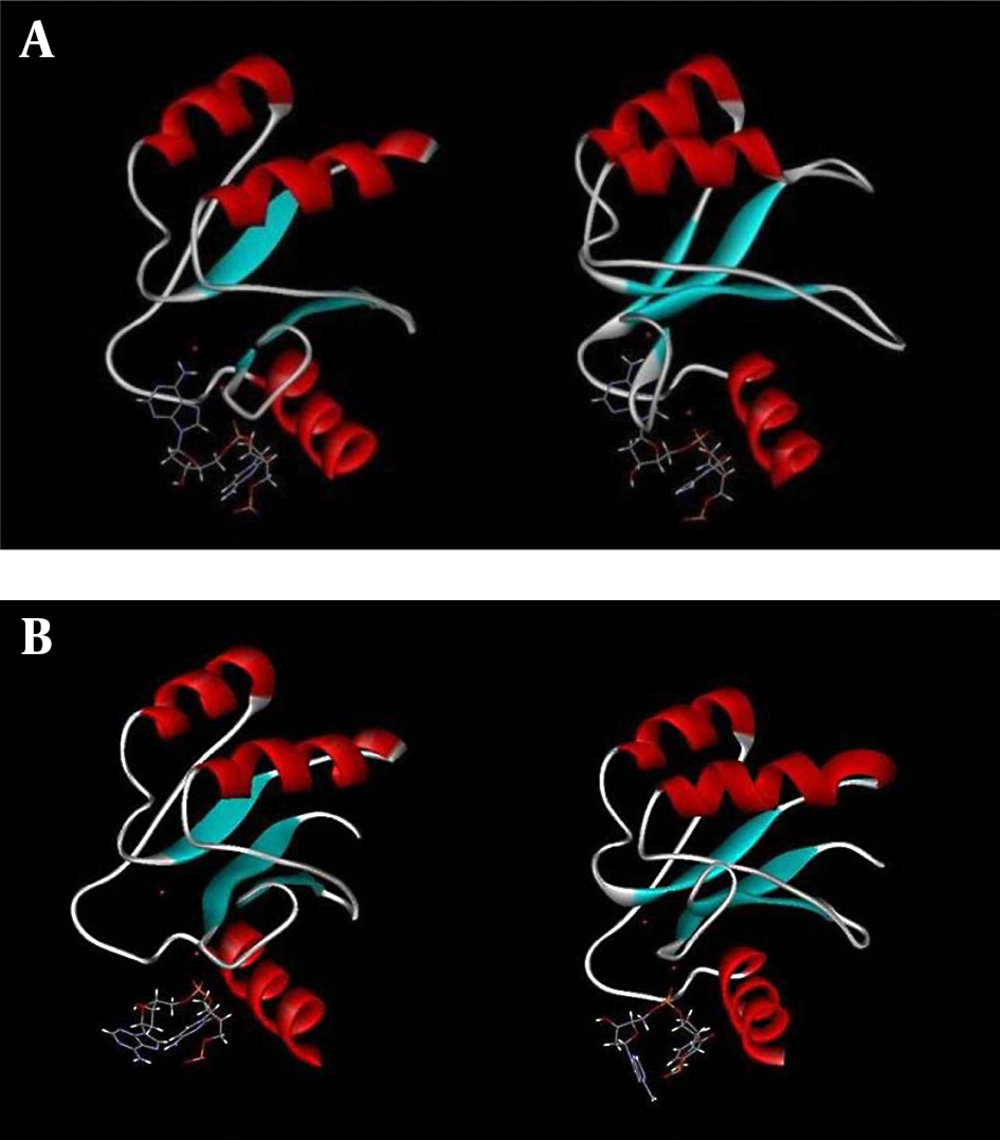
Structural survey of HIV-1 and PFV integrase active sites and their changes during simulation reveals very interesting facts regarding different arrangements of active site residues around the 3'-dA nucleotide and magnesium ions at B-sites. Figure 5 A shows the arrangement of active site residues of HIV-1 integrase around 3'-dA and Mg2+ ion before (left) and after (right) simulation. Figure 5 shows that 3'-dA and Mg2+ are inserted into a binding cleft during simulation to a place far from the accessibility of foreign ligands such as enzyme inhibitors.
A, Graphic representation of DNA binding site of HIV-1 integrase before (left) and after (right) simulation showing the movement of the 3'-dA through the binding site cleft obtained from 10 ns simulation at 37°C and one atmospheric pressure, in the presence of SPCE water box; B, Graphic representation of DNA binding site of PFV integrase before (left) and after (right) simulation showing the situation of 3'-dA and magnesium ions of A and B sites obtained from 10 ns simulation at 37°C and one atmospheric pressure, in the presence of SPCE water box.
Figure 5 B shows the same change in PFV integrase. As shown, in the case of PFV integrase, dA and Mg2+ did not enter in the same active site cleft as in the case of HIV-1 integrase. We, therefore, hypothesized that the chelation of B-site magnesium ion by 3’-processing inhibitors is more difficult in HIV-1 than in PFV integrase. In other words, the PFV binding site seems to be more extended and its magnesium ions are more accessible to enzyme inhibitors attack compared to HIV-1.
5. Discussion
It is well known that there is two types of integrase inhibitors used in chemotherapy of HIV-1 infected patients. The first type (IBIN) attacks DNA binding site on the integrase, binds magnesium ions and prevents viral DNA to bind and interact with the 3’-OH group. In most cases, this inhibitor fails because viral DNA binds to integrase prior to drug therapy and there is no free enzyme to be attacked by inhibitors.
The second type of inhibitor (INSTI) binds to magnesium ions and stacks to penultimate nucleotide of cytidine, pushes the last nucleotide of adenosine and its 3’-OH group outside the enzyme binding site and prevents integrase to recruit 3’-OH to attack host cell DNA. Our findings show wide structural differences between HIV-1 and PFV integrases, which make them behave differently against inhibitors.
Figure 2 A and B indicate that the equilibrated structure of HIV-1 integrase has a more stable structure with lower RMSD than PFV. Figure 3 A - C emphasize the more stable structure of HIV-1 integrase with lower RMSF especially at the CCD domain. Our data also indicate a more hydrophobic binding site for HIV-1 integrase with stronger binding capacity to viral DNA. Measurements of direct binding energy of DNA to integrase systems confirm our findings about higher HIV-1 affinity for DNA binding (~ 14 KJ/Mol higher). Finally, Figure 5 A and B precisely show the difference between the active site configuration around 3'-dA and Mg2+ of HIV-1 and PFV integrase. The active site configuration of HIV-1 hides the Mg2+ ion of the B-site to be away from the reach of inhibitors. We hypothesized that this is the main cause for higher resistance of HIV-1 against metal chelating inhibitors.
Based on our findings, we can conclude that viral DNA-PFV integrase complex that is widely used in recent studies as a representative model for HIV-1 integrase does not seem to be a reliable model for drug design against AIDS. Hence, we recommend that relevant reports should be rechecked using more realistic models as the one we constructed.