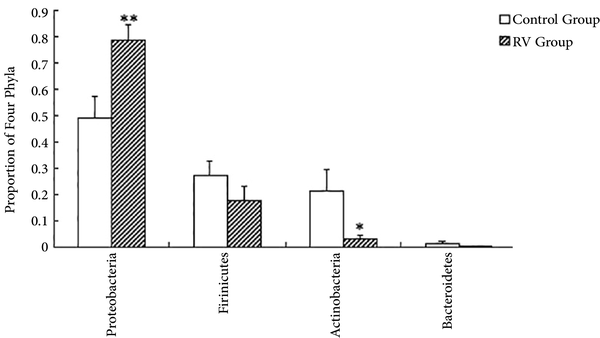1. Background
To accomplish the establishment of the complex microbial ecosystem, the early neonatal period is composed of the foundation of a healthy intestinal microbiota (1, 2). For the normal development of the intestine, infant gut microbial colonization always connects with the homeostasis of the intestine and the barrier function of mucous (3). In the case of neonates, appropriate signals for intestine and immune maturation have been provided by healthy gut microbiota due to a reduced risk of infection (4). During this relatively sensitive and unstable initial stage, any variation in the microflora development process may rise up disease risk in later life. After weaning, the richness, complexity and diversity of the intestinal microflora increases quickly and the infant gut microbiota begins to resemble that of an adult and stabilizes after one year of age (5).
Rotaviral-induced diarrhea (RD) is the leading cause of severe diarrhea in young children and infants (6). An estimated 48 to 64 million deaths in children aged < 5 years old are caused by rotavirus (RV) (6). Rotavirus infection also leads to the cost of approximately 21.3% to 39.5% of hospital admission spending for RD in Europe, even less the cost of rotavirus vaccines (7). The rotavirus can infect intestinal epithelium villi cells, increase intestinal motility, destroy gut microbial barrier, and lead to patients suffering from a watery diarrhea (8, 9). The etiology of typical intestinal diseases had proved that gut intestinal microflora had a close association and influence with the appearance of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and even colon cancer (10). Highly elevated levels of Proteobacteria species and increased levels of Enterobacteriaceae species were observed in disrupted intestine bacteria communities, which were laid in those individuals with IBS (11).
Tazume et al. firstly reported that the anaerobic bacteria in the intestines declined among RD patients and provided a new direction for understanding rotavirus infection (12). The author’s previous study analyzed the dominate genus in RV infants and healthy infants by using polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE) and indicated the dominate genus was Escherichia coli, Bacteroidetes vulgatus, Enterococcus faecium, and Clostridium in RV infants (13). Strains of Bifidobacteria have an improved effect on diarrhea infected rotavirus and Clostridium difficile (14, 15). Another researcher found a significant negative linkage between Bifidobacterium and abdominal pain in adults with acute viral gastroenteritis. However, the above correlation cannot be copied in fecal samples of children with acute viral gastroenteritis (16). The possible explanation may be that the species and amounts of Bifidobacterium in the infant microbiota is not stable and alternates swiftly in comparison with adult microbiota (17). Therefore, it is irreplaceable to demonstrate the relationship between the diversity and richness of gut microbiota and RV infection.
As the major end products of bacterial metabolism, short chain-fatty acids (SCFAs) are produced in human large intestine, which play a variety of physiological functions (18, 19). The changes in production levels of lactic acid and SCFAs, both as total levels that produced the pattern of individual acids can be used as markers of calculating the bacterial growth activity (20). Lactic was observed and there were higher levels in fecal samples of IBD compared with those in healthy subjects (21). Acetic acid also produced by Bifidobacterica can improve intestinal defense and protect against the contamination of Escherichia coil (22). Its concentration was decreased in Crohn’s disease subjects (23). The differences in SCFAs in fecal samples between RD infants and H infants were analyzed to deepen the understanding of the relationship between RD and fecal metabolites profile.
2. Objectives
The study focused on the intestinal microecology through a study of intestinal microflora structure and changes of SCFAs of RD infants. It aimed to elucidate the effects on the establishment of the infant gut microbiome by RV infection and accompanying changes in bacteria metabolism products.
3. Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Total DNA Extraction
The twenty-five infant (0 to 6 months) fecal samples used in this study were collected from November, 2016 to February, 2017. Thirteen samples were obtained from the infants diagnosed with RD patients by using specific enzyme immunoassay method in Harbin Children’s Hospital. During the study enrollment period, the other 12 fecal samples were recruited from age- and gender-matched healthy infants (six females and six males) in Harbin city as control samples. All infants were provided with the same diet, including equal amounts of breast milk, fruit puree, and rice flour. All fecal samples after collection were transferred to sterile plastic tubes, immediately dispatched to the laboratory where the study was conducted, and then stored at -80°C before analysis. In the previous months, fecal samples were prepared for being collected, no infants in this study had taken antibiotics, probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics. QIAamp DNA Stool Mini kit (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) was used to extract DNA. The extraction method followed the manufacturer’s specifications as the same as previously described (4). The extracted DNA was kept frozen (-80°C) before analysis.
3.2. 16S rRNA Gene Amplification and Sequencing
The V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene as the target was amplified using the primer 338F (ACTCCTAGGGAGGCAGCAG) and 806R (GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT) (24). Amplicons of at least 450 bp were extracted from 2% agarose gels and purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union city, CA, U.S.), according to the protocol. The concentrations of amplicon DNA were quantified using a QuantiFluor™ - ST Fluorometer (Promega, Madison, WI, U.S.). Purified amplicons were pooled and mixed in equimolar and sequenced (2 × 250) on an Illumina MiSeq platform at Maforbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China (25). The PCR program was set by following the method described by Costa et al. (26).
3.3. Miseq Platform of Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
Raw files after demultiplexed were quality-filtered using QIIME (version 1.17) with the criteria, according to Li et al. (27) described. The similar steps were followed and performed based on the description by Jia et al. (28) and Hao et al. (25). The chimeric sequences were removed using UPARS (version 7.1 http://drive5.com/uparse/), and operational units (OTUs) were clustered with the similarity cut-off set at 97%, while chimeric sequences were removed. The analysis of phylogenetic affiliation of 16S rRNA gene sequence was performed by RDP Classifier (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/) against the Silva (SSU115) 16S rRNA database using confidence threshold of 70% (28).
3.4. Measurement of the Fecal Lactic Acid and Short-Chain Fatty Acids
The fecal samples placed in the refrigerator at -80°C were taken out and put in the lyophilizer immediately. Then fecal samples were frozen and dried to the constant weight according to the method described by Alexandra Dostal et al. (29) with minor modifications. Fifty milligrams of freeze-dried samples were weight to tube of 10 mL accurately, and 1 mL of 0.15 mmol/L H2SO4 and 1 mL pure water were added after blending and centrifugation (11000 r/minute, 4°C, 20 minutes). The supernatants were extracted and filtered via 0.22 µm organic filter to 1.5 mL vials for HPLC, or sealed and placed at 4°C for the subsequent HPLC analysis.
The injection volume for HPLC analysis was 10 µL. Separation was carried out on an Aminex HPX-87H column (300 mm × 7.8 mm, Bio-Rad, USA), with column temperature 40°C, flowing phase 10 mmol/L H2SO4, and flowing rate 0.6 mL/minute. The ultraviolet detector was operated at λ = 210 nm, and the total running time was set at 28 minutes. The concentrations of lactic acid and SCFAs in the samples were calculated according to the standard curves of the corresponding standard for HPLC, under the same conditions (29).
3.5. Statistical Analysis
All the test data were the averages of three parallel tests. The results of lactic acid and SCFAs were expressed as µmol/g dried feces. All data analyses were conducted by the SPSS 17.0 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The “Mann-Whitney U” Test was used for difference analysis. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Analysis of the structure of intestinal microflora diversity and phylogenetic analysis were carried out using the R language tool for plotting.
4. Results
4.1. Assays of Diversity Indexes and Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) of fecal Microbiota
Nearly 1,100,000 gene sequences with an average length of 447 bp were adequately classified. After trimming the primers, 556,382 reads were remained from the fecal samples of RD infants and 537,733 reads were remained from the fecal samples of H infants. The bacterial richness estimators (ace and chao) and the indexes of diversity (Shannon and Simpson) at a 3% sequence dissimilarity level were summarized in Table 1, using the MOTHUR program based on estimating the operational taxonomic units (OTUs). The bacterial richness in RD infants feces significantly decreased (P < 0.05). Shannon diversity and Simpson indexes of fecal microbiota were lower in RD infants than in H infants.
