1. Introduction
Incidence of congenital coronary anomalies in general population is about 0.3% - 0.9% (1). Anomalous origin of the right coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ARCAPA) is a very rare and potentially fatal. It has a very wide spectrum of clinical courses, ranging from incidental finding in asymptomatic patients and chronic ischemia presenting with chest pain or dyspnea and sudden death. Transthoracic echocardiogram can guide us in the first step and final diagnosis is confirmed on a conventional coronary angiogram or coronary CT angiography.
2. Case Presentation
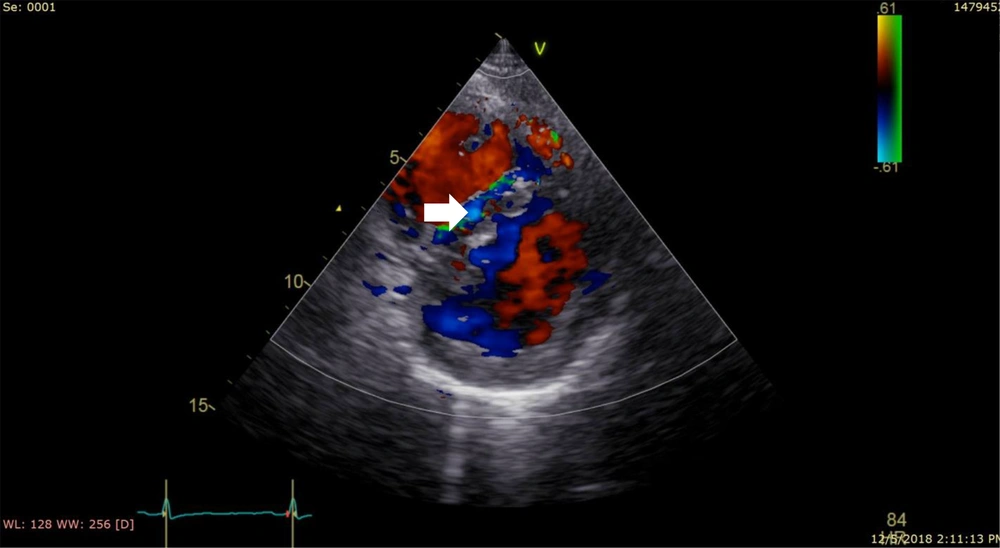
A 26-year-old woman presented to cardiology clinic complaining about dizziness and exertional and chest discomfort for several months. Electrocardiogram revealed T inversion in inferior leads, heart examination revealed a 3/6 grade systolic murmur in upper left sternal border. An echocardiogram revealed normal biventricular contractility and abnormal turbulent flow in the interventricular septum, which raised the suspicious of a coronary fistula (Figure 1). She was referred to cardiology center for further evaluation.
