1. Context
The global prison population has exceeded 11 million and continues to rise. Drug-related mortality is a significant issue in discussions on public and global health. Individuals with a history of incarceration show notably poorer health, marked by a higher prevalence of substance abuse, mental health conditions, and physical ailments (1). Studies indicate that adults released from prison face a greater risk of mortality, with drug-related incidents being the leading cause of death (2, 3). In general, prisoners are at elevated risk for mental disorders, including acute and chronic conditions linked to alcohol and drug addiction, as well as hospital admissions for injury and poisoning (3). Contributing risk factors include unclear knowledge about appropriate dosages, interactions with other substances, or the greater accessibility of methadone compared to heroin (4).
Previous studies suggest that the increased risk of mortality post-release is linked to individual factors such as inadequate education, unstable housing, and mental and physical health problems, which may contribute to the heightened risk of mortality after release (5). It remains unclear whether prisoners with a history of harmful drug use recover post-incarceration. Upon release, they may relapse into injecting drug use, and the social and health challenges they face further increase the risk of relapse. This emphasizes the importance of improving the health status of prisoners after release (6).
Loss of tolerance and potential concurrent misuse of other drugs, particularly methadone, may have contributed as risk factors. It remains unclear whether this was due to a lack of knowledge regarding appropriate dosage, interactions with other substances, or greater accessibility of methadone compared to heroin (4).
There is an increased risk of drug overdose among formerly incarcerated individuals. This heightened risk is associated with drug use and incarceration-related characteristics, including drug use disorders and mental health problems. A history of imprisonment has been identified as a risk factor for opioid overdose among individuals who inject drugs, and opioid overdose has been suggested as the leading cause of death in persons who have been formerly incarcerated (7). Therefore, understanding and addressing the causes of drug-related mortality after release from prison might contribute to reduced mortality in vulnerable populations. Understanding prison-related mortality factors is crucial for preventing the negative health consequences of incarceration.
2. Objectives
This research aims to investigate the causes of drug-related deaths (DRD) among individuals released from prison.
3. Methods
3.1. Search Strategy
The protocol for this study was registered in PROSPERO under the CRD code CRD42024571756. We conducted a systematic search in PUBMED, SCOPUS, and WEB OF SCIENCE from January 1, 1980, to December 30, 2023, to explore the association between drug-related mortality risks following release from prison. Keywords used for the electronic searches, based on a combination of MeSH terms (Medical Subject Headings), were as follows: [Drug OR (Drug-Related Side Effects) OR (Drug Interactions) OR (Drug Overdose) AND (Death) OR (Cause of Death) OR (Mortality) AND (Release) AND (Prisons) (all-cause and cause-specific)] and risk factor. Additionally, a manual search was conducted by reviewing the reference lists of the selected publications. The studies were independently reviewed by two authors. Table 1 was used to select the studies. This model is one of the most commonly used frameworks for structuring observational research articles, ensuring that the relevant components of the research question are clearly defined (Table 1).
| POLIS Criteria | Patients | Outcome | Location | Indicator | Study Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | All individuals released from prison | Death with overdose and suicide with drug | All world | All-cause, and cause-specific | Observational study with cross-sectional, case-control, cohort design |
The Patients, Outcome, Location, Indicator, and Study Design.
