1. Background
Delayed graft function (DGF) is defined as acute renal failure leading to increased immunogenicity of post-transplant grafts and the risk of rejection and mortality in post-transplant patients. Numerous studies have been conducted to assess the incidence and risk factors of DGF, especially in patients with positive panel-reactive antibody (PRA) and negative/positive donor-specific antibodies (DSA), as well as in deceased donor kidney transplantation (1-3). Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) usually leads to the loss of the graft. Transplantation across human leukocyte antigen (HLA) barriers, including positive PRA can be a risk factor for acute humoral rejection and worsening transplant results (4-6).
Some authors have previously confirmed that ischemia and continuous immune response to the graft were the main causes of DGF and acute graft rejection. Optimal induction interventions should be able to repair renal structural damage while inhibiting the immune response (7-11). There are some studies about DGF, acute rejection, and graft loss in donation after cardiac death and brain death; however, studies on living donation are limited (12-14). In this study, we focused on the association between DGF and acute rejection in patients who received kidneys from living donors with positive PRA and negative DSA.
2. Objectives
The current study aimed at the evaluation of delayed graft function (DGF) and acute rejection (AR) in highly sensitized patients and their effects on kidney function for six months post-transplantation.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design and Setting
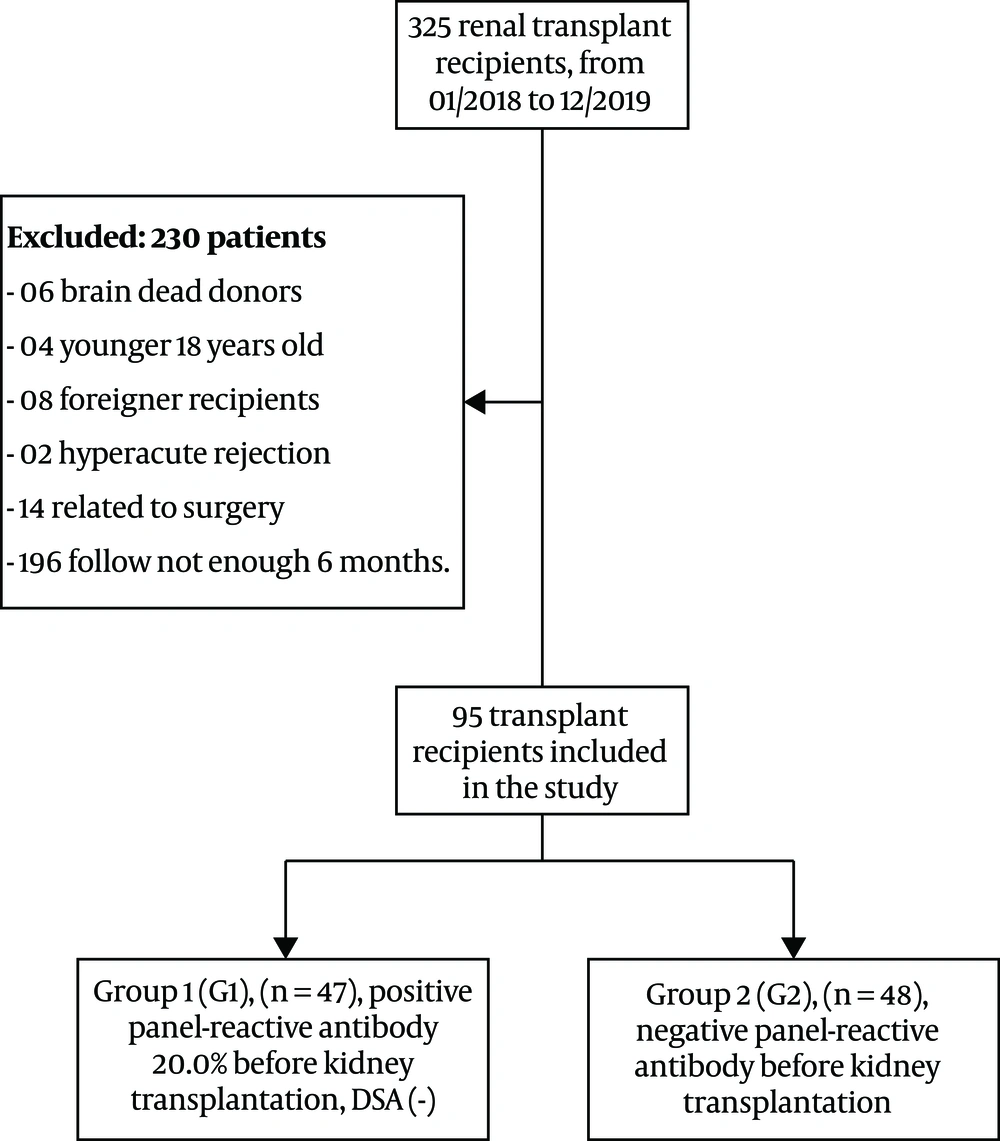
We studied 325 patients undergoing kidney transplantation from living donors at the Department of Nephrology and Hemodialysis, Military Hospital 103, from January 2018 to December 2019. The inclusion criteria were living-donor kidney transplantation, ages above 18 years, and positive PRA < 20.0%. We excluded patients with ages below 18 years, the persistence of positive DSA before and after transplantation, transplanted nephrectomy due to hyper-acute rejection, DGF related to surgery, lack of a follow-up for six months, signs of infection at the study time, and renal biopsy-diagnosed post-transplanted chronic kidney disease. The remaining 95 kidney transplant patients gave their written informed consent before participation in the study.
We performed cross matches and tests for the HLA phenotype and anti-HLA antibody screening in all donors and patients according to the criteria proposed by the Vietnam Health Ministry and the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) in 2003 (15). We divided all patients into two groups based on the status of positive PRA before transplantation. Group 1 (G1, n = 47) included patients with positive PRA < 20.0% and negative donor-specific antibodies, and group 2 (G2, n = 48) included patients with negative PRA.
We asked and examined the patients and collected data from medical records to fully determine clinical characteristics and laboratory parameters at the time of transplantation and seven days (D7), one month (M1), three months (M3), and six months (M6) after transplantation. We estimated graft function as an outcome using the chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation (16).
