1. Context
Mental illnesses pose a serious global health challenge, impacting millions of individuals and their families. The World Health Organization reported that in 2019, over 970 million people faced mental disorders, including major depressive disorder (MDD), bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The MDD has a global prevalence of approximately 2.49%, while ASD affects about 1 in 36 children in the United States as of 2019. Schizophrenia occurs in around 0.3% of the population, with ADHD and bipolar disorder having a lifetime prevalence of about 1.1% and 0.5%, respectively (1-3). Traditionally, these mental disorders have been viewed mainly through neurobiological and psychological lenses. However, recent studies highlight the gut microbiome’s impact on mental health, indicating that gut well-being can influence psychological health via the microbiota-gut-brain axis (4). This bidirectional communication reveals that gut bacteria may affect brain function and behavior, potentially opening new therapeutic opportunities for treating mental illnesses (5).
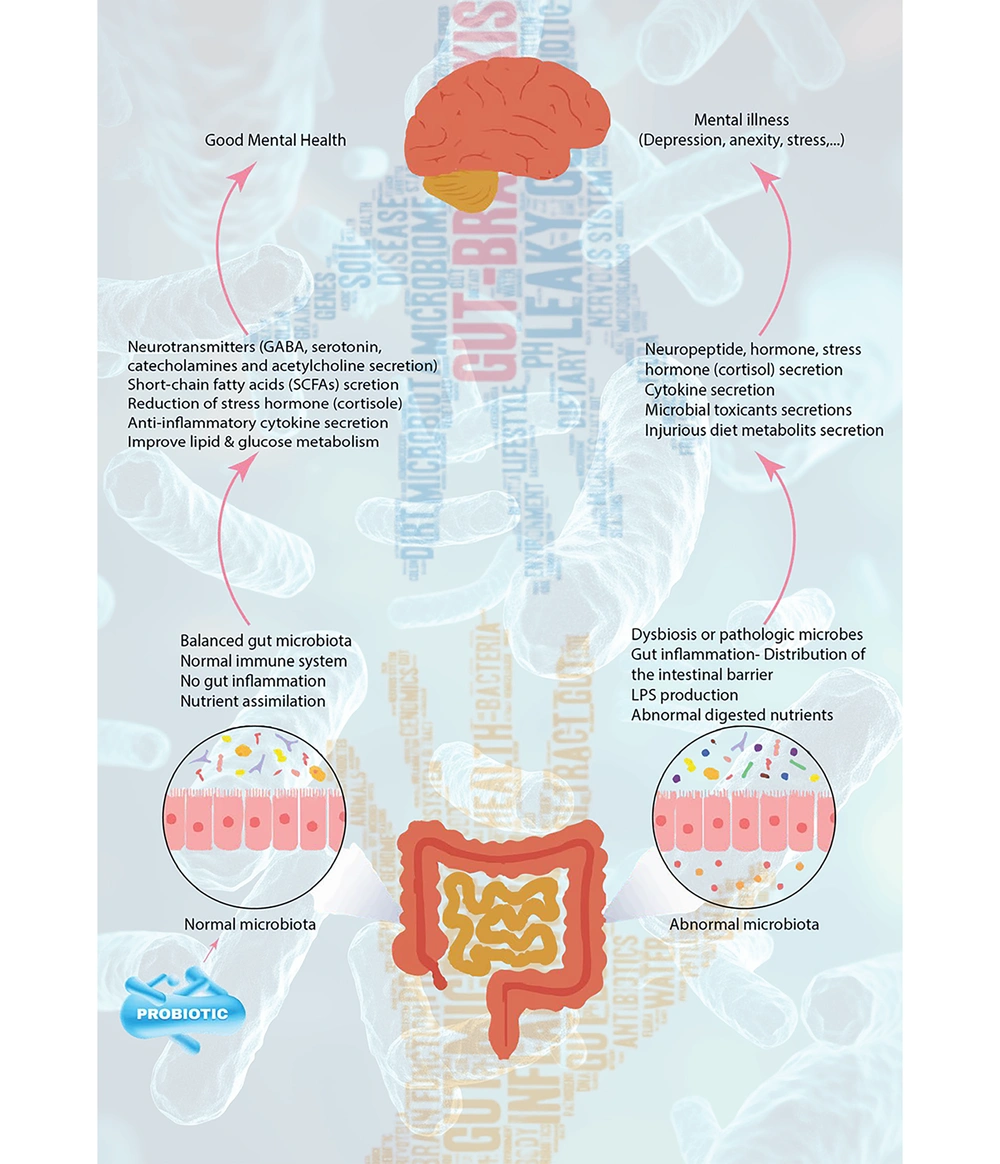
Probiotic supplementation shows promise as a treatment for various mental health issues. When taken in adequate amounts, these live microorganisms may benefit the health of their host. Studies have indicated that individuals with MDD often experience dysbiosis, a condition marked by reduced levels of beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus (6). Probiotics can also strengthen gut barrier function, lower systemic inflammation, and adjust gut microbiota composition (7). Evidence links probiotic supplementation to improved mood and reduced depression symptoms (8) (Figure 1).
