1. Background
Staphylococcus aureus is gram-positive, coagulase-positive cocci of the Staphylococcus family and an opportunistic infection agent in humans (1). In the past, these bacteria were considered non-pathogenic, weak pathogens, or secondary infectious agents and are also among the most common pathogens that cause infection through venous catheters, grafts and hemodialysis shunts, peritoneal dialysis catheters, artificial joints, vascular grafts, and artificial valves (2, 3). Staphylococcus aureus is particularly important due to increased antibiotic resistance and is also a leading cause of nosocomial infections worldwide (4).
Antibiotic resistance in S. aureus is carried through chromosomes and plasmids and intensifies with indiscriminate antibiotic use (5). Contact with infected patients or their personal belongings (eg, clothing, towels, sheets, and bedding) could spread S. aureus infection (6). Colonization is the first step in the pathogenesis of S. aureus infection. Asymptomatic colonized individuals are a source of the human-to-human transmission of the disease (7). Staphylococcus aureus is colonized in the nasal passages in approximately 27% of the general population. However, the bacterium may also be colonized in other parts of the body, such as the armpits, groin, and gastrointestinal tract.
2. Objectives
The present study aimed to discover and characterize the pattern of antibiotic resistance in S. aureus isolated from patients admitted to Imam Reza Hospital in Kermanshah, Iran during 2016 - 2017.
3. Methods
In this descriptive cross-sectional study, a laboratory expert provided a list of the patients who were admitted to Imam Reza Hospital during 2016 - 2018 with a positive S. aureus culture sample (sputum, urine, blood, wound, fecal, and eye samples). The susceptibility pattern and antibiotic resistance of S. aureus isolated from each patient were reported. Following that, the samples were delivered to the microbiology laboratory, cultured in eosin methylene blue and blood agar, and incubated for 24 hours at the temperature of 37°C. The bacteria were identified based on the colony color, the presence/absence of hemolysis, and the gram-smear staining produced from the colonies after colony development and the first identification.
At the next stage, an antibiogram was conducted using the disk diffusion method, and the precise dimension of the growth inhibition zone was measured in millimeters using the Müeller-Hinton agar (MHA) medium and compared to the standard table of the Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) to test ampicillin (10 µg), gentamicin (10 µg), ciprofloxacin (5 µg), imipenem (10 µg), ceftazidime (30 µg), cotrimoxazole (1.25 µg), nitrofurantoin (300 µg), ceftriaxone (30 µg), clindamycin I (10 µg), piperacillin (100 µg), vancomycin (30 µg), erythromycin (15 µg), penicillin G (10 units), cefoxitin (30 µg), teicoplanin (30 µg), amikacin (10 µg), doxycycline (30 µg), and ofloxacin (5 µg).
Initially, a bacterial suspension was prepared with a turbidity equivalent to 0.5 McFarland tube (108 CFU/1.5 mL), and a lawn culture was conducted three times using a sterile swab on the MHA medium plate. The discs were removed from the freezer one hour before, placed on the culture media with pliers, and stabilized with the tip of a pair of pliers, and the plates were incubated at the temperature of 37°C for 24 hours. The diameter of the inhibition zone was measured in millimeters using an accurate ruler in order to read the results. The findings were classified as sensitivity (S1), resistance (R2), and semi-sensitive zones (I3).
This study was conducted in accordance with ethical principles, and the confidentiality of the information was preserved.
4. Results
In 2016, 2017, and 2018, 686 (30%), 714 (31.2%), and 888 (38.8%) positive cases of S. aureus were respectively reported in the patients admitted to Imam Reza Hospital. Table 1 shows the number of the positive S. aureus cases per section of the hospital. Out of 2,266 patients with S. aureus-positive cultures during this period, 56.9% were male, and 43.1% were female. The positive culture samples were collected from urine samples (23.9%), wound samples (13.8%), sputum samples (10.3%), blood samples (40.1%), and fecal samples (8.4%). In addition, 1.2% of the positive cultures were collected from eye samples, 5.4% from wound samples, 1.4% from eye cultures, and 1.6% from nose cultures (Table 2).