3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
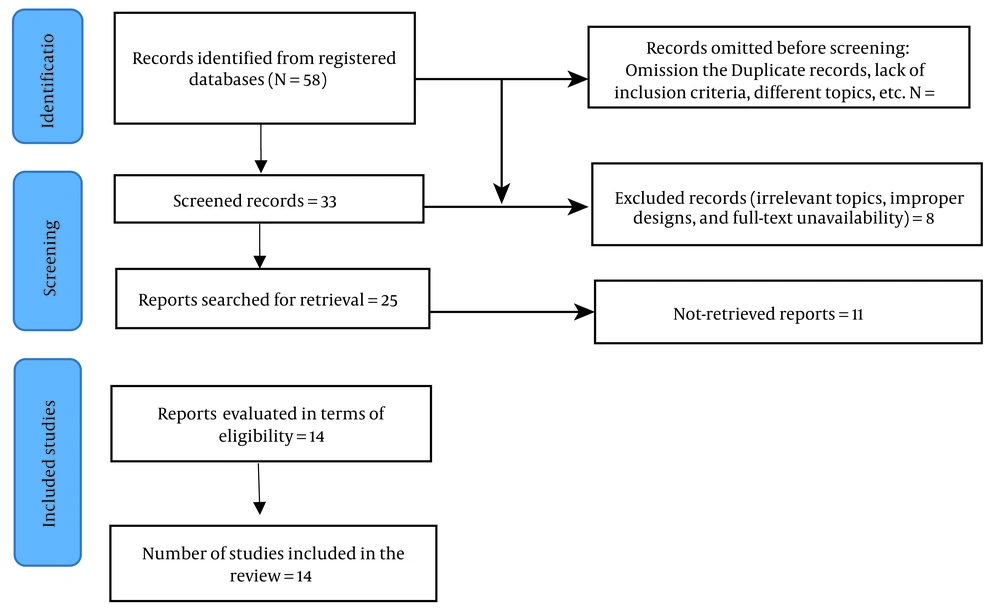
The primary search yielded 58 studies. Among these, observational studies were included without restrictions based on participant age, gender, ethnicity, language, nationality, publication language, or search period. As empirically-based, we only examined studies that focused on the causes of drug-related mortality and prevention (typically in the form of suicide or overdose immediately after release from prison). Randomized controlled trial (RCT) studies were excluded from this review. Case studies (case report collections or case series) were also excluded, along with studies that lacked full-text access or focused on deaths unrelated to addiction, such as food-related deaths, or those that targeted comorbidities (e.g., schizophrenia). Articles were then grouped according to subject area. All abstracts were visually inspected to determine their relevance to the review. Ultimately, 14 articles were selected for this review (3, 4, 8-17) (Figure 1).
Identifying studies from databases and documents with PRISMA flow diagram (2020) (18)
3.3. Data Extraction
The data extraction form and the qualitative evaluation of the articles, previously designed in Excel, were provided to two evaluators. To extract the data, the variables considered included the first author's name, year of publication, geographical location, study type, sample size, average age, target population, and causes of death.
3.4. Quality Assessment
To implement this section, two authors independently utilized a modified version of the Department of Health & Human Services tool for cohort and observational studies, as well as case-control studies. The original version of this tool contains 14 questions designed to assess the risk of bias (19). Any disagreements at each stage of this process were resolved through consultation with a third independent reviewer.
3.5. Synthesis
We performed random-effects meta-analyses on the frequency of DRD occurring within two weeks of release from prison using the "meta-prop" command in STATA (version 10, Stata Corp LP, College Station, TX). The aim of this meta-analysis was to calculate pooled estimates for DRD by synthesizing data from studies that addressed the prevalence of such deaths among recently released prisoners. The results were reported with a 95% confidence interval. The I-squared (I²) test was used to assess heterogeneity among the studies, with the following interpretation: I² < 25% indicates no heterogeneity, I² between 25% and 50% indicates moderate heterogeneity, and I² > 50% suggests significant heterogeneity (20). Meta-regression was conducted to explore potential covariates (effect modifiers) that could explain any observed heterogeneity in treatment effects across studies. The Begg test was applied to evaluate publication bias, with a p-value less than 0.05 considered statistically significant.