3.2. Immunosuppressive Therapy
Monoclonal anti-IL-2 receptor antibodies (Basiliximab 20 mg, IV) were applied for all patients on the day of transplantation and the fourth day after transplantation. Besides, all patients received methylprednisolone 500 mg, IV, on the day of transplantation that was maintained after transplantation.
Maintenance immunosuppression therapy included a combination of calcineurin inhibitor (Tacrolimus 0.1 mg/kg bid or Neoral 5 mg/kg bid, dose adjusted according to drug levels in the blood) and sodium mycophenolate (1000 mg bid, adjusted according to the body surface, gastrointestinal tolerance, peripheral white and red blood cell counts).
3.3. The Diagnosis of Delayed Graft Function and Graft Rejection
The peripheral blood of the patient was taken, and the serum was collected to determine complete blood counts, glucose, urea, creatinine, protein, albumin, hs-CRP, and the level of calcineurin inhibitor drugs in the first seven days after transplantation. DGF was defined as decreased serum creatinine < 25% within the first 24 hours compared to pre-transplantation, and the need for hemodialysis in the first seven days (17).
Graft rejection was determined by elevated serum creatinine or a new appearance of proteinuria, confirmed by allograft biopsy based on Banff classification in 2013, revised in 2015 (18). Antibody-mediated acute rejection was diagnosed based on the histological criteria and the presence of DSA following the Banff classification (18). The patients with AMR were treated by plasmapheresis, a low-dose of intravenous immunoglobulin, and anti-thymocyte globulin for three to five days. Patients with acute cellular rejection were treated by three pulses of methyl-prednisolone.
3.4. Statistical Analysis
Normally distributed continuous data were represented as mean ± SD and analyzed by student t-test, one-way ANOVA, and post hoc Bonferroni test. Data with skewed distributions were represented as median (25 percentile-75 percentile) and analyzed by the Mann-Whitney and Friedman tests. Categorical data were presented as the frequency with percentages and analyzed by the chi-square test. Multivariable-adjusted regression analysis was performed to predict DGF. receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to predict acute rejection in all patients. All data were calculated by the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 20.0 software (Chicago, IL, USA). A P value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
4. Results
The results in Table 1 showed no differences in the mean age, etiology of CKD, treatment method of CKD before kidney transplantation, the ratio of hepatitis infection, level of serum urea, creatinine, hs-CRP, hemoglobin, the ratio of anemia, WBC, and HLA matching between G1 and G2 with P > 0.05. However, the ratio of males, history of sensitizing events, serum albumin level, and GFR were significantly different between the two groups (P < 0.05). Specifically, the DGF and GR proportion in group 1 were significantly higher than those of group 2 with P < 0.05 (P < 0.05).
