1. Background
The reproductive system is a highly sensitive structure that can be adversely affected by toxic compounds, including pesticides. These chemicals, formulated for pest repulsion or elimination, have been integral to agriculture and public health since ancient times, dating back to the Roman era when substances such as sulfur, salts, ashes, and bitters were used to manage pests and weeds (1). Today, pesticides are widely applied in agriculture, industry, residences, and public health to control or eliminate pests. However, their widespread use has raised significant concerns due to the toxicological interactions of their active ingredients and breakdown products, which often persist in the environment and can have detrimental impacts on both ecosystems and human health (2, 3). Pesticides are known to exert various toxic effects on biological systems, including additive, potentiating, antagonistic, and synergistic interactions. A key area of concern is their impact on reproductive health, particularly in males. Studies have consistently linked pesticide exposure to impaired sperm motility, reduced sperm counts, abnormal sperm morphology, and decreased testosterone levels, highlighting their role as endocrine disruptors (4). Male infertility, estimated to contribute to 40% of infertility cases, has been associated with pesticide exposure, particularly in occupational and environmental settings (5).
Certain pesticides, such as cypermethrin (CYP), mancozeb, and metalaxyl, have been reported to impair spermatogenesis, as well as the quality of semen produced by the testes and epididymis (6). Additionally, pesticides may disrupt the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, further exacerbating reproductive dysfunction (7). For instance, dichlorvos has been shown to reduce sperm motility and negatively impact testicular function in rats (8). Similarly, carbaryl, a carbamate insecticide, has been associated with increased sperm abnormalities and adverse reproductive outcomes in workers exposed during manufacturing processes compared to unexposed controls (9, 10). These findings indicate dose-dependent toxic effects, including increased abnormalities in sperm morphology involving the head, neck, and tail regions. While the reproductive toxicity of many pesticides has been extensively studied, most investigations have focused on individual compounds rather than the mixtures commonly employed in agricultural and public health practices. Approximately 95% of these studies examine single-pesticide exposures, which may not adequately represent the additive or synergistic effects observed with pesticide combinations (11). Globally, an estimated 4.6 million tons of pesticides are released into the environment annually, raising significant concerns about their endocrine-disrupting capabilities and long-term reproductive health impacts (12). These risks are particularly pronounced in developing countries, such as Nigeria, where local manufacturers often produce pesticide mixtures instead of using individual compounds (13). Despite consuming a smaller percentage of the global pesticide production, these regions experience disproportionately high rates of pesticide-related deaths. Persistent and bioaccumulative pesticides, like organochlorines, continue to contribute to severe health impacts in these areas.
Human exposure to pesticides occurs through multiple routes, including ingestion, inhalation, dermal, and ocular pathways (2, 13). However, most research has focused on ingestion and dermal exposure, with limited emphasis on inhalation. This knowledge gap is critical, as inhalation exposure represents a significant route of pesticide uptake, particularly for volatile substances like dichlorvos, CYP, synthetic camphor, pinenes, and kerosene (14).
2. Objectives
This study aims to evaluate the effects of individual and combined pesticide exposure on sperm parameters in male Wistar rats via inhalation. By focusing on inhalation toxicity, we seek to address the existing research gaps and provide insights into the reproductive toxicity of pesticide mixtures. Additionally, the study investigates the potential for recovery or reversibility of reproductive outcomes after the cessation of pesticide exposure. Our findings will contribute to the growing body of evidence on pesticide-induced reproductive toxicity and inform regulatory and public health interventions.
3. Methods
3.1. Ethical Approval
All experimental protocols were approved by the Health Research Ethics Committee (HREC) of Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, in accordance with institutional guidelines for animal care and use (HREC No.: IPH/OAU/12/1075).
3.2. Chemicals
The pesticides used in this study included DDForce (Hubei Sanonda Co. Ltd., China), Sniper (Forward BEIHAI Hepu Pesticide Co. Ltd., China, Batch Number F18003), Blue Diamond Naphthalene Balls (produced by ULYSSES Nigeria Limited, Batch Number 1/11), Refined (edible) camphor (Sihong Huizhi Fine Chemical Co. Ltd., India), and Kerosene.
3.3. Formulation of Combined Pesticides
The pesticides were sourced from the local market in Ile-Ife, Nigeria, and combined as follows: 750 mL of Kerosene, 250 mL of DDForce, 50 mL of Sniper, 63 g of ground Naphthalene Balls, and 63 g of ground edible camphor were mixed at 100% concentrations. The pesticides were blended by first combining Kerosene with DDForce, Sniper, Industrial camphor, and edible camphor. The mixture was stirred in a plastic bowl and allowed to fully dissolve before use.
3.4. Animal Care and Management
Wistar rats, weighing between 150 - 200 g, were obtained from the Animal Holding Unit, College of Health Sciences, Obafemi Awolowo University (OAU), Ile-Ife, Nigeria. The rats were housed in clean plastic cages, exposed to a natural light-dark cycle, and had ad libitum access to a standard pellet diet and water. They were allowed to acclimatize in the laboratory for two weeks before the commencement of the study.