4. Results
The final draft consisted of 14 observational studies on released prisoners, reporting on more than 4,969 deceased prisoners (2-4, 8-17, 21). Most of the overdose deaths were reported within the two weeks following release. The causes of death were most frequently associated with heroin use in previous years, prior experiences with drug withdrawal, drug injection, and the use of sedatives in the six months preceding death. Compared to other unnatural causes, there was an increased risk of fatal drug overdose for individuals who died within the first two months of release. Men had higher rates of death from all causes than women. Most of the studies indicated that treatment for substance abuse disorders received during imprisonment provided protection against mortality and all causes of death (Table 2).
| Study | Place | Sample Size | Age | Period of Release | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seaman et al., 1998 (8) | Edinburgh | 316 | Not reported | Between 1983 and 1994 | Twenty of these males died from drug overdoses between 1983 and 1994; six of these deaths happened within two weeks of their release within the 5903 days they were at risk. The study examines the relative risks of poisoning and all causes of death before AIDS development in the two weeks after prison release. |
| Graham, 2003 (9) | Victoria | 820 | Not reported | Between January 1990 and December 1999 | Heroin-related deaths accounted for more than half of the unnatural deaths. At least 25% of heroin-related deaths in Victoria were related to heroin use by ex-prisoners. |
| Andrews and Kinner, 2012 (10) | Australia | 388 | Median age in years = 30 | Ex-prisoners from 2000 - 2007 | Coronial records were identified for 388 deceased ex-prisoners accidental drug-related causes accounted for nearly half of these deaths (45%); seventy-two percent of DRD were found to have included polysubstance use at the time of death. The majority of accidental DRD were in household environments. Compared to ex-prisoners who died from all other reportable causes, those who died from accidental drug-related causes were, on average, younger and less likely to be Australian-born, indigenous, married, or living alone at the time of death. Among unintentional DRD, there was less evidence of mental illness or self-harm; instead, there was higher evidence of prior drug overdose, injecting drug use, heroin usage, and history of drug withdrawal in the preceding six months. |
| Farrell and Marsden, 2007 (11) | England and Wales | 261 | Not reported | During 1998 - 2000 | Drug-related mortality was attributed mainly to substance abuse disorders and drug overdose. Coronial records cited the involvement of 95% opioids of deaths, 20% benzodiazepines, 14% cocaine, and tricyclic antidepressants in 10%. Drug-related mortality among males were more likely to involve heroin and deaths among female were more likely to include benzodiazepines, cocaine, and tricyclic antidepressants. |
| Krinsky et al., 2009 (12) | State of New Mexico | 96 | Not reported | 2001 through 2003 | For those who died in the first two months after release, there was an increased risk of drug overdose death compared with mortality of other unnatural causes. Of those who died of fatal drug overdoses within the first two months, the average incarceration time was significantly longer than those who lived longer than two months after release and they were more likely to have used opiates and sedatives. |
