1. Background
Nowadays, sports psychology has become more popular than ever. Sports psychologists are working in more than 70 different countries, mostly in North America and Europe (1). During the last decade, there has been a great scientific effort in Latin America, Asia, and Africa in the field of sports psychology (2), and Iran country was not exempt from this development.
In Iran, until the last few years, those interested in sports psychology had to travel to other countries to be able to study in their desired field of study (3). But now, due to the efforts of the country's sports specialists, some domestic universities are accepting students in this field (4). This issue has caused a huge number of students to become interested in this field. Until recently, Iran suffered from a lack of sports psychology specialists, but fortunately, there are many graduates now (5). Nevertheless, these graduates can play an effective role in advancing the objectives of this field when they spend ample amount of time studying and researching and, have the characteristics of a good psychologist (6).
Personality traits are defined as a set of stable mental, emotional, behavioral and moral characteristics of the psychologists that makes them distinct from others, such as having an acceptable level of self-confidence, being good-tempered and friendly in relation to others, having common sense, emotional maturity and the ability to withstand mental pressure in critical situations, the ability of correct self-evaluation and problem solving and the ability to experience natural human emotions that play a very effective role in the successful and efficient psychological process (7).
In research believe that successful psychologists should have five characteristics of self-awareness, focus and calmness, sense of humor, honesty, and a non-judgmental attitude towards themselves and others before using basic skills in consulting process (8). Weslender & Wiggins' (9) research in the field of predicting the performance of consultants found that there is a positive and significant correlation between the personality traits and psychologists’ successful job performance. Sharp & Hodge (10) in a study reported that effective psychologists are able to demonstrate self-confidence to establish a professional relationship and respect for the client and knowledge in order to develop and maintain a strong, balanced and collaborative relationship that meets customer needs. Eriksen & Mc Auliffe (11) have shown that personality traits and moral development predict about 18% of the variance of psychologists' career success. Cooper’s research (12) results suggest that effective psychologists avoid lying and have a good sense of worthiness and competence and are more extroverted than other psychologists in terms of personality type.
In general, sports psychology is a newly-established discipline in Iran, and capable and effective graduates are needed to grow and expand this knowledge and use it in practice and the world of sports. Based on the investigations, the field of current research in Iran is new and no study has been conducted in this field so far. Therefore, the main question in this study is what are the characteristics of an effective sports psychologist?
Research that can provide the necessary prerequisites for training and education of specialists will undoubtedly help to improve the academic educational level. Basically, training of specialists is based on two main axes: One is what are the needs of the beneficiaries and the other is what are the characteristics of an effective expert, both of which will help in effective training. On one hand, there are sensitivities to the presence of psychologists in sports situations in Iranian society, and on the other hand, there are high expectations of sports psychologists regarding their effectiveness in solving athletes’ problems. The innovation of the current research compared to the previous research is that this research consists of the opinions of both sports consultants and athletes, which can cause a transformation in examining the views related to the characteristics of an effective sports psychologist. Both perspectives can help sport psychologists do their work and communicate more effectively with athletes.
Identifying characteristics of an effective sports psychologist is scientifically significant. Based on this, it is obvious that conducting such researches has a great scientific and practical necessity.
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
According to the project process, the statistical population of the research is domestic and foreign documents (Persian and English database), sources and reference books, a relatively limited number of prominent experts in sports psychology, athletes of the adult national teams in various sports fields, and sports psychologists active in sports teams.
In the first (qualitative) part, to conduct field interviews, the statistical population of the research includes consultants’ experts in sports psychology, who were purposefully selected for qualitative interviews in the research topic (n = 11 interviews). In the second (quantitative) part, after collecting information obtained from the qualitative section, a questionnaire was developed and distributed among the athletes of the adult national teams in various sports fields and sports psychologists working in sports teams. Given the number of the statistical population and its diversity, it was determined separately in each group. the total number of samples in this research section was N = 108 (n = 64: Athletes of adult national teams, n = 44: Sports psychologists).
2.2. Procedure
To identify the characteristics of an effective sports psychologist, a mixed research method has been used in this research. In the first stage, the qualitative method of content analysis was used to create the model; To test the model, correlation type based on structural equation model were used. The mixed research method is a sequential exploratory type, i.e., it was qualitative first and then quantitative., Exploratory research designs have been used in this study, because the researcher is trying to find the context of an uncertain situation under the title of identifying the characteristics of an effective sports psychologist. For this purpose, the researcher first identified the phenomenon and collected qualitative data through exploratory interviews, and then by developing a model and collecting quantitative data, has tested the extractive model of identifying the characteristics of an effective sports psychologist.