3.5. Range-Finding Test
A range-finding test was carried out to determine the amount of each pesticide required for the definitive test. This test aimed to determine the quantity of the pesticide that would cause 100% mortality of the rat using the same volume of each pesticide that vendors used locally in formulating the indigenous pesticides. Twenty-one rats were divided into seven groups containing three rats per group exposed to the individual pesticide and the combined pesticide in a range-finding test that lasted for 24 hours. The combined pesticide was prepared by mixing kerosene with DDForce, Sniper, industrial camphor, and edible camphor. The results were reported earlier by the authors (15).
3.6. Animal Selection and Housing
One hundred and fourteen adult male Wistar rats, aged 8 - 10 weeks and weighing 180 - 200 g, were used for this study (13, 15). Statistically, five rats are sufficient; however, the Ethical Board approved six rats per group. The rats were housed in standard laboratory conditions, with a 12-hour light/dark cycle, at room temperature, and relative humidity. Rats were given ad libitum access to standard rat chow and water. The one hundred and fourteen rats were randomly grouped into nineteen (n = 6).
3.7. Sub-chronic Toxicity Study
A total of 114 adult male Wistar rats were allocated into six experimental groups (B-G) with 18 rats each and a control group (A) with six rats. Each exposed group was divided into three subgroups of six rats to test three graded pesticide concentrations. All rats, including the control group exposed to natural air, were placed in an improvised inhalation chamber for 4 hours per day at 3-day intervals over four weeks (Table 1).
| Pesticide/Constituents and Groups | No. of Animals | Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Control | ||
| A | 6 | Natural air |
| DD-force (dichlorvos) (mL) | ||
| B1 | 6 | 47 |
| B2 | 6 | 94 |
| B3 | 6 | 141 |
| Snipers (bifenthrin) (mL) | ||
| C1 | 6 | 31.25 |
| C2 | 6 | 62.5 |
| C3 | 6 | 93.75 |
| Kerosene (paraffin, naphthene and aromatic hydrocarbon) (mL) | ||
| E1 | 6 | 32.5 |
| E2 | 6 | 65.50 |
| E3 | 6 | 98.25 |
| Industrial camphor (terpenoid) (g) | ||
| D1 | 6 | 52.5 |
| D2 | 6 | 105 |
| D3 | 6 | 157.5 |
| Edible camphor (turpentine) (g) | ||
| F1 | 6 | 31.5 |
| F2 | 6 | 63 |
| F3 | 6 | 94.5 |
| Combined pesticide (kerosene750ml, DD Force 250 mL, snipers 50ml, industrial camphor 63 g and edible camphor 63 g) (mL) | ||
| G1 | 6 | 32.5 |
| G2 | 6 | 65.5 |
| G3 | 6 | 98.25 |
Experimental Design for Sub-chronic Toxicity of Common Pesticide
3.8. Recovery Groups
Out of the 114 Wistar rats exposed to the pesticides, 57 were withdrawn for a two-week recovery period. During this time, the rats were provided rat pellets and water ad libitum. After the recovery period, the rats were sacrificed, and the effects of the pesticides on their reproductive profiles were assessed and compared with those of the treated groups (13, 15).
3.9. Sperm Collection
At the end of the exposure period, all the rats were euthanized under anesthesia. The cauda epididymis was carefully excised for sperm collection.
3.10. Sperm Analysis
3.10.1. Sperm Count
Sperm count was determined using a hemocytometer. Epididymal sperm was diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and the number of sperm cells was counted under a microscope.
3.10.2. Sperm Motility
Sperm motility was assessed by placing a drop of diluted sperm suspension on a microscope slide and observing the motility under a light microscope. The percentage of motile sperm was recorded.
3.10.3. Sperm Morphology
Sperm morphology was evaluated by staining sperm smears with eosin-nigrosin stain. Abnormalities in the head, midpiece, and tail were recorded.
3.10.4. Viability
Sperm viability was assessed using the eosin-nigrosin exclusion test. Viable (live) sperm excluded the stain, whereas non-viable (dead) sperm took up the stain (14).
