1. Introduction
Ovarian tumors are rare in pregnant females. The most frequent ovarian tumors during pregnancy are mature cystic teratomas. They are present in 0.3% of pregnancies and usually between 16 - 20 weeks of gestation (1, 2). Benign cystic teratomas are most non physiological ovarian masses during pregnancy and the association of these cysts with pregnancy is reported since 1918 (3). The incidence of all ovarian tumors discovered during pregnancy is 0.3% to 5.4%. Functional cysts usually diagnosed incidentally in the first trimester, ultrasound are common and frequently regress spontaneously. The most frequent benign ovarian tumors diagnosed during pregnancy are cystic teratoma and cystadenoma (4).
The gold standard to determine an ovarian tumor during pregnancy is ultrasound, but it has a lower specificity in the diagnosis of pelvic malignancy. Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a suitable choice in the diagnosis of ovarian tumors during pregnancy that gives more information compared to ultrasound. Ultrasound-guided aspiration of ovarian tumors is not recommended during pregnancy (4). During pregnancy, the main complication of benign ovarian tumor is torsion of the adnex and it occurs in about 8% of the cases usually at the end of the first and during the second trimester (4).
The risks of surgery versus observation in females with dermoid cysts during pregnancy are a dilemma of weighing the risks of untreated mass versus surgery (3). Persistent, large size, complex or solid component and bilateral location of adnexal masses can be managed surgically that can decrease the risk of complications such as torsion, rupture and diagnosis of malignancies early (5). The influence of surgical intervention on gestational outcomes of females who underwent elective surgery of an adnexal mass in the second trimester of gestation in one study showed that one out of eight females had no complications after surgery and delivered healthy newborns at term. It was concluded that elective surgery of an adnexal mass in the second trimester of pregnancy is safe both for the mother and the fetus (6).
However, the most common benign ovarian tumor during pregnancy is dermoid cyst and the bilateral, multiple, large size and uncomplicated dermoid cysts are rare. On the other hand, there are many controversies regarding the management of dermoid cysts during pregnancy such as observation versus surgery. Therefore, it was decided to report the current case.
2. Case Presentation
A 28-year-old, pregnant, primipara female referred to gynecologist with complaint of pelvic mass that was incidentally reported in her sonography. The patient had no symptoms at that time and the gestational age based on her last menstrual period date and sonography was 20wk+4 days .She had no prior history regarding the presence of pelvic mass report in sonography before pregnancy.
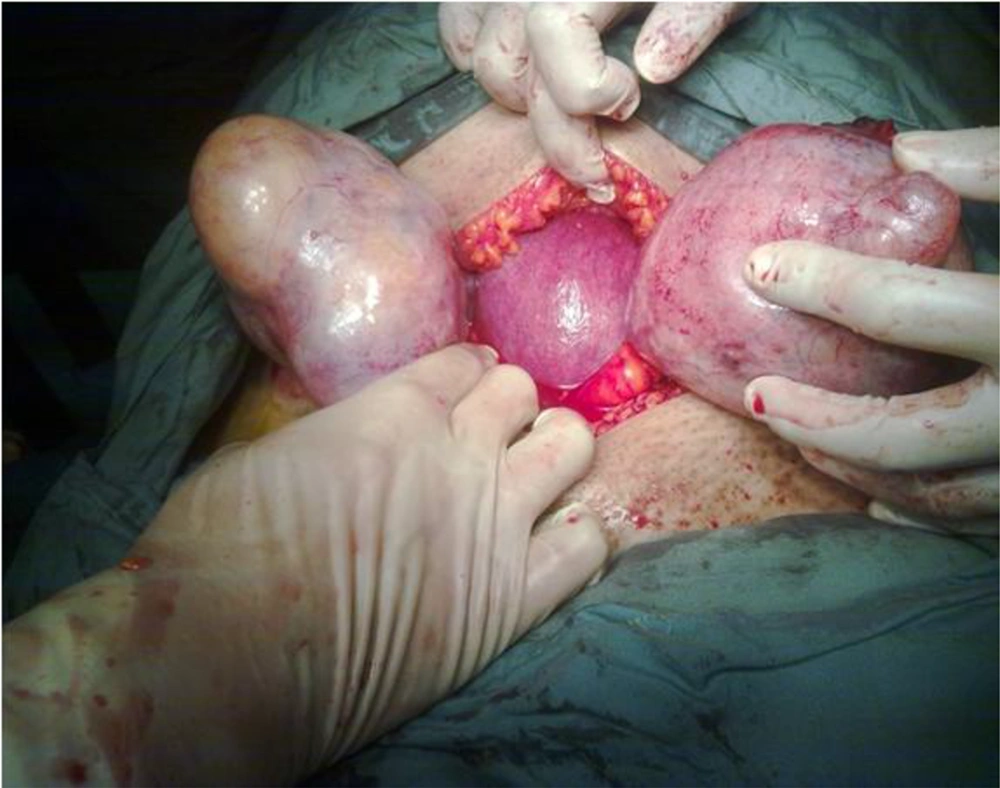
Her marriage date was one year ago and two times sonography during pregnancy in the 13th and 16th weeks of pregnancy showed bilateral ovarian mass that was suspicious to benign dermoid cysts. The last sonography was reported by two sonologists and there were a left adnexal mass 98 × 71 × 95 mm in diameter plus and echogenic area 31 × 21 × 25 mm in diameter with some calcification next to this mass. Also, there was a cystic mass 71 × 61 × 51mm in diameter in right adnexa (Figure 1) plus an alive, normal, breech fetus with gestational age of 20wk+4 days and posterior placenta was reported by sonography at that time. The serum tumor marker test consisted of alfa feto protein; CA125, BHCG, LDH, CEA and CA19-9 were in normal range.