| Characteristics | All (N = 95) | G1 (N = 47) | G2 (N = 48) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 39.76 ± 12.56 | 39.85 ± 12.36 | 39.67 ± 12.88 | 0.943 |
| Gender | 0.008 | |||
| Male | 61 (64.2) | 24 (51.1) | 37 (77.1) | |
| Female | 34 (35.8) | 23 (48.9) | 11 (22.9) | |
| Donation | N/A | |||
| Living donors | 95 (100) | 47 (100) | 48 (100) | |
| Brain/cardiac dead donors | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Etiology | 0.322 | |||
| CGN | 82 (86.3) | 41 (87.2) | 41 (85.4) | |
| CPN | 3 (3.2) | 0 (0) | 3 (6.3) | |
| DN | 8 (8.4) | 5 (10.6) | 3 (6.3) | |
| Hypertension | 2 (2.1) | 1 (2.1) | 1 (2.1) | |
| Pre-transplantation treatment | 0.17 | |||
| Hemodialysis | 78 (82.1) | 41 (87.2) | 37 (77.1) | |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 6 (6.3) | 3 (6.4) | 3 (6.3) | |
| Transplanted | 3 (3.2) | 2 (4.3) | 1 (2.1) | |
| Pre-dialysis | 8 (8.4) | 1 (2.1) | 7 (14.6) | |
| History of sensitizing events | 0.002 | |||
| Blood transfusion | 22 (23.2) | 12 (25.5) | 10 (20.8) | |
| Pregnancy | 11 (11.6) | 7 (14.9) | 4 (8.3) | |
| Pregnancy + Blood transfusion | 10 (10.5) | 10 (21.3) | 0 (0) | |
| Transplanted | 3 (3.2) | 2 (4.3) | 1 (2.1) | |
| None | 49 (51.6) | 16 (34) | 33 (68.8) | |
| Hepatitis infection | 0.108 | |||
| No infection | 79 (83.2) | 36 (76.6) | 43 (89.6) | |
| HBV | 4 (4.2) | 2 (4.3) | 2 (4.2) | |
| HCV | 11 (11.6) | 9 (19.1) | 2 (4.2) | |
| HBV + HCV | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.1) | |
| Urea, mmol/L | 16.1 (13.66 - 23.1) | 16.74 (13.61 - 23.51) | 16.05 (13.74 - 22.41) | 0.985 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 697 (581.5 - 832.7) | 727.51 (581.5 - 865.3) | 665.78 (578.74 - 795.42) | 0.252 |
| Albumin, g/L | 41.5 ± 4.34 | 42.53 ± 4.34 | 40.5 ± 4.14 | 0.022 |
| hs-CRP, mg/L | 2 (0.69 - 5.92) | 1.83 (0.57 - 4.16) | 2.35 (0.8 - 6.47) | 0.268 |
| Hemoglobin, g/L | 104.78 ± 13.85 | 103.66 ± 15.22 | 105.83 ± 12.51 | 0.454 |
| Anemia | 88 (92.6) | 41 (87.2) | 47 (97.9) | 0.059 |
| WBC, g/L | 7.4 (5.97 - 9.37) | 7.2 (5.95 - 9.3) | 7.84 (6.02 - 9.82) | 0.409 |
| HLA matching | 0.922 | |||
| 0/6 | 1 (1.1) | 1 (2.1) | 0 (0) | |
| 1/6 | 7 (7.4) | 4 (8.5) | 3 (6.3) | |
| 2/6 | 28 (29.5) | 15 (31.9) | 13 (27.1) | |
| 3/6 | 36 (37.9) | 17 (36.2) | 19 (39.6) | |
| 4/6 | 16 (16.8) | 7 (14.9) | 9 (18.8) | |
| 5/6 | 4 (4.2) | 2 (4.3) | 2 (4.2) | |
| 6/6 | 3 (3.2) | 1 (2.1) | 2 (4.2) | |
| GFR of donor, mL/min | 57.73 ± 5.72 | 59.28 ± 5.61 | 56.25 ± 5.47 | 0.009 |
| DGF | 14 (14.7) | 13 (27.7) | 1 (2.1) | < 0.001 |
| GR | ||||
| All | 8 (8.4) | 7 (14.9) | 1 (2.1) | 0.031 |
| Humoral rejection | 5 (5.3) | 4 (8.5) | 1 (2.1) | 0.204 |
| Cellular rejection | 3 (3.2) | 3 (6.4) | 0 (0) | 0.117 |
Abbreviations: CGN, chronic glomerulonephritis; CPN, chronic pyelonephritis; DN, diabetic nephropathy; DGF, delayed graft function; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; GR, graft rejection; G1, group 1 with the presence of positive panel-reactive antibody, DSA (-) before transplantation; G2, group 2 with negative panel-reactive antibody before transplantation; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; hs-CRP, C-reactive protein-high sensitivity; N/A, not available; PRA, positive panel-reactive antibody; WBC, white blood cell.
