1. Background
Food security is defined as the condition where all individuals consistently have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences, enabling them to maintain active and healthy lives (1). Conversely, food insecurity (FINS) emerges due to a variety of factors, including poverty, poor health within households, and inadequate management of livelihoods and household resources. The severity and categorization of food insecurity depend on how household members perceive and prioritize their spending on food (2). Currently, over 821 million people worldwide face hunger every night, attributed to governmental conflicts, such as those in Ukraine, Syria, Yemen, and Afghanistan, along with climate change and human-induced economic downturns. The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic has exacerbated this issue (3, 4), pushing over 100 million people into severe and extreme hunger. The International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) has, for the first time during the COVID-19 pandemic, issued a warning that without appropriate actions, COVID-19 could precipitate a food security crisis. The pandemic has hit the vulnerable poor hardest, adding a new demographic to the global hunger population, including urban residents in low- and middle-income countries (5, 6).
While global hunger has traditionally been viewed as a rural issue, COVID-19 has had a disproportionate impact on urban areas in developing countries, exacerbating existing food shortages and heightening the risk of food insecurity. This situation is aggravated by natural disasters such as floods and droughts, along with market forces that elevate food prices (5).
The pandemic has resulted in significant income losses, especially for those in vulnerable groups, such as informal workers and individuals who have been terminated from their jobs. Disruptions in food production and distribution, including market closures and restrictions on transportation, have further exacerbated food insecurity. Those living in slums, homeless individuals, and people with chronic illnesses are especially at risk of food insecurity due to a combination of biological and socioeconomic factors (5). Additionally, the threat of severe illness and death from COVID-19 is higher among those who are malnourished or facing moderate to severe food insecurity, as poor immune function can heighten the risk of complications and the spread of infectious diseases (5).
Addressing these challenges necessitates that governments devise robust and unified strategies to accelerate COVID-19 vaccination campaigns and establish a resilient food system. Understanding the various aspects of the disease and its potential impact on food security and dietary diversity within specific populations is crucial (7). While some research suggests that the COVID-19 outbreak has significantly affected food security, other studies argue that there is no substantial link between these issues (2, 3, 5, 6, 8-24).
Pakravan-Charvadeh et al. (21) emphasized the importance of categorizing the study duration into short, mid, and long-term periods before evaluating the impact of COVID-19 on food security levels. They suggested that the effects of COVID-19 on food security are likely to differ depending on the duration of the study. Furthermore, it was proposed that various strains of COVID-19, such as delta and omicron, might have distinct impacts on food security, warranting further investigation. The objective of this research was to evaluate the food security status of the Iranian population during the omicron outbreak in Semnan province.
2. Objectives
This study sought to assess the food security status of the Iranian population amid the omicron outbreak in Semnan province. This rapid assessment aimed to identify the critical needs of the population, which could inform the development of targeted programs, particularly for households facing food insecurity in Semnan province, Iran. To fulfill these goals, the study was organized into multiple sections. The following section detailed the materials and methods, including the study location, population, sample size, and analytical approaches used. The results section then provided a descriptive analysis and quantitative models. Finally, the discussion offered an interpretation of the findings and proposed policy recommendations.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Location
This study, designed as a cross-sectional survey, was conducted in Semnan province, located on the alluvial fan of Golrudbar Creek in north-central Iran, home to approximately 702,000 residents. The province spans 96,816 square kilometers, nestled south of the Alborz Mountain range and north of the Kavir plain.
3.2. Study Sample and Data Collection Process
Data collection was facilitated through a structured questionnaire at the study site. Employing the Cochran formula, 231 households were randomly selected between December and April 2022. The questionnaire comprised three parts: The first section detailed households' socioeconomic characteristics; the second focused on a food security survey based on the U.S Household Food Security Survey Module; and the third section featured questions derived from the literature to assess an indicator of households' vulnerability to food insecurity (21). Six trained experts conducted the questionnaire remotely using an online platform, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Following the assessment of food insecurity severity across these periods, the study explored the correlation between socioeconomic factors and household food insecurity in Semnan province. Before data collection, the validity of the questions in the third section was verified by a panel of experts, including an agricultural economist, psychologists, public health and social science professionals, as well as three nutritionists. A pilot study with 20 households in the target area was carried out to minimize errors in questionnaire completion. Additionally, interviewers from the public health department underwent a two-day workshop to ensure uniformity and minimize inter-personal variations during the data collection process, with questionnaires completed via face-to-face interviews with household heads.
