1. Background
Lower Back Pain (LBP) is the most common musculoskeletal disorder (1, 2). The coordination between deep and superficial trunk muscles is altered in recurrent LBP (3). Delayed and reduced activity of the lumbar multifidus muscles has been reported during functional and postural activities (4, 5). However, an increased activity of superficial trunk muscles is often reported (6, 7), with variation between subjects and activities (6, 8). The intervertebral motion is controlled by the lumbar multifidus (LM), transverses abdominis, diaphragm and pelvic floor muscles (9, 10). Increased activities of superficial trunk muscles, in addition to delayed and reduced activity of the LM muscles are the major contributing factors in patients with chronic LBP (6). Spinal stability is provided by trunk muscles functions such as strength, endurance and coordination (11).
In the LBP, the treatment program aims to target deep muscle contraction to prevent muscle atrophy of the deep muscles and enhance stability of the lumbar spine segments (12, 13). A previous study reported an increased LM cross sectional area following functional stabilization training using low level, isometric LM contraction through mat based strengthening exercises (14). Moon et al. (15) reported significant improvements in lumbar extensors strength and reduced LBP symptoms following lumbar stabilization exercise in patients with chronic LBP. Another study reported significant reduction of functional disability and lumbar lordosis angle following lumbar stabilization exercise in patients with chronic LBP (16). In addition, Hicks et al. (17) reported significant reduction in functional disability following eight weeks of lumbar stabilization exercises. More recently, Kong et al. (18) investigated the effects of prone bridge exercises compared to conventional supine bridge exercises in the lumbar stabilization protocol in individuals with chronic LBP. They observed significant improvements in the trunk stability following prone bridge exercises compared to conventional supine bridge exercises in individuals with chronic LBP (18).
Recently, the use of labile surfaces in lumbar stabilization programs were investigated to provide a multi-planar challenge to the body, and it was shown to improve LM recruitment compared to similar exercise on a firm surface (19-27). Marshall and Murphy (19) reported that the use of the SB might enhance functional capacity of individuals with chronic nonspecific LBP. Similarly, Marshall and Murphy (21) reported a significant improvement in self-rated disability and greater improvement in the low back flexion-relaxation response after supervised SB training in individuals with chronic LBP. In addition, Chung et al. (23) reported an increased functional ability and cross-sectional area of the LM following lumbar stabilization exercise using a ball in individuals with chronic LBP. Furthermore, Yoon et al. (24) reported a significant reduction in pain intensity and a higher rate of increased bone mineral density following a lumbar stabilization exercise on a ball compared to lumbar stabilization exercise on the floor. Moreover, Scott et al. (27) showed increased cross-sectional area of LM as the lability of the sitting surface increased, indicating that the Swiss Ball (SB) was more effective to enhance LM activity compared to a non-labile sitting surface. More recently, O’Keeffe et al. (26) suggested that more investigations of lumbar stabilization training using a ball are required before making any strong conclusions about their efficacy.
2. Objectives
The purpose of the present study was to compare the effectiveness of trunk stabilization exercises using a gym ball and conventional back exercises in increasing the stability of trunk muscles in chronic LBP.
3. Patients and Methods
3.1. Participants
Thirty male subjects were randomly assigned to two groups. The experimental group received trunk stabilization exercises whereas the control group received conventional back care exercises. The criteria for inclusion were: age of 30 - 40 years and having lower back pain as a primary complaint due to a mechanical cause, for a duration of more than three months. Subjects were excluded if they had a history of spinal tumor, spinal infection, or inflammatory disease affecting the spine, lower limb or spinal surgery, fractures of spine or spinal deformities, for example, spondylolisthesis, contraindications to exercise therapy, sign of nerve root compression (defined as decreased tendon reflexes), sensory loss and motor deficits, severe osteoporosis, lumbar canal stenosis and acute disc herniation. All the participants provided a signed written informed consent.
3.2. Sample Size Estimation
Based on the results of power analysis, a total sample of thirty subjects was required to achieve 80% power at P < 0.05. The GraphPad StatMate version 2.00 for Windows (GraphPad software, San Diego California USA) was used to calculate the sample size.