Comparison pf Phylotype Coverage and Diversity Estimation of the 16S rRNA Gene Libraries at 3% Dissimilarity from the Pyrosequencing Analysis
4.2. OTU Taxonomic Analysis
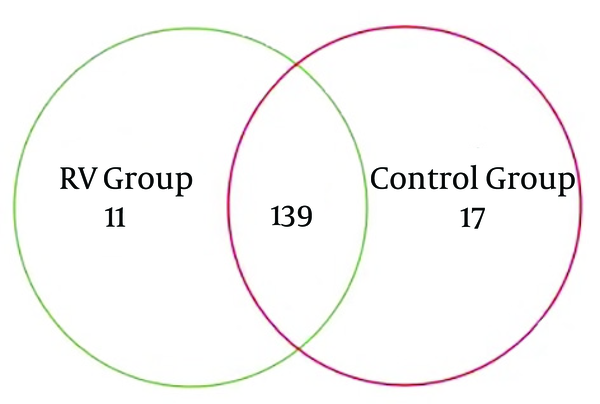
The overlapping areas of circles in Venn diagrams represented that RD and H infants apportioned a large number of OTUs, despite significant interpersonal variations (Figure 1). Based on the diagrams, the relatively unified and stable components were remained across intricate microbial accumulation or assemblages. The RD and H infants also apportioned a great deal of OTUs (167 OTUs), in term of male and female individuals. This result indicated that a core or “home” microbiome might be remained in the fecal microbiota of infants. Nine phyla identified including to Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria, Chloroflexi, Verrucomicrobia, Acidobacteria, and Saccharibacteria. Overall, 99.86% of sequences were attached to the four dominant phyla (Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria and Bacteroidetes) of the infant intestine. However, the proportions of each group were different (Figure 2). Compared with H infants, infants infected RD had a greater abundance of Proteobacteria (P < 0.01) and a decrease in the abundance of Actinobacteria (P < 0.05).
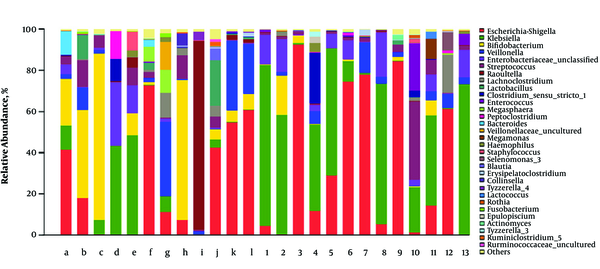
The fecal microbial composition at the genus level in RD and H infants is shown in Figure 3. The most abundant bacterial genera in all fecal samples were Escherichia-shigella, Bifidobacterium, Klebsiella, Veillonella, Streptococcus, and Lachnoclostridium. These species represented more than 80% of the total abundance. Other four genera (Enterococcus, Clostridium-sensu-stricto-1, Lactobacillus, and raoultella) were considered as the sub-dominant population, which represented more than 1% abundance each. Enterococcus and Clostridium-sensu-stricto-1 were mainly found in the feces of RD infants while Lactobacillus and Raoultella were mainly found in the feces of RD infants. Additionally, other 22 bacterial genera belonged to the non-dominant population (< 1% abundance). Fecal samples in RD infants had a greater abundance of Klebsiella than H infants (P < 0.05). The abundance of Knoellia as the non-dominant genus was decreased in RV infants (P < 0.05).
Relative abundance of fecal flora at the genus level. The predominant genera in RD and H infants feces were respectively (RD: 1 - 13 vs. H: a-l), Escherichia-shigella (37.06% vs. 26.13%), Bifidobacterium (2.78% vs. 23.55%), Klebsiella (38.73% vs. 10.49%), Veillonella (3.78% vs. 9.92%), Streptococcus (5.14% vs. 5.01%), Lachnoclostridium (2.02% vs. 1.95%).