3.3. Food Security Analysis
The Household Food Insecurity Access Scale (HFIAS) is adapted from the methodology currently utilized in the United States for estimating household food insecurity at both household and national levels. It serves to gauge the extent of a household's concerns about food insecurity (25). The HFIAS questionnaire comprises nine questions aimed at evaluating household food insecurity over the span of one month (4 weeks). This tool assesses three distinct aspects of household food security (26, 27): The initial question addresses the household's uncertainty and worries about securing needed food; questions 2 to 4 focus on the quality of household food, including dietary diversity and food preferences; and questions 5 to 9 cover food consumption and its physical implications (28, 29). Through the HFIAS index calculation, food security status is categorized into four levels: Food secure, marginally food insecure, moderately food insecure, and severely food insecure. The index ranges from 0 to 27, where 0 indicates the highest level of food security and 27 denotes severe food insecurity (25).
3.4. Quantitative Model
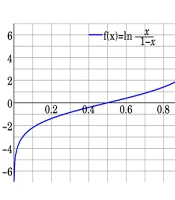
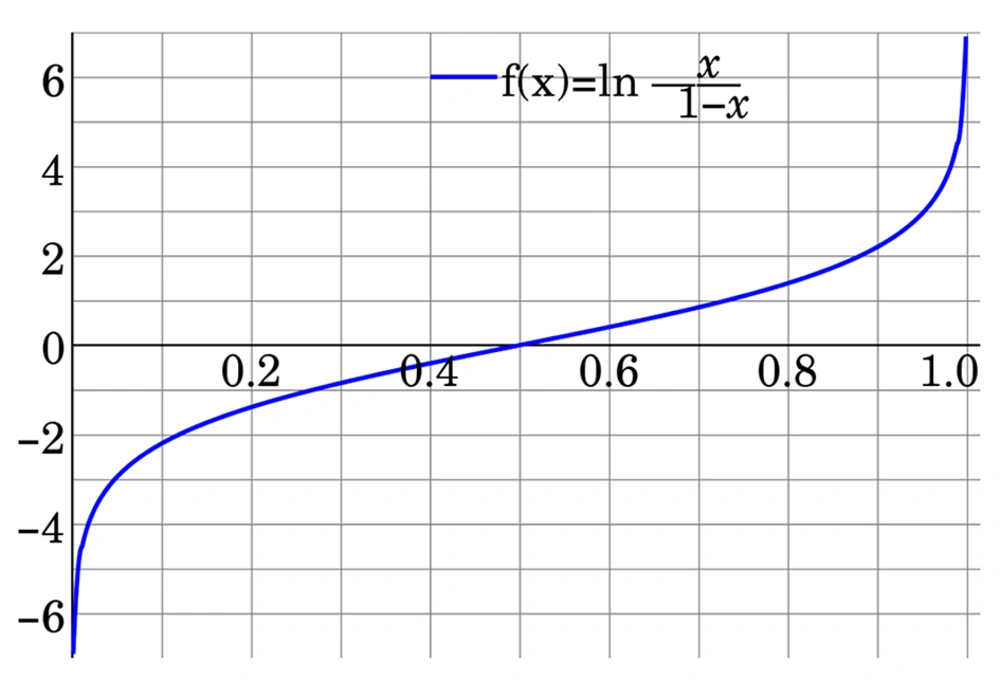
The logit function is mathematically tied to the standard logistic distribution and finds extensive application in data analysis and machine learning, particularly for data transformation. Logistic regression is employed to depict the relationship between a categorical outcome (response factor) and a set of predictor variables. The categorical outcome might be binary (e.g., the presence or absence of an event) or ordinal (e.g., mild, marginal, and severe categories). Predictor variables can be either continuous or categorical. Mathematically, the logit is the inverse of the standard logistic function
The parameters of the Logit Model are determined using the maximum likelihood estimation method, which stands as the predominant approach for estimating the Logit Model. Consequently, the logit function converts probability values ranging from (0, 1) to real numbers in (-∞, +∞), operating similarly to the probit function (Figure 1) (27-30).
4. Results
The descriptive analysis of socio-economic factors revealed that 88% of household heads are male, with females constituting only 12%. The majority of household heads (64%) have attained university-level education, while 21% hold a diploma. Regarding employment status, 73% of the sample were employed, and 21% were retired. As for mothers' occupational status, approximately 54% were homemakers, and 39% were employed outside the home. Nearly 78% of participating households owned their homes, and 57% lacked personal savings in either government or private banks. Additionally, 71% of the households reported not receiving any form of government subsidy support, such as financial aid or food packages.