| Hospital Wards | Percentage |
|---|---|
| ICUs (general, infants, children) | 13.1 |
| Emergency | 43.7 |
| Internal (internal, infectious, pediatric, neurology) | 18.9 |
| Surgery (general, gynecological, urology) | 14.4 |
| Outpatients | 8.7 |
| Transplantation (bone marrow and kidneys) | 1.1 |
| CCU | 0.1 |
| Total | 100 |
Positive Cases of Staphylococcus aureus by Wards of Imam Reza Hospital (2016 - 2018)
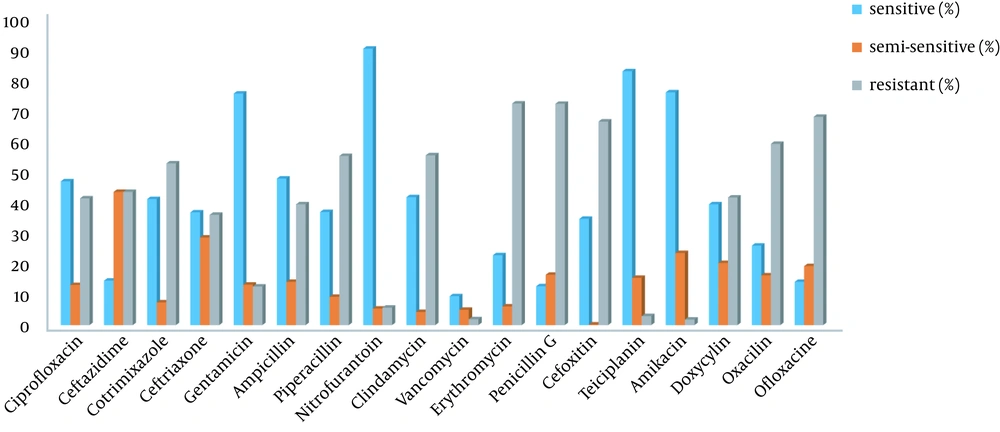
| Antibiotic | Sensitivity (%) | Semi-sensitivity (%) | Resistance (%) | Samples Tested on Antibiotics, No. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciprofloxacin | 46.3 | 12.9 | 40.8 | 2,012 (89.9) |
| Ceftazidime | 14.3 | 42.9 | 42.9 | 2,274 (99.4) |
| Cotrimoxazole | 40.6 | 7.3 | 52.1 | 1,542 (67.4) |
| Ceftriaxone | 36.3 | 28.2 | 35.5 | 124 (5.4) |
| Gentamicin | 74.6 | 13 | 12.4 | 1,668 (72.9) |
| Ampicillin | 47.2 | 13.9 | 38.9 | 36 (1.6) |
| Piperacillin | 36.4 | 9.1 | 54.5 | 33 (1.4) |
| Nitrofurantoin | 89.1 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 432 (18.9) |
| Clindamycin | 41.2 | 4.2 | 54.7 | 1,826 (79.8) |
| Vancomycin | 93.3 | 4.9 | 1.9 | 535 (23.4) |
| Erythromycin | 22.5 | 6 | 71.4 | 1,415 (61.8) |
| Penicillin G | 12.5 | 16.2 | 71.3 | 550 (24) |
| Cefoxitin | 34.2 | 0.2 | 65.6 | 1,176 (51.4) |
| Teicoplanin | 81.8 | 15.2 | 2.9 | 341 (14.9) |
| Amikacin | 75 | 23.2 | 1.8 | 56 (2.4) |
| Doxycycline | 38.9 | 20 | 41.1 | 95 (4.2) |
| Oxacillin | 25.6 | 16 | 58.4 | 125 (5.5) |
| Ofloxacin | 13.9 | 19 | 67.1 | 88 (3.8) |
Antibiogram of Staphylococcus aureus in Positive Cultures (2016 - 2018)
Figure 1 depicts the antibiogram results. As can be seen, the highest antibiotic resistance was observed against erythromycin, penicillin G, ofloxacin, cefoxitin, clindamycin, and piperacillin. Furthermore, vancomycin, teicoplanin, nitrofurantoin, and gentamicin were the most effective antibiotics against S. aureus.
5. Discussion
Staphylococci are a group of bacteria with have high resistance to various antibiotics. Examination of antibiotic resistance helps prevent the spread and transmission of resistant strains. Moreover, adequate knowledge of developing resistance to multiple antibiotics and the influential factors could effectively prevent the spread of these infectious isolates.
In the present study, most of the S. aureus isolates were obtained from blood and urine cultures, which is similar to the study by Tabaei et al. (8). In the study conducted by Rahimipour et al., the highest prevalence of S. aureus was observed in the emergency department and ICU (9). In the research by Tabaei et al., most of the methicillin-resistant strains of S. aureus were isolated in the emergency and internal wards, respectively (8). In the present study, the highest frequency of S. aureus was observed in the emergency department, which is consistent with the results of aforementioned studies.
According to the current research, S. aureus had the highest antibiotic resistance to erythromycin, penicillin G, ofloxacin, cefoxitin, clindamycin, and piperacillin. In addition, the highest antibiotic susceptibility was observed to vancomycin, teicoplanin, nitrofurantoin, and gentamicin. The results obtained by Tabaei et al. (8) in Mashhad (Iran) also indicated the highest level of resistance against penicillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, methicillin, gentamicin, and ciprofloxacin, respectively. Accordingly, vancomycin was the most effective agent against S. aureus, while penicillin, erythromycin, and methicillin had the lowest sensitivity. This is consistent with the result of the present study in terms of resistance to penicillin, erythromycin, and clindamycin and sensitivity to vancomycin
Since methicillin-resistant strains are only sensitive to vancomycin, the excessive use of this antibiotic in the treatment of patients with methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections could lead to fatal consequences possibly due to factors such as the use of contaminated equipment in surgery, contamination of hospital facilities, and the overuse or improper use of antibiotics.
In another study in this regard, Reisi et al. reported that S. aureus isolates had 95% sensitivity to erythromycin and 99.5% sensitivity to vancomycin, which is inconsistent with the results of the present study in terms of erythromycin sensitivity (10). This discrepancy could be due to the locality of various regions, applied methods to determine the degree of sensitivity, and the influential factors in drug resistance. In the research conducted by Rahimi et al., the highest antibiotic resistance was reported against penicillin, clindamycin, tobramycin, and tetracycline, respectively (11). Another study also reported the highest antibiotic resistance to ciprofloxacin, clindamycin, and erythromycin (12).
5.1. Conclusions
According to the results, the examined S. aureus isolates studied had multiple resistance to various antibiotics, which doubles the risk of antibiotic overuse. Therefore, employing standard and accurate methods in clinical laboratories could largely contribute to selecting effective and useful antibiotics. Otherwise, antibiotic resistance will increase drastically due to unnecessary antibiotic use against sensitive bacterial strains.