1. Background
Toxoplasma gondii is a cosmopolitan protozoan that infects the human body and many warm-blood animals including wild boars (1). Infection in the human body occurs through digestion of raw or undercooked meat containing parasite tissue cysts or by the consumption of vegetables, soil or water contaminated with T. gondii oocysts (1). Wild boars are reservoirs of several diseases that can infect wildlife, livestock, as well as humans. These animals are hosts to bacterial infections such as cholera, swine brucellosis, bovine tuberculosis, and also viral infections such as foot and mouth disease, and pseudorabies. Moreover, they may act as a reservoir of parasitic diseases such as echinococcosis, trichinosis, toxoplasmosis, balantidiasis, and a few of other parasitic diseases, which can be transmitted to humans (2-6).
Wild boars may be involved in direct or indirect maintenance, transmission or circulation of T. gondii to wildlife or humans. These animals may become infected with T. gondii through ingestion of food or water that is contaminated with sporulated oocysts or ingestion of cysts in infected animals’ tissues. Wild boars are omnivores that consume variety of foods, depending on the location and time of year. Plants usually make up more than 80% of a wild boars diet. When temperatures are high, wild boars seek water and dense vegetation and also feed at night. Wild boars, as vertebrate pests, have destructive behaviors causing damage to livestock, agricultural fields, forests, and the environment. Due to these frustrating behaviors, locals used to shoot and kill these animals. The hunted wild boars are usually consumed by hunters, which may transmit T. gondii if the meat is infected. Moreover, feral cats and wildlife may become infected by feeding on carcasses of these animals, left by the hunters in the field.
Seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis among wild boars varies from country to country based on the climatic condition, the cat population, and it also ranged from 5 to more than 50% (7-10). In general, T. gondii was considered as having a clonal population with 3 major lineages (types I, II, and III). Nevertheless, recent studies have revealed a greater genetic diversity of T. gondii called recombinant, atypical, and mixed genotypes. All of the three common clonal lineages of T. gondii, known as types I, II, and III, have been isolated from the wild boars, although type II strain represent the most prevalent strain type in these animals (11, 12). Toxoplasmosis is a common infectious disease found in humans and also in domestic livestock species in Iran (13-17). However, there is no data regarding the seroprevalence or genotypes of T. gondii in wild boars in Iran.
2. Objectives
The current study, for the first time, was conducted to find out the seroprevalence and genotypes of T. gondii in wild boars in southwest of Iran.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Area
The current study was performed in the Bushehr province (28.9184° N, 50.8382° E), in southwest Iran. Bushehr is a coastal province with a long coastline onto the Persian Gulf. Temperatures range from 6°C in the winter and up to 50°C in the summer, with an average annual temperature of about 24°C. Highland nature and dense forests in the northern part of this province provide a unique environment for wild boars. Wild boars act as vertebrate pests and cause significant damages by feeding on fruit and crops in agricultural fields. Landowners in Bushehr kill these animals during hunting season.
3.2. Sample Collecting
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran. With coordination to local hunters, samples were collected from 25 adult wild boars, which were hunted by local hunters in 2013. The 25 wild boars included 11 males and 14 females. Approximate ages of the animals were recorded, based on their teeth eruption patterns. Right after the hunting, blood samples were collected from each animal and sera were separated from the blood after centrifugation and kept at -20°C until use. At necroscopy, samples were taken from different muscles, tongue, liver, and brain of each animal and stored in either 10% formalin for histopathological evaluation or 70% ethanol for molecular studies.
3.3. Serological Evaluation
Blood samples collected from the wild boars were assessed for antibodies against T. gondii by a modified agglutination test (MAT). Modified agglutination test was performed in U-bottom 96-well microplates (Nunc, Denmark) as originally described by Desmonts and Remington (18). Briefly, sera samples were diluted with phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2) and antigens were diluted with antigen diluent (contained bovine serum albumin (BSA), 2-mercaptoethanol and Evans blue dye solution). Formalin fixed whole RH strain of T. gondii tachyzoites were used as antigens. Sera were tested in two-fold dilutions starting from 1:20 to 1:160 dilutions. Positive and negative sera were incorporated in each plate. Blue pellets at the base of the U-bottom microplates were considered as negative, whereas agglutination of the parasite in a mat covering about half of the well base was considered as positive. Antibody titers of ≥ 1:20 were considered as positive. Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS Ver. 22 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Chi square was used to determine the correlation between seropositivity with T. gondii and features of the animals. P value less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3.4. Molecular Evaluation of Wild Boars Tissues Samples
DNA was extracted from muscle and brain tissues of each wild boar, using genomic DNA extraction kit, (QIAamp DNA Mini Kit, QIAGEN GmbH-Germany) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. A 200 - 300 folds repetitive 529 bp DNA fragment of T. gondii was PCR-amplified as previously described by Edvinsson et al. (19). A pair of PCR primers, TOXOF CAGGGAGGAAGACGAAAGTTG and TOXOR CAGACACAGTGCATCTGGATT was used to amplify the target gene (19). The PCR reaction mixture (25 µL) contained 1.25 units of Taq DNA polymerase, 1 μL of extracted DNA, 1.5 mM of MgCl2, 10 pmol of each primer, 0.2 mM of dNTP, and 10x PCR buffer. The PCR program was one cycle of initial denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes, 35 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 35 seconds, annealing at 56°C for 1 minute, extension at 72°C for 1 minute, and final extension at 72°C for 10 minutes. PCR products were separated by electrophoresis in 1.5% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. The PCR products were purified using Vivantis PCR purification kit (Vivantis Technologies Sdn. Bhd. Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia) and sequenced using the same primers used for PCR amplification. To find out the type of T. gondii isolates, the sequences of isolates were aligned, using BLAST program and compared with those of published sequences related to the genotypes of T. gondii, available in the GenBank.