In terms of continuous variables, the study found that the average age of household heads was 46 years, with the oldest being 83 years old. Household sizes ranged from 1 to 8 members, with an average size of 3.4 (Table 1).
| Discrete Factors and Category | No. (%) | Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Gender of the HH | ||
| Male = 1 | 205 (88) | ✓ |
| Female = 2 | 26 (12) | |
| The education level of the HH | ||
| Illiterate = 0 | 3 (1) | |
| Under diploma = 1 | 32 (14) | |
| Diploma = 2 | 48 (21) | |
| Collegiate (academic) = 3 | 148 (64) | ✓ |
| Occupation of the HH | ||
| Unemployed = 0 | 11 (4.7) | |
| Employed = 1 | 170 (73.6) | ✓ |
| Retired = 2 | 50 (21.7) | |
| Occupation of the MH | ||
| Employed = 0 | 90 (39) | |
| Housewife = 1 | 126 (54.5) | ✓ |
| Retired = 2 | 15 (6.5) | |
| The status of home ownership | ||
| Rental = 0 | 51 (22) | |
| Personal = 1 | 180 (78) | ✓ |
| Personal saving | ||
| Not having = 0 | 98 (42.5) | |
| Having = 1 | 133 (57.5) | ✓ |
| Government subsidy support | ||
| Not receiving = 0 | 67 (29) | ✓ |
| Receiving = 1 | 164 (71) | |
| Continuous factors and scale | Min - Max | Mean |
| Age of the HH (y) | 23 - 83 | 46.5 |
| Household size (N) | 1 - 8 | 3.4 |
| Number of sick members (N) | 0 - 4 | 0.73 |
| Number of educated members (N) | 0 - 4 | 1.03 |
| Employed members (N) | 0 - 4 | 1.45 |
Descriptive Analysis of Socio-Economic Factors at the Study Location
The descriptive analysis indicated that households had an average of 0.73 sick members and 1.03 educated members, with typically more than one individual working within each household.
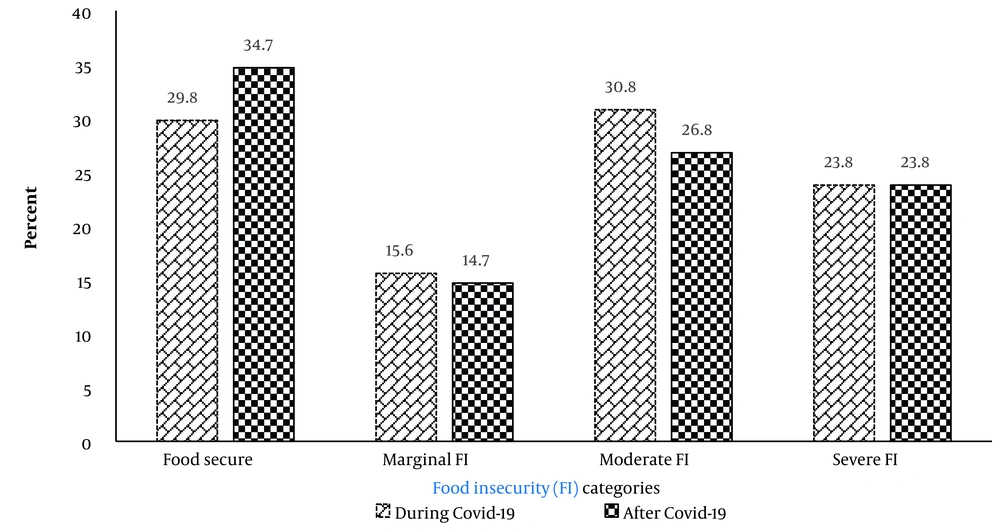
The evaluation of the food security levels among participating households showed that food security status post-COVID-19 improved compared to during the disease outbreak, with this difference being statistically significant. While the percentage of households experiencing marginal and moderate food insecurity decreased following the omicron variant, the proportion of households facing severe food insecurity remained unchanged across both periods (Figure 2).
Table 2 displays the statistical analysis comparing the relationship between socioeconomic factors and food security during versus after the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings reveal that with the exception of the head of the household's occupation status, personal savings, and number of educated and employed members within a household, all other factors were significantly related to food security. These outcomes suggest that the impact of various socioeconomic factors on food security levels may vary with the pandemic's timeline, environmental conditions, and household resilience. For example, while the male gender of a household head was positively and significantly related to food security during the COVID-19 outbreak, it did not significantly influence food security after the pandemic. These findings emphasize the need for policymakers to tailor their strategies to the prevailing circumstances, adjusting their focus on relevant factors as conditions evolve.
