1. Context
Chronic diseases are among the greatest health challenges of the 21st century, significantly impacting individual health and healthcare systems due to their long duration and associated complications (1). One of the most prevalent chronic diseases globally is chronic kidney disease (CKD), which, in its advanced stages, progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requiring alternative treatments such as hemodialysis (HD) (2, 3). Although HD is a life-sustaining therapy, it is associated with multiple complications, including cardiovascular disorders, malnutrition, sleep disturbances, and hormonal imbalances (4). Beyond physical health concerns, these complications negatively affect mental health, daily functioning, and overall quality of life, leading to anxiety, depression, and social limitations in affected patients (5). Furthermore, the complexity of HD management places a significant burden on healthcare systems, necessitating strategies to enhance patient autonomy and treatment adherence (6).
One of the most effective strategies to empower patients, enhance disease control, and reduce healthcare dependency is self-management (SM) (7). However, SM is a multidimensional and evolving concept, making it difficult to establish a single, universally accepted definition. According to Lorig and Holman (2004), SM is “an individual’s ability to manage symptoms, treatment, physical and psychosocial consequences, and lifestyle changes inherent in living with a chronic condition” (8). Barlow et al. (2002) define it as “the patient’s ability to manage the symptoms, treatment, physical and psychological consequences, and lifestyle modifications necessary to maintain quality of life” (9). Schulman-Green et al. (2012) describe SM as “a dynamic, daily decision-making process that includes the skills needed to manage an illness and its treatment” (10).
Despite these definitions, there is no consensus on the exact scope of SM, particularly in HD patients, where treatment-related constraints and psychosocial challenges demand a more tailored conceptualization. Among HD patients, SM takes on a distinct meaning due to the physical, psychological, and lifestyle constraints imposed by treatment, requiring a context-specific approach to its understanding (11). While many definitions focus primarily on medical aspects, such as treatment adherence and symptom monitoring, other dimensions — such as behavioral, emotional, and social aspects — are often overlooked (12-14). This lack of conceptual clarity poses challenges in designing effective educational programs and SM interventions, as the absence of a precise definition makes it difficult to establish standardized guidelines for clinical practice (15).
Walker and Avant emphasize that concept selection should be both significant and inadequately defined, necessitating further exploration (16). Self-management in HD patients meets this criterion as it is crucial for improving treatment adherence, reducing complications, lowering healthcare costs, and ultimately enhancing survival and quality of life (17, 18). Despite its importance, existing literature lacks a comprehensive definition of SM specific to HD patients, leaving some dimensions unclear or insufficiently explored (19-21). Moreover, many studies have primarily examined the therapeutic and medical aspects of SM, with limited focus on psychosocial, emotional, and lifestyle-related components (11).
Given this conceptual ambiguity and the critical role of SM in HD care, this study aims to analyze and clarify the concept, providing an empirically grounded and comprehensive definition. Such an analysis will contribute to a better understanding of SM, facilitate the development of more effective patient education programs, and support the design of holistic interventions tailored to enhance SM behaviors and improve health outcomes in this population.
2. Evidence Acquisition
This concept analysis study was conducted in Tehran in 2024 to clarify the concept of SM in HD patients using Walker and Avant’s eight-step method. These steps include selecting the concept, determining the aim, identifying all uses, defining attributes, constructing model cases, analyzing additional cases, identifying antecedents and consequences, and specifying empirical referents (16, 22). This structured approach ensured a comprehensive understanding of SM in clinical nursing practice.
2.1. Design
A concept analysis design was employed for its systematic methodology in clarifying complex healthcare concepts (16). Walker and Avant’s framework facilitated an in-depth exploration of SM, identifying key attributes, antecedents, and consequences essential to its application in HD care. This approach is particularly valuable in nursing research as it ensures a rigorous examination of abstract concepts, enhancing their relevance to clinical practice.