The data collection and analysis operation start from the first case and is repeated by selecting the next one. But the main question here is how far the selection of cases and examination of this process should continue. This process continues until the researcher realizes that the information obtained from the new samples has become repetitive, and no new information is obtained from the observations and interviews. This state is called "theoretical adequacy". Theoretical saturation occurs when: a) It seems that there is no relevant or new data related to that category; b) that category is well developed in terms of the features and dimensions that describe it; c) the relationship between the categories is well established and validated. In other words, the researcher continues to increase the sample size until the interviews become repetitive and no new data is obtained (13). In this research, this number included 12 people, 1 of them was conducted as an experiment, and finally the data of 11 interviews were analyzed.
The instruments used to collect information, in this research, were interviews and questionnaires; in the first part of the research, semi-structured interviews were used. In the process of interviewing the elites, conversations were recorded with the help of a tape recorder, and in the interview, the interviewees answered the 4 questions designed for this purpose. In the second part, the data obtained from the qualitative section included 10 values, in 53 questions.
2.3. Data Analysis
The data analysis in two sections of qualitative and quantitative data was performed. To study the procedures and interaction between individuals in the processes of identifying the characteristics of an effective sports psychologist, the interview has been used. After conducting the interview and recording the extracted data daily, a matrix of interview questions and the interviewee was formed and the data related to 8 interviewees were recorded and became the basis of the analysis. For this purpose, content analysis method was used.
3. Results
The sociodemographic variables of the athletes (N = 64; male n = 33, female n = 31) are presented in Table 1. The participants’ average age in this study was 25 years old (SD ± 3.46 years old). In summary, the athletes played in 1 of 7 sports: Volleyball (n = 9); basketball (n = 9); taekwondo (n = 8); wrestling (n = 4); handball (n = 11); ping pong (n = 12); running (n = 11).
| Sport | Volleyball | Basketball | Taekwondo | Wrestling | Handball | Pingpong | Running |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 6 |
| Female | 4 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 9 | 5 |
| Total | 9 | 9 | 8 | 4 | 11 | 12 | 11 |
To check the reliability, the composite reliability index was used, the results of which are brought in Table 2.
| Structure (Manual Variables) | Cronbach's Alpha | rho_A | Composite Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Counseling skills | 0.912 | 0.915 | 0.932 |
| Personality characteristics | 0.738 | 0.756 | 0.841 |
| Cognitive skills | 0.927 | 0.933 | 0.940 |
| Communication skills | 0.916 | 0.922 | 0.934 |
| Ethics | 0.972 | 0.974 | 0.974 |
| Sport knowledge | 0.785 | 0.714 | 0.825 |
According to the results of Table 3, the values higher than 0.7 for each construct indicate its appropriate reliability.
3.1. Internal Consistency Reliability
Factor loading of each indicator on the corresponding construct is reported in Table 3. Acceptable factor loading for each variable is 0.7.
| Number | Structure (Manual Variable) | AVE |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Counseling skills | 0.696 |
| 2 | Personality characteristics | 0.577 |
| 3 | Cognitive skills | 0.637 |
| 4 | Communication skills | 0.670 |
| 5 | Ethics | 0.616 |
| 6 | Psychological knowledge | 0.612 |
Based on Table 4, it can be observed that the constructs obtained have an average extracted variance (AVE) above 0.50.