3.11. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using the statistical software GraphPad Prism 5.03. Results were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by post hoc Tukey’s test was used to compare the differences between the control and exposed groups. A P-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
4.1. Effects on Sperm Motility in Exposed and Recovery Groups
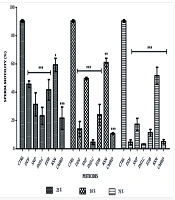
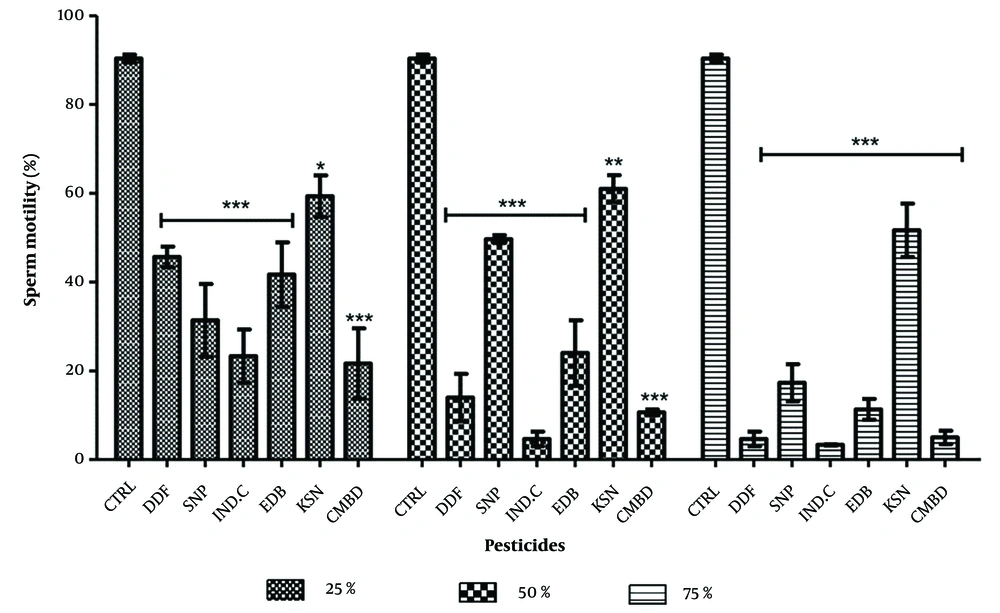
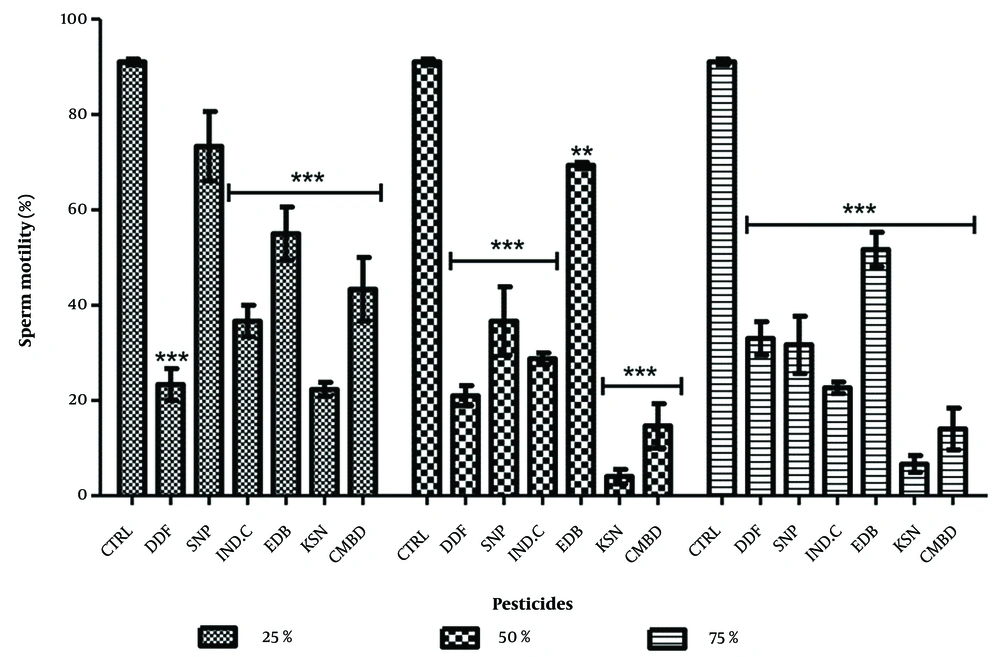
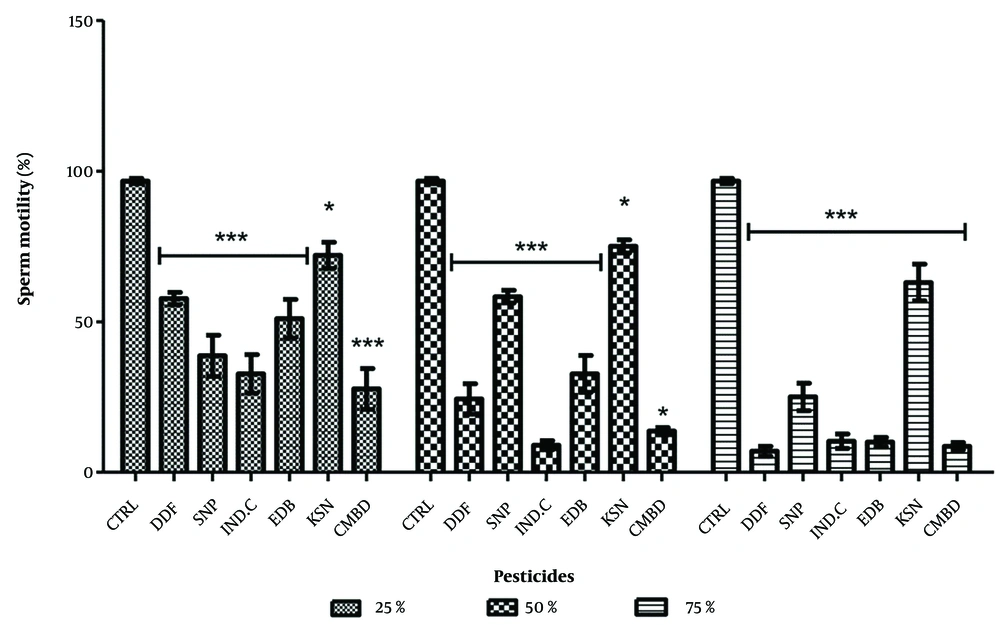
Significant decreases in sperm motility were observed in pesticide-exposed groups compared to controls (P < 0.0001). Dose-dependent decreases were seen with DDForce, industrial camphor, edible camphor, and combined pesticides. Sniper showed higher motility at 50% concentration (49.67 ± 0.88), and kerosene had consistent motility across concentrations (59.33 ± 4.47; 61.01 ± 3.06; 51.67 ± 6.01) (Figure 1). In recovery groups, significant decreases in motility were noted, with kerosene showing the least decrease (22.33 ± 1.45; 4.03 ± 1.51; 6.67 ± 1.76) (Figure 2).