2.2. Literature Review
A systematic literature search was conducted in major databases, including PubMed, Scopus, Embase, MEDLINE, ProQuest, CINAHL, and the Iranian Scientific Information Database (SID). Additionally, Google Scholar and relevant library resources were used to identify supplementary studies. The search included all available publications up to November 2024, with no time restrictions. Keywords such as SM, HD, and ESRD were combined using Boolean operators (AND, OR) and truncation (*) to refine results. Filters were applied to include only peer-reviewed journal articles and scholarly books relevant to the study’s objectives (Table 1).
| Databases | Syntax | Publication Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | ("Self-Management"[MeSH Terms] OR "Self-Management"[Title/Abstract]) AND ("hemodialysis"[Title/Abstract] OR ("Renal Dialysis"[MeSH Terms] OR "Dialysis"[MeSH Terms]) OR "Renal Dialysis"[Title/Abstract]) | 237 |
| Embase | ('hemodialysis'/exp OR 'blood dialysis' OR 'dialysis center' OR 'dialysis, blood' OR 'extracorporeal blood cleansing' OR 'extracorporeal dialysis' OR 'haemodialysis' OR 'haemodialysis center' OR 'haemodialysis centre' OR 'haemodialysis department' OR 'haemodialysis unit' OR 'haemodialysis units, hospital' OR 'hemodialyse' OR 'hemodialysis' OR 'hemodialysis center' OR 'hemodialysis department' OR 'hemodialysis unit' OR 'hemodialysis units, hospital' OR 'hemorenodialysis' OR 'hemotrialysate' OR 'hospital haemodialysis units' OR 'hospital hemodialysis units' OR 'renal dialysis') AND ('self care'/exp OR 'self care' OR 'self management' OR 'self treatment' OR 'self-management' OR 'self-nurturance' OR 'selfcare' OR 'selfmanagement' OR 'selftreatment') | 1431 |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY ["Self-Management" AND ("hemodialysis" OR "Renal Dialysis" OR "Dialysis" )] | 492 |
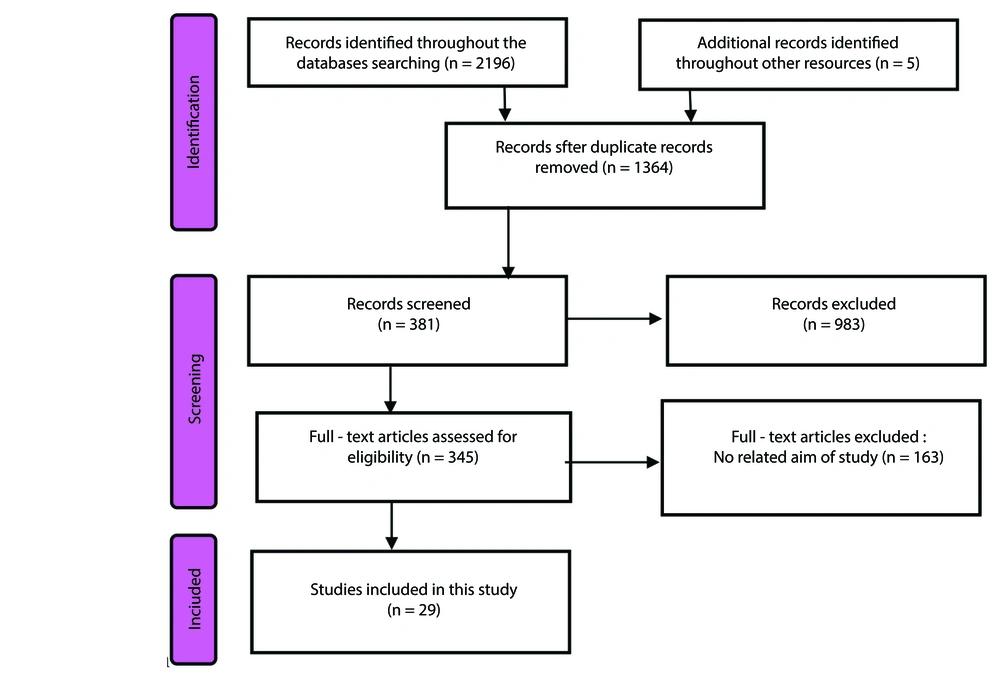
The article selection process, illustrated in Figure 1, followed a structured methodology. Initially, 343 articles, two books, and two theses were identified. Duplicate records were removed using EndNote X20. The remaining articles were independently screened by four reviewers (LRV, NR, FMSH, KNT). Titles and abstracts were reviewed to exclude irrelevant studies, followed by full-text assessments of eligible articles. Inclusion criteria were limited to peer-reviewed studies published in English or Persian focusing on SM in adult HD patients. Studies on other chronic conditions, pediatric populations, or unrelated topics were excluded. Disagreements between reviewers were resolved through discussion, and if consensus was not reached, a senior researcher (NA) mediated the decision. Ultimately, 29 articles and one book were selected for in-depth analysis.