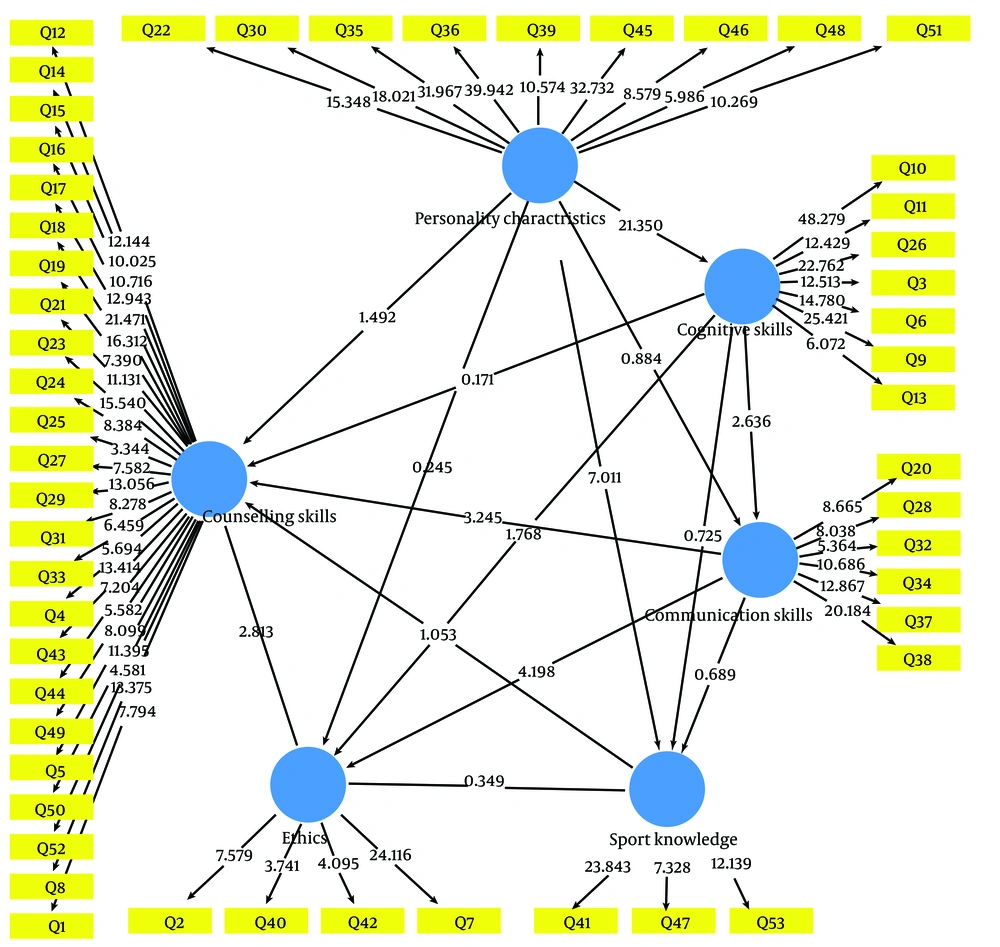
By using partial least squares structural equation modeling, the conceptual model of the research has been examined to check the relationships between the obtained variables, validity, reliability coefficients, and the model quality using the test results. The conceptual model is reported in (Figure 1).
According to the results of Table 4, it has been determined that the proposed research model has been able to explain at least 52% and at most 82% of the criteria variables by personality characteristics. Chin (1998) introduced the value of R2 as an index for model fit and introduced three values of 0.19, 0.33 and 0.67 as weak, medium, and strong values for the model fit.
| Criterion Variables | The Value of R2 | Adjusted R2 Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Communication skills | 0.524 | 0.510 |
| Ethics | 0.681 | 0.666 |
| Cognitive skills | 0.691 | 0.686 |
| Counseling skills | 0.817 | 0.803 |
| Sports knowledge | 0.630 | 0.608 |
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Based on the qualitative and quantitative research results, six categories of characteristics and capabilities were identified as the characteristics of a sports psychologist. These characteristics and abilities included consulting skills, personality traits, communication skills, cognitive skills, professional ethics, and sports knowledge.
Regarding consulting skills, it included respect and valuing the athlete, cheerfulness, openness and acceptance, having enough experience, education and knowledge of psychology, leadership and management power, high self-confidence and self-belief, empathy, having attitude and view without judgment and prejudice, possessing new and updated specialized knowledge, appropriate appearance and physical condition, having self-assessment, being lively and cheerful, appropriate mental and emotional stability, having appropriate professional skills, the ability to create a good and effective communication with the athlete, high communication and social skills, responsibility, having sufficient self-confidence and self-esteem, awareness of environmental conditions, sense of humor and having behavioral and moral stability (14).
According to the results of this research, both sports consultants and athletes emphasized that characteristics and abilities included consulting skills, personality traits, communication skills, cognitive skills, professional ethics, factors have a significant impact on the characteristics of a good psychologist. But in the variable sports knowledge the athletes emphasized this factor more and believed that an effective sports psychologist should have the necessary sports knowledge in that field.