Effects of pesticides on percentage sperm motility of the treated groups. Abbreviations: CTRL, control; DDF, DD force; SNP, Sniper; IND.C, industrial camphor; EDB, edible camphor; KSN, kerosene; CMBD, Combined. * P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001, *** P < 0.0001. Values without (*) indicate no significant difference compared with control. One way ANOVA followed by post-tests.
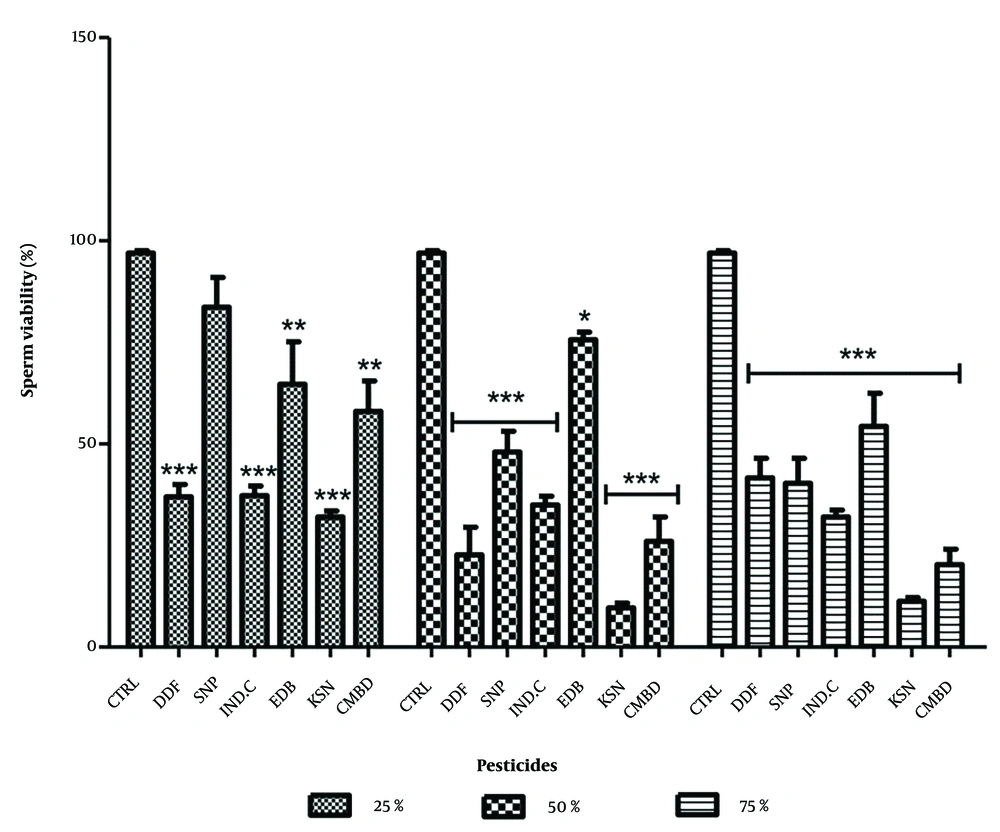
4.2. Effects on Sperm Viability in Exposed and Recovery Groups
In the exposed groups, significant decreases in sperm viability were observed: DDForce (25%: 57.67 ± 2.03, 50%: 24.33 ± 5.03, 75%: 7.01 ± 1.61), edible camphor (25%: 51.01 ± 6.35, 50%: 32.67 ± 6.08, 75%: 10.02 ± 1.51), and combined pesticides (25%: 27.67 ± 6.81). The lowest decreases were in combined pesticides at 25% (27.67 ± 6.81) and DDForce at 75% (7.01 ± 1.16) (Figure 3). In recovery groups, significant decreases were noted for Sniper (25%: 83.67 ± 7.36) and edible camphor (50%: 54.33 ± 8.17). Sniper and combined pesticides showed dose-dependent reductions, while others did not (Figure 4).