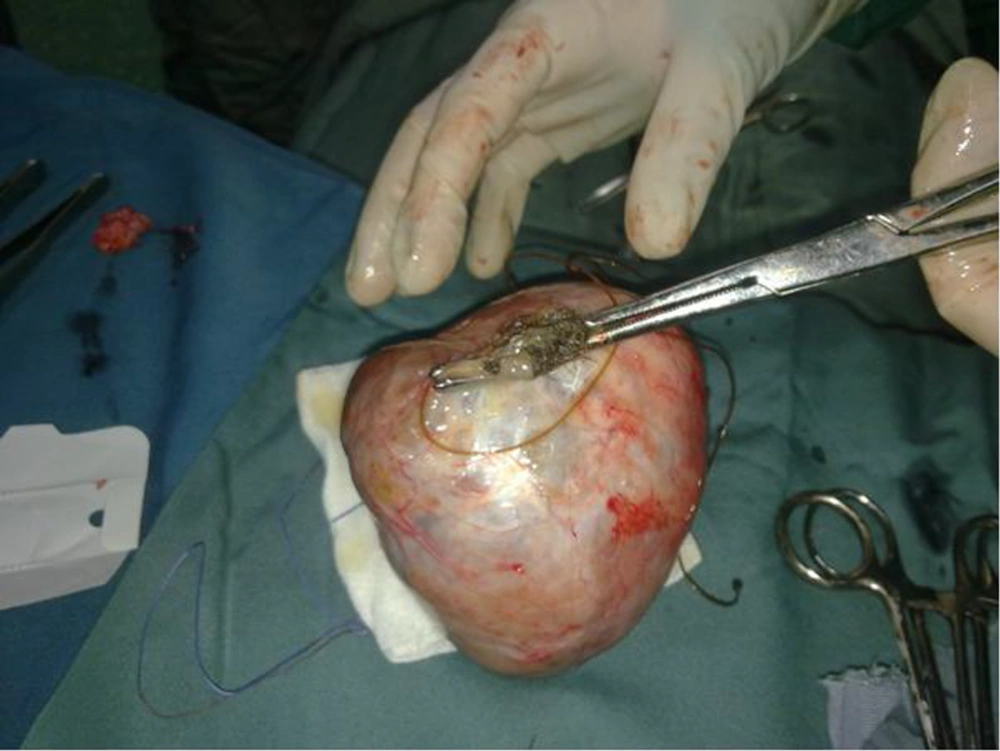
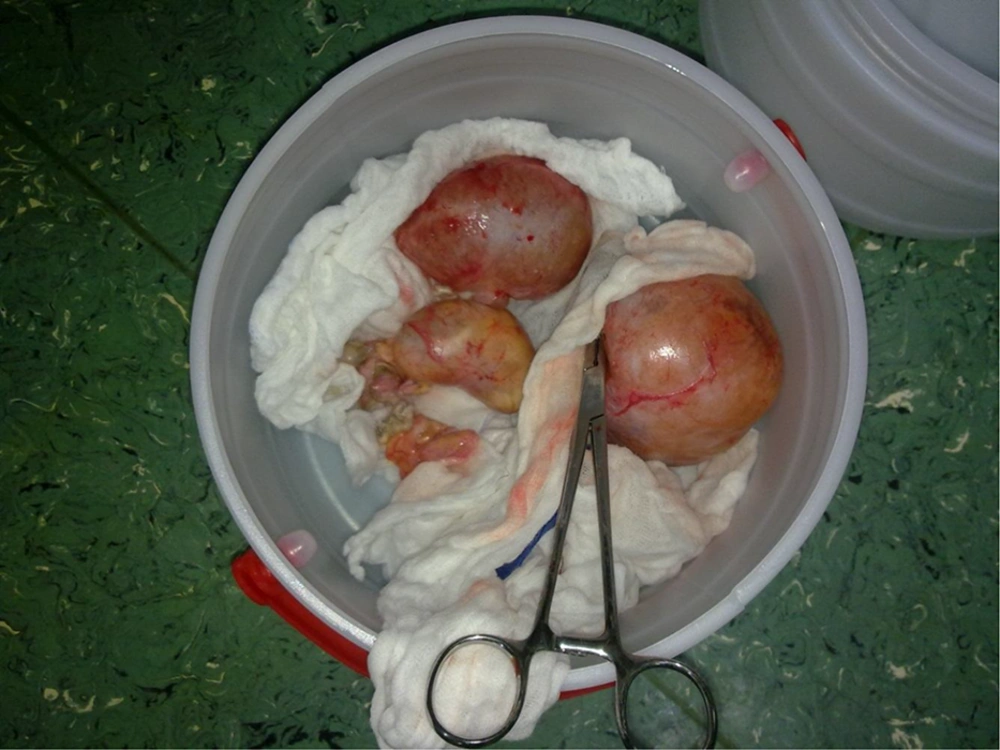
A laparotomy procedure with low transverse abdominal incision under spinal anesthesia was performed and six dermoid cysts including one dermoid cyst 10 × 70 × 96 mm in diameter (Figure 2) plus five dermoid cysts that two larger ones were 70 × 40 × 38 mm and 60 × 26 × 21 mm in diameter with three smaller one about 0.5 - 1 cm in diameters were removed (Figure 3). No spillage from the removed cysts happened during surgery. Also, during surgery it was tried to preserve every piece of normal ovary as much as possible.
