1. Background
Heart failure as an epidemic disease, with different etiologies and wide variety of symptoms finally leads to high rate of mortality and morbidity which is increasing in spite of development of new therapeutic options due to longer survival and ageing of population in recent years (1). Its prevalence in Asia pacific area is between 1.26% - 6.7% and affected patients are younger and more symptomatic (1).
Heart failure has poor prognosis such as many cancers or even worse (2). Psychosocial factors have prognostic importance in the management of heart failure patients (3). Self- management had been a pivotal component of adherence to treatment and can reduce heart failure mortality (4) and morbidity (5) according to different studies.
A known important factor in patient compliance and prognosis is self-efficacy and perceived social support (PSS) which plays an effective role in patient-care giver interactions and has a positive effect on patient activity and taking medications (6). Cardiac self-efficacy is defined as a person’s belief in her/his ability to manage the challenges posed by a cardiac disease. A systematic review in 2014 in Iran revealed that interventional programs can improve the level of self-efficacy and can also affect the patient activity (7). It made the idea of the importance of determining the level of self-efficacy in order to improve patients’ health status with appropriate interventional programs. Self-efficacy was not in an acceptable level in heart failure patients evaluated in Sanandaj (8). Another study in Isfahan in 2018, expressed that there is a strong relationship between the quality of life and self-efficacy in these patients (9).
Some studies show unacceptable rate of treatment compliance in HF patients which leads to higher mortality and rehospitalization (10, 11). It is estimated that hospitalization in 2/3 of HF patients might be prevented by increasing patient compliance (12). Patients’ compliance is affected by self-efficacy which can predict better treatment outcome in patients’ suffering from chronic diseases regardless of the severity of disease or disability (10).
Perceived social support (PSS) is another factor that can improve the quality of life in heart failure patients. There is also a correlation between social support with self-care (13), level of stress, adherence to treatment (14), rehospitalization and mortality rate (15). PSS is defined as the patient’s cognition toward available support, high quality assessment of his disease and the quality of this assessment in emergent situations (16). It could also be defined as a guaranteed potential life support and cooperation for the patient’s therapy during disabled time. Supporting health care team and relatives can help patients and motivate them to react to their diseases in a very different way (17).
2. Objectives
The aim of this study is to evaluate the level of self-efficacy, PSS and patient adherence to treatment in a selected group of patients with HFrEF. According to our knowledge, limited similar studies have been conducted in our country which can be influenced by different regional cultures (18, 19). Results of this study can help patients, caregivers and physicians to make a sense for improvement of psychosocial support for heart failure patients. Appropriate interventions in patients with low levels of self-efficacy and PSS and adherence to treatment could have a positive impact on treatment outcomes and reduce morbidity and even mortality rate of heart failure.
3. Methods
3.1. Patients’ Selection
Between October - December 2014 among patients referred to heart failure clinic at Rajaie Cardiovascular, Medical and Research Center, a total of 120 patients were consecutively enrolled by convenient sampling according to the following inclusion criteria:
Definite heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF ≤ 35%) with any etiology (ischemic or non-ischemic) diagnosed by expert heart failure cardiologist according to the international heart failure guidelines who were on guideline directed medical therapies, the age of 18 years or more, New York Heart Association function class (NYHA FC) 1 - 3, ability to read, write and speak and not having mental, neurological and cognitive disorders.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Rajaie Cardiovascular Medical and Research Center and informed consent was given to all study population.
3.2. Research Tools
Four different questionnaires were explained for patients:
3.2.1. Demographic Characteristics Questionnaire
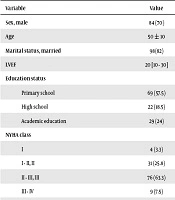
It designed by the study investigators (including some questions which are explained in Table 1).
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Sex, male | 84 (70) |
| Age | 50 ± 10 |
| Marital status, married | 98(82) |
| LVEF | 20 [10 - 30] |
| Education status | |
| Primary school | 69 (57.5) |
| High school | 22 (18.5) |
| Academic education | 29 (24) |
| NYHA class | |
| I | 4 (3.3) |
| I - II, II | 31 (25.8) |
| II - III, III | 76 (63.3) |
| III - IV | 9 (7.5) |
| Heart failure etiology | |
| Ischemic | 80 (67) |
| Non-Ischemic | 40 (33) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 36 (30) |
| Hypertension | 28 (23.3) |
| Chronic lung disease | 9 (7.5) |
| Chronic kidney disease | 13 (10.8) |
| Drug history | |
| ACEI/ARB | 84 (70) |
| Beta blocker | 91 (75) |
| Diuretics | 94 (78.3) |
| MRA | 77 (64.2) |
| Digoxin | 46 (38.3) |
| Aspirin/Clopidogrel | 81 (67) |
| Warfarin | 35 (29.2) |
Abbreviations: ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor blocker; NYHA, New York Heart Association.
aValues are expressed as mean ± SD, No. (%), or median [IQR].