The present review aims to summarize the available evidence on the effects of probiotic supplementation in five major mental illnesses. We will explore how probiotics may be an effective complementary medicine for managing these complex disorders through a review of clinical trials and mechanistic studies.
2. Major Depressive Disorder
The MDD is a widespread mental illness with an unclear etiology. Psychosocial issues, sleep disturbances, and persistent stress or anxiety can trigger depression by activating the immune system through the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This hyperactivation leads to elevated production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, which can damage cellular components, and reduced levels of antioxidants and certain amino acids (9, 10). Emerging research suggests that gut microbiota imbalance and dysfunction of the microbiota-gut-brain axis may significantly contribute to its pathophysiology. Patients with MDD show distinct gut microbiota compared to healthy individuals, and transferring fecal microbiota from these patients to germ-free animals can induce depressive behaviors, while transferring healthy microbiota can relieve symptoms in MDD patients. Additionally, antibiotics may disrupt gut microbiota and potentially trigger depression, whereas specific probiotics, prebiotics, fermented foods, and a balanced diet have shown antidepressant effects. Chronic and early life stress, known risk factors for depression, can also adversely affect gut microbiota and exacerbate microbiota-gut-brain axis dysfunction (11).
The existence of a subtype of depression influenced by gut microbiota changes due to diet has been discovered. Probiotics have been shown to enhance the relative abundance of beneficial gut bacteria (Bifidobacterium, Lactococcus, and Lactobacillus) specifically in rats fed a high-fat diet (12). It is more common for patients with MDD to have lower Bifidobacterium and/or Lactobacillus counts than controls. These probiotics are linked to improved stress responses and reduced symptoms of depressive disorders. Research indicates that they lower the HPA axis response in humans and alleviate chronic stress-induced changes in brain function and neurogenesis in mice with depression. Additionally, patients with MDD frequently experience irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and these probiotics also benefit individuals suffering from IBS (13).
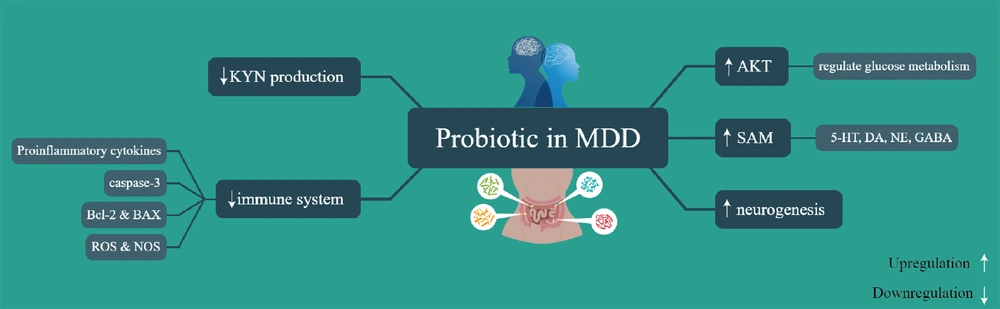
Rudzki et al. discovered that adding the probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus plantarum 299v to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment enhanced cognitive performance and reduced kynurenine (KYN) levels in patients with MDD. The improvement in cognitive performance seen in the LP299v group compared to the placebo group might have been influenced by the decrease in KYN concentration. Although KYNs have neurotoxic and neurodegenerative effects on the central nervous system, they are important for immunomodulation, neuroprotection, and maintaining the energetic balance of the central nervous system at physiological levels (14).