aValues are expressed as No. (%) or mean ± SD.
Table 2 shows that there were no differences in the mean age, the ratio of males, etiology of CKD, treatment method of CKD before kidney transplantation, the ratio of hepatitis infection, hs-CRP, hemoglobin, the ratio of anemia, WBC, and HLA matching between DGF (+) patients and DGF (-) patients, with P > 0.05. However, in the DGF (+) group, the level of serum urea, creatinine, and the ratio of PRA were significantly higher than those in the DGF (-) group (P < 0.05).
| Characteristics | All (N = 95) | DGF (+) (N = 14) | DGF (-) (N = 81) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 39.76 ± 12.56 | 39.86 ± 13.08 | 39.74 ± 12.55 | 0.975 |
| Gender | 0.225 | |||
| Male | 61 (64.2) | 11 (78.6) | 50 (61.7) | |
| Female | 34 (35.8) | 3 (21.4) | 31 (38.3) | |
| Donation | N/A | |||
| Living donors | 95 (100) | 14 (100) | 81 (100) | |
| Brain/cardiac dead donors | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Etiology | 0.807 | |||
| CGN | 82 (86.3) | 13 (92.9) | 69 (85.2) | |
| CPN | 3 (3.2) | 0 (0) | 3 (3.7) | |
| DN | 8 (8.4) | 1 (7.1) | 7 (8.6) | |
| Hypertension | 2 (2.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.5) | |
| Pre-transplantation treatment | 0.825 | |||
| Hemodialysis | 78 (82.1) | 11 (78.6) | 67 (82.7) | |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 6 (6.3) | 1 (7.1) | 5 (6.2) | |
| Transplanted | 3 (3.2) | 1 (7.1) | 2 (2.5) | |
| Pre-dialysis | 8 (8.4) | 1 (7.1) | 7 (8.6) | |
| History of sensitizing events | 0.888 | |||
| Blood transfusion | 22 (23.2) | 3 (21.4) | 19 (23.5) | |
| Pregnancy | 11 (11.6) | 2 (14.3) | 9 (11.1) | |
| Pregnancy + blood transfusion | 10 (10.5) | 1 (7.1) | 9 (11.1) | |
| Transplanted | 3 (3.2) | 1 (7.1) | 2 (2.5) | |
| None | 49 (51.6) | 7 (50) | 42 (51.9) | |
| Hepatitis infection | 0.156 | |||
| No infection | 79 (83.2) | 10 (71.4) | 69 (85.2) | |
| HBV | 4 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 4 (4.9) | |
| HCV | 11 (11.6) | 4 (28.6) | 7 (8.6) | |
| HBV + HCV | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.2) | |
| Urea, mmol/L | 8.11 (6.8 - 10.02) | 13.53 (8.82 - 28.67) | 7.92 (6.71 - 9.11) | < 0.001 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 86.45 (72.52 - 102.52) | 119.3 (84.93 - 248.79) | 85.38 (68.5 - 95.67) | 0.001 |
| Hemoglobin, g/L | 100.89 ± 14.24 | 104.58 ± 16.45 | 100.34 ± 13.92 | 0.339 |
| Anemia | 88 (94.6) | 11 (91.7) | 77 (95.1) | 0.627 |