| Binswanger et al. ,2011 (13) | USA | 103 | 33.6 (SD = 9.8) | 1999 through 2003 | Longer prison terms were linked to a lower incidence of overdose and all-cause fatalities, but not premature deaths. |
| Binswanger et al., 2014 (14) | United States | 533 | 40 | 1999 - 2009 | Opioids were a factor in 58.6% (n = 327) of overdose deaths. Men had lower mortality rates from unintentional poisoning than women did, despite the fact that men had higher all-cause mortality rates. |
| Binswanger et al., 2016 (21) | USA | 699 | 40 | Between 1999 and 2009 | Findings key independent risk factors for all-cause deaths included homelessness injection, drug use, tobacco use and cirrhosis and psychiatric medications before release. Independent risk factors for overdose mortality included substance use disorder and injection drug use and panic disorder and psychiatric prescriptions before release and problems with opiates/sedatives. Substance use disorder treatment during the index incarceration was protective for all-cause and overdose deaths. |
| Bukten et al., 2017 (15) | Norway | 493 | Not reported | 1 January 2000 to 31 December 2014 | Eighty five percent of all deaths in the first week after release were due to overdose deaths, with an increase occurring in the two days following release; the possibility of overdose death was highest for those incarcerated for 3 - 12 months compared with those who were incarcerated for shorter or longer times, and the risk of overdosing mortality was associated with recidivism. |
| Spittal et al., 2017 (16) | Australia | 186 | 28.0 ± 8.5 | Between 1994 and 2007 | A history of problematic alcohol use in the community, the use of heroin and other opioids in the community, a prescription for antidepressants during the current prison sentence, and having served two or more custodial sentences were all associated with an increased risk of external cause mortality. |
| Harding-Pink and Fryc, 1988 (4) | Switzerland | 42 | Not reported | During 1982 - 1986 | During this initial stage, all deaths were caused by heroin, morphine, methadone, or both; alcohol and benzodiazepines were also frequently discovered during deaths. Six deaths occurred within fourteen days of release from prison, and methadone was thought to be the primary cause of all of them. |
| Lyons et al., 2010 (17) | Ireland | 105 | Median age = 26 Years | 1998 to 2005 | Thirty four percent of those who died away were reported to have been injecting drugs, and almost a third (61%) had a history of doing so. Within the first week following their release from prison, almost a third (28.1%) of the deaths took place, and another 18% occurred within the first month. Eighty nine percent of all poisonings that occurred in the first month following release from prison were caused by opioids. |
| Hobbs et al., 2006 (3) | Australia | 531 | Range age 20 - 39 years | 1995 - 2001 | Among released prisoners, over 60% of deaths were caused by injuries, poisoning, alcoholism, or drug addiction. Most mortality rates occurred within six months of release, indicating a four-fold increase over subsequent periods. Higher mortality risks were also shown to be connected to older age, Indigenous status, and multiple prison releases, according to multivariate analysis. |