| Factors | During | After | Parameter Difference (P-Value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff a | Z | Coeff a | Z | ||
| Gender of the HH | 0.648 ** | 2.59 | 0.293 | 0.86 | 0.001 |
| The education level of the HH | 0.006 | 0.09 | -0.263 * | -2.16 | 0.020 |
| Age of the HH | -0.04 ** | -4.58 | -0.019 ** | -4.65 | 0.090 |
| Occupation of the HH | 0.256 ** | 77.71 | -0.144 ** | -2.82 | 0.120 |
| Occupation of the MH | 0.165 | 1.60 | 0.860 ** | 90.65 | 0.020 |
| The status of home ownership | -0.493 * | -2.26 | -0.719 ** | -3.40 | 0.080 |
| Personal saving | -2.681 ** | -44.78 | -2.046 ** | -36.84 | 0.230 |
| Government subsidy support | -0.223 ** | -10.60 | 0.126 | 0.70 | 0.001 |
| Household size | 0.738 ** | 12.01 | 0.441 ** | 6.62 | 0.091 |
| Sick members | 0.371 ** | 7.74 | 0.012 | 0.07 | 0.036 |
| Educated members | -0.138 ** | -6.05 | -0.102 ** | -4.74 | 0.241 |
| Employed members | -0.154 | -2.98 | 0.188 ** | 11.89 | 0.130 |
| Constant | -3.183 | -1.35 | -2.269 | -0.83 | 0.109 |
The Results of the Quantitative Model to Determine the Associated Factors with Food Insecurity
5. Discussion
In this research, we conduct a comprehensive long-term evaluation of how the COVID-19 pandemic affected food security, aiming to derive insights applicable to future outbreaks. The study progresses through multiple phases. Initially, a descriptive analysis of socio-economic factors within the study area is performed. This analysis shows that the heads of the majority of households are of middle age, suggesting they have the requisite knowledge and experience to manage during a pandemic. Following this, the study examines the food security status of households both prior to and following the outbreak of COVID-19. Over time, there was a noticeable improvement in the food security status among Iranian households, a change that can be linked to various factors. Pakravan-Charvadeh et al. highlighted an enhancement in food security among Iranian households shortly after the commencement of the Coronavirus pandemic (21).
One primary observation was that at the start of the pandemic, households were initially unprepared and lacked critical information about the disease, which led to inefficient financial management (3, 21).
Over time, households learned to better allocate their income towards improving nutrition. Additionally, as more information about COVID-19 control measures and reducing transmission risk became available, households could repurpose funds from non-essential expenses to essential food purchases, thereby enhancing food security. Furthermore, the pandemic-induced shifts in dietary patterns, influenced by television and social media health and nutrition promotion programs, along with health authority initiatives, likely contributed to improved food security. Initially, the pandemic led to significant job losses and financial strain due to government-imposed lockdowns, resulting in decreased food security (7, 21). However, post-pandemic recovery allowed many individuals to resume employment and sustain their households, improving food security levels. Pakravan-Charvadeh et al. highlighted an increase in food security among Iranian households shortly after the onset of the coronavirus (21).
The study's second phase underscores the distinct socio-economic factors influencing food security during versus after the COVID-19 pandemic, aligning with findings from other research (31, 32). The employment status of household heads significantly correlated with food insecurity during the pandemic but was inversely related post-pandemic, underscoring the importance of stable employment in maintaining household income and food supply. Pandemic-related restrictions hindered work opportunities for many, escalating stress and anxiety levels (21). Moreover, the study confirmed that government subsidies effectively mitigated food insecurity, though this support was not directly linked to food insecurity levels. Government assistance was crucial in addressing food insecurity in a developing country amidst a pandemic, serving as a vital substitute for the lost income of many household heads during the COVID-19 crisis (21).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the presence of sick individuals in households was positively linked to food insecurity, a correlation that diminished once the pandemic was controlled (6). In Iran, where medical expenses are high, an increase in sick household members necessitated a reallocation of household spending from food to medical needs, heightening the risk of food insecurity for these families (33).
Self-reporting surveys, while cost-effective and convenient, present inherent limitations. They depend on the respondents' subjective assessments, reflecting personal perceptions of food insecurity. In this study, the focus on the quantity of meals consumed during quarantine failed to account for how food was obtained. Conducted within a specific demographic, this cross-sectional study underscores the importance of broader governmental research due to its limitations.
This research delved into the long-term effects of COVID-19 on food security, finding an overall improvement post-pandemic. Besides the occupation of household heads, personal savings, and the presence of educated and employed members within households, all variables were significantly linked to food security. With 65% of households in the province experiencing food insecurity, there's a pressing need for immediate measures such as government aid, distribution of support packages to the needy, and healthful eating campaigns on television. Educating households on the potential of future pandemics could enhance preparedness for such events. It is advised that educational initiatives be initiated and information on epidemic readiness be distributed. Our study showed that socioeconomic factors' impact on food insecurity varied at different stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Understanding these dynamics in relation to the pandemic's timeline is vital for crafting effective health policies. The employment status of household heads was a notable determinant of food security after the pandemic, suggesting that policy interventions could include easing business operations, offering temporary tax breaks, and providing low-interest, long-term financing. Additionally, our findings stress the importance of supportive policies during pandemics, such as both conditional and unconditional cash grants, unemployment benefits, better access to credit, food aid, and price regulation, to robustly address food insecurity.