In all cases, both sports counselors and athletes stated that an effective sports psychologist must have a series of distinct personal and professional characteristics, which are acceptable and lovable and can be helpful in practice. They are flexible and consider the needs of each person completely individually. They are accessible and interactive. They don't give up on problems suddenly and they continue to solve the problem. Counseling sessions are considered based on the range of problems and do not set a specific time limit.
Regarding the personality traits, having behavioral objectivity and pragmatism, being original, being noble and rooted, having a dynamic and active mind and not being stagnant, being aware and sensitive to the cultural and ethnic backgrounds of athletes, having foresight and appropriate forecasting, good-natured and good-mannered, and openness to experience are taken into consideration.
In relation to cognitive skills, capabilities such as optimism and realism, the power of thinking and high initiative, behavioral transparency, creativity and resourcefulness, conscientiousness and fairness were identified. Communication skills included features such as accessibility and ease of communication, having a mutual understanding of the problems and conditions of athletes, warmth and appropriate acceptance, high mental health and personality, the ability to create an effective consulting relationship, privacy and confidentiality, high emotional and social intelligence, having the capacity to bear mental pressure and problems, the ability to solve conflicts and problems and have sufficient knowledge of them, keeping calm, high self-awareness and self-knowledge, and a high sense of worthiness and self-efficacy (15).
Findings of the current study are consistent with some features obtained from foreign researches regarding the effective and efficient psychologist characteristics. For example, Boards and Brown described the characteristics of a good psychologist as a strong love and interest in learning, showing compassion and empathy, having strong communication skills, the art of deep listening, adhering to the beliefs and values of society, and Confidentiality and secrecy (16). Corsini and Gross (1991) believe that successful psychologists should have five characteristics of self-awareness, concentration and calmness, sense of humor, honesty, and a non-judgmental attitude towards themselves and others before applying basic skills in consulting process (17).
The athletes emphasized that if the sports psychologist has the necessary sports knowledge, he can be effective in critical times. Basically, it is better to have more practical courses and training sessions in the process of training a sports psychologist and reduce the number of theoretical explanations. Teaching techniques must be experienced so that this new field becomes stronger.
Also, the demographic characteristics of the consultant, such as the consultant's appearance and physical condition, marital status, religion, nationality, age, gender, professional experience, and educational field, can play an effective role in guiding the successful consulting process (18).
Personality traits are defined as a set of stable mental, emotional, behavioral and moral characteristics of each psychologist that differentiates him/her from others, such as having an acceptable level of self-confidence, being good-natured and friendly in relation to others, having common sense, emotional maturity and the ability to withstand psychological pressure in critical situations, the ability to correctly assess oneself and solve problems, and the ability to experience natural human emotions that play a very effective role in the successful and efficient psychological process (19).
Some domestic researches have pointed out some of the obstacles in the training sports psychologists and their professional activities. Poucher et al. suggested the lack of knowledge and sports experience of psychologists, lack of athletes’ awareness about psychology, and lack of transparency in sports psychology services as the most important obstacles for psychologists to enter sports teams, respectively (20). In the study of Williams et al., lack of sports psychologist's sufficient sports experience, athletes' lack of knowledge about sports psychology, and lack of transparency in the service of consultants and their ineffectiveness were stated as the most important obstacles for making sports psychology more practical (21).
In general, sports psychology is newly-established field in our country, and there is a need for capable and effective graduates to grow and expand this knowledge and use it in practice and the world of sports. Sports psychologists have become one of the fundamental parts of professional sports and have become more important in the last few years, while the use of psychologists in sports teams has become an undeniable necessity (such as coaches, supervisors, etc.), there are still few teams in Iran that apply psychologists. An issue that, according to many experts, has not been without influence in some of the recent failures of Iranian athletes, whether in the continental arena, the world, or the Olympics.
In sum, the findings of the current study indicated that an effective sports psychologist must have various characteristics and skills in the aspects of personality, cognitive, consulting, communication, professional ethics, and sports knowledge. Meanwhile, the role of personality traits, cognitive skills and communication skills has been more prominent than consulting skills, professional ethics, and sports knowledge. Most of the characteristics discovered were related to the area of consulting skills. Most of the characteristics and abilities identified have a great affinity with the existing research literature and are evidence of the scientific significance of the results of this research.