3.2.2. Self-Efficacy Questionnaire
This questionnaire has been designed by Bajelani et al. (13) to measure cardiac self-efficacy in patients with cardiovascular diseases in Iran. Its reliability was reported using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for a total scale from 0.84. This questionnaire has 10 questions, in which patients were asked to rate how confident they are that they know or can ... on a five-point Likert scale (1 = not at all, 2 = somewhat confident, 3 = moderately confident, 4 = very confident, 5 = completely confident). Total score would be between 10 to 50 based on patients' answers. The higher score they take, the more efficacy is expected.
3.2.3. Perceived Social Support (PSS) Questionnaire
This questionnaire was comprised of 30 questions in 3 domains [emotional (questions 1 to 12), informational (questions 13 to 20) and positive social interaction (questions 21 to 30)], graded based on a 4-point Likert scale. (1 = never, 2 = sometimes, 3 = often,4 = always). This questionnaire has been designed by Cheraghi and Davari Dolatabadi (20). Its reliability was reported using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for a total scale from 0.87 and test-retest consistency was from 0.895.
Emotional questions is related to patients’ feelings about the people around them and their support. Informative questions discuss about the information that patients receives from family and caregivers about the disease and finally positive social interactions ask about any kind of financial support (from family, friends or support organizations) or if the patient needs help for his/her activities.
The patients are categorized into 3 categories for PSS, based on their achieving score as low, median and high. The scores between 30 - 59, 60 - 89 and 90 - 120 show low, median and high PSS, respectively
3.2.4. Adherence to Treatment Questionnaires
This questionnaire was designed by Thomas in 2004 (21) and the validity and reliability of its Farsi version has been determined by Ahrari et al. (22) (Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for the overall questionnaire was 0.76).
The questionnaire consists of three domains for adherence: adherence to the diet (questions 1 to 4), adherence to the physical activity (questions 5 to 8), and adherence to the medications (questions 9 to 12). Questions 5, 6, 7, 8, and 12 of this questionnaire are rated on a 4-point Likert scale from never (1 point) to ever (4 points). Questions 1, 2, 4, 9, and 11 are rated from never (4 points) to ever (1 point). These questions are recoded statistically and higher scores indicate better adherence.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
SPSS 20 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for all statistical analyses. All data were initially analyzed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to assess normal distribution. Quantitative variables were presented as means (standard deviation [SD]) and categorical variables as counts and percentages. The chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, or the Mann-Whitney tests, Kruskal-Wallis, Spearman correlation coefficient (CC) were used to compare variables or find their correlation. Multivariate binary logistic regression analyses were used for multivariable analyses and determination independent predictors of treatment adherence. The values of P < 0.05 was considered significant.
4. Results
A total of 120 patients with chronic heart failure were enrolled according to the inclusion criteria. The mean (SD) of age was 50 (± 10) years. Most patients were male, between 40 - 59 years old. The median (IQR) of LVEF was 20 (10 - 30) and most of them had a NYHA FC III. Table 1 shows demographic, clinical findings and past medical history of study population.
4.1. Cardiac Self-Efficacy
In this study the mean (SD) score of cardiac self-efficacy was 30.6 (± 2.4), between 23 and 36, which shows a fair self-efficacy in our study population.
4.2. Perceived Social Support (PSS)
The mean (SD) score for PSS was 94.6 (± 10), between 53 - 115, which shows a high social support in our study population. Among the different dimensions of PSS, the emotional domain showed better score than the two other domains (informational and positive social interaction).
The mean (SD) scores for emotional, informational and positive social interaction were 35 (± 4), 27 (± 3), and 26 (± 4), respectively.
4.3. Adherence to Treatment
The mean (SD) score for adherence to treatment in our study population was 33.2 (± 4.8), between 17 and 147. The mean (SD) scores for the three domains of adherence to treatment were 7.4 (± 1.5) for diet, 13.2 (± 2) for physical activity and 10 (± 1.4) for medications which shows a poor adherence to the diet in our study population.