4. Results
Serological evaluation of toxoplasmosis by MAT revealed anti-T. gondii antibodies in sera of 4 out of the 25 wild boars, indicating an overall seroprevalence of 16%. Mean age of the wild boars was 3.6 years (ranged 1 - 9 years). Animals were clustered into 4 groups based on their age. The highest rate of T. gondii infection (20%) was found in the age group of 3 - 4 years. The differences between the age group and seropositivity to T. gondii was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). Mean weight of animals was 130 (± 43) kg (ranged 45 - 275 kg).
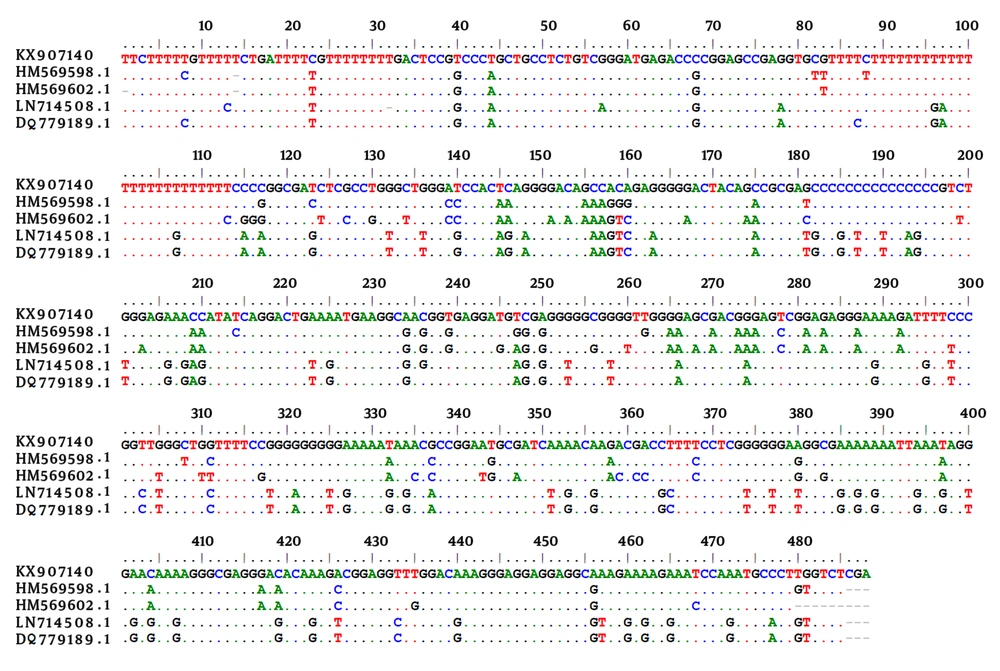
Considering the sex of the animals, seroprevalence showed a tendency towards higher prevalence amongst males (18%) compared to females (14.2%), however, the differences were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). Muscles and brain samples of all wild boars were tested for the presence of T. gondii DNA. Molecular study revealed a 529 bp band of T. gondii in brain samples of 5 out of 25 (20%) animals. Four of these cases were MAT positive and the remaining 1 case was amongst the seronegative cases. An almost perfect agreement (κ = 0.865) was found between MAT and PCR assay for detection of the T. gondii infection. Sequence analysis demonstrated that 4 cases had the highest identity with those of available sequences in GenBank for type III of T. gondii and 1 case with type I. The sequence data for 1 of the 529 bp sequence obtained in this study was deposited in GenBank with accession number of KX907140. Figure 1 shows the alignment of T. gondii isolated from the wild boars in the current study in comparison with a few of the available sequences in the GenBank.