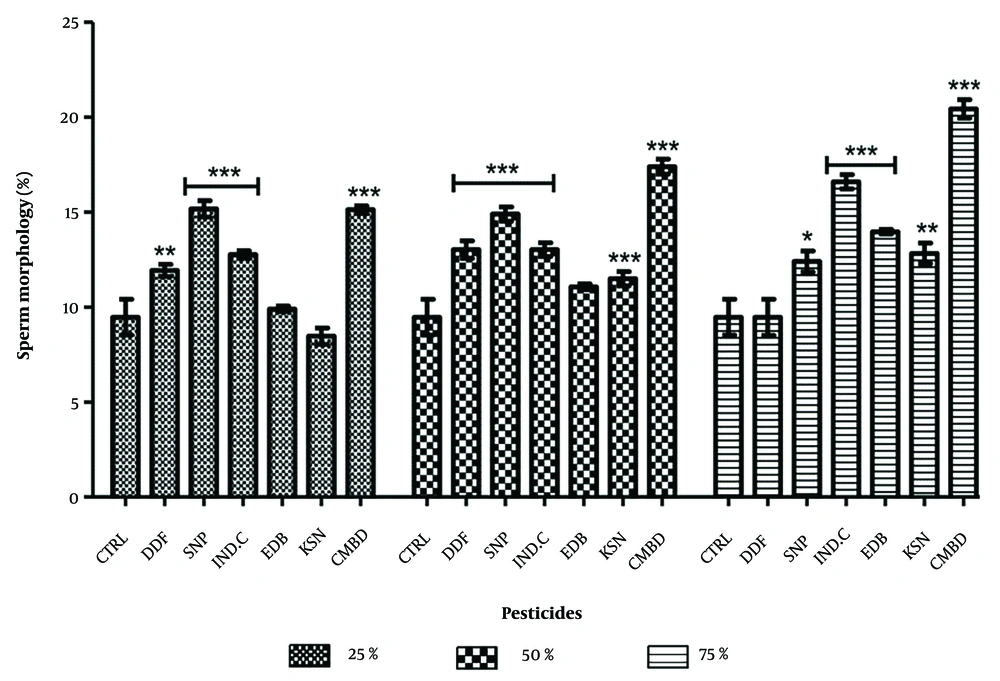
4.3. Effect on Sperm with Abnormal Morphology in Exposed and Recovery Groups
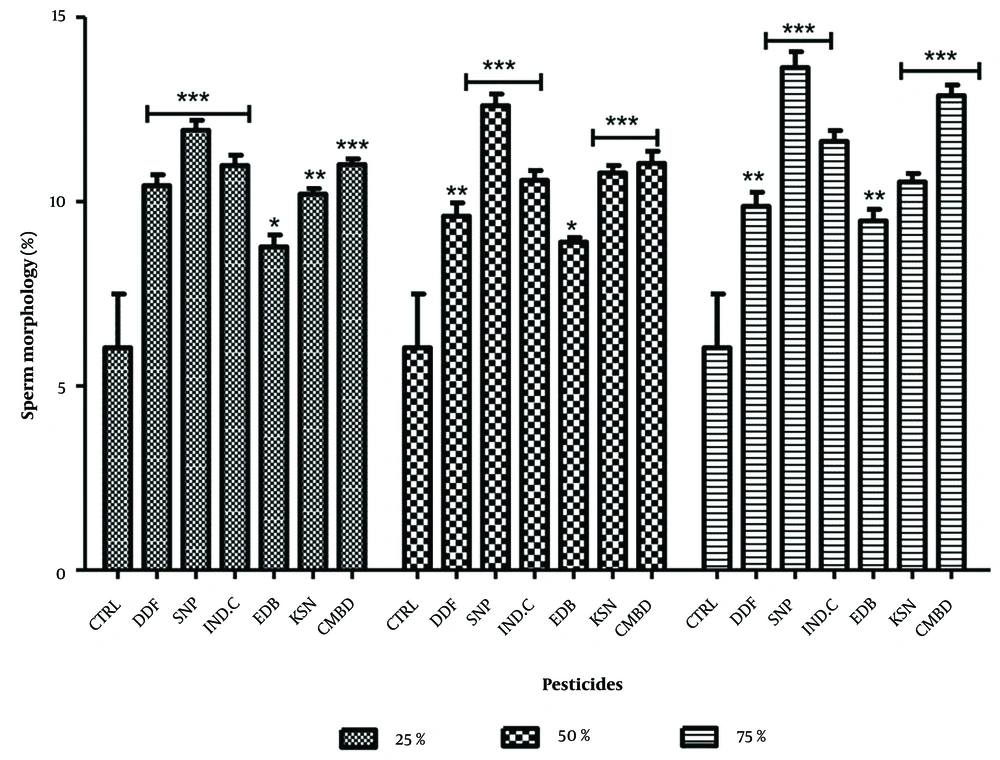
Significant increases in sperm cells with abnormal morphology were observed in exposed groups compared to the control (9.47 ± 0.94). The highest values were recorded for Sniper (25%: 15.17 ± 0.43, 50%: 15.13 ± 0.20) and combined pesticides (25%: 14.90 ± 0.38, 50%: 17.40 ± 0.40). Industrial camphor also showed significance at 75% (16.60 ± 0.33) and combined pesticides (20.43 ± 0.49). Dose relationships were seen in industrial camphor, edible camphor, kerosene, and combined pesticides, while DDForce and Sniper were dose-independent (Figure 5). In recovery groups, significant increases were noted compared to control (6.03 ± 1.46), with Sniper showing the highest values (11.93 ± 0.27, 12.60 ± 0.31, 13.63 ± 0.43) (Figure 6).