3.3. Randomization
All the subjects, who fulfilled the inclusion criteria, signed a written informed consent form approved by the institution ethics committee. The study followed the principles of the declaration of Helsinki. Subjects were allowed to withdraw from the study at any time. All the subjects received explanation about the procedures and purposes of the study. After baseline assessment, subjects were allocated randomly to the experimental group (trunk stabilization exercises) or control group (conventional back care exercises) by choosing an opaque envelope, which contained the names of the groups.
3.4. Outcome Measures
The baseline measurements were carried out for abdominal muscle endurance, pain intensity and functional disability. Measurements were obtained by an independent therapist, who was unaware of the group assignment. Abdominal muscle endurance was measured using the pressure Biofeedback unit (PBU) (28, 29). The PBU was placed at the lower abdomen in line with the anterior superior iliac spine and center using the naval as reference. The PBU was inflated to a baseline pressure of 70 mm Hg. The subject was asked to draw-in their abdomen, so that the pressure in the bag drops. A drop in pressure of 6 - 10 mm Hg indicates that the contraction was correctly performed. The examiner noted the drops in pressure from the baseline. The reading of the PBU was taken three times, with a 20 second rest interval. The pain intensity and functional disability were measured using the visual analog scale (VAS) and modified oswestry disability questionnaire (MODQ), respectively (30, 31).
3.5. Interventions
The participants received a 40-minute session of supervised exercise program, two times a week for six weeks as detailed in Table 1 (12). For each exercise, the subjects performed 10 repetitions with 10-second holds and 5-second rest in between the repetition. The patient was given a one- to two-minute rest in between each type of exercise. The participants were asked to report any adverse event related or unrelated to the exercises. The participants were asked to avoid any other physical activity program during the study period.
| S. N. | Experimental Group (Trunk Stabilization Exercises) | Control Group (Conventional Back Care Exercises) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The subjects lifted the gym ball up and held it between their legs with both knees flexed in the supine position. Later, the subjects lifted the gym ball up and held it between their legs with knee extended in supine position. | Supine lying-leg lifts: The participants were made to lie down in the supine position. The participants were instructed to lift their leg one-by-one and hold it for ten seconds. After that, the participants were asked to lift both their legs simultaneously and hold it for ten seconds. |
| 2 | Subjects lifted their pelvis up to the bridged position and held it, while supporting themselves with both legs on the gym ball and with their knees extended in supine position. Later, subjects lifted their pelvis up to the bridged position and held it, while supporting their head on the gym ball and with their feet on the floor, with both knees flexed in the supine position. | Abdominal crunches in crook lying position: The participants were made to lie in a crook position with their hands placed behind their head and were asked to lift their trunk upwards, rotate to either side towards their knee and hold this position for ten seconds. |
| 3 | Subjects placed both their hands on the gym ball and their knees flexed on the floor, maintaining four- point kneeling position. Later, subjects maintained a four-point kneeling position with one arm and leg in extension. | Prone lying-LEG lifts: The participants were made to lie in a prone position. The participants were instructed to lift their leg one-by-one and hold it for ten seconds. After that, the participants were asked to lift both their legs simultaneously and hold it for ten seconds. |
| 4 | The subjects lifted their body up to the push up position and held it, while supporting themselves with both legs on the gym ball and hands on the floor in prone position. Later, subjects lifted their body up to the push up position and held it, while supporting themselves with their hand on the gym ball and their toes on the floor in prone position. | Prone lying-trunk lifts: The participants were made to lie in a prone position and kept both their hands by the side of their body. The participants were instructed to lift their trunk off the bed and hold the position for ten seconds. |
Exercise Program
3.6. Data Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 16 version software. Repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) (multivariate test) was done to find differences between baseline and measurements taken during weeks two, four and six for all the outcomes including abdominal muscle endurance, VAS score, and MODQ score in both groups. Post hoc analysis using Bonferroni’s test was done to find pairwise differences. Univariate ANOVA test was done to compare differences between baseline measures and those taken during weeks two, four and six for all the outcomes. The alpha (probability) level was P < 0.05.