Slykerman et al. (15) revealed that women who received the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 had significantly lower levels of depression and anxiety in the postpartum period. This probiotic may be beneficial for preventing or treating symptoms of postpartum depression and anxiety. The findings of Strodl et al. (16) suggest that a combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Streptococcus thermophilus, magnesium orotate, and CoQ10 may be a safe and effective treatment for MDD. In another study, probiotics (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and B. longum R0175) decreased the flow of methyl groups through betaine, raised S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) in the liver, and decreased norepinephrine and dopamine in the plasma (17). The combined administration of the probiotic strains B. longum and L. helveticus has been found to reduce activation of caspase-3, alleviate depressive-like symptoms, and decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines in rats. It was suggested that neuron loss, linked to reduced neuronal activity of trophic support, could increase levels of depression or contribute to the pathophysiology of dementia. The presence of B. longum R0175 was associated with lower plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations, emphasizing the connection between CRP levels and depression, demonstrating the importance of inflammation in depression (18).
Furthermore, oxidative stress is crucial in the development of depression by targeting various cellular signaling pathways, such as the AKT pathway. Decreased AKT phosphorylation can reduce antiapoptotic and antioxidant activity in depressed individuals. Conversely, increased AKT phosphorylation can activate the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and deactivate pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak, ultimately inhibiting the caspase pathway and reducing apoptosis. Interestingly, chronic probiotic administration has been shown to enhance phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) and Bcl-2 levels, while decreasing Bax and cleaved caspase-3 levels (19) (Figure 2).
As with MDD, there are important connections between bipolar disorder and gut health that need more research.
Regulated pathways induced by probiotic in major depressive disorder (MDD). 5-HT, serotonin; DA, dopamine; NE, norepinephrine; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; AKT, protein kinase B; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; BAX, Bcl-2-associated X protein; KYN, kynurenine.
3. Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a severe mental illness that impacts various aspects of patients’ lives, influenced by both psychiatric and physical comorbidities. It is a major worldwide factor that causes disability and chronicity. The underlying digestive mechanisms linked to the onset and progression of bipolar disorder remain incompletely understood, despite the substantial burden of these conditions. The shared effects of different therapies on oxidative, inflammatory, and neurotrophic pathways seem to be linked to their efficacy in treating bipolar disorder (20). The brain-gut axis, which facilitates communication between the gut and the brain, has gained attention due to its relationship with inflammatory pathways linked to microbiota products (21).
From a clinical perspective, probiotic supplements may be a well-tolerated approach to positively impacting gastrointestinal (GI) function, mental and physical health, cognition, and immune response, potentially influencing psychiatric symptoms, particularly in individuals with GI issues like flatulence and constipation. The high clinical applicability and compliance with probiotic supplements in euthymic bipolar disorder patients suggest they could be a promising add-on therapy (21). Probiotics have the potential to enhance the effectiveness of traditional medication therapy in reducing symptoms of depression. Research has shown that B. animalis subsp. lactis BAMA-B06/BAu-B0111 can improve glucose metabolism disorders in patients with depressive bipolar disorder type I (BD-I). This suggests that probiotics may play a role in adjuvant therapy for depression by addressing underlying mechanisms such as glucose metabolism (22).
The findings of Eslami Shahrbabaki et al. (23) showed that probiotic intake (including B. bifidum, B. lactis, B. longum, and L. acidophilus) did not significantly alter the intensity of manic episodes and depression between the two study groups, but it did significantly decrease the intensity of manic episodes and depression over time within the probiotic group.
4. Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental health condition characterized by symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions (psychotic symptoms), lack of emotion or motivation (negative symptoms), and problems with thinking or memory (cognitive dysfunction) (24). Studies comparing the gut microbiota of patients with schizophrenia to those without highlight critical contrasts at the phylum and genus levels, providing evidence of gut microbiome modification (25-27). The lack of microbiota diversity in schizophrenia patients can be altered and improved to a beneficial microbiome through dietary intervention. Dietary probiotics or prebiotics are examples of interventions that target the gut-brain axis and may help reduce some of the symptoms of schizophrenia while also enhancing patients' quality of life (28).
Research has demonstrated that taking probiotics can help with digestive issues, decrease the severity of symptoms, lower rehospitalization rates, and improve cognitive function (29). Certain biomarkers, such as those indicating aggression severity, systemic inflammation, leaky gut, and oxidative stress, are moderately to strongly positively correlated with increased levels of the genus Prevotella, and weakly to strongly negatively correlated with decreased levels of other genera. This supports the idea that an imbalance in gut microbiome, or enteric dysbiosis, contributes to aggression by driving inflammation and oxidative stress responses in schizophrenia patients. Additionally, short-chain fatty acids and neurotransmitters, including 5-hydroxytryptophan, levodopa, noradrenaline, adrenaline, kynurenic acid, and histidine, are significantly decreased in schizophrenia cases with aggression compared to those without (30).
Preliminary evidence indicates that individuals with schizophrenia exhibit a reduced relative abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria in their gut microbiota. Butyrate plays a vital role in preserving the integrity of the gut-blood barrier and possesses significant anti-inflammatory properties. Treatment with the prebiotic oligofructose-enriched inulin (OEI) has been shown to selectively elevate plasma butyrate levels in individuals with schizophrenia (31).
5. Autism Spectrum Disorder
The ASD encompasses a variety of common neurodevelopmental disorders marked by ongoing challenges in social interactions and the emergence of repetitive behaviors and interests, as outlined in the DSM-5. These challenges can hinder communication and daily functioning. Despite common traits, ASD presents a diverse range of characteristics, highlighting its heterogeneous nature (32). The estimated prevalence of ASD increased from one in 110 children in 2006 to one in 36 children by 2020 (1). Recent studies show that functional GI disorders are more prevalent in individuals with ASD compared to the broader population (33, 34). The diversity of the gut microbiome is reduced in children with ASD compared to children without developmental disorders, but this difference is lessened after a short probiotic treatment (33, 35).
Microbial species play unique roles in producing compounds like short-chain fatty acids, which are linked to neurobiological effects within the microbiome-gut-brain axis, and 4-ethylphenylsulfate, a byproduct of dietary tyrosine thought to contribute to behaviors resembling ADHD (36). Probiotic use effectively reversed the alterations in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels induced by valproic acid (VPA). When probiotics were administered alongside treatment, there was an increase in IL-10 levels. The VPA exposure during pregnancy resulted in decreased serotonin (5-HT) levels in the prefrontal cortex; however, this decline was mitigated with combined treatment. Furthermore, prenatal exposure to VPA led to a lower Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio within the gut microbiota, but probiotic treatment significantly enhanced this ratio. These findings suggest that employing probiotics and prebiotics to restore microbial balance may represent a novel approach for addressing autism-like symptoms (37).
The VISBIOME® formulation (containing eight probiotic species, mostly Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) was found to be safe and showed potential health benefits in children with ASD and GI symptoms who maintained Lactobacillus levels (38). Moreover, research indicates that oxytocin and the probiotic L. plantarum PS128 have a synergistic effect on individuals with ASD (39). PS128 can boost dopamine and serotonin levels in animals. A proposed mechanism for the increased serotonin involves bacterial tryptophan metabolites interacting with intestinal enteroendocrine cells, which could enhance intestinal motility, modulate the central nervous system, and alleviate the symptoms of this condition (40).
6. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
The ADHD is recognized as a neurodevelopmental disorder that results in disruptions in dopamine transmission and reward processing (41). Currently, the pathophysiology of ADHD has not been precisely discovered; however, it has been established that genetic predisposition has a direct relationship with the pathophysiology of ADHD (42). A study also indicated that environmental factors, such as stress, smoking, mineral deficiencies, and premature birth, play a role in increasing the risk of developing ADHD (43).
Based on the results obtained from recent studies, it is evident that the composition of gut microbiota can influence brain development through the bidirectional interaction between the gut and the brain (the gut-brain axis) (44, 45). Some recent studies (46) have revealed that the composition of gut microbiota differs between individuals with ADHD and the control group, while other studies found no difference in gut microbiota composition between individuals with ADHD and those without (47). However, in a study by Partty et al. (as cited by Boonchooduang et al.), it was noticed that the relative abundance of Bifidobacterium species in children with ADHD was reduced compared to non-affected children (48).
According to a study by Jiang et al., it was found that the level of Faecalibacterium in the gut microbiome of children with ADHD in the age range of 6 - 10 years decreased, and the level of Faecalibacterium was negatively correlated with the severity of ADHD (49). In another study, it was observed that the levels of Bacteroidaceae in adolescents with ADHD in the age range of 12 - 14 years increased, resulting in a positive correlation with clinical symptoms of ADHD (50). Reports from several recent studies indicating changes in the gut microbiome showed a reduction in the abundance of Coprococcus and Ruminococcaceae species in adults with ADHD compared to non-affected individuals (51, 52).
Further results from recent data report changes in the composition of the gut microbiome in individuals with ADHD. In fact, the maturation of microbiota and the development of the nervous system occur simultaneously, and for this reason, alterations in microbiota are associated with ADHD (53).
The method of delivery, maternal stress, the promptness of initiating breastfeeding, the prescription of antibiotics, and exposure to various chemicals play a vital part in microbial dysbiosis and changes in gut microbiota function (54). Microbial dysbiosis in individuals with ADHD is also associated with GI symptoms, including constipation and abdominal pain (55). Since microbial dysbiosis is linked to an increased entry of metabolites from pathogenic bacteria into the bloodstream, it may be related to changes in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier and lead to neuroinflammation (56). According to this hypothesis, probiotics, due to their anti-inflammatory properties, may have a potential role in improving intestinal epithelial integrity (57). After 8 weeks, it was observed that the severity of ADHD symptoms in this group decreased (58).
In another study, patients with ADHD were affected by the probiotic supplement B. bifidum-688 (Bf-688), and after 8 weeks, it was observed that the supplement (Bf-688) led to an improvement in the gut microbiome composition, an increase in Body Mass Index, and a reduction in clinical symptoms associated with ADHD in patients aged 4 - 16 years (59). According to reports from a study by Liu et al., the psychobiotic supplement Lactobacillus PS128 increased monoamine neurotransmitters (serotonin and dopamine) in the brains of mice with ADHD (60). Several years later, it was found that PS128 has therapeutic potential for behavioral disorders associated with ADHD in children with Tourette syndrome (61).
In this study (62), an investigation was conducted to understand the psychobiological effects of L. plantarum. As a result of this investigation, it was observed that L. plantarum plays a role in stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiome, reducing neuroinflammation through its effect on the HPA axis, and decreasing intestinal permeability. In another study aimed at examining the potential effects of probiotics on children with ADHD, L. rhamnosus GG (LGG) supplementation was used, which was associated with improvements in emotional and behavioral functions, resulting in an increased quality of life related to mental health in children with ADHD who were affected by probiotic supplements (63). However, additional research is required to assess the precise mechanisms of probiotic effects on gut microbiota and subsequently the brain-gut axis, involving more participants from different age groups. The summary of included studies are mentioned in (Table 1).