2.3. Data Analysis and Synthesis
Data extraction and analysis were conducted independently by LRV and NR using a standardized extraction form to ensure consistency. This form included sections for study characteristics, definitions of SM, key attributes, antecedents, and consequences. An inductive content analysis approach was employed, systematically coding and categorizing extracted data to identify recurring themes. The defining attributes of SM were determined by analyzing conceptual descriptions across the selected studies.
Model cases were developed based on the literature to illustrate core characteristics, while additional cases (borderline, related, and contrary) were examined to distinguish SM from similar concepts. Antecedents and consequences were identified by analyzing contributing factors and outcomes associated with SM in HD patients. Finally, empirical referents were established to provide measurable indicators of SM in clinical practice.
3. Results
3.1. Identifying All Uses of the Concept
To explore the concept of SM in HD patients, we conducted a comprehensive review of literature, dictionaries, nursing thesauruses, and interdisciplinary sources. The term "self-management in HD patients" lacks a precise and universally accepted definition. As a result, we examined existing definitions of "self-management in chronic patients" and "self-management" more broadly.
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, SM refers to the ability to control and organize one’s work, health, or behavior (23). Merriam-Webster’s Dictionary defines SM as "the ability to control and organize one’s own affairs, especially one’s own health or well-being" (24). Historically, the concept of SM has evolved over time. Hartweg (1991) first introduced the concept of self-care, which included three dimensions: Co-occurring needs, growth and development, and deviation from health (25). Creer (2000), building on Bandura’s self-efficacy theory, applied this concept to chronic disease management, emphasizing the active participation of patients in their care (12, 26, 27). Later, Corbin and Strauss (1988) categorized SM behaviors in chronic disease into three primary domains: Medical service management, behavioral management, and emotional management (28).
Although self-care and SM are closely related, they are not interchangeable (29). Self-care refers to general actions taken to maintain health, while SM specifically applies to individuals managing a chronic illness or deviation from health. Self-management involves active engagement in symptom monitoring, treatment adherence, and emotional coping strategies to improve quality of life (8, 29). In the nursing literature, SM overlaps with related concepts such as self-regulation, self-monitoring, and therapeutic adherence. Richard and Shea (2011) define self-care as "actions taken to promote physical, mental, and emotional health", self-regulation as "the ability to control and adjust one’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors", and self-monitoring as "the continuous observation and evaluation of one’s own health condition" (30).
Currently, there is no single definition of SM specific to HD patients. However, it is generally understood as the active participation and responsibility that patients assume in managing their health, care, and treatment (31). The concept is shaped by cultural, social, and healthcare system factors and varies across populations (32, 33). Curtin et al. (2004) conducted a foundational study in the United States, identifying key components of SM in HD patients, including communication with healthcare providers, maintaining self-care during dialysis, seeking information, symptom management, self-confidence, and shared responsibility (21). Welch et al. (2015) expanded on this, emphasizing fluid retention monitoring, medication adherence, and dietary modifications as critical SM behaviors (34). Beyond medical management, Corbin and Strauss’ (1988) three-category model highlights the importance of behavioral and emotional SM in chronic illness (28). Expanding on this, Curtin et al. (2005) classified SM into two categories: Self-management of healthcare — focusing on adherence to medical recommendations, and SM of daily life — emphasizing the patient’s ability to maintain social and occupational roles despite their illness (35). Ultimately, SM is an interaction-driven process, requiring collaboration between patients, caregivers, and medical professionals (31).