| Spittal et al., 2014 (2) | Australia | 396 | Range age 17 - < 40 years | 1994 - 2007 | The risk of drug-related death, especially after the 2-weeks period after release from prison is at a very high risk. People released from prison are at a higher risk of mortality than their peers in the general population. |
Characteristics of the Included Studies
Almost 53.8% of the included studies demonstrated moderate bias, while 46.1% showed a low risk of bias, and no study exhibited a high risk of bias. A notable limitation was that many articles did not disclose the methods used to determine their sample size, which was one of the primary weaknesses in the quality of the evaluated studies (Table 3).
| Author, Year | 1. Was the Research Question or Objective in This Paper Clearly Stated? | 2. Was the Study Population Clearly Specified and Defined? | 3. Was the Participation Rate of Eligible Persons at Least 50%? | 4. Was a Sample Size Justification, Provided? | 5. Was the Timeframe Sufficient so that One Could Reasonably Expect to See an Association Between Exposure and Outcome if It Existed? | 6. Were Key Potential Confounding Variables Measured and Adjusted Statistically for Their Impact on the Relationship Between Exposure(s) and Outcome(s)? | SCORE | Results of Quality Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seaman et al., 1998 (8) | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | 5 | High quality |
| Graham, 2003 (9) | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | 4 | Moderate quality |
| Andrews and Kinner, 2012 (10) | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | 3 | Moderate quality |
| Farrell and Marsden, 2007 (11) | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | 5 | High quality |
| Krinsky et al., 2009 (12) | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | 4 | Moderate quality |
| Binswanger et al., 2011 (13) | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | 6 | High quality |
| Binswanger et al., 2014 (14) | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | 5 | High quality |
| Binswanger et al., 2015 (21) | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | 6 | High quality |
| Bukten et al., 2017 (15) | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | 4 | Moderate quality |
| Spittal et al, 2017 (16) | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | 5 | High quality |
| Harding-Pink and Fryc, 1988 (4) | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | 3 | Moderate quality |
| Lyons et al., 2010 (17) | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | 3 | Moderate quality |
| Hobbs et al., 2006 (3) | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | 3 | Moderate quality |
| Spittal et al., 2014 (2) | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | 6 | High quality |
Evaluating the Quality of the Studies to Investigate the Risk of Bias a
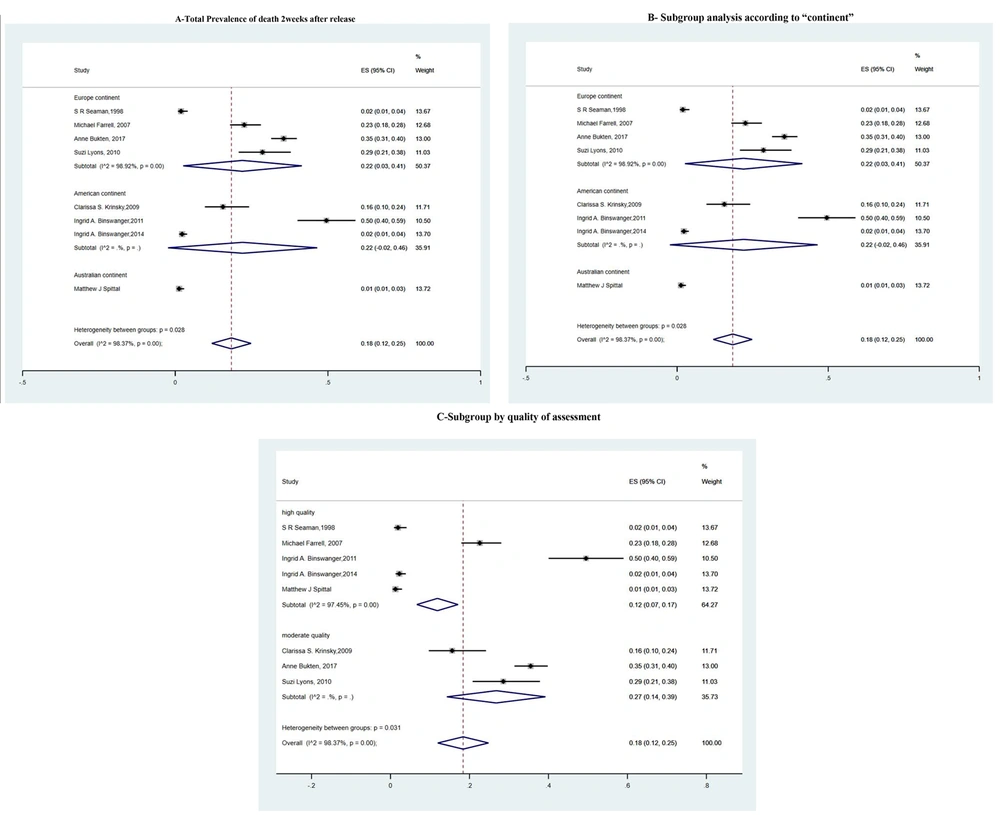
In eight of the studies, the prevalence of DRD was reported two weeks after release from prison (2, 8, 11-15, 17). These articles were included in the meta-analysis. Due to the high heterogeneity [I² = 98.37%, ES (95%) = 0.18 (0.12 - 0.25)], we conducted subgroup analyses based on the region and the quality of the studies. The results of the subgroup analysis are presented in Table 4 (refer to Table 4 and Figure 2 for detailed information).