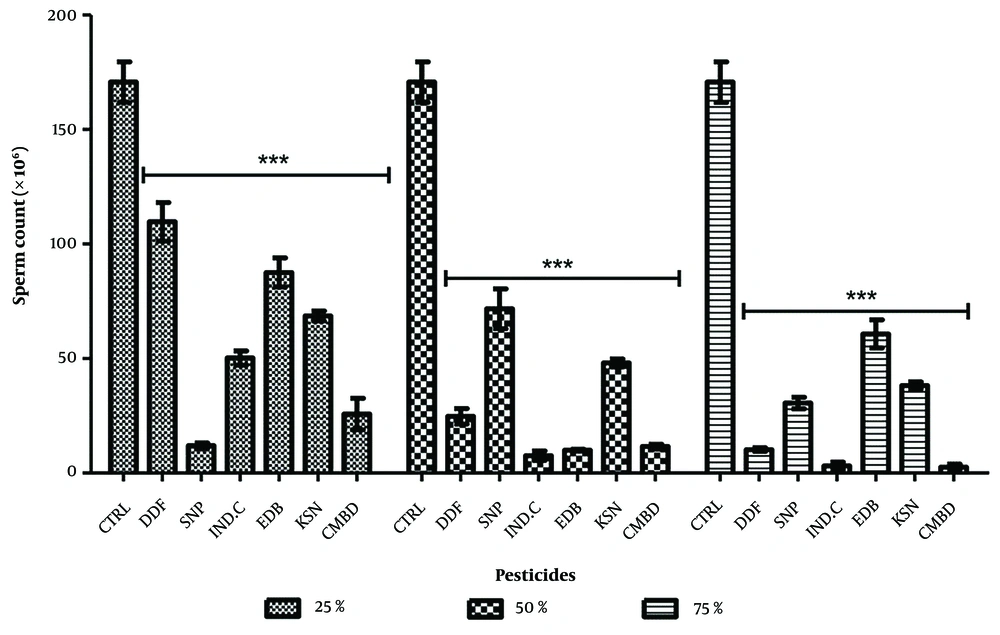
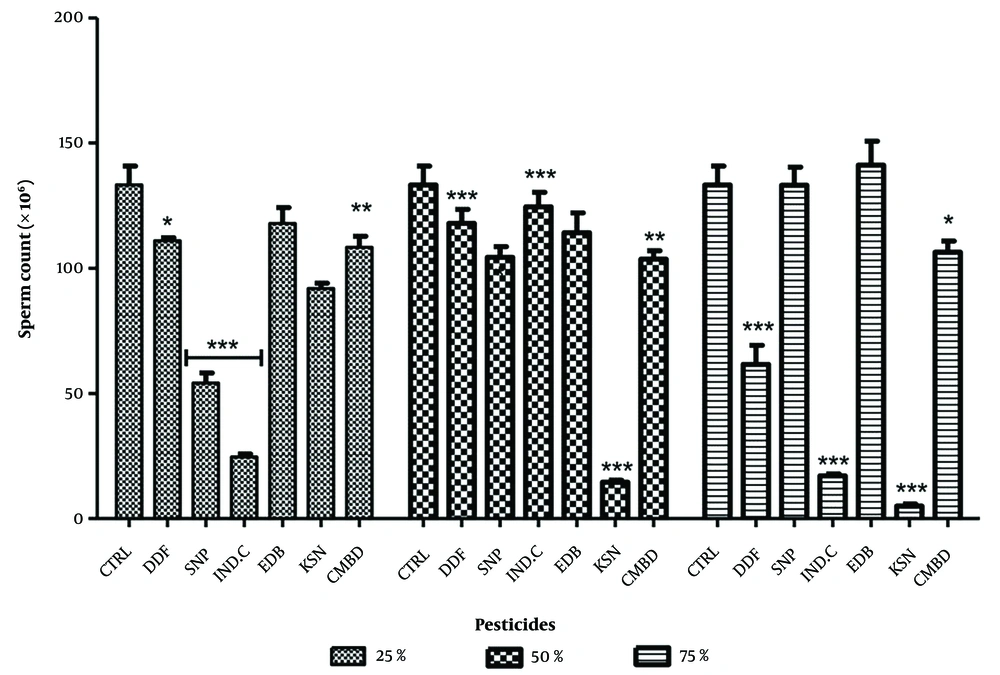
4.4. Effect on Sperm Count in the Exposed and Recovery Groups
Significant decreases in sperm counts were observed in exposed groups compared to control (170.70 ± 8.46), with values at 25%, 50%, and 75% concentrations for Sniper (11.89 ± 1.29), industrial camphor (7.56 ± 2.08), and combined pesticides (2.56 ± 1.32) showing p < 0.0001. All pesticides exhibited a dose-dependent relationship, except Sniper, which was dose-independent (Figure 7). In recovery groups, significant decreases were noted against control (133.30 ± 7.46), particularly for Sniper (54.11 ± 4.06), industrial camphor and kerosene (91.89 ± 2.10) at 25%, kerosene (14.56 ± 0.78) at 50%, and DDForce (61.67 ± 7.54), industrial camphor (17.11 ± 0.77), and kerosene (5.01 ± 0.87) at 75%. Edible camphor (141.2 ± 9.54) showed a non-significant increase at 75% (Figure 8).
5. Discussion
The impact of common pesticides on reproductive health has garnered significant attention, particularly concerning their effects on sperm parameters in animal models. This study investigated the toxicity of dichlorvos, bifenthrin, terpenoid, turpentine, and kerosene on reproductive functions in adult male Wistar rats. Sperm parameters, including sperm motility, viability, morphology, and counts, were analyzed to elucidate the potential adverse effects of these pesticides. Sperm motility denotes the ability of sperm to move effectively, which is essential for successful fertilization. Sperm viability quantifies the percentage of live sperm in a sample, reflecting overall sperm health. Sperm morphology evaluates the shape and structure of sperm, where abnormalities can impact fertility. Sperm counts measure sperm concentration within a specific volume of semen, a critical determinant of reproductive capacity.
In this study, the sperm motility of rats in the control group was significantly higher than in the exposed groups, indicating that pesticide exposure caused the deformation of sperm cells, rendering them less motile or immotile. The significant decrease in sperm motility across various concentrations suggests that all pesticides permeated the blood-testes barrier, altering the microenvironment of the seminiferous tubules (16-18). This reduction may be due to the impact of pesticides on the epididymis and oxidative stress induced by the pesticides (17, 