3.2. Determination the Identifying Attributes of the Concept
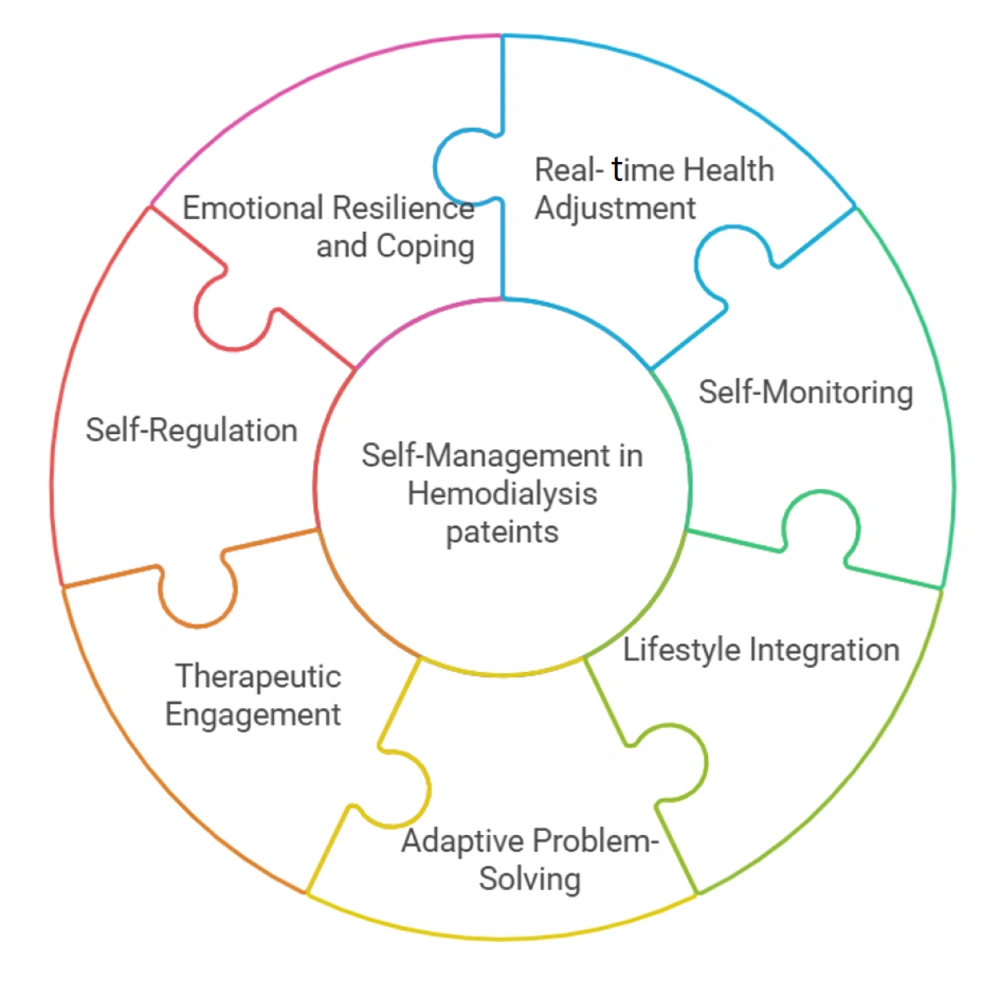
Self-management in HD patients is a proactive, dynamic, and interactive process that involves cognitive, behavioral, and emotional strategies to optimize health outcomes. Based on a comprehensive literature review, seven key attributes have been identified, each playing a crucial role in promoting SM behaviors and improving the quality of life for HD patients (Figure 2).
3.2.1. Real-time Health Adjustment
The ability to promptly recognize and respond to changes in health status is crucial for preventing complications (36). Hemodialysis patients must constantly adjust fluid intake, diet, and medications based on real-time changes in blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and other vital signs (37, 38).