| WBC, g/L | 10.2 (7.56 - 12.9) | 10.81 (7.93 - 12.92) | 9.95 (7.45 - 12.9) | 0.761 |
| GFR, mL/min | 83.9 (72.25 - 97.32) | 58.83 (23.71 - 87.08) | 85.2 (73.98 - 98.16) | 0.003 |
| HLA matching | 0.793 | |||
| 0/6 | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.2) | |
| 1/6 | 7 (7.4) | 2 (14.3) | 5 (6.2) | |
| 2/6 | 28 (29.5) | 3 (21.4) | 25 (30.9) | |
| 3/6 | 36 (37.9) | 6 (42.9) | 30 (37) | |
| 4/6 | 16 (16.8) | 3 (21.4) | 13 (16) | |
| 5/6 | 4 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 4 (4.9) | |
| 6/6 | 3 (3.2) | 0 (0) | 3 (3.7) | |
| PRA | < 0.001 | |||
| Positive | 47 (49.5) | 13 (92.9) | 34 (42) | |
| Negative | 48 (50.5) | 1 (7.1) | 47 (58) |
Abbreviations: CGN, chronic glomerulonephritis; CPN, chronic pyelonephritis; DGF, delayed graft function; DN, diabetic nephropathy; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; N/A, not available; PRA, positive panel-reactive antibody; WBC, white blood cell.
aValues are expressed as No. (%) or mean ± SD.
We found no differences in the mean age, etiology of CKD, treatment method of CKD before kidney transplantation, the ratio of hepatitis infection, level of serum urea, creatinine, hs-CRP, hemoglobin, the ratio of anemia, WBC, and HLA matching between the GR group and the non-GR group, with P > 0.05. However, the level of serum urea, creatinine, the ratio of PRA (+), and DGF (+) in the GR group were significantly higher than those in the non-GR group (P < 0.05) (Table 3).
| Characteristics | All (N = 95) | GR (N = 8) | Non-GR (N = 87) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 39.76 ± 12.56 | 36.38 ± 12.46 | 40.07 ± 12.59 | 0.429 |
| Gender | 0.252 | |||
| Male | 61 (64.2) | 7 (87.5) | 54 (62.1) | |
| Female | 34 (35.8) | 1 (12.5) | 33 (37.9) | |
| Donation | N/A | |||
| Living donors | 95 (100) | 8 (100) | 87 (100) | |
| Brain/cardiac dead donors | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Etiology | 0.709 | |||
| CGN | 82 (86.3) | 8 (100) | 74 (85.1) | |
| CPN | 3 (3.2) | 0 (0) | 3 (3.4) | |
| DN | 8 (8.4) | 0 (0) | 8 (9.2) | |
| Hypertension | 2 (2.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.3) | |
| Pre-transplantation treatment | 0.292 | |||
| Hemodialysis | 78 (82.1) | 6 (75) | 72 (82.8) | |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 6 (6.3) | 1 (12.5) | 5 (5.7) | |
| Transplanted | 3 (3.2) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (2.3) | |
| Pre-dialysis | 8 (8.4) | 0 (0) | 8 (9.2) | |
| History of sensitizing events | 0.302 | |||