19). Notably, kerosene showed a non-significant decrease in motility, suggesting less toxicity compared to other pesticides, while significant decreases in combined and industrial camphor groups depict higher toxicity. The dose-dependent relationship was most evident at 75% exposure, possibly due to reduced ATP levels, crucial for sperm motility and fertility (20, 21).
In rats left for two weeks post-exposure, significant recoveries in sperm motility were recorded, although values remained significantly lower compared to the control group. The significant decreases in motility post-exposure with DDForce, edible camphor, and combined pesticides can be attributed to cell deformation and testicular oxidative stress. The significant decreases in kerosene, industrial camphor, and Sniper at various concentrations suggest a duration-dependent relationship, highlighting the potency of kerosene over time. The decline in sperm motility in both exposed and recovered rats may be due to androgen insufficiency, impairing testicular functions by altering spermatogenesis enzymes, indicating an antiandrogenic effect. Similar reproductive toxicity was observed in Wistar rats exposed to pesticide fumes, showing significant decreases in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and testosterone levels after four weeks (22).
Sperm viability was significantly lower in all rats exposed to various pesticide constituents compared to the control, indicating a high proportion of motile spermatozoa with damaged membranes. This significant decrease in sperm viability across all pesticide groups depicts the detrimental effects of pesticides on spermatozoa viability. Reduced motility coupled with a high percentage of viable sperm suggests structural or metabolic abnormalities in sperm due to testicular dysfunction or anti-motility factors in seminal plasma. Combined pesticide and DDForce showed reduced toxic responses, whereas kerosene exhibited a significant increase in sperm motility at all concentrations, indicating higher toxicity. A dose-response relationship was evident, with pesticide severity increasing from 25% to 75% exposure levels. Sniper demonstrated significant decreases in sperm viability at all concentrations in the recovery groups, underscoring its severe impact on testicular function. However, indications of recovery were observed as significance increased compared to exposed rats.