3.2.2. Self-Monitoring
The continuous tracking of health parameters (e.g., weight, blood pressure, dietary intake) is essential for early detection of trends and complications (39). Self-monitoring enables patients to maintain awareness of their condition, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions about their SM practices (7, 34, 40).
3.2.3. Lifestyle Integration
The ability to embed SM behaviors into daily life while maintaining personal, social, and professional commitments is crucial (41). Long-term disease management requires patients to adjust their routines without disrupting their overall quality of life (8, 42-44).
3.2.4. Adaptive Problem-Solving
The ability to identify challenges in SM and develop flexible, effective solutions to overcome them is essential (45). Hemodialysis patients encounter dietary restrictions, medication adherence issues, and treatment-related side effects. Adaptive problem-solving enables them to create strategies — such as meal planning, using medication reminders, or adjusting daily activities — to maintain adherence (46, 47).
3.2.5. Therapeutic Engagement
The active participation of patients in their treatment through collaboration with healthcare providers and adherence to medical recommendations is vital (48). Patients who engage in their care — by asking questions, following treatment plans, and making informed decisions — experience better adherence, fewer complications, and improved health outcomes (21, 31, 49).
3.2.6. Self-Regulation
The ability to control, direct, and adjust one's own behaviors, emotions, and decision-making to adhere to treatment plans is crucial (50). Self-regulation includes setting goals, maintaining self-discipline, and making ongoing adjustments to maintain treatment adherence (26, 51, 52).
3.2.7. Emotional Resilience and Coping
The capacity to manage emotional stress, maintain motivation, and utilize coping strategies to navigate the psychological challenges of chronic illness is essential (53). Emotional resilience is crucial for handling the long-term psychological burden of HD, reducing stress, and preventing burnout. Coping strategies — such as cognitive reframing, stress management techniques, and social support — enhance mental well-being and contribute to long-term SM success (46, 54).
3.3. Identifying Model Cases
A 58-year-old man has been on HD for three years. He actively monitors his blood pressure, fluid intake, and weight daily (self-monitoring). When he notices a slight increase in weight between dialysis sessions, he immediately adjusts his fluid intake to prevent overload (real-time health adjustment). He has incorporated his dietary restrictions into his daily life, meal-prepping and ensuring that his food choices align with medical recommendations (lifestyle integration). Despite facing occasional dietary challenges, Mr. J finds creative solutions, such as using salt-free spices to maintain flavor without exceeding sodium limits (adaptive problem-solving). He engages in discussions with his healthcare team, asking questions about his lab results and collaborating on medication adjustments (therapeutic engagement). When he struggles with motivation, he sets small, achievable health goals and follows structured reminders to stay on track (self-regulation). Although he sometimes feels frustrated, he copes by practicing mindfulness and seeking support from a patient community, which helps him maintain a positive outlook (emotional resilience & coping).
3.4. Examining Additional Cases
3.4.1. Contrary Case
A 62-year-old HD patient, does not track her weight, blood pressure, or dietary intake, believing that the medical team is solely responsible for her care (lack of self-monitoring). When her legs begin to swell, she does not take any action and continues to drink excessive amounts of fluids, leading to severe fluid overload (lack of real-time health adjustment). She makes no effort to adjust her lifestyle, frequently eating high-sodium fast food and skipping dialysis appointments due to inconvenience (lack of lifestyle integration). When faced with difficulties, such as experiencing fatigue, she simply gives up rather than seeking solutions (lack of adaptive problem-solving). She avoids discussions with her healthcare providers and does not follow their recommendations (lack of therapeutic engagement). Without a structured approach, she frequently forgets to take her medications and misses dialysis sessions (lack of self-regulation). She becomes frustrated easily, expressing anger toward her situation but refusing emotional support or counseling (lack of emotional resilience & coping).