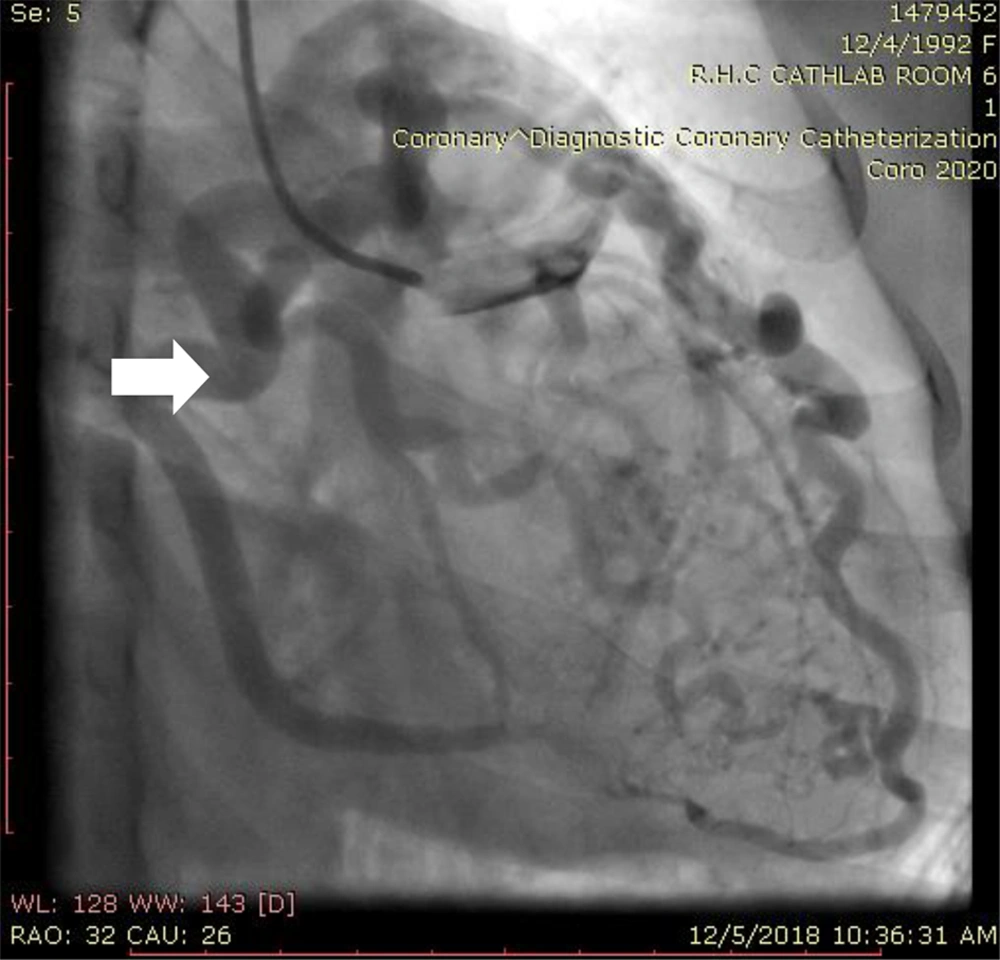
In our center, selective coronary angiography and right heart catheterization revealed normal origin of left main with very tortuous dilated LAD and normal LCX. Retrograde filling of the tortuous dilated right coronary artery from collateral vessels and drained to pulmonary artery (Figure 2). In aortic root injection RCA, origin was not visualized. Right heart catheterization and pressure study revealed normal PA pressure and no significant shunt.
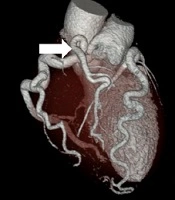
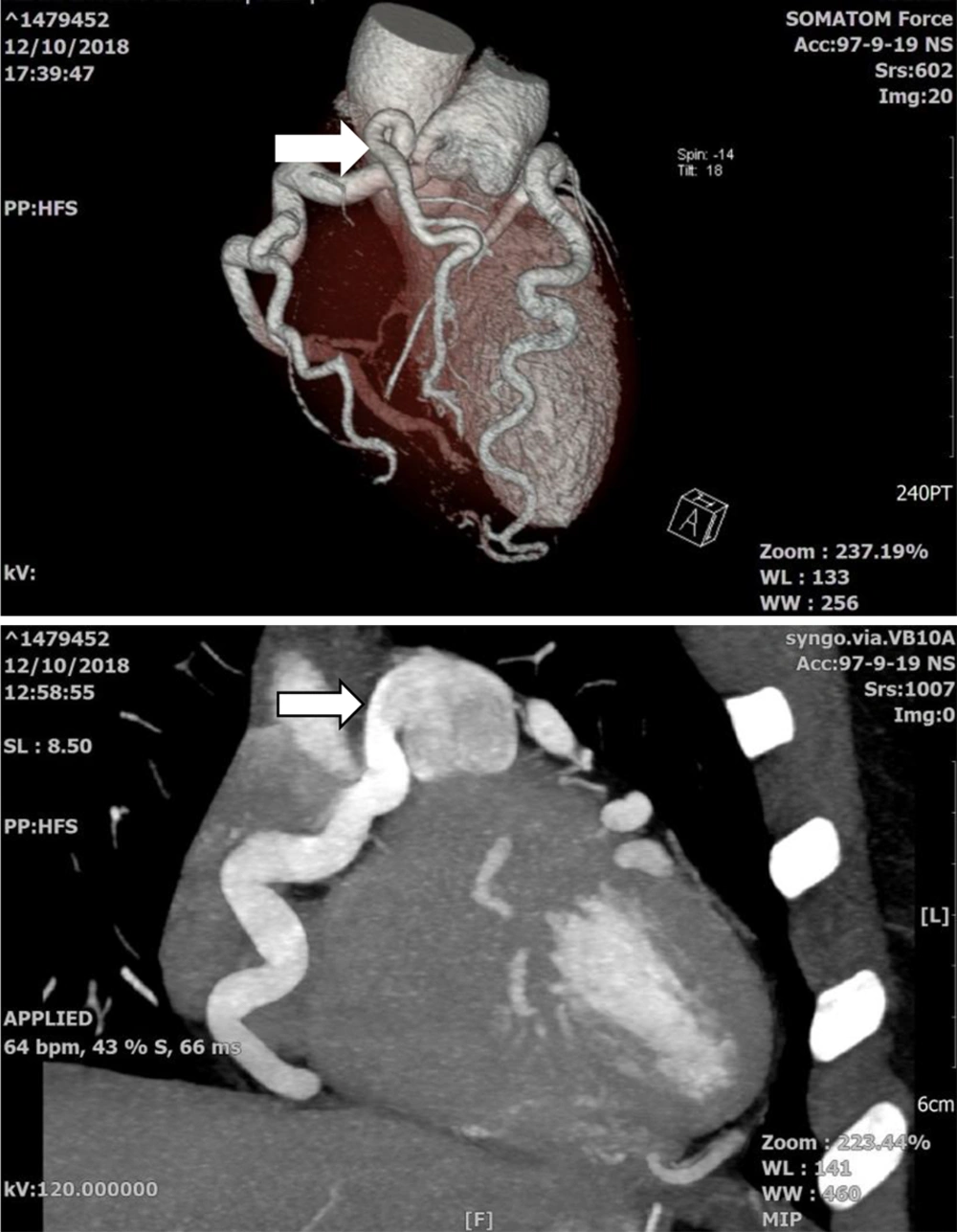
In the next step, coronary CT angiography confirmed our prior findings (Figure 3).
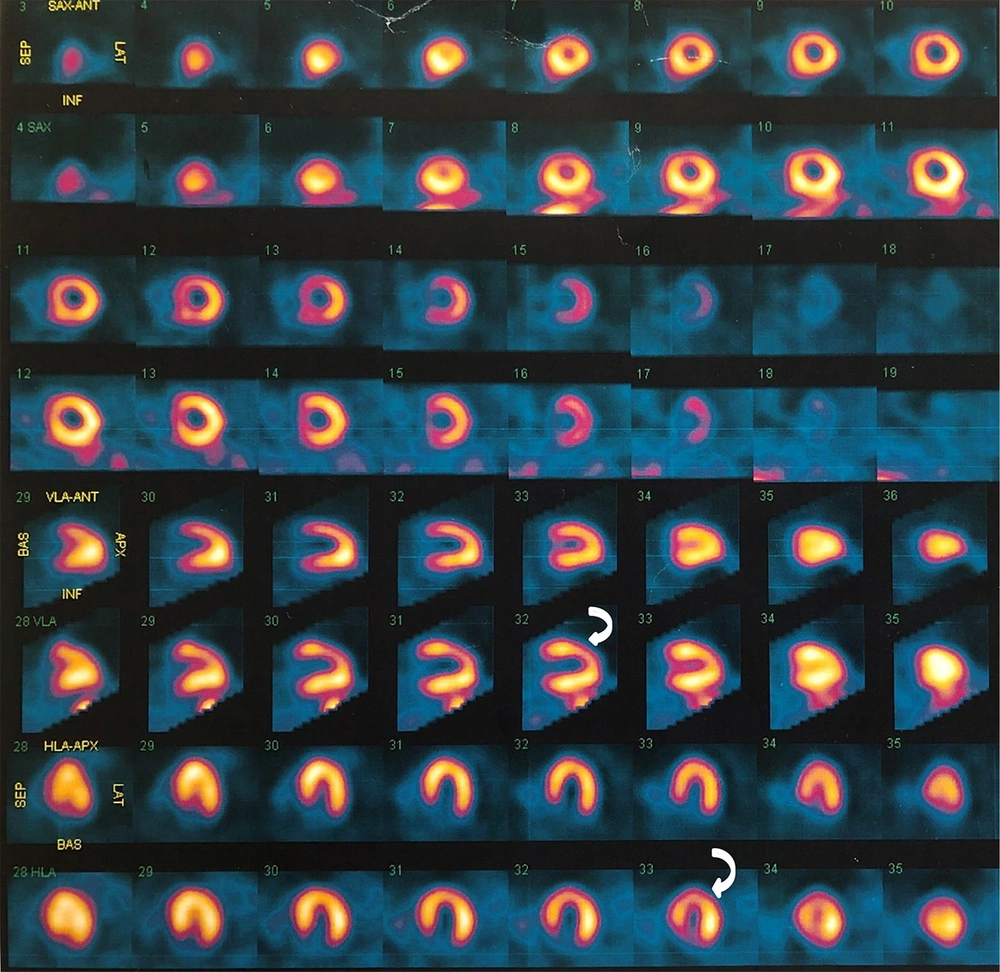
We ruled out any associated cardiac anomaly in our studies. We decided to evaluate ischemia, myocardial perfusion imaging revealed mild stress induced ischemia in anterolateral segment (Figure 4).
After presenting all data in the heart team, we planned for surgically repairing anomalous origin of RCA from pulmonary artery but our patient refused it. In one-year follow up she had mild symptoms without heart attack.
3. Discussion