4.4. Relationship Between Study Variables
There was no relationship between sex, marital status, educational status, LVEF, functional capacity, presence of comorbidities including diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HTN), chronic lung disease (CLD), chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cardiac self-efficacy (All P > 0.05, between 0.06 - 0.94).
PSS was significantly correlated with marital status (P = 0.001) and NYHA FC (P = 0.001) (lower PSS in single persons with higher NYHA function class).
Adherence to treatment was significantly correlated with NYHA FC (P = 0.02) and presence of HTN (P = 0.05) (lower adherence in hypertensive patients with higher NYHA FC).
4.5. Relationship Between Adherence to Treatment, Cardiac Self-Efficacy and PSS
There was no statistically significant correlation between adherence to treatment and PSS (Spearman’s correlation coefficient (CC) = 0.15, P = 0.1). However, a weak but significant correlation was noticed between adherence to treatment and informational domain of PSS (Spearman’s CC = 0.18, P = 0.04).
Also PSS was not statistically correlated with cardiac self-efficacy (Spearman’s CC = 0.17, P = 0.06).
However, there was a weak but significant correlation between cardiac self-efficacy and adherence to treatment (Spearman’s CC = 0.22, P = 0.01) which was because of a modest but significant correlation between the domain of physical activity and cardiac self-efficacy (Spearman’s CC = 0.35, P = 0.001).
4.6. Independent Predictors of Adherence to Treatment
The multivariate binary logistic regression analysis showed that cardiac self-efficacy may be more important independent predictor for adherence to treatment than PSS. The odd ratio (95% confidence interval) = 0.16 (0.02 - 1.3), P = 0.05 for cardiac self-efficacy versus odd ratio (95% CI) = 0.1 (0.01 - 1.1), P = 0.1.
5. Discussion
Our study implies that that psychosocial aspects of life should be considered in the management of patients with heart failure and they also affect the adherence to treatment.
Social support helps patients to follow their treatment schedule better including diet, medication use and regular exercise and have more compliance (23). Eventually higher level of social support can improve their self-confidence and decrease the amount of negative pressure and anxiety and ameliorate treatment outcomes in chronic diseases such as stroke (24). In 2017 Patel et al. could demonstrate the inverse association of self-efficacy and depression in heart failure patients (25). Comparing to their study, our investigation revealed negative relation of NYHA FC (which can be a marker of disease severity and advanced heart failure) and self-efficacy which can be affected by disability and psychologic problems in advanced heart failure and is comparable to findings of Cheraghi et al.’s study (19). Poor compliance of hypertensive patients could be due to more complicated treatments and higher rates of medications prescribed for these patients.
In this study 77.5% of our study population had high social support. However, only informational domain of social support was significantly correlated with adherence. On the other hand, we could find a relatively good relationship between adherence and cardiac self-efficacy in both univariate and multi variate analyses specially in the following exercise programs.
Chen et al. proved that self-efficacy has substantial effect on compliance of patients with heart failure. It means that patients with higher level of self-efficacy actively participate in treatment strategies (26) and they believe that they can overcome the disease. Patients would follow the diet and other useful programs effectively if they have positive attitudes about themselves and treatment modalities (23).
In 2001, Bennete et al. (27) demonstrated moderate to high levels of social support in heart failure patients which is compatible with our study. Alizadeh et al. (28) showed strong emotional support in patients with heart failure. In addition Cheraghi et al. (19) denoted that in spite of high levels of emotional support, heart failure patients are affected by low informational perceived social support. Similar findings are obtained in our investigation.
We could define the more prominent role of self-efficacy in contrast to PSS in patient compliance and treatment follow up which is indicative of pivotal role of patient attitudes and desires in adherence to treatment strategies.
Maeda et al. (10) showed a significant correlation between the rate of social support and compliance; the higher the social support the more compliance could be expected among all patients with chronic disease such as heart failure and our study demonstrated similar results with more than %50 compliance in exercise but lower in diet.
5.1. Conclusions
Social support, adherence and self-efficacy among all patients with HFrEF were in acceptable levels in this study. However, both patients and care givers should be more educated in this regard. Understanding the influence of self-efficacy and social support on adherence to treatment can help nurses and physicians to develop special educational and motivational programs to improve self-care behaviors which are among the most important factors affecting adherence to different aspect of treatment in these patients.
5.2. Study Limitations
This study is based on self-report method which may cause a kind of bias because of differences in patients' attitudes and expectations. Further evaluation of these items in HF patients with a larger sample size with interview method and evaluation of proper interventions to improve outcomes is recommended.