1. Background
Nosocomial infections are hospital-acquired infections that develop within 48 hours of admission up to three days of discharge or 30 days after surgery (1). However, various definitions have been offered by multiple authorities (2). The most common nosocomial infections include urinary tract (31%), respiratory tract (24%), and bloodstream (16%) infections (1, 3). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 15% of hospitalized patients are complicated by nosocomial infections. A systematic review of 55 hospitals in 14 countries in Europe, Eastern Mediterranean, Southeast Asia, and the Western Pacific revealed that about 7.8% of hospitalized patients developed at least one nosocomial infection (4, 5). The prevalence of nosocomial infections varies from 5% in Europe and North America to 40% in sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, and some regions of Asia (2). Considering the increased number of healthcare centers and hospitals, factors including the increasing prevalence of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases, changes in disease patterns, increasing microbial resistance, and prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) hospitalization increase the rate of nosocomial infections (6). Despite the efforts to control nosocomial infections, it is estimated that these infections are responsible for approximately 80,000 deaths annually in the United States (7). According to the proposed Ministry of Health and Medical Education regulation launched in March 2007, each hospital must have an active Nosocomial Infection Control Committee (7).
2. Objectives
The prevention and control of hospital-acquired infections can be improved by reporting hospital infections annually and comparing them with previous years. Hence, the present study was conducted to report the prevalence and types of nosocomial infections in Imam Reza Hospital in Kermanshah, Iran, in 2020 and compare the corresponding rates in 2019.
3. Methods
This Descriptive, cross-sectional study compared nosocomial infections at Imam Reza Hospital during 2019 and 2020. The results of the nosocomial infections were reported based on the guidelines of the Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System (NISS) from the Iranian Center for Disease Control (ICDC). Ventilator-Associated Events (VAE), Urinary Tract Infections (UTI), Respiratory Tract Infections or Pneumonia (PNEU), Bloodstream Infections (BSI), Surgical Site Infections (SSI) and other infections (Other) were examined to report nosocomial infections. The data collection tool was a researcher-made checklist, including age, sex, ward of hospitalization, the type of nosocomial infections (ventilator-associated infections, respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, bloodstream infections, surgical site infections, etc.), and the responsible microorganisms were extracted from the infection control department of the hospital through electronic records.
3.1. Data Analysis
The frequency and percentage were used to describe the data after completing the checklists and entering the data into SPSS software version 24. Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used to determine the relationship between the variables. A statistical difference of 0.05 was considered significant.
4. Results
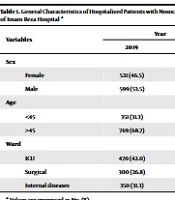
In this study, 2201 out of 66691 hospitalized patients (3.3%) developed nosocomial infections during 2019 - 2020. In 2019, 38743 patients were hospitalized, of whom 1120 developed at least one nosocomial infection (2.9%). Among the nosocomially infected patients, 46.5% (n = 521) were female. Intensive care units (ICUs), internal diseases wards, and surgical wards were the most commonly involved wards with nosocomial infection, with a prevalence of 42, 26.8, and 31.3%, respectively. In 2020, 27948 patients were hospitalized, among whom 1081 developed nosocomial with a prevalence of 3.9% (46.4% (n = 501)) were female and 53.6% (n = 580) were male). The most prevalent wards for nosocomial infections included the ICUs (n = 486, 45.0%), internal diseases wards (n = 317, 29.3%), and surgical wards (n = 278, 25.7%) (Table 1).
| Variables | Year | |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 521 (46.5) | 501 (46.4) |
| Male | 599 (53.5) | 580 (53.6) |
| Age | ||
| <45 | 351 (31.3) | 333 (30.8) |
| >45 | 769 (68.7) | 748 (69.2) |
| Ward | ||
| ICU | 470 (42.0) | 486 (45.0) |
| Surgical | 300 (26.8) | 278 (25.7) |
| Internal diseases | 350 (31.3) | 317 (29.3) |
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
The most common nosocomial infections in 2019 were UTI (n = 431, 38.5%), SSI (n = 281, 25.1%), and PNEU (n = 136, 12.1%). The most prevalent nosocomial infections in 2020 were UTI (n = 429, 39.7%), BSI (n = 154, 14.2%), and PNEU (n = 151, 14.0%). There was a significant difference between the prevalence of infections during the two years (P < 0.05) (Table 2). UTI (n = 221, 36.9%) and SSI (n = 115, 19.2%) were the most common nosocomial infections in the male in 2019 and 2020, with the highest prevalence for UTI (n = 180, 31.0%) and SSI (n = 88, 15.2%). The most common nosocomial infections in the females were also UTI (n = 210, 40.3%) and SSI (n = 165, 31.7%) in 2019, UTI (n = 249, 49.7%) and SSI (n = 52, 10.4%) in 2020.