| Variables | Number of Studies | Heterogeneity Chi-squared | P-Value | Overall I-squared; (%) | z | P-Value | ES (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total result | |||||||
| DRD | 8 | 429.09 | 0.000 | 98.37 | 5.61 | 0.000 | 0.18 (0.12 - 0.25) |
| Subgroup analysis according to “quality assessment” | |||||||
| High quality | 5 | 156.95 | 0.000 | 97.4 | 4.46 | 0.000 | 0.12 (0.07 - 0.17) |
| Moderate quality | 3 | 0 | 0.000 | 98.3 | 4.20 | 0.000 | 0.27 (0.14 - 0.39) |
| Subgroup analysis according to “continent” | |||||||
| Europe continent | 4 | 278.87 | 0.03 | 98.92 | 2.22 | 0.000 | 0.22 (0.03 - 0.41) |
| American continent | 3 | 0 | 0.08 | 0 | 1.77 | 0.000 | 0.22 (-0.02 - 0.46 |
| Australian continent | 1 | 0 | 0.02 | 0 | 2.25 | 0.000 | 0.01 (0.01 - 0.03) |
Prevalence of Drug-Related Death in Two Weeks After Releasing
4.1. Meta-regression
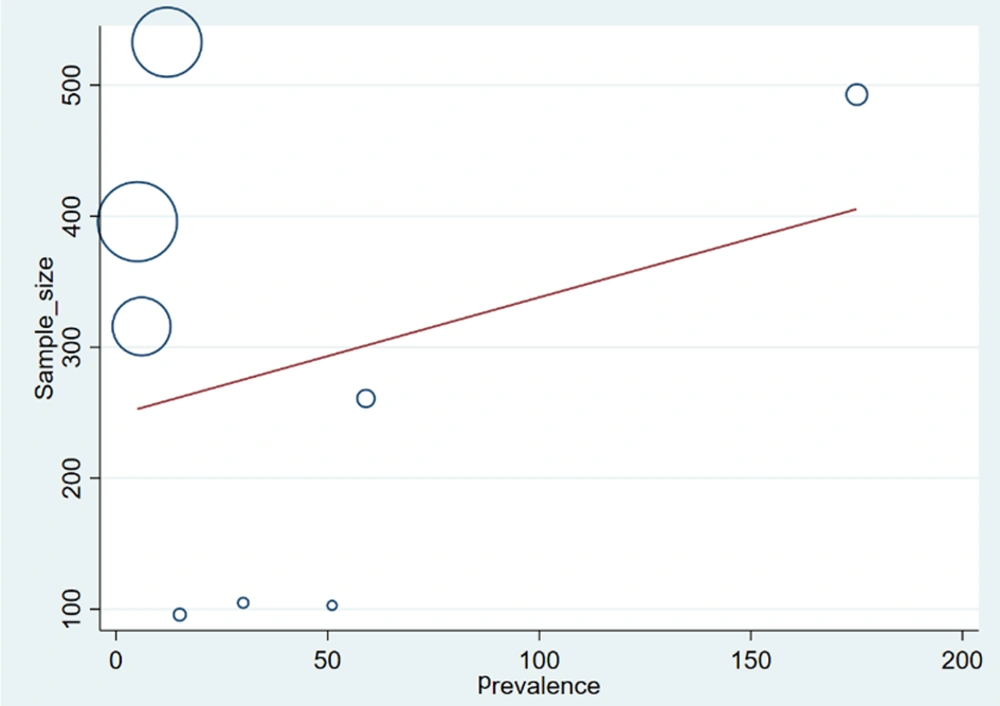
A meta-regression approach, as proposed by Cochrane (22), was used to investigate potential factors affecting the heterogeneity of treatment effects, specifically focusing on the impact of sample size on the prevalence of DRD. According to Figure 2, the results indicate that as the sample size increases, the prevalence of DRD also increases. However, this finding is statistically significant (P-value for sample size = 0.02) (Figure 3).
4.2. Publication Bias
The Begg test was utilized to assess publication bias in this outcome. The test evaluates the impact of small studies on the results, and a P-value of 0.04 was reported. Since this value is significant, it suggests the presence of publication bias. The adjusted Kendall's Score (P - Q) was 16, with a standard deviation (SD) of 8.08, a z-value of 1.98, and Pr > |z| = 0.063.
4.3. Suggestions for Prevention of Drug-Related Deaths After Release
We included four studies because they proposed measures to prevent DRD immediately after release from prison.
1. Preventing the loss of opiate tolerance and thereby lowering the risk of DRD after release may be one of the greatest benefits of prison-based opiate substitution therapy (OST). The suggested treatment involves the daily supervised intake of oral methadone tablets (23). The heightened risk of overdose is most prevalent during the first two weeks after release from prison. If opiate use continues after release, the loss of opiate tolerance may result in a fatal overdose. Oral methadone tablets provides safer alternatives, such as oral methadone, to reduce the use of illicit and injectable opiates. Besides being a good clinical practice, providing OST in prisons has appeared to reduce the number of suicides among younger inmates who inject drugs while incarcerated, despite the associated risks of blood-borne virus transmission (23). This measure has contributed to reductions in drug-related poisoning deaths and all-cause mortality within the first month following release (24).