4. Results
4.1. Participants Characteristics
The participant’s demographic details including age, weight, height and body mass index are given in Table 2. These variables had no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05).
4.2. Abdominal Muscle Endurance
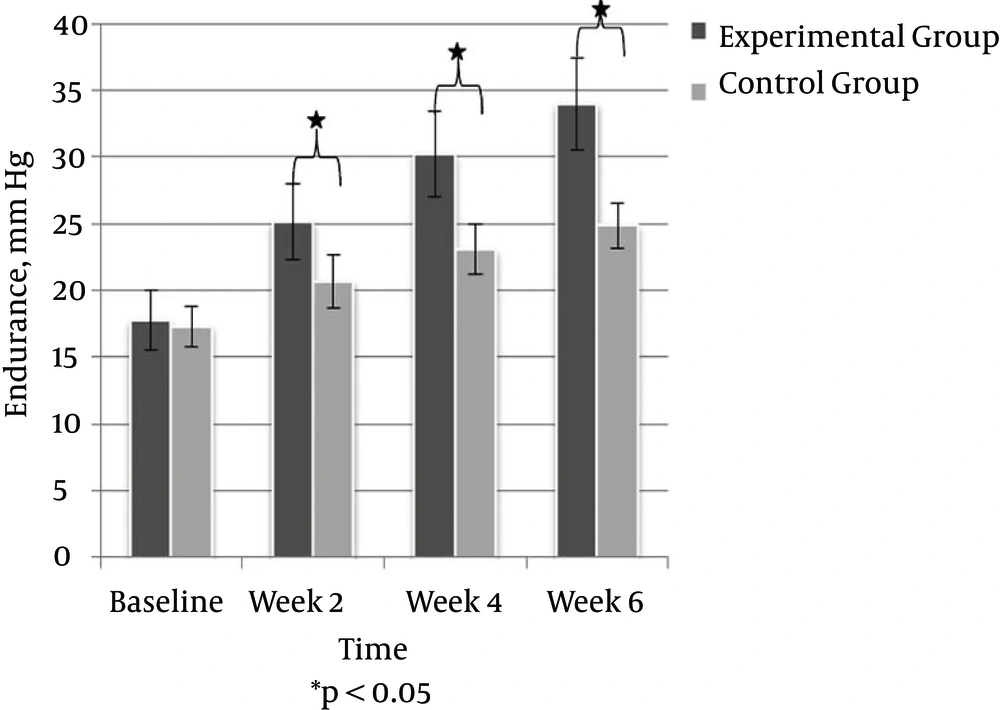
Abdominal muscle endurance was significantly improved at the end of week two in both groups, (P < 0.001) which was maintained until the end of the treatment (P = 0.001) in both groups (Table 3). Regarding between group comparisons, the abdominal muscle endurance was significantly improved in the experimental group compared to the control group at the end of week two (P = 0.001), which remained significant till week six (P = 0.001) (Figure 2).
| Variables | Baselinea | Week 2a | Week 4a | Week 6a | Repeated Measure ANOVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | |||||
| Endurance | ||||||
| Experimental Group | 17.76 ± 2.25 | 25.13 ± 2.86 | 30.23 ± 3.19 | 33.99 ± 3.48 | 255.782 | 0.001 |