| Blood transfusion | 22 (23.2) | 2 (25) | 20 (23) | |
| Pregnancy | 11 (11.6) | 1 (12.5) | 10 (11.5) | |
| Pregnancy + blood transfusion | 10 (10.5) | 1 (12.5) | 9 (10.3) | |
| Transplanted | 3 (3.2) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (2.3) | |
| None | 49 (51.6) | 3 (37.5) | 46 (52.9) | |
| Hepatitis infection | 0.596 | |||
| No infection | 79 (83.2) | 6 (75) | 73 (83.9) | |
| HBV | 4 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 4 (4.6) | |
| HCV | 11 (11.6) | 2 (25) | 9 (10.3) | |
| HBV + HCV | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Urea, mmol/L | 8.11 (6.8 - 10.02) | 10.7 (9.5 - 39.26) | 8 (6.75 - 9.3) | 0.001 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 86.45 (72.52 - 102.52) | 112.2 (94.7 - 666) | 85.39 (71.85 - 95.9) | 0.004 |
| Hemoglobin, g/L | 100.89 ± 14.24 | 111 ± 16 | 100.19 ± 13.95 | 0.072 |
| Anemia | 88 (94.6) | 5 (83.3) | 83 (95.4) | 0.205 |
| WBC, g/L | 10.2 (7.56 - 12.9) | 12.38 (7.5 - 15.15) | 9.95 (7.5 - 12.8) | 0.352 |
| GFR, mL/min | 83.9 (72.25 - 97.32) | 50.45 (9.43 - 86.72) | 84.48 (72.87 - 97.84) | 0.01 |
| HLA matching | 0.517 | |||
| 0/6 | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| 1/6 | 7 (7.4) | 2 (25) | 5 (5.7) | |
| 2/6 | 28 (29.5) | 2 (25) | 26 (29.9) | |
| 3/6 | 36 (37.9) | 2 (25) | 34 (39.1) | |
| 4/6 | 16 (16.8) | 2 (25) | 14 (16.1) | |
| 5/6 | 4 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 4 (4.6) | |
| 6/6 | 3 (3.2) | 0 (0) | 3 (3.4) | |
| PRA | 0.031 | |||
| Positive | 47 (49.5) | 7 (87.5) | 40 (46) | |
| Negative | 48 (50.5) | 1 (12.5) | 47 (54) | |
| DGF | 14 (14.7) | 7 (87.5) | 7 (8.0) | < 0.001 |
Abbreviations: CGN, chronic glomerulonephritis; CPN, chronic pyelonephritis; DGF, delayed graft function; DN, diabetic nephropathy; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; GR, graft rejection; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; hs-CRP, C reactive protein-high sensitivity; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; N/A, not available; PRA, positive panel-reactive antibody; WBC, white blood cell.
aValues are expressed as No. (%) or mean ± SD.
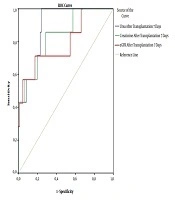
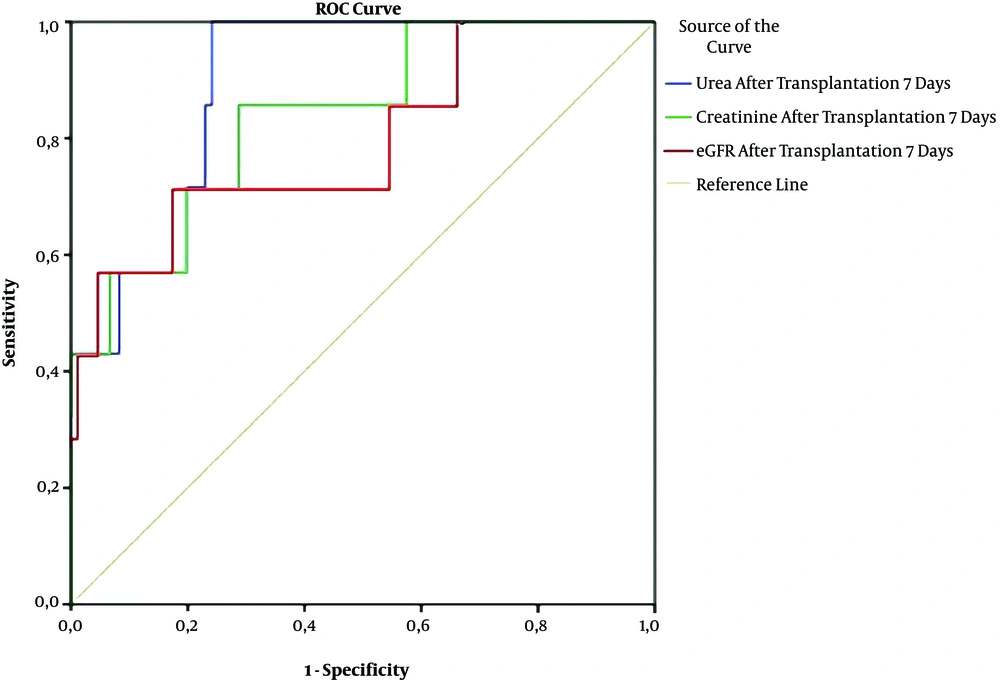
The male sex, PRA (+), and GFR had independent relationships with DGF in patients with PRA (+) after kidney transplantation (Table 4). Urea, creatinine, and GFR were good predictors of graft rejection in patients with PRA (+) and DSA (+) based on the ROC curve model (Figure 1).