5. Discussion
Wild boars, as omnivorous, are considered as a good indicator for the monitoring of T. gondii environmental contamination (7). There is no data regarding the seroprevalence and genotypes of T. gondii in Iran and the lack of such information justified the current study, which aimed to assess the seroprevalence and genotypes of T. gondii in hunter-killed wild boars in southwestern Iran. Anti-T. gondii antibodies were detected in 16% of the wild boars and Toxoplasma DNA was detected in tissues of 20% of the animals.
Consumption of undercooked meat is the main route of transmission of T. gondii to humans. In Europe, pork meat was considered as the main source of Toxoplasma infection (20), yet other sources of T. gondii infection including wild boar meat are being considered due to the decrease of the infection in pigs. In Iran, considering the Islamic rules, eating pigs and wild boar meat is prohibited. After the Islamic revolution in Iran, pig-raising was no longer allowed and all commercial piggeries were closed. However, some ethnic minorities and gypsy tribes hunt wild boars and use their undercooked meat. Therefore, it is not uncommon for hunted wild boar meat to be consumed by some of the local people, as was seen during the course of this study. Since consumption of wild boar meat is not common in Iran, therefore this route of T. gondii infection is not very important. However, wildlife may be infected through consumption of T. gondii-infected wild boar carcasses, left by the hunters in the field. Therefore infection of wild boars with T. gondii is important in the epidemiology of this parasitic disease.
Variation in seroprevalence of T. gondii in wild boars in different regions of the world may be linked to contamination of the environment by cats and differences in climatic condition, which affect the oocyst survival in the environment. The study of Touloudi et al. (2015) in Greece, revealed that 5.2% of European wild boars have anti-T. gondii antibodies (21). A seroprevalence of 23.8% was reported for toxoplasmosis in wild boars in the southwestern area of Spain and a 20.6% in Portugal (22, 23). In another study done by Gauss et al. in Spain, anti-T. gondii antibodies were detected in sera of 38.4% of wild boars (8). In Poland, antibodies to T. gondii were detected in 37.6% of hunted wild boars (10). Seroprevalence of T. gondii in 320 hunted wild boars in Slovak Republic was found to be 8.1% (24). Bartova et al. documented a seroprevalence of 26.2% for toxoplasmosis in wild boars in the Czech Republic (7). Matsumoto et al. reported a seroprevalence of 6.3% for T. gondii in wild boars in Japan (25).
In our study, there was no gender or age-related differences in seroprevalence of T. gondii in the studied wild boars. However, such correlation has been found in some studies. Jokelainen et al. showed that female wild boars are more likely to be seropositive for T. gondii (2). Ranucci et al. found anti-Toxoplasma antibodies in sera of 14% of wild boars from central Italy (9). Significant correlation was found between age and seropositivity to T. gondii in that study (9). Similar to this study, an age-dependent seroprevalence of T. gondii was reported in Swedish wild boars where adult animals were more seropositive (55%) for T. gondii than younger (< 12 months) animals (34%) (26).
Toxoplasma gondii isolates from humans and animals have been grouped into 3 clonal linages, type I, II, and III. However, atypical isolates of T. gondii have been reported from humans and animals (27, 28). Toxoplasma gondii atypical isolates from North America were found to comprise an entirely new and separate lineage, designated as type 12 (27). Different genotypes have different pathogenicity to mice and to some extent to humans as well. Type I is considered as virulent and type II and III are considered as non-virulent in mice. Type II and III of T. gondii were reported from organic pigs in northern USA (29). In the western Alps, a prevalence of 16.9% was reported in the wild boars tissues by PCR, however, the genotypes of the parasite were not determined (4).
In our study, type I and III of T. gondii were detected in the wild boars tissues, with type III as the prominent genotype. A study in wild boars done in France documented type II genotype as the most prominent genotypes of T. gondii strains in wild boars (12). It has been suggested that the pathogenicity of toxoplasmosis in wild boars is linked to the infecting T. gondii genotype (11). Calerobernal et al. described a case of congenital toxoplasmosis in a wild boar. Toxoplasma mixed infection, type I and III, were detected in the mother whereas type I, III and also mixed infection were found in the fetus (11). The fetus infected with type III had no apparently malformalities (11). Type III of T. gondii has been reported in patients undergoing chemotherapy in Iran (30). Type I has been associated with human congenital toxoplasmosis in France and also in Iran (31, 32).
Taken together, findings of the current study demonstrated that the T. gondii infection is common in wild boars in southwestern Iran. The findings indicate that wild boars could represent significant health risks for animals, hunters, and local residents who may consume wild boar meat. The study also confirmed type III as the prominent genotype of T. gondii strains in wild boars in this region.