4.3. Assays of Intestinal Microbiota Structure and Similarity
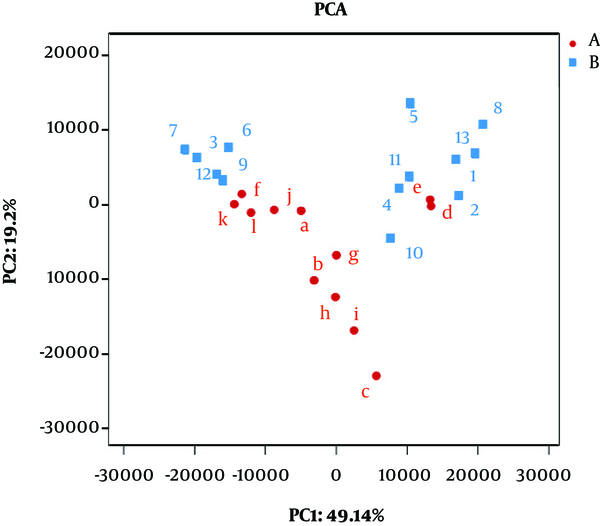
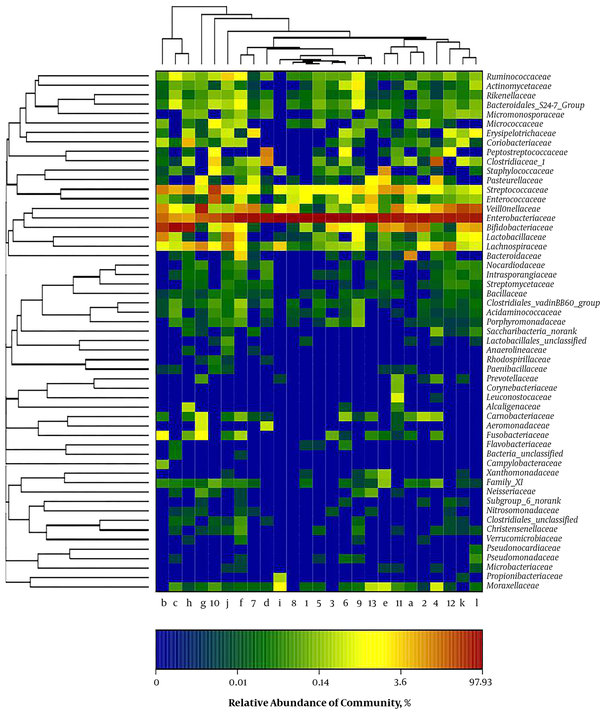
A clear clustering was observed using unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean in Figure 4. The results of dendrograms showed similarity between fecal microbiota in RD and H infants, despite significant inter-individual variability (for example, sample c, d and e). The samples were clustered together because of the similarity of both infected rotavirus. In PCA analysis, fecal samples in RD and H infants were separated in the direction of PC2 (19.2%) and were clustered together due to RV infection (Figure 5). Enterobacteriaceae as a dominant family in all samples is demonstrated in the heatmap (Figure 6). It was obviously significant that an unidentified strain of Bacteroidales S24-7 group differed in fecal samples of RD and H infants (P < 0.05). It is noted that clustering in the heatmap was similar with Hierarchical clustering (Hcluster).
4.4. Assays of fecal Lactic Acid and SCFAs
Total SCFAs content of all feces varied from 1.37 mmol/kg to 1.83 mmol/kg (Table 2). Only lactic acid content in fecal samples of RD infants was lower than that of H infants (P < 0.05). In this study, acetic acid was the dominant SCFA, followed by butyric and propionic acids. However, the content of total SCFAs had no significant difference in all samples.