| Variable | Adjusted HR | 95% Cl | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male gender | 10.733 | 1.427 - 80.704 | 0.021 |
| Pre-transplantation anemia | 0.294 | 0.018 - 4.781 | 0.39 |
| Donor age | 1.111 | 0.952 - 1.297 | 0.181 |
| Positive PRA | 324.78 | 3.351 - 31475.3 | 0.013 |
| GFR, mL/min | 0.917 | 0.868 - 0.97 | 0.002 |
Abbreviations: DGF, delayed graft function; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; PRA, positive panel-reactive antibody.
Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves of serum urea, creatinine, and GFR for prediction of graft rejection after kidney transplantation. (Urea: AUC = 0.885; P = 0.001; cut-off value = 9.35; Se= 100%; Sp = 75.9%; Creatinine: AUC = 0.831; p = 0.004; cut-off value = 94.36; Se = 85.7%; Sp = 71.3%; GFR: AUC = 0.794; P = 0.01; cut-off value = 69.77; Se = 71.4%; Sp = 82.6%).
Kidney function was significantly better in negative PRA + DGF + GR patients than in positive PRA + DGF and/ or GRGR patients (P < 0.01) only in day 7 post-transplantation. However, there was no difference in kidney function between the two groups from one month afterward (P > 0.05) (Table 5).
| Index | Urea, mmol/L | Creatinine, µmol/L | GFR, mL/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive PRA + DGF and/or GR (n = 14) | |||
| D7 (1) | 10.7 (8.82 - 20.63) | 112.2 (84.93 - 189.06) | 64.33 (30.57 - 87.08) |
| M1 (2) | 7.28 (5.6 - 8.97) | 108.59 (92.95 - 116.97) | 73.61 (62.4 - 75.98) |
| M3 (3) | 6.21 (5.49 - 6.64) | 109.9 (88.8 - 117.1) | 67.88 (58.3 - 78.78) |
| M6 (4) | 6.88 (4.82 - 7.4) | 90.65 (80.71 - 113.59) | 76.19 (66.77 - 84.61) |
| Negative PRA + DGF + GR (n = 33) | |||
| D7 (5) | 6.7 (6.17 - 7.79) | 76.2 (63.56 - 86.68) | 87.19 (77.7 - 102.64) |
| M1 (6) | 5.95 (4.83 - 7.7) | 87.7 (77.75 - 109.7) | 71.07 (62.89 - 77.05) |
| M3 (7) | 5.35 (3.93 - 5.98) | 81.4 (75.7 - 100.35) | 74.45 (65.51 - 82.91) |
| M6 (8) | 5.12 (3.66 - 5.99) | 84.94 (73.63 - 100.65) | 75.0 (66.66 - 85.42) |
| P | |||
| P (1, 5) | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | 0.001 |
| P (2, 6) | 0.045 | 0.073 | 0.528 |
| P (3, 7) | 0.126 | 0.112 | 0.182 |
| P (4, 8) | 0.104 | 0.567 | 0.712 |
Abbreviations: DGF, delayed graft function; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; GR, graft rejection; PRA, positive panel-reactive antibody.
5. Discussion
5.1. Positive Panel-Reactive Antibody with Delayed Graft Function and Graft Rejection
Kidney transplantation is the ultimate treatment option for patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease, which reduces the mortality rate and improves the quality of life. The post-transplantation outcome is related to many factors such as HLA matching, presence of DSA, level of positive PRA, and crossmatch reaction. Santos et al. (19) conducted a study on 16 patients with positive flow cytometry crossmatch who underwent kidney or kidney-pancreas transplantation. The outcome was good, except for one patient with chronic humoral rejection. There was no dead patient, but there were a few complications related to immunosuppression. Kidney transplant in highly sensitized patients (HLA class I PRA > 50%; deceased donor renal transplant) was reported in the Yuan et al. study (20). The patients who received desensitization with plasmapheresis and low-dose intravenous immunoglobulin before kidney transplantation experienced successful transplantation. Betjes et al. (5) confirmed that the presence of DSA against HLA before kidney transplantation was a risk factor for early graft rejection (mostly AMR). The above results have led nephrologists to believe that highly sensitized patients would increase the chances of successful kidney transplantation. In the above studies, most of the highly sensitized patients have emerged in a kidney transplant from brain/cardiac dead donors. In our study, the subjects were livingdonors, patients with PRA < 20.0%were related to blood transfusion, pregnancy, and renal re-transplantation (Table 1).