| Type of Disorder | Function | References | Type of Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| MDD | |||
| Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium | Lower the HPA axis alleviate chronic stress-induced changes in brain function and neurogenesis | (13) | Animal study |
| Lactobacillus plantarum 299v | Enhanced cognitive performance and reduced KYN levels | (14) | Human study |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 | Lower levels of depression and anxiety | (15) | Human study |
| Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175 | Decreased the flow of methyl groups, SAM in the liver, and decreased norepinephrine and dopamine in the plasma reduce activation of caspase-3, alleviate depressive-like symptoms, and decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines, CRP. | (17, 18) | Animal study |
| Bipolar disorder | |||
| Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BAMA-B06/BAu-B0111 | Improve glucose metabolism | (22) | Human study |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum, B. lactis, B. longum, and Lactobacillus acidophilus | Decrease the intensity of manic episodes and depression over time within the probiotic group | (23) | Human study |
| Schizophrenia | |||
| OEI | Elevate plasma butyrate levels, preserve the integrity of the gut-blood barrier and possesses significant anti-inflammatory properties. | (31) | Human study |
| Autism | |||
| VPA + Probiotic | Increased IL-10 levels, decreased 5-HT levels in the prefrontal cortex, lower Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio within the gut microbiota | (37) | Animal study |
| VISBIOME® | Potential health benefits and GI symptoms | (38) | Human study |
| Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 | Boost dopamine and serotonin levels, enhance intestinal motility, modulate the central nervous system, and alleviate the symptoms | (39, 40) | Animal study |
| ADHD | |||
| Bifidobacterium bifidum-688 | Improvement in the gut microbiome composition, an increase in Body Mass Index, and a reduction in clinical symptoms associated with ADHD | (59) | Human study |
| Lactobacillus PS128 | Increased serotonin and dopamine | (60) | Animal study |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | Improvements in emotional and behavioral functions, resulting in an increased quality of life related to mental health. | (63) | Human study |
Abbreviations: ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; MDD, major depressive disorder; OEI, oligofructose-enriched inulin; VA, valproic acid; HPA, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; KYN, kynurenine; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; CRP, C-reactive protein; IL-10, interleukin-10; 5-HT, serotonin; GI, gastrointestinal.
7. Conclusions
The growing body of evidence indicates a significant role for the gut microbiome in mental wellness, largely due to the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Millions of people live with mental health issues such as depression, schizophrenia, and autism. Currently, probiotic supplements have proven to be useful as complementary medicine to help restore gut balance and support gut health, creating pathways that may improve mood and general mental status. Clinical studies have acknowledged that probiotics can reduce symptoms of five mental disorders when taken alongside pharmacological drugs that affect the central nervous system. This alleviation of symptoms is possible through restoring microbial balance, reducing inflammation, modulating oxidative stress, enhancing antioxidant capacity, regulating neurotransmitter production, and improving gut barrier function.
In the case of MDD, supplementation with Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium significantly reduced depressive symptoms, improved mood, and decreased anxiety. In bipolar disorder, L. rhamnosus has been shown to stabilize mood variations and reduce depressive episodes. For schizophrenia, probiotics like B. longum improved GI health, leading to fewer digestive issues and enhanced well-being. Probiotic supplementation showed reduced GI symptoms and better social interactions, emphasizing the gut-brain connection in children with ASD. Finally, in ADHD, L. plantarum was associated with decreased hyperactivity and improved attention span.
While earlier studies left this explanation to speculation, recent evidence is providing a clearer picture of how gut health may contribute to the amelioration of mental illness. Probiotics could be integrated into a multimodal treatment approach, combining various treatments with pharmacological drugs, offering better management of these common disorders. Although certain probiotic strains have shown promising results in preclinical and some clinical studies, the specific microbial signatures and relationships underlying different mental illnesses remain unknown. Additionally, mental illnesses often present with diverse symptomatology, complicating the identification of specific microbiome-based biomarkers or therapeutic targets. Clinicians also face challenges in interpreting complex and sometimes contradictory findings into routine mental healthcare. The translation of research findings into clinical practice has been slow, so further studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms at play, allowing for a focused approach to developing probiotic therapies in mental health.