| Organic Acids | RD Infants, µmol/g | H Infants, µmol/g |
|---|---|---|
| Lactic acid | 191.36 ± 134.91a | 222.63 ± 49.48 |
| Formic acid | 5.07 ± 2.82 | 13.04 ± 7.35 |
| Acetic acid | 1321.04 ± 681.99 | 1783.34 ± 488.39 |
| Propionic acid | 19.77 ± 9.84 | 10.50 ± 5.17 |
| Butyric acid | 65.04 ± 55.57 | 33.64 ± 29.13 |
| Total SCFAs | 1373.00 ± 690.06 | 1829.30 ± 494.37 |
Comparison of the Concentrations of Fecal SCFAs in the Two Infants Groups
5. Discussion
Microbial colonization of the intestine can be beatification for infants to develop a normal and healthy intestine, establish the intestinal homeostasis and prevent of infections by pathogenic bacteria and virus (3). To some extent, the levels of later health were mainly influenced by controlling or minimizing the invasion of postnatal gut diseases. However, the cognition about the process of microbiome establishment and development in the neonatal and infants gut is still limited. This research showed that some RD infants reflected an altered intestinal microbiota based on the results of fecal microbiota. This may lead to these infants developing elevated risk of health problems in the future, because the matagenomic analyses of the gut microbiota of RD infants taking part in the study propose that rotavirus infection has necessarily influenced on the establishing gut microbiome, even though drawing the firm conclusions need large numbers of RD infants participated in the study.
Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria have a major impact on human health (30, 31). Proteobacteria was elevated and Actinobacteria was reduced in the study, and the fact could be viewed as a marker for disruption of gut microbiota. In Crohn’s disease, Norovirus infection and ulcerative colitis, increased Proteobacteria had been found to be in linage to intestinal inflammation or without inflammation (10). The current study found multiple mechanisms may contribute to the explanation for increased Proteobacteria levels, particularly elevated E. coli levels in fecal samples (32). It is hardly available to measure the illness severity in the current research. Therefore, as a future direction, investigating potential connection between inflammation and severity may be achieved, such as vomiting or diarrhea frequency increased in RD infants. This study was the first testing of increasing Klebsiella, which belonged to Proteobacteria in RD infants. More recent studies suggested Klebsiella may contribute to inflammation (33, 34), such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and meningitis (35). Therefore, it could be supposed that RD infection, as the major cause of the viral gastroenteritis might disrupt the gut microbiota and introduce more effects from Klebsiella.
The health can be long lasting effects due to microbiota disruption; unfortunately, the impact of disruption on health is a known limited. Bacterial gastroenteritis had previously been associated with post-infectious IBS (PI-IBS), a subset of IBS, following pathogenic E. coli, Salmonella, and Campylobacter infections (36). Less attention has been paid for the relationship between viral gastroenteritis and PI-IBS. Microbiota disruption existing in RD infants intestine if microbiota disruption increases the potential risk of long-term illness, following episodes of Rotaviruses needed to be researched (36). The samples examined in this study had limited the availability of the medical data of RD infant, therefore, did not measure the duration of illness. It was unavailable to measure the baseline microbiota before illness or after the path of recovery, due to lacking the information on the samples from various times following the illness onset. Based on these considerations, future study to treat these limitations may enroll human volunteers, to supervise the gut microbiota before and after RV infection, as this treatment could determine specific responses to infection.
Marchesi et al. had observed that IBD patients were correlated with lower levels of SCFAs in feces, compared with healthy controls (37). The reduction of SCFAs was due to the decrease of Clostridium groups in fecal samples of IBD patients (37). However, no correlation between total SCFAs of feces and RV infection had been observed in this study. The possible reason of this fact may be that no changes were found in Clostridium groups in RD infants feces compared with H infants feces. This study showed that the metabolism production in large intestine of RD infants had lower level of lactic acid. The metabolite of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus were lactic acid and acetic. Future research may focus on the relationship between the lactate and the abundance of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus genus because viral gastroenteritis might correlate with the change of the acetic acid.
5.1. Conclusions
In conclusion, because the host immunity interacts with the gut microbiota at different and complex levels, the relationship between pathologies and dysbiosis may be built. Butto and Haller (38) had mentioned that it was worthy to debate whether the dysbiotic state is consequence of the pathology. Variation of the composition of the gut intestine microflora may happen upon exposure to infections (39). It has been proved the directly effects of the interactions between the gut microbiota and host immunity in asthma and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) (40, 41). Therefore, the intestinal microbiota composition of infants with RV infection and its correlation with SCFAs and lactic acid were evaluated. Rotaviral infection in infants lead to the alteration of fecal microbiota and lactic acid concentration compared with healthy infants. Fecal microbiota and metabolite may advance our understanding and treatment of RD.