1. Background
The percentage of people over the age of 60 years in the global population, according to the forecast of the World Health Organization will increase from 10.0% in 2000 to 21.8% in 2050, and then to 32.2% in 2100 (1). The natural aging process is associated with poor balance ability and reduction in the joint position sensation (2, 3). Women are generally weaker than men in all age groups (4, 5). Their differences can lead to increases in their relative number of problems with balance and various conclusions regarding gender and steadiness of posture (5, 6). Postural steadiness is essential for activities of daily living (ADLs) of the elderly (7, 8). Its impairments when responding to unbalanced internal and external stimuli can increase the incidence of falls (9). Physical exercise, including aerobics (10), anaerobic exercise (11), and water sports (12) within several weeks, are one of the main interventions to improve the steadiness of posture in older people. In addition to the long-term influences of physical activity on postural balance, its acute influences have also been studied; but the population of these studies included those who faced a disease (13, 14). Thus, it is assumed that acute improvements in control ability following one session of exercise can be observed in healthy elderly females who have a better steadiness of posture compared to patients, but face a gradual decline in postural steadiness (15-17). Postural steadiness is derived through central processing, neuro-muscular reactions, and sensory input of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive systems (18). Neuromuscular and proprioceptive training (NPT) is commonly used by young athletes to improve postural steadiness (19-21) but there is no evidence of its use in older adults. A composition of balancing, running, strengthening, agility, plyometrics, and stretching exercises creates an NPT program (22-24). These types of exercise are either too intensive or too monotonic for the elderly to sustain for a long time. There is also strong evidence that the volume and intensity of physical exercise reduces as individuals age (25). Adverse effects of exercise are a concerning problem that physicians and instructors should always keep in mind, especially when prescribing exercise for the elderly. Since in the modern literature, there is no consensus on specific parameters or guidelines for incorporating plyometric training (26), as a result, the plyometric and agility components of the NPT protocol were modified using the ACSM recommendations for prescribing in the elderly (25).
The center of pressure (COP) parameters, such as the velocity of COP can become categorized as relative to postural swaying to ensure postural steadiness (27). Measurement of COP velocity is of critical importance for understanding the neural mechanisms of postural control (28, 29), as well as for better diagnosis of the severity of neurological problems with imbalance (29, 30). The COP velocity also has a minimum standardized interpersonal coefficient of variation, i.e. the smallest reproducibility error (31). Thus, similar to previous studies, to evaluate postural steadiness, COP velocity parameters have been chosen which include total mean velocity (V) and the mediolateral (ML) and anteroposterior planes (AP).
2. Objectives
The study was aimed at measuring the velocity of COP in different directions to estimate acute improvements in postural steadiness through a modified NPT program in elderly females with sedentary lifestyles. If the hypothesis of the study is confirmed, the physicians and instructors will be able to provide one session of physical exercise to improve the postural steadiness of the elderly.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design, Sample, and Randomization
This quasi-experimental research comprised forty-eight females from 65 to 75 years old (69.7 ± 4.7 years) with a sedentary lifestyle, who had come to the Ukrainian Center for sports medicine (Kiev) during the winter of 2018. Participants were derived from a convenience sample and were randomly divided into two groups: the NPT exercise group (n = 24) that carried out a modified NPT session for one hour and then finished it in 5 minutes as cooldown, and the seated rest group (n = 24), which spent the same time rested in a sitting position. The Cochran’s sample size formula was applied to calculate the sample size for 0.05 (error 5%). Participants underwent a medical examination and were enrolled in the study after receiving a health certificate. The criteria for exclusion, when diagnosed by a doctor, were the presence of a fall history, disorders of Parkinson, neuromuscular, circulatory, diabetes mellitus, as well as regular exercises since three months ago (22, 27, 32). Although studies of the relationship between vestibular function and falls in older adults are sparse and contradictory (33); but participants who had uncorrected problems in the visual or auditory apparatus were also excluded. A customized self-report questionnaire was used for choosing participants with a sedentary lifestyle. The questionnaire had a Likert’s scale type with seven points in the range of “not quite” (one point) to “every day” (seven points) (22, 25). Twice a month or less exercise frequency was considered to be an inactive lifestyle (22, 25). This investigation complies with all relevant national statutes, institutional policies, and Helsinki Declaration Principles. They granted physician permission that the offered intervention was not contraindicated for participants. Samples were obtained after informed consent and with the approval of the Institutional Research Ethics Committee.