3.4.2. Borderline Case
A 54-year-old HD patient, checks her weight daily and monitors her blood pressure (self-monitoring). However, when she notices an increase in weight, she does not make any adjustments to her fluid intake, assuming that one dialysis session will correct it (lack of real-time health adjustment). She follows a low-potassium diet at home but frequently eats out without considering dietary restrictions (partial lifestyle integration). When faced with dietary challenges, she sometimes tries to find lower-sodium options but often gives up and eats whatever is available (inconsistent adaptive problem-solving). She attends all her dialysis sessions but rarely asks her doctor questions or participates in treatment decisions (lack of therapeutic engagement). She attempts to follow a routine but struggles with consistency in taking her medications on time (weak self-regulation). She often feels anxious about her condition and isolates herself rather than seeking emotional support (lack of emotional resilience & coping).
3.4.3. Related Cases
A 60-year-old patient, is highly engaged with his medical care. However, instead of making self-directed decisions about his diet, fluid intake, and medication, he relies entirely on his healthcare team to dictate his behavior. His nurse schedules all of his appointments, manages his diet plan, and reminds him to take his medications. While he follows every medical recommendation precisely, he does not independently monitor his health or make proactive adjustments.
3.5. Identifying Antecedents and Consequences
3.5.1. Antecedents
The antecedents of SM in HD patients can be classified into patient-related, cognitive-emotional, and healthcare-related factors.
- Patient-related antecedents include a minimum level of physical and cognitive stability, as severe impairments may prevent effective SM. Additionally, disease awareness and health literacy are essential, enabling patients to understand HD principles, recognize complications, and apply medical information regarding medication, diet, and symptom management (55, 56).
- Cognitive-emotional antecedents such as motivation, personal responsibility, and self-efficacy are crucial, as patients must be willing to manage their condition and believe in their ability to perform self-care tasks. Furthermore, emotional readiness and coping capacity are necessary for accepting the chronic nature of the disease and developing adaptive strategies (41, 54).
- Healthcare-related antecedents include structured patient education, clear communication from healthcare providers, and a gradual transition from provider-led care to patient-driven SM, ensuring patients acquire the necessary skills before full autonomy (49, 57) (Table 2).
| Attributes | 1. Real-time Health Adjustment, 2. Self-Monitoring, 3. Lifestyle Integration, 4. Adaptive Problem-Solving, 5. Therapeutic Engagement, 6. Self-Regulation, 7. Emotional Resilience and Coping |
|---|---|
| Antecedent | |
| Patient-related factors | Physical and mental stability: A patient must possess a minimum level of physical health and cognitive function to engage in SM effectively. Severe cognitive impairment or extreme physical frailty would prevent the initiation of self-care behaviors; understanding of the disease: Basic knowledge of HD, its complications, and treatment regimen is a fundamental prerequisite for patients to take responsibility for their care; health literacy: Patients must have the ability to process and apply medical information related to their condition, including medication management, dietary restrictions, and symptom recognition; motivation and personal responsibility: Patients must have an intrinsic willingness to manage their condition, which includes a sense of accountability for their health outcomes; self-efficacy: If a patient does not believe they can effectively perform SM tasks, adherence is unlikely. A strong sense of self-efficacy is therefore a fundamental prerequisite for engaging in self-care activities; emotional readiness and coping capacity: The ability to emotionally accept the chronic nature of the disease and develop adaptive coping strategies is a necessary precondition for initiating SM. |
| Healthcare system-related factors | Adequate patient education: Structured education on dialysis procedures, dietary management, and complication prevention must occur before a patient can successfully engage in SM; clear communication from healthcare providers: Patients require accurate, understandable, and ongoing information from their medical team to build confidence in their ability to self-manage; structured transition from dependence to autonomy: The healthcare system must facilitate a gradual shift from provider-led care to patient-driven SM, ensuring that the necessary skills are developed before full autonomy is expected. |
| Consequence | |
| Patient-related factors | Improved quality of Life: Improved management of the disease leads to an improved quality of life and a healthier, more active lifestyle, which increases overall satisfaction; reduced complications: Reduced complications as a result of effective SM; enhanced psychological well-being: A reduction in psychological distress (lower levels of stress and anxiety); Hospitalization and mortality reduction: A decrease in hospitalizations and a reduction in mortality; Increased treatment compliance: Improvement in compliance with treatment regimens, dietary and fluid restrictions, medications, and dialysis schedules. |
| Family and social support-related factors | Reduced caregiver burden: Reduced family members' stress and workload; Strengthened family support: The dynamics and support systems of the family have been improved; positive feedback loop: A supportive environment is created by encouraging participation and acknowledging efforts; positive family dynamics: Improved relationships within the family due to a reduction in stress and tension; reduced emotional burden: Reduced stress and worry for family members and caregivers; Reduced financial burden: Loss of income and increased healthcare costs; stronger social support networks: Increased support from friends and family members |
| Healthcare system-related factors | Optimized resource utilization: Reduction in the frequency of hospital visits and interventions; positive clinical outcomes: Improved health outcomes as a result of improved management of ESRD; Reduced healthcare costs: Increased utilization of healthcare resources, such as medications, dialysis, and transplants |
3.5.2. Consequences
The consequences of SM in HD patients can be categorized into patient-related, family and community-related, and healthcare system-related outcomes.