| Control Group | 17.28 ± 1.48 | 20.66 ± 2.01 | 23.08 ± 1.83 | 24.85 ± 1.67 | 227.068 | 0.001 |
| VAS | ||||||
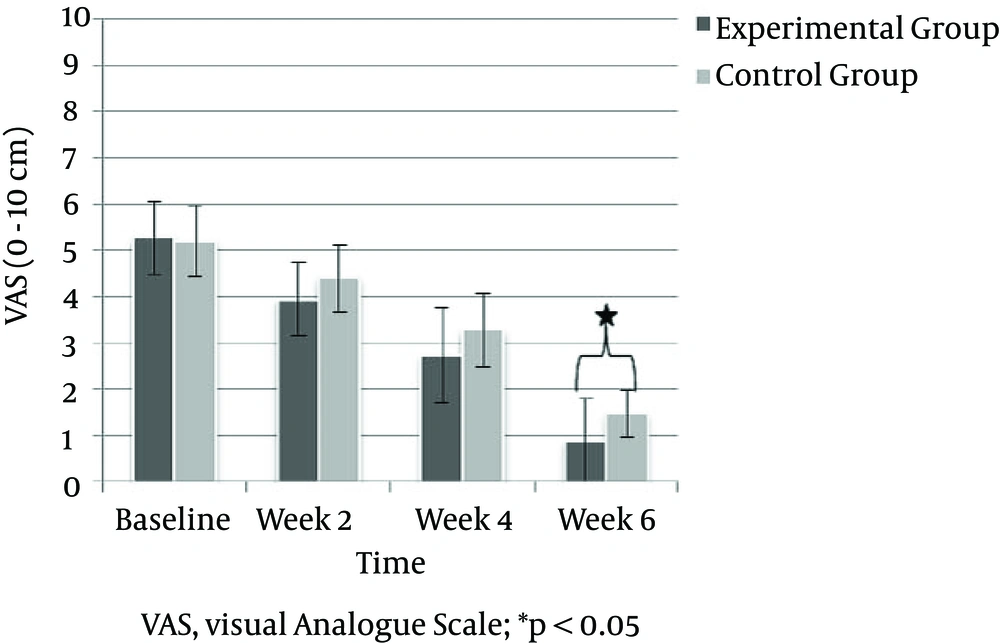
| Experimental Group | 5.27 ± 0.79 | 3.93 ± 0.79 | 2.73 ± 1.03 | 0.87 ± 0.91 | 184.268 | 0.001 |
| Control Group | 5.20 ± 0.77 | 4.40 ± 0.73 | 3.27 ± 0.79 | 1.47 ± 0.51 | 159.758 | 0.001 |
| MODQ | ||||||
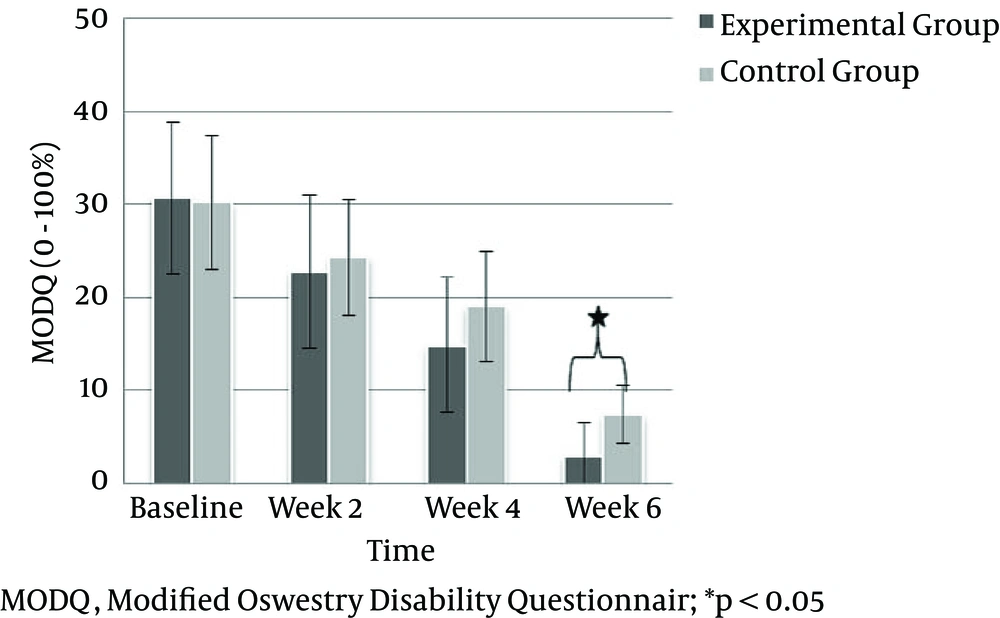
| Experimental Group | 30.67 ± 8.05 | 22.80 ± 8.30 | 14.80 ± 7.24 | 2.93 ± 3.53 | 178.255 | 0.001 |
| Control Group | 30.13 ± 7.19 | 24.27 ± 6.22 | 18.93 ± 5.84 | 7.33 ± 3.08 | 176.685 | 0.001 |
Comparison of Endurance, Pain Intensity and Functional Disability
4.3. Pain Intensity
The VAS score was significantly decreased at the end of week two in both groups (P < 0.001), which was maintained until the end of the treatment in both groups (P < 0.001). Regarding between-group comparisons, the VAS score remained statistically insignificantly until week four (P > 0.05). At week six, the VAS score was significantly reduced in the experimental group compared to the control group (P = 0.035) (Figure 3).