3.2. Intervention
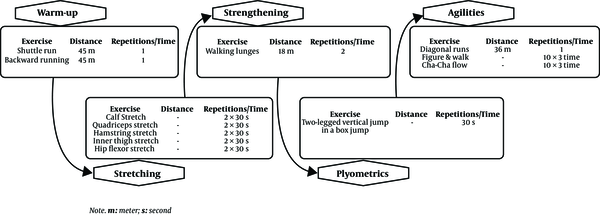
As mentioned earlier, a modified version of the NPT program based on previous studies of older people (22, 23) has been used in this study. Lateral hops, forward hops, and single-legged hops were removed from the plyometric section, and low-impact training techniques, such as jumping in box jumps, as well as doing two-leg versus one-leg jumping exercises were replaced. Bounding runs in the agility section of the NPT program have also been modified to walking and Cha-cha flow into form 8. See Figure 1 for the modified NPT scheme. The study method did not change during its implementation.
3.3. Assessments
Anthropometric assessments for body height and weight were finished by the participants after getting a medical wellness document. Heart rate (HR) was monitored using (Bowflex, Nautilus Inc., Canada) to measure HR induced by physical activity at base-level activity [220 - age × (51% to 65%)]. Postural steadiness was evaluated by measuring COP swings in the plane of ML and AP in quiet stance with open (OE) and closed eyes (CE) in random order by a force platform (Kistler Instruments AG, Winterthur, Switzerland).
3.4. Static Balance
The COP measurements were carried out twice (5-minute rest period between each test) in barefoot conditions: first with OE and later with CE at a sampling frequency of 200 Hz in 60 seconds. Participants were requested to stand as motionless and normally as home or at work and to look directly in front of themselves at a point on the wall at a distance of 2 meters when OE measurement. Changes in COP swaying caused by physical exercise were compared to changes in COP swaying caused by resting in a sitting position, in addition to comparisons between pre- and post-study.
3.5. Statistical Analysis
Study outcomes are filtered by a Butterworth filter under a lower passage of the fourth-order with a cutoff rate of 7 Hz applying the MATLAB software (Version R2010b; Math Works, Inc., Natick, MA, USA) (27, 34). The normality of data distribution was confirmed by the Shapiro-Wilk test and expressed in the form of mean values ± SD. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied to evaluate the steadiness of posture by 2 × 2 × 2 [group (NPT exercise and seated rest) × time (pre- and post-training) × eye condition (open and closed)]. Moreover, the results were corrected using the Bonferroni adjustments test. Differences between the means were considered statistically significant if P values were < 0.05. Bonferroni adjustment was computed by dividing alpha by the number of tests. Statistical significance level was lowered from 0.05 to ≤ 0.008. Data entry and statistical analysis were done utilizing IBM SPSS 21.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc.; USA).
4. Results
4.1. Pre-Study Outcomes
The average age and body mass index (BMI) of the NPT exercise group were 70.1 ± 4.6 years and 22.34 kg/m2, respectively, and those of the seated rest group were 69.3 ± 6.8 years and 22.47 kg/m2, respectively. Mean HR was 104.3 ± 7.5 BPM (beats per minute), which is related to the intensity of exercise 61.8 ± 3.1% MHR (maximum heart rate). There was no significant difference between groups of NPT exercise and seated rest according to the parameters of the COP in OE [ML (P = 0.13), AP (P = 0.11), and V (P = 0.12)] and CE [ML (P = 0.11), AP (P = 0.13), and V (P = 0.11)].
4.2. Post-Study Outcomes
All participants finished the study. Significant interaction influences were only found in V (P = 0.004) and ML (P = 0.003) of the NTP exercise group under CE condition. The results obtained are presented in Table 1.