- Patient-related outcomes: Effective SM enhances quality of life, reduces complications, decreases hospitalization rates, and lowers mortality.
- Family and community-related outcomes: It alleviates caregiver burden, strengthens family support, fosters a positive feedback cycle, improves family dynamics, and reduces both financial and emotional strain. Additionally, it promotes the development of stronger social support networks.
- Healthcare system-related outcomes: Self-management optimizes resource utilization, minimizes unnecessary hospital visits, and facilitates the implementation of targeted interventions, ultimately reducing overall healthcare costs (21, 35, 58, 59) (Table 2).
3.6. Determining Empirical Referents
A review of existing instruments identified two primary SM tools for HD patients: The Curtin et al. (2004) SM Tool (21) and the Self-Management Questionnaire for Hemodialysis Patients (21). While the Curtin et al. tool assesses self-care during dialysis, symptom management, and shared responsibility, it focuses mainly on in-clinic behaviors and lacks measures for daily self-monitoring, real-time health adjustments, and lifestyle integration (21). Similarly, Song’s questionnaire categorizes SM into problem-solving, emotional management, self-care, and participation but does not clearly distinguish therapeutic engagement from self-regulation or account for real-time adjustments necessary to prevent complications (60). Both tools primarily reflect general chronic disease SM rather than the unique, multidimensional nature of SM in HD patients. The absence of a comprehensive, validated instrument that integrates real-time health adjustment, lifestyle adaptation, self-regulation, and emotional resilience highlights the need for refined tools that accurately measure all seven defining attributes.
3.7. Empirical Definition
Self-management in HD patients is a proactive and multidimensional process that involves continuous self-monitoring, real-time health adjustments, and lifestyle integration to maintain treatment adherence and prevent complications. It requires adaptive problem-solving to overcome challenges, therapeutic engagement to collaborate with healthcare providers, self-regulation to sustain behavioral discipline, and emotional resilience to manage the psychological burden of chronic illness. Rather than merely following medical instructions, SM is a dynamic, patient-driven approach that integrates cognitive, behavioral, and emotional strategies to enhance autonomy, optimize clinical outcomes, and improve quality of life.
4. Discussion
This study provides a comprehensive framework for understanding SM in HD patients, identifying seven key attributes: Real-time health adjustment, self-monitoring, lifestyle integration, adaptive problem-solving, therapeutic engagement, self-regulation, and emotional resilience and coping. These findings refine previous definitions by emphasizing SM as a dynamic, multidimensional process that integrates cognitive, behavioral, and emotional strategies to enhance treatment adherence and quality of life. Previous studies have provided narrow definitions of SM, often emphasizing medication adherence, symptom monitoring, or patient education, without capturing its interactive and patient-driven nature (21, 61, 62). For example, the Curtin et al. self-management tool primarily assesses in-clinic behaviors but does not address real-time health adjustments or lifestyle integration (21, 61, 62). Similarly, Song’s Questionnaire categorizes SM into problem-solving, emotional management, self-care, and participation but lacks a clear distinction between therapeutic engagement and self-regulation (61, 62).