Histopathologic evaluation of frozen section during surgery and final histopathology survey confirmed multiple, benign, mature dermoid cysts of ovaries. On the second day after operation the patient was discharged from hospital without any complications. The remained period of pregnancy was also uneventful and she had a cesarean delivery because of breech presentation, with alive, normal, female fetus, 3,430 grams on weight in 38th weeks of gestation.
3. Discussion
Most studies state that it is necessary to surgically treat bilateral dermoid cysts of the ovaries during pregnancy if they are more than 60 mm in diameter. Laparotomy is a common procedure for surgery (3), while laparoscopy is also sometimes used (3). The preferred time of surgery is the second trimester of gestation (3) the current study patient was a case of bilateral multiple benign dermoid cysts and was treated surgically by laparotomy approach in the 21st week of gestation.
The surgical approach of the dermoid cysts is important and most of the ovarian surgeries can be performed by laparoscopy. Mini laparotomy is another alternative between laparoscopy and laparotomy. Shorter operation time, removal of the mass with lower risk of rupture and preserving more ovarian tissue are some advantages of this approach in comparison to laparoscopy (7). In the selected cases of adnexal mass during pregnancy, close observation is an accepted alternative to surgery in patients with an adnexal mass (8). The gold standard to detect an ovarian tumor during pregnancy is ultrasound (4).
Laparotomy was performed for the present case because there were bilateral, multiple dermoid cysts and intact removal of all cysts and preserving healthy remnant ovarian tissue were very important. To prevent complications such as torsion and based on the insistence of the patient to do surgery, surgical approach was employed. The ovarian mass was diagnosed by trans abdominal ultrasound performed by two sonologists.
During pregnancy, tumor markers are not reliable to assess the risk of malignancy of ovarian masses (4). Surgery is recommended in patients with symptoms of adnexal torsion at any gestation. Laparoscopy is possible during the first and second trimester to manage symptomatic presumed benign ovarian tumors. The risk of miscarriage following surgery for ovarian tumor during pregnancy is estimated 2.8% and the risk of torsion is increased during the postpartum period (4). Complete removal of the cysts, reduction of the risk of recurrence, prevention of the risk of tumor dissemination and preservation of healthy ovarian tissue should considered during the surgery of benign ovarian tumors (9).
In the current case, the serum tumor markers were in normal ranges and complications did not occur before or after surgery; the route of surgery was laparotomy. In this case, all cysts were completely removed, all removed cysts were kept intact during surgery and the preservation of healthy ovarian tissue was performed optimally too.
Auto amputation of ovary may rarely develop following torsion of dermoid cysts and it may be more commonly implanted on the greater omentum. During cesarean section of a 33-year-old pregnant female the absence of the right ovary implanted in the cul-de-sac following torsion of dermoid cyst was incidentally observed (10). A very rare complication of ruptured dermoid cysts is granulomatous peritonitis. Granulomatous peritonitis happened in a 27-year-old primigravida female postoperatively following surgical removal of a ruptured dermoid cyst in the second trimester of pregnancy (11); another rare but ominous complication of mature cystic teratomas is malignant transformation. A case of squamous cell carcinoma developed from a dermoid cyst during pregnancy is reported (12).
Fortunately, none of these complications occurred in the current study patient and her pregnancy was uneventful.
In conclusion, it seems that intact removal of multiple ovarian benign dermoid cysts by laparotomy during the second trimester of pregnancy could prevent complications of cysts and adverse pregnancy outcome.