4.4. Functional Disability
The MODQ score was significantly decreased at the end of week two in both groups (P = 0.001), which was maintained until the end of the treatment in both groups (P = 0.001). Furthermore, the MODQ score remained statistically insignificant until week four (P > 0.05). At week six, the MODQ score was significantly reduced in the experimental group compared to the control group (P = 0.001) (Figure 4).
5. Discussion
This study was designed to compare the efficacy of trunk stabilization exercises using a gym ball and conventional back care exercises for patient with chronic LBP. The results of this study demonstrated that trunk stabilization exercises bring greater gains in all the outcomes including, endurance, VAS score, and MODQ score. Analysis of the results indicates greater improvement in the abdominal muscle endurance at week two, four, and six in the trunk stabilization exercises group compared to the conventional back care exercises group. However, greater reduction of pain intensity and functional disability was seen only at week six in the trunk stabilization exercises group compared to the conventional back care exercises group.
In agreement with the present study, Franca et al. (12) reported that six weeks of lumbar stabilization exercises was superior to superficial strengthening for reducing pain, functional disability, and improving transverse abdominis activation capacity in individuals with chronic LBP. In a systematic review, Ferreira et al. (13) concluded that specific stabilization exercise was effective in reducing pain intensity and functional disability in chronic LBP. Another study reported a significant improvement in self-rated disability in individuals, who received supervised SB exercise compared to an exercise advice group (22). Similarly, Cho et al. (16) concluded that the lumbar stabilization exercise was more effective compared to the conservative treatment for reducing functional disability and lumbar lordosis angle. In addition, Moon et al. (15) reported significant improvements in the lumbar extensor strength and function following lumbar stabilization exercise compared to dynamic strengthening exercise in individuals with nonspecific chronic LBP. Furthermore, Marshall and Murphy (19) reported significant improvement in pain and function in individuals with chronic nonspecific LBP over the course of a 12-week rehabilitation program using the SB. Moreover, Marshall and Murphy (21) reported that the supervised exercise program using SB leads to a greater improvement in self-rated disability in individuals with chronic nonspecific LBP. Recently, a study by Chung et al. (23) indicated that stabilization exercises using a ball could improve the cross-sectional area of LM, pain and function in individuals with non-specific chronic LBP. In addition, Oh et al. (25) reported significant improvement in the Oswestry Low Back Pain Disability Index and VAS scores following SB exercise in chronic LBP patients. More recently, Scott et al. (27) reported an increased cross-sectional area of LM in individuals sitting on a liable surface, indicating that the SB was more effective to enhance LM activity compared to a non-labile sitting surface.
Exercises on unstable surfaces, such as SB exercises, cause co-contraction of global and local muscles at the beginning of motor control, thereby improve stability of the spine (32). Similarly, Imai et al. (33) suggested that the use of SB exercises resulted increased activity of all trunk muscles compared to exercises on the floor. Better improvements seen in the lumbar stabilization exercises group may be explained due to the fact that this exercise program specifically targets those muscles, which are primarily affected in LBP (12). Previous studies identified selective atrophy of the LM and decreased activity of transverse abdominis in individuals with LBP (34, 35). In addition, Richardson et al. (36) reported that both these muscles are vital for the stability of the lumbar spine, reducing compressive forces on the spinal structures.
The present study had several potential limitations. The study protocol had a short duration of only six weeks. Long-term follow-up was not part of the present study. In addition, the present study was limited to only male participants.
In conclusions, trunk stabilization exercises have shown greater gains in endurance, reduction of pain intensity and functional disability. This study may provide the rational for clinical use of trunk stabilization exercises. Future research is needed with long-term follow-ups.