DGF and AR post-transplantation usually appear in highly sensitized patients with positive PRA or positive crossmatch (5, 19, 20). We had two patients whose hyperacute rejection was related to positive PRA and needed to come back to use hemodialysis after transplanted nephrectomy (Figure 2). The ratio of DGF was 14.7%, and it was significantly higher in positive PRA patients than in negative PRA patients (27.7% versus 2.1%, P < 0.001). The proportion of AR was 8.4%, and it was higher the positive PRA group than in the negative PRA group (14.9% versus 2.1%, P = 0.031) (Table 1). To further clarify the relationship between the presence of PRA, DGF, and GR, we divided 95 subjects into two groups with or without DGF and with or without GR. Our results showed that the group with DGF or GR had a higher proportion of PRA-positive than the group without DGF or GR (P <, 0.001 and P = 0.031, respectively) (Tables 2 and 3). Specifically, positive PRA was independently related to DGF (P = 0.013) (Table 4). Several studies showed that the presence of PRA is a risk factor for AMR and reduced graft survival after transplantation (21, 22).
In our study, there were 5.3% humoral rejections and 3.2% cellular rejections, which were not significantly different between the positive PRA group and the negative PRA group (Table 1). This means the mechanisms of acute rejection not only related to the presence of positive PRA but also others. There are three main types of graft rejection: Hyperacute rejection that occurs minutes after transplantation (n = 2 in this study), AR that occurs days to months after transplantation (n = 8 in this study), and chronic rejection that occurs long after transplantation. AR is divided into antibody-mediated rejection (AMR), T cell-mediated rejection, C4d-negative AMR, and mixed one. So far, AR has been linked to genes and other risk factors, including deceased donors, a high number of HLA mismatches, and immunosuppressive therapy (23, 24). Renal biopsy seems to be the gold standard to diagnose GR; however, the reduction of kidney function and some clinical symptoms can suggest GR, as well. Our results also confirmed that serum urea, creatinine, and GFR can predict GR after kidney transplantation based on the ROC curve model results (AUC of urea: 0.885; of creatinine: 0.831; of GFR: 0.794, P = 0.001, 0.004, and 0.01, respectively) (Figure 1).
5.2. Kidney Function in Kidney Transplant Patients with Positive Panel-Reactive Antibody
To evaluate highly sensitized patients with positive PRA affecting kidney function after transplantation, we followed all patients for six months. Interestingly, the levels of both serum urea and creatinine were higher and GFR was lower in patients with positive PRA, DGF, and/or GR than in patients with negative PRA + DGF + GR only on the seventh day after kidney transplantation (P < 0.001 and P = 0.001, respectively). We found no significant difference between the two groups at one, three, and six months (Table 5). DGF and GR are caused by complex factors with varying severities. However, both DGF and GR seem to be good predictors for long-term outcomes after kidney transplantation, especially deceased donors (25-27). Ischemia and reperfusion injury are complex pathophysiological phenomena, inevitable in kidney transplantation, and are major mechanisms for DGF after transplantation. Ischemia and reperfusion injury can also result in acute rejection (28-30). Long-term ischemia and reperfusion injury are in a relationship with AR and chronic graft dysfunction due to interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy so that long-term outcomes are worse in patients with DGF and/or AR (25, 27). To recognize the long-term effects of DGF and ARin highly sensitized patients with positive PRA on transplanted kidney function, the patients need to be followed up for longer times.
5.3. Limitations
In this study, we had some limitations. First, our monitoring time was not long. Second, we did not investigate various factors of surgery that could affect delayed kidney function. We would like to overcome these limitations in our subsequent studies.
5.4. Conclusions
In conclusion, kidney transplantation in patients with HLA panel-reactive antibody (negative DSA) was related to the increasing ratio of DGF and AR. Transplanted kidney function was significantly worse in patients with positive PRA + DGF and/or GR than in negative PRA + DGF + GR patients only on the seventh day, but no significant differences were seen between the two groups at one, three, and six months.