Incidence of congenital coronary anomalies in general population is about 0.3% - 0.9% (1). Congenital anomalous origin of the coronary artery arising from the pulmonary artery was described by Soloff in four different categories:
(1) ALCAPA (anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery) that is a common type with a total incidence of 0.008%
(2) ARCAPA (right coronary artery from the pulmonary artery), with about 0.002% incidence rate in general population
(3) Both coronary arteries from the pulmonary artery
(4) An accessory coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (2)
ARCAPA is associated with structural heart anomalies in 25% - 30% of cases. Tetralogy of Fallot and aorta-pulmonary window, aortic stenosis, septal defects and aortic coarctation are associated anomalies with ARCAPA (3).
ARCAPA can cause myocardial ischemia with coronary steal phenomenon or abnormal left to right shunt, indeed pulmonary trunk steals oxygenated blood from normal coronary arteries through well-developed collateral vessels (4). Cardiac computed tomography coronary angiogram and cardiovascular magnetic resonance are excellent diagnostic methods for coronary artery anomalies. They are providing detailed anatomic information of origin, course, and relationship of the anomalous coronary artery (5).
After diagnosis, we should prevent myocardial ischemia and sudden death. The treatment of choice for ARCAPA is surgical transfer of anomalous RCA to aorta; this correction can eliminate the left to right shunt and provide normal bicoronary circulation (6). Surgical correction of ARCAPA has low operative mortality ranging from 2% to 3% (5). Alternative surgical technics are ligation of the abnormal pulmonary origin of the coronary artery, and arterial bypass grafting (7). We have limited data about post-surgery follow up in ARCAPA.
3.1. Conclusion
An anomalous origin of the right coronary artery is a rare congenital anomaly with a wide range of clinical importance mostly detected incidentally in asymptomatic patients and sometimes can cause myocardial ischemia or sudden cardiac death, coronary CT angiography is the best modality for diagnosis, and its appropriate treatment is surgical correction of anomalous right coronary artery from pulmonary trunk.