The significant increase in abnormal sperm morphology across exposed groups suggests pesticide-induced damage to germinal cells. Normal sperm morphology in rats exposed to edible camphor, kerosene, and DDForce indicates non-toxicity relative to the control. The increased abnormalities in sperm morphology in recovery groups, particularly with Sniper, reflect ongoing toxicity effects. A study by Cuthbert et al. revealed that CYP exposure in mice significantly impacts spermatogenesis and male reproductive organs (23). Mice treated with CYP exhibited a 20% decrease in sperm count compared to controls. There were also notable morphological changes in sperm, particularly in the flagella, and histological impairments in the testis and epididymis. These findings suggest that CYP induces morphological and functional alterations in the male reproductive tract, aligning with our results on the reproductive toxicity of pesticide exposure in Wistar rats (19).
There was a significant increase in abnormal sperm morphology in the exposed rats compared to the control, indicating germinal cell damage from pesticide exposure. Conversely, normal sperm morphology in rats exposed to edible camphor, kerosene, and DDForce suggests non-toxicity. The significant increase in sperm abnormalities in the recovery groups, particularly with Sniper exposure, highlights the persistence of toxicity. This is consistent with the study by Ahmad et al. (3), which demonstrated that individual and combined exposure to chlorpyrifos (CPF) and CYP significantly impair reproductive function in male albino rats. The exposure resulted in reduced testicular weight, decreased sperm count, motility, and viability, along with an increased percentage of morphologically abnormal spermatozoa and elevated sperm DNA Fragmentation Index.
There was a decreased sperm count among pesticide-exposed rats, indicating an inhibition of spermatogenesis. The observed oligospermia in rats treated with Sniper, DDForce, and combined pesticides suggests their toxic effects on spermatogenic cells, leading to reduced sperm production linked low sperm counts to impaired testicular function affecting spermatogenesis-related enzyme activities (24). Other organophosphate pesticides, such as malathion and CPF, have also been associated with decreased sperm counts (25, 26). Additionally, Celik-Ozenci et al. reported that abamectin was linked to reduced sperm motility. Notable recovery signs observed upon withdrawal from pesticides suggest regeneration of spermatogenic cells, although significant sperm count reductions persisted (25). Previous research has shown that insecticide exposure in animal models results in decreased testicular sperm counts, increased abnormal sperm percentages, and decreased normal sperm morphology (26).
The dose-dependent relationships observed in rats exposed to Sniper and kerosene likely result from synergistic interactions and increased concentrations. These findings align with Sengupta and Banerjee, who reported significant decreases in spermatogenic cells and Leydig cells with higher dicofol doses, leading to reduced sperm counts (27). In a study assessing the toxicological effects of diflubenzuron (DFB) in adult male rats, subacute exposure to doses of 2, 4, and 8 mg/kg over 28 days revealed significant adverse effects on reproductive parameters. While no clinical signs of toxicity were noted, the highest dose (8 mg/kg) resulted in elevated serum alanine aminotransferase levels, and doses of 4 and 8 mg/kg increased urea levels. Importantly, the lowest dose led to significant reductions in testis weight, daily sperm production, and sperm counts in the epididymis compared to controls (28).
The findings of this study highlight the significant adverse effects of pesticide exposure on male reproductive health, specifically targeting sperm motility, viability, morphology, and count. These outcomes emphasize the potential for pesticides to disrupt critical processes like spermatogenesis and damage the delicate structure of sperm cells, ultimately impairing fertility. The study also underscores the persistence of these toxic effects, as evidenced by the slow and incomplete recovery of sperm parameters even after exposure ceased. These results carry important implications for human health, particularly in occupational or environmental settings where pesticide exposure is prevalent. The dose-dependent and duration-specific effects observed suggest that stricter regulatory measures and public health interventions are needed to mitigate reproductive risks. Furthermore, the potential for pesticides to act as endocrine disruptors reinforces the urgency for developing safer alternatives and protective guidelines for pesticide usage. By shedding light on the prolonged and multifaceted impacts of pesticide exposure, this study provides a critical foundation for addressing reproductive toxicity and safeguarding fertility.
5.1. Conclusions
This study highlights the significant reproductive toxicity of common pesticides — dichlorvos, bifenthrin, terpenoid, turpentine, and kerosene — on adult male Wistar rats. The exposure resulted in marked reductions in sperm motility, viability, and count, along with morphological abnormalities, revealing the harmful impact on spermatogenesis. The observed dose-dependent toxicity, with kerosene showing relatively lower effects, emphasizes the importance of managing exposure levels. While some recovery was noted, reproductive impairments persisted, suggesting long-term damage to testicular function. These findings reinforce the need for informed policies to mitigate pesticide-related health risks and promote safer usage, particularly in domestic environments. In light of this study, we recommend that pesticides should be used in strict adherence to safety guidelines and manufacturer instructions to minimize risks to both human health and the environment. Proper protective equipment, accurate dosage, and appropriate application techniques are essential to ensure effective and responsible pesticide use.