| Open Eyes (OE) | P Value | Closed Eyes (CE) | P Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPT Exercise Group | Seated Rest Group | NPT Exercise Group | Seated Rest Group | |||||||
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |||
| AP, cm/s | 0.73 ± 1.7 | 0.72 ± 1.8 | 0.63 ± 1.3 | 0.64 ± 1.6 | 0.09 | 1.1 ± 2.8 | 1.0 ± 2.2 | 0.93 ± 2.6 | 0.95 ± 3.1 | 0.06 |
| ML, cm/s | 0.69 ± 2.2 | 0.61 ± 1.5 | 0.78 ± 2.7 | 0.79 ± 3.1 | 0.01 | 1.0 ± 3.2 | 0.91 ± 2.6 | 1.1 ± 3.1 | 1.2 ± 3.7 | 0.003b |
| V, cm/s | 1.2 ± 2.6 | 1.0 ± 2.3 | 1.1 ± 2.7 | 1.1 ± 2.9 | 0.02 | 1.8 ± 3.5 | 1.5 ± 2.3 | 1.6 ± 3.1 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 0.004b |
The Results of Center-of-Pressure Velocity Parameters in Both Studied Groupsa
5. Discussion
The study suggests that a modified NPT session will have an acute positive effect on the ability to maintain balance in elderly females by slowing down the spontaneous COP swings during quiet standing. Decelerating the COP swings after training occurred mainly in the ML plane under the CE condition. Previous research has shown that elevated postural swinging in the ML plane is closer to the deficit of balance in aging (35) and falling (36) than the postural swing in the AP plane. Therefore, these conclusions provide additional support to the idea that one session of exercise can have a positive impact on balance ability.
The steadiness of posture in an upright standing is controlled by adjusting the sensorimotor system in unifying sensory input from the somatosensory, vestibular, and visual systems (18). In these processes, lower extremity proprioception is considered to be one of the main agents contributing to the postural steadiness in an upright position (37, 38). The foregoing researches has shown that even only one exercise session has a positive effect on proprioception of the lower extremities; for example, warm-up improves the ability of the person to feel the knee position (39, 40). Besides, one exercise session may increase the conductivity of the nerves (41-43), which is part of the sensorimotor mechanism. The sensitivity of lower extremity proprioception declines with normal aging (43, 44), and this decline has been associated with an increase in postural swaying (2, 3, 38, 45, 46) and with a history of falling (38). According to the study, the decrease in COP velocity after a single NPT session occurred in the ML plane under the CE condition. Although, some researchers believe that the increase and fall in age are associated with increased COP velocity in the direction of the AP (47). Previous studies have shown that improved postural swings in the ML plane are more closely connected with balance deficiency following an increase and fall in age than the postural swing in the AP plane (23, 48). The current results, therefore, provide further support for the idea that NPT has a positive impact on postural steadiness. The speed of neural conduction also declines with natural aging (49, 50), and this descent slows the reaction of muscles to postural disturbances, thus raising postural swaying (51, 52). Therefore, one session of exercise may counteract and, at least temporarily, reduce the steadiness of posture due to aging, thus improving control ability. As a result, physicians and sports trainers will have new opportunities to present an effective session of physical exercise. They need to choose the right type and intensity of exercise carefully to gain acute exercise benefits. Fatigue due to intense pressure on the muscles can weaken the postural steadiness (43). Donath et al. (53) demonstrated a slight increase in the swing of the COP after an exercise. The intensity of exercise in their study was designed to be heart health activity levels (66% - 85% MHR) and the type of exercise was dissimilar. Obviously, the difference in the type of exercise and it being higher than the current study can cause the different results seen in studies. Aging is linked to poor balance ability (2, 3) and ADL disorders in the elderly (7, 8). When responding to internal and external unbalancing stimuli, its disturbances can also increase the falling frequency (9). Although they may be temporary and not last for a long time, the acute improvement of postural steadiness through modified NPT exercise achieved in the current study will help to prevent falls and subsequent damages, and further ADL disorders.
5.1. Limitations and Future Research
Since we have studied only females, the effects of a modified NPT session on men remain unclear. Therefore, it is proposed to conduct a study on men. Another limitation of this study was that the distribution was blind to participants and researchers at the time of randomization; however, because of the nature of the current study, the distribution cannot persist blindly. There were no limitations on the conduct of the study such as potential bias, the plurality of analyzes, and so on.
5.2. Conclusion
The current study shows that a modified NPT session improves acute balance ability in sedentary older females, particularly indicated by the slowing of COP swings in upright standing. The modified NPT exercise used in this study is a good choice for physicians and exercise trainers of the elderly, which should be taken into account when designing training plans that use the acute positive effects of exercise to enhance balance.