This study expands the understanding of SM by recognizing it as a continuous, interactive process requiring real-time adjustments, proactive decision-making, and psychosocial adaptation to optimize patient autonomy and treatment adherence. The ability to recognize and respond to health fluctuations is crucial for preventing complications in HD patients. Prior research supports this, emphasizing continuous symptom tracking, fluid management, and real-time decision-making as fundamental to SM (10, 63). However, existing SM tools largely fail to measure real-time health adjustments (64). Our study highlights the importance of integrating digital health tools, such as real-time potassium monitoring devices, which have shown promise in improving treatment outcomes and reducing hospitalizations (31).
Effective SM depends on patient engagement in tracking diet, fluid intake, and medication adherence. Research indicates that structured self-monitoring interventions enhance treatment compliance and clinical outcomes (10). While previous studies focus on traditional self-monitoring methods, our findings emphasize the growing role of digital health applications in providing real-time feedback and facilitating early intervention (63). Expanding access to remote monitoring systems may further optimize self-monitoring effectiveness in HD patients (65).
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle is one of the greatest challenges for HD patients, as treatment schedules disrupt work, social life, and daily routines (66). While some studies suggest peritoneal dialysis offers greater lifestyle flexibility, both HD and peritoneal dialysis patients experience declining quality of life over time (11). Our study underscores the need for flexible care models that enable better lifestyle integration, such as home-based dialysis options and enhanced scheduling accommodations (67).
The ability to overcome treatment barriers is critical for successful SM. Previous research identifies knowledge, self-efficacy, and family support as key factors influencing problem-solving capacity in HD patients (68). While existing studies often focus on educational interventions, our study highlights the need for problem-solving strategies tailored to individual challenges — such as meal planning for dietary restrictions, medication adherence strategies, and symptom management techniques (69).
Active collaboration with healthcare providers is essential for effective SM. Studies have demonstrated that patient-centered medical home models improve care coordination and access to primary care for HD patients (63). However, gaps remain in implementing shared decision-making approaches. Our findings emphasize that strengthening therapeutic engagement through structured patient-provider communication and personalized coaching can improve adherence and reduce complications (67).
Long-term treatment adherence requires self-discipline and behavioral control. Research has shown that self-efficacy is strongly correlated with SM behaviors, including patient partnership, problem-solving, and emotional management (10). While prior studies emphasize motivational interventions, our study highlights the need for ongoing behavioral reinforcement, integrating goal-setting techniques, habit formation strategies, and digital reminders to sustain self-regulation over time (70).
Managing the psychological burden of chronic illness is fundamental to long-term SM success. Depression is a strong predictor of poor SM behaviors, negatively impacting motivation, adherence, and overall health outcomes (11). While existing studies focus on individual coping strategies, our findings emphasize the importance of integrating mental health support, stress management techniques, and peer support networks into routine HD care to enhance emotional resilience (70).
This study’s strength lies in its systematic and rigorous concept analysis, offering a novel, multidimensional perspective on SM in HD patients. By identifying seven defining attributes, it provides a comprehensive and adaptable framework that enhances understanding and informs patient-centered care. However, its reliance on existing literature rather than direct patient experiences may limit real-world applicability. Additionally, the absence of a validated assessment tool incorporating all attributes hinders standardized evaluation, and constraints in full-text access restrict the depth of analysis.
4.1. Conclusions
Self-management in HD patients is a multidimensional process encompassing real-time health adjustment, self-monitoring, lifestyle integration, adaptive problem-solving, therapeutic engagement, self-regulation, and emotional resilience. Effective SM requires a patient-centered approach that prioritizes education, empowerment, and robust support systems. A collaborative, multidisciplinary strategy involving healthcare providers, family, and peers is crucial to reinforcing these attributes. Future research should aim to strengthen patient empowerment, refine assessment tools, and foster supportive healthcare environments to enhance clinical outcomes, quality of life, and healthcare efficiency.