| Variables | Year | P-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | ||
| Infections | 0.001 | ||
| VAE | 131 (11.7) | 110 (10.2) | |
| PNEU | 136 (12.1) | 151 (14.0) | |
| UTI | 431 (38.5) | 429 (39.7) | |
| BSI | 82 (7.3) | 154 (14.2) | |
| SSI | 281 (25.1) | 140 (13.0) | |
| Other | 59 (5.3) | 97 (9.0) | |
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
5. Discussion
The results of this study showed a prevalence of 3.3% for nosocomial infections in Kermanshah, Iran. The overall prevalence of nosocomial infections has been reported as much as 0.6% in Iran (8). According to the studies, the prevalence of nosocomial infection was 3.3% in Tehran, 2.6% in Hamedan, 0.2% in Ahvaz, 0.4% in Qom, and 0.6% in Zanjan (8, 9). However, the factors related to the prevalence of nosocomial infections have not been determined in a detailed and prospective study. Therefore, prospective studies should be designed and conducted with a larger sample size to investigate and identify the risk factors for hospital-acquired infections.
In this study, UTI, SSI, and BSI were the most common nosocomial infections, which was similar to the results of Zahraei et al. (7), Yaghubi et al. (3), Rahmanian et al. (9), Behzadnia et al. (4), and Mosadeghrad et al. (8), all of which were conducted in Iran. Hence, the following measures are required to prevent nosocomial infections: paying attention to the sources of infection, correct use of the resources, implementing comprehensive and regular infection control measures like hand washing by the hospital staff, personal hygiene by the patients, health control of the hospital environment, and preventing the unnecessary use of antibiotics. Therefore, medical centers and institutions should establish an organization to monitor nosocomial infections. Moreover, reporting the associated results of every institution regularly is essential to improving hospital infection control measures.
This study demonstrated that BSI was more common in men than women. However, UTI was more common in women than in men. The results of the present study were consistent with Teymourzadeh et al. (10), Mosadeghrad et al. (8), Chen et al. (11), and He al. (12). The similar results among various regions of Iran may be due to the same hospital infection control and prevention protocols.
The prevalence of nosocomial infections was higher in the ICUs than in the internal diseases and surgical wards. Mahmoudi et al. (13), Rosenthal et al. (14), Rahimi-Bashar et al. (15), Bijari et al. (16), and Edwardson and Cairns (17) also showed the same results.
Factors related to the high prevalence of nosocomial infections in the ICU department compared to other departments are the severity of the patient’s illness, the response to the physiological stress of injury and pain, anxiety, age, inappropriate use of antibiotics, sleep deprivation, and malnutrition. On the other hand, prolonging patients’ hospitalization period and using various holding devices increases hospital infection in these departments and causes the metabolic and immunological reaction of failure of other organs.
The study’s limitations included its retrospective nature and the inadequacy of file-based data. Moreover, this study was conducted in only one of the general hospitals of the province, which can reduce the conciseness of the results. Therefore, it is recommended to perform the same study in other cities or hospitals of the province. In addition, this study examined only six types of nosocomial infections. Hence, it is recommended to evaluate other nosocomial infections in future studies. Another limitation can be the absence of patients’ follow-up after discharge. Therefore, hospitals should pay special attention to the systematic and organized monitoring of nosocomial infections in high-risk wards, especially for older patients with those with more risk factors of hospital-acquired infections.
Conclusion: Based on the results, the prevalence of nosocomial infection was higher in men than women, in people over 45 years old than under 45. Urinary tract infection and surgical site infection in 2018, urinary tract infection, and blood infection were, respectively, the most common hospital infections in 2019. Infection in Imam Reza Hospital was high compared to other hospitals in Iran. In addition, the prevalence of nosocomial infection in the ICU ward was higher than in the internal and surgery wards. On the other hand, the health protocols in each hospital are unique, and hospital employees may not follow them correctly. Therefore, Imam Reza hospital's health protocol should be prepared and regulated in accordance with hospitals of low prevalence in the province. Also, managers and executives are suggested to take measures to monitor the implementation of the protocol.