2. Providing take-home emergency naloxone before a prisoner is released could be a life-saving preventative measure against heroin overdose deaths (25, 26).
5. Discussion
The systematic review on "Mortality after Release from Prison" underscores a critical public health concern, shedding light on the significant issue of post-release mortality among individuals with a history of incarceration. A substantial body of literature consistently highlights that a significant proportion of post-release deaths are attributable to drug overdose (14, 27).
Similar studies conducted a comprehensive analysis of post-release mortality and found that drug overdose was a leading cause of death, particularly in the initial weeks following release (14, 28). These results align with the Merrall et al. study, which identified the period shortly after release as a time of increased risk for fatal overdose incidents (29). The vulnerability of individuals with a history of incarceration to overdose-related mortality is further corroborated by a meta-analysis conducted by Bukten et al., where a substantial increase in mortality due to drug-related causes post-release was observed (15). Similar to our findings, the drug-related death risk was highest in the first two weeks after release (29).
The association between substance use disorders and post-release mortality has been a focal point in the literature, with studies such as that by Zlodre and Fazel emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to mitigate the risk of fatal drug overdoses (27). Furthermore, the disproportionate burden of overdose-related mortality on specific subpopulations, such as those with a history of opioid use disorders, is elucidated by Larney et al. (30).
A large number of the included studies were conducted in industrialized nations, so the findings cannot be generalized to societies with lower income privilege. For future review studies, it is suggested that articles reporting protective factors on substance abuse deaths after release from prison be conducted.
Reducing DRD post-release from prison, especially due to opiate tolerance loss, remains a significant challenge. However, implementing prison-based OST has emerged as a promising solution. By administering oral methadone tablets daily, particularly during the initial two weeks post-release, when the risk is heightened, OST helps maintain opiate tolerance, thereby reducing the likelihood of fatal overdoses from continued opiate use. This approach not only offers a safer alternative to illicit and injectable opiates but also contributes to reducing suicides among younger inmates who inject while incarcerated. Despite concerns about blood-borne virus transmission, studies show that providing OST in prisons effectively reduces drug-related poisoning deaths and overall mortality rates within the first month following release. Furthermore, equipping prisoners with take-home emergency naloxone before release serves as a crucial life-saving intervention against heroin overdose deaths. These proactive measures emphasize the significance of comprehensive harm reduction strategies in addressing the multifaceted challenges of drug-related mortality post-incarceration (14, 24).
Preventing post-prison mortality poses a major challenge, requiring diverse solutions. Offering accessible health and mental health services upon release, including counseling and alternative drug access, improves post-release quality of life and mortality rates. Moreover, providing training in stress management, communication, and substance abuse helps address prisoners' psychological and physical challenges. Additionally, establishing employment and educational opportunities post-release reduces recidivism and enhances life satisfaction. Implementation by a multidisciplinary team, tailored to local contexts and individual needs, is crucial (31, 32).
One limitation of this study is that it focuses on ex-prisoners and does not include other groups of prisoners, such as parole prisoners. It is suggested that future research should investigate the effectiveness of interventions to reduce mortality after release from prison.
5.1. Conclusions
In conclusion, these findings confirm that there is an increased risk of drug-related death during the first two weeks after release from prison, and this risk persists throughout the first two months post-release. The causes of death were most often associated with prior heroin use, previous experiences with drug withdrawal, drug injection, and the use of sedatives in the six months preceding the death. The evidence from these systematic investigations emphasizes the urgent need for tailored interventions to address substance use disorders and implement overdose prevention strategies for individuals recently released from prison. Efforts to bridge the gap between incarceration and community reintegration should prioritize comprehensive substance abuse treatment programs to reduce the heightened risk